Spasm of accommodation
Accommodation spasm, also called false myopia and tired eyes syndrome, is a violation of distance accommodation (disaccommodation), which causes a fixed tension in the ciliary muscle.
This condition is especially common in pediatric ophthalmology (2nd place after myopia). According to statistics, at least 15% of schoolchildren suffer from spasm of accommodation. Up to a certain point, this condition is reversible, but prolonged absence of correction of false myopia eventually turns into true myopia. With true myopia, accommodation spasm enhances the manifestations of myopia.
All of the above makes it clear why it is so important to promptly diagnose a spasm of accommodation and carry out treatment. It allows you to both restore the quality of vision and prevent complications associated with impaired accommodation.
Means for treating children
Despite the analogy of the treatment of spasm of accommodation in children and adults, the course of therapy for any child is always selected individually. The causes of the pathology, the general condition of the baby’s body and the condition of the organ of vision are taken into account.
The treatment program uses mydriatics, physiotherapy, hardware treatment and gymnastics.
Drops approved for children:
- Irifrin is the most commonly prescribed. Dilates the pupil and the spasm of the ciliary muscle is temporarily relieved.
- Lutein is good because it is applicable even to the smallest.
- Cyclomed is often prescribed as an addition to the main therapy. Relieves itching and burning in the eyes, redness.
- Tropicamide is widely used, but is prescribed to children after 12 years of age.
All of these drugs are classified as mydriatics. The use of vitamin drops is also not prohibited.
As an addition to drug treatment, doctors often prescribe:
- Laser therapy - to slow down the development of pathology and improve vision in general;
- Magnetic therapy slows down the development of the disease.
- Electrophoresis.
Among other alternative methods, eye gymnastics is considered mandatory, which is recommended to be performed 2-3 times a day. A set of exercises is selected by a doctor.
The duration of the treatment course in children does not exceed 3 weeks.
Sidorenko's glasses are an innovative eye trainer that has a positive effect on them through a gentle vacuum massage. Externally, the device looks like swimmers' goggles. The lenses are equipped with small pressure chambers on the inside, which gently massage the eyes with a vacuum, simultaneously capturing the soft tissue around them.
This improves nutrition and blood circulation automatically. The glasses emit intermittent light of a different spectrum, which provokes a rhythmic contraction and dilation of the pupil like a pump. In this case, the eye muscles easily relax.
How does a spasm of accommodation occur?
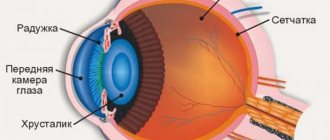
Accommodation is a mechanism that allows the gaze to focus at different distances. Normally, this process is regulated by the coordinated function of the accommodative apparatus, which includes three anatomically interconnected structures of the eye: the ciliary muscle, the ligaments of Zinn, and the lens. The accommodative ciliary muscle consists of three main types of smooth muscle fibers: meridional in the Brücke muscle, radial in the Ivanov muscle, circular in the Müller muscle.
During disaccommodation (distance accommodation), the muscles are relaxed. When it is necessary to focus the gaze on nearby objects, the meridional fibers of the accommodative muscle tense, the zonules of Zinn are weakened, which causes an increase in the curvature of the lens with an increase in the refraction of the eye. An accommodation spasm prevents the relaxation of the radial and circular fibers of the ciliary muscle, which are disaccommodative in their function. As a result, the ciliary body experiences a state of persistent, prolonged contraction and is called a spasm of accommodation.
Constant tension of the ciliary muscle causes disruption of its blood supply, which is a potential risk of chorioretinal dystrophy.
Reasons for development
Spasm of accommodation, as a rule, occurs in children or fairly young people, which is due to age-related characteristics of the function of the accommodative apparatus. The main causes of accommodation spasm in school-age children are high visual loads caused by prolonged viewing of TV, working with a computer, classroom furniture that is inappropriate for the student’s height, violation of the optimal reading distance, insufficient lighting, exposure to too much bright light on the eyes, etc. Development of spasm accommodation can be facilitated by an irrational daily routine, in which little time is devoted to sleep, walks in the air, exercise for the eyes and physical activity.
Among all the factors, the following are of particular importance: hypovitaminosis, asthenia, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, spinal curvature, juvenile osteochondrosis.
The list of reasons for spasm of accommodation in children also includes doing homework in the evening or at night. In this case, two factors play a role: natural fatigue of the visual organs, which occurs towards the end of the day, and increased stress on the eyes under artificial lighting.
The causes of spasm of accommodation in adults are the same as in children: excessive visual stress, unhealthy diet, violations of work and rest schedules, physical inactivity and vitamin deficiencies. In addition, along with age, other health disorders often come that directly or indirectly affect the accommodative apparatus: diseases of the spine (in particular, the cervical spine), vascular disorders, etc.
Over the course of life, the lens gradually loses its properties, and by about 45 years of age, it becomes less elastic and thickens. Such changes are associated with a decrease in the ability to see well near, that is, an age-related weakening of accommodation, called presbyopia (age-related farsightedness). Therefore, in adulthood, a spasm of accommodation occurs rarely and, as a rule, is secondary to causes such as hysteria, neurosis, traumatic brain injury, menopause, etc. The occurrence of a spasm of accommodation is often facilitated by activities that are associated with small work at close range (watchmakers , jewelers, embroiderers, etc.).
Types of drugs
There are many drops that eliminate the manifestation, one of which is Cyclopentolate.
There are the following drops that relieve spasm of accommodation:
- "Cyclomed". Used only on people with light eye color. The effect develops half an hour after instillation and lasts throughout the day.
- "Cyclopentolate". Not for use by pregnant and breastfeeding women as it contains toxic substances.
- "Midrum". It has a short-term effect of 6 hours, so it is rarely used.
- "Mydriacyl." The effect does not last long. These eye drops are used in the treatment of children.
- "Irifrin." They help relieve spasms of accommodation even in infants, since the components of this drug are completely harmless. Duration of action is from 2 to 7 hours.
- "Atropine". It has a long-lasting effect of up to 10 days, but has a number of side effects and is very toxic.
Predisposition to the disease is inherited and the pathology manifests itself in childhood.
Classification of spasm of accommodation
Ophthalmologists distinguish several types of this disease:
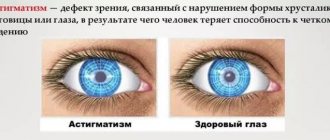
- Physiological (accommodative) - occurs as a response to visual overload, prolonged visual work at close range in people with uncorrected farsightedness or astigmatism. With a physiological spasm of accommodation, spectacle correction and restoration of the functionality of the ciliary muscle are required.
- Artificial (transient) - occurs under the influence of a number of ophthalmic miotic drugs (eserine, pilocarpine, phosphacol, etc.). Such a spasm of accommodation does not require treatment; it disappears on its own with the abolition of miotics.
- Pathological - accompanied by a change in refraction (hypermetropia, emmetropia, myopia), as well as a decrease in visual acuity. For pathological spasms of accommodation, I use the division into unstable and persistent; fresh and old (more than a year); uneven and uniform.
In practice, as a rule, there are mixed types of spasm of accommodation, which combine pathological and physiological mechanisms.
Features of the pathology
Spasm can be of 3 types:
- Physiological is a response to visual overload when the eye tries to turn on the compensation mechanism. Characteristic of farsightedness and astigmatism.
- Artificial is always temporary, because it is associated with taking certain medications for eye examination, for example, Pilocarpine. This spasm does not require treatment and disappears on its own.
- Pathological – characterized by increased refraction. In this case, vision deteriorates sharply. The most dangerous variety.
In practice, spasm is more often of a mixed nature.
Causes
This type of disorder often occurs among schoolchildren and young people. This is due to high visual loads during this period.
Prolonged work at a short distance from the eyes is the basis of the violations. This could be reading, working on a computer, watching TV for a long time, or using gadgets. Another common reason is imperfection of the eye itself. After all, in order to look at an object better, you have to bring it closer to your eyes and strain your vision. At this moment, an increase in accommodation occurs, followed by a spasm. This often happens when the workspace is poorly lit.
- astigmatism;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- unhealthy food;
- lack of vitamins;
- physical overload;
- vascular diseases;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- injuries to the eye area;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hormonal changes during menopause;
- metabolic disorders;
- incorrect selection of lenses and glasses for astigmatism.
For schoolchildren and adolescents, the reasons may be:
- unlimited time in front of the TV and computer;
- incorrect furniture for working at a desk;
- reading in low light and at close distances - for example, lying down;
- long bright light in the eyes;
- violations of the daily routine: regular lack of sleep, sitting at home without fresh air;
- asthenia;
- poor nutrition – without vitamins and minerals;
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis of the neck.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye muscle spasm are as follows:
- decreased vision when looking into the distance;
- rapid eye fatigue even with light loads and pain in them;
- dry eyes;
- burning and stinging;
- redness of the sclera and photophobia;
- temporal headaches, dizziness;
- double vision;
- general fatigue and irritability (especially in children).
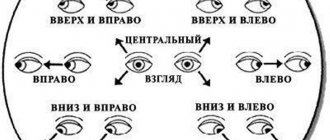
Useful video
Mechanisms of visual accommodation:
Accommodation indicators
The eye's ability to accommodate can be measured. This allows you to evaluate:
- area of accommodation. At its core, this parameter determines in what range a person maintains clarity of vision. To do this, the farthest and closest points are measured, between which the accommodation area is located - the interval in which the normal quality of vision is maintained.
- volume of accommodation. This indicator measures the difference in refraction between two points - the closest and the farthest - within which clarity of vision is maintained.
- Accommodation reserve. When measuring this parameter, the fixation point is used - the area on which the patient keeps his gaze. The volume of accommodation that is not used when installed at the fixation point determines its reserve or reserve.
Forms of violation
In case of accommodation disorders, it is important to determine the characteristics of this condition in order to draw up the correct treatment plan. In addition to accommodation spasm, there are the following forms of this disorder:
Accommodative asthenopia. At its core, this condition is permanent fatigue of the muscles that are responsible for the mechanism of accommodation. This condition is observed most often in those who are subject to increased visual stress associated with:
- with farsightedness;
- astigmatism;
- incorrectly selected optical correction or its complete absence.
Patients suffering from accommodative asthenopia are characterized by complaints of increased fatigue when reading, watching movies and other visual stress, and decreased image clarity (printed text, images on the screen, etc.). In addition, there may be itching, a burning sensation in the eyes, complaints about the presence of a foreign body in the eyes. With prolonged visual stress, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Paralysis of accommodation. This condition often develops in response to dysfunction of the nervous system, including as a complication of injury or toxic damage involving the central nervous system. Paralysis of accommodation in those who suffer from myopia may not have an effect on visual acuity, or such changes may occur gradually. On the contrary, with farsightedness and normal visual acuity, there is a noticeable decrease in visual acuity when studying nearby objects.
Age-related weakening of accommodation . This form of disorder is natural, physiological. With age, inevitable changes occur in the lens - compaction of its tissues and a gradual decrease in its elasticity.
The loss of the ability to accommodate with age is irreversible. But with the help of methods used in modern ophthalmology, the quality of vision can be restored.
What to do if you are diagnosed with a spasm of accommodation? Eye drops that relax muscles
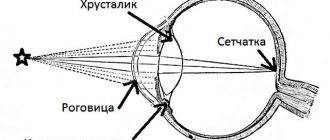
Eye accommodation is the ability to see objects at different distances. This depends on the elasticity of the lens and its ability to bend to the required degree. The process of accommodation is normal only at a young age, because the elasticity of the lens during this period is greatest.
On the subject: Muscles hurt under the shoulder blade during pregnancy
With age, it loses these properties and at the age of 40-45 a person often develops farsightedness. At the age of 70, the ability to accommodate in general is lost. Spasm of accommodation or false myopia refers to the category of functional visual impairment that is associated with spasm of the ciliary muscle. It is she who supports the lens.
Symptoms of the disease
A subjective manifestation of a spasm of accommodation can be a deterioration in distance vision. In addition, the symptoms of this disease are: rapid visual fatigue when working close, a burning sensation, stinging and pain in the eyes, double vision, pain in the forehead and temples. Eye redness and watery eyes are often observed. Often children present vague complaints of fatigue and headache; become irritable, school performance declines, which is often incorrectly interpreted by adults as hormonal changes in the body, according to age. The duration of the spasm of accommodation varies from several months to several years, often turning into persistent myopia.
Depending on the form and type of accommodation disturbances, and on the level of visual stress, other symptoms may be observed, such as nausea, vomiting, and problems maintaining balance.
Pathological spasm of accommodation is characterized by both ocular symptoms (anisocoria, nystagmus, eyelid tremor) and general manifestations. Patients often experience vegetative-vascular dystonia, decreased mood, emotional lability, hyperhidrosis of the palms, migraine attacks, and trembling fingers.
Diagnosis and treatment
A patient with complaints of decreased vision and visual fatigue should undergo a comprehensive ophthalmological examination, with a mandatory study of visual acuity, volume and accommodation reserve. In addition, the patient should be prescribed refractometry, skiascopy, and convergence testing.
To identify the causes of accommodation spasm, it is most often recommended to consult a neurologist and orthopedic traumatologist.
Treatment for diagnosing spasm of accommodation is complex and includes hardware methods, drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, recreational and hygienic measures.
Treatment for accommodative asthenopia and age-related weakening of accommodation is often limited to correction of visual acuity using optical glasses or contact lenses. This allows you to reduce the load on the muscles responsible for the mechanisms of accommodation and both restore the quality of vision and eliminate the symptoms accompanying accommodation disorders (headache, increased fatigue, etc.).
Drug therapy for spasm of accommodation involves the use of eye drops that cause dilation of the pupil and relax the ciliary muscle (irifrin, tropicamide, midriacil), and vitamin therapy. Of the physiotherapeutic procedures, electrophoresis and magnets are especially often prescribed for the eye area. If the cause of accommodation spasm is a spinal disease, the patient is recommended to undergo a course of therapeutic massage of the back and cervical-collar area, acupuncture, manual therapy, and exercise therapy.
To train the accommodative muscle, exercises with the Relax software-computer module, the use of electrooculostimulation, magnetic stimulation, laser stimulation, and color stimulation of the visual analyzer are effective. At home, the doctor may recommend using Sidorenko glasses (for children over three years old).
Hardware treatment improves blood circulation in the tissues of the eyes and, accordingly, in the muscles that are responsible for accommodation. This allows you to normalize the supply of nutrients and oxygen. Also, hardware treatment helps stimulate retinal neurons, which has a positive effect on visual acuity and overall eye health.
The general health of the body is also important - hardening, playing sports, performing special exercises for the eyes, maintaining visual hygiene, switching to a healthy diet that includes a maximum of nutrients.
Treatment
Treatment of spasm of accommodation should be comprehensive. This means relaxation of spasm (direct impact on accommodation), active training treatment and general sanitation of the body.
Therapy includes medication and hardware treatment, gymnastics, and partial elimination of spasms using optical fogging. Radical methods such as surgical ones are not used. The success of treatment depends on the timeliness of treatment and detection of pathology.
Successful treatment will restore visual acuity by 70%. In 21.5% of cases, the pathology cannot be treated and remains unchanged, 8.5% is complicated by the transition to true myopia. This usually happens when treatment is started late and in children with a tendency to spasms.
To prescribe treatment, it is necessary to establish the causes of the disorder. Any therapy is prescribed only by a doctor; no amateur activity is allowed.
At an early stage, pathology can be treated without drugs, solely with exercises. They are selected by a doctor. Drug therapy includes eye drops, tablets to relieve spasms of the ciliary muscle, complexes of minerals and vitamins.
Hardware treatment
Electrical stimulation of the eyes with weak current pulses perfectly relaxes the ciliary muscle.
- Laser exposure activates biophysical and biochemical processes in the human body. The laser beam is directed directly into the eye, it inhibits all pathological processes, stimulating visual functions. This normalizes vision, relaxes and improves the functioning of the ciliary muscle. Moreover, the effectiveness of the laser is inversely proportional to the patient’s age. The laser does not give any untreated percentages; everything is restored 100%.
- Not long ago, a new ultrasound device that relieves ocular spasm of accommodation, especially in children. The method is based on the complex effect of pulsed red, infrared radiation and a constant magnetic field. They affect the area of the carotid sinuses, the neck and some active points of the body. All this has a beneficial effect on the accommodative apparatus and visual center in the cerebral cortex. Blood circulation in the cervical region improves, spasm and pain are relieved. The ultrasound method is safe and easy to use.
- Magnetic therapy - a special eye magnet with an alternating field is applied to the eyeball. The development of accommodation spasm slows down and vision improves
- Electrophoresis - allows you to use minimal doses of drugs, quickly delivering them to the posterior pole of the optical media of the eye. This makes it an indispensable method of treatment.
- Training computer programs (Flower, Relax-2, Contour, etc.) in combination with other methods of hardware treatment. They can alleviate the condition of many ophthalmological problems, including spasm of accommodation. The type of software is selected by a specialist individually, after studying the anamnesis in each specific case.
- The use of the Visotronika ophthalmic simulator-relaxator improves vision in patients with accommodation spasms. The device relaxes the ciliary muscle using automatic lens selection, which leads to the restoration of its functionality.
- At home, Sidorenko glasses . The range of effects of this device is quite wide, since it affects not only vision directly, but also all nearby muscles. Due to the light pulses, the pupil is, as it were, “massaged”, and the spasm of accommodation, thanks to this, is completely removed. The glasses have no side effects and can be prescribed to children from 3 years of age.
Prognosis and prevention
Spasm of accommodation is a reversible functional disorder that responds well to treatment. Drug therapy quickly relieves spasm of the ciliary muscle through forced relaxation. But in order to achieve a good result, it is necessary to carry out a full program of therapeutic measures, eliminating the causes that led to the occurrence of the disease. Its early detection and treatment can prevent the development of myopia.
Prevention of accommodation spasm usually includes measures for the general health of the body, frequent walks, proper nutrition, a good night's rest, sports or physical exercise. An important point in this complex is compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards for visual work: proper illumination of the workplace, control of sitting and posture, maintaining the required distance when working with a monitor or printed text, taking mandatory breaks during work, etc. For farsightedness and astigmatism, you need selection of optical correction and regular completion of functional rehabilitation courses.
Prevention
To prevent such problems from occurring, you need to adhere to certain recommendations:
- Ensure good lighting for any type of work. All visual loads should be carried out in excellent lighting. The use of fluorescent lamps is not recommended.
- Maintain a work and rest schedule. After any exertion, you should give your eyes time to relax.
- Do special exercises and massage. Gymnastics helps to relax and strengthen the muscle tissue of the eyes. It is also useful to massage the collar area.
- Exercise. It is important that the loads are moderate. With this diagnosis, walking, swimming, and cycling are suitable.
- Eat right, create a balanced and fortified diet.
- Preventive intake of eye vitamins, which include lutein, as well as minerals in the form of zinc and magnesium.
Recommendations for parents
The child's visual organs are not adapted to prolonged or excessive loads. But the main mistake of parents lies in the fact that they consider only reading, writing and other school tasks to be such loads. But the vision of a preschooler who is interested in drawing, putting together puzzles and other similar activities experiences no less strain. Therefore, in order to minimize the risks of visual impairment in children, it is important to follow the following rules of visual hygiene:
Organize a comfortable workplace . Considering that children grow very quickly, it makes sense to purchase a table and chair with height adjustment. This will create optimal conditions under which the child will not slouch, lie with his chest on the table or “hang” on a chair.
Make sure you sit correctly at the table
With proper seating and correctly selected furniture, the child:
- sits straight on a chair, back and lower back pressed against the back of the chair;
- the feet are completely on the floor, do not hang or rest on the toes;
- The pelvis and hips, thighs and shins form an angle of approximately 90° between themselves.
Watch your diet. Nutrition is of fundamental importance for eye health. Therefore, include fresh fruits and vegetables and dairy products in your child’s daily menu - they contain substances that help maintain eye health and visual acuity. If necessary, contact a pediatric ophthalmologist or pediatrician, who can select vitamin and mineral complexes designed for children.
Teach your child eye exercises . Simple exercises (circular eye movements, tightly closing your eyes and opening your eyelids wide, etc.) take only a few minutes, but help relieve tension from the eye muscles and prevent overwork of the accommodative apparatus.
Adjust your daily routine . The child needs to spend at least 1 hour a day in the fresh air. It is best if he is busy during this time with games, sports and other types of physical activity. It is also important that children sleep at least 9 hours at night - this, among other things, allows the eye muscles to rest after the stress of the previous day.
Liquid preparations
Liquid medications include eye drops. There are quite a lot of them, but you can’t self-medicate.
Therapy with drops in children and adults is similar. Special drops for relieving accommodation spasms belong to the category of indirect mydriatics or M-anticholinergics.
Such agents help relax the orbicularis muscle of the iris and affect the ciliary muscle, which is responsible for the shape of the lens. In this case, muscle relaxation changes the curvature of the lens, which is initially configured for distance vision. At the same time, the pupil dilates (mydriasis).
Indications for use
Indications may include functional visual impairment - spasm of the ciliary muscle. Its spastic contraction requires treatment, being the main cause of the spasm. Drops can be used for physiological or artificial spasms.
The essence of the effect on spasm of the ciliary muscles is that the tone of the ciliary body improves, the lens changes its refractive abilities and curvature in the desired direction. Visual acuity in these cases normalizes and the negative manifestations of spasm go away.
What types of drops are there?
The choice of eye drops that relieve spasm of the ciliary muscle is very wide. More often than others, ophthalmologists use eye drops that expand the icon (Atropine or its analogues). These drops relax the ciliary muscle so much that the effect lasts for several days.
After a course of treatment for 10 days, the spasm of accommodation completely disappears. But according to the observations of the same ophthalmologists, after the end of the course of treatment, a relapse and deterioration of vision may occur. The reason for this phenomenon is that the muscle is forced to artificially relax, but is not trained. This weakens her.
Drops to relax the ciliary muscles are best taken before bedtime. The longevity of the effect depends entirely on the patient himself. The ciliary muscle needs training.
How long does the treatment last?
The use of eye drops can last from 5 days to a month. The duration depends on the degree of pathology and type of spasm. Restoration of vision with the return of its clarity and elimination of accommodation spasm occurs on average within 2-3 weeks. However, upon completion of the course, the disease will not completely go away immediately; the effect will be noticeable only after some time.
Our advantages
"Moscow Eye Clinic" is a modern medical institution that provides a full range of professional services in the field of ophthalmology. The clinic has at its disposal the best examples of modern equipment from the world's leading manufacturers.
The Clinic employs leading domestic specialists with extremely extensive practical experience. Thus, a surgeon of the highest category Natalia Ivanovna Fomenko consults at the clinic. Thanks to the professionalism of doctors and the use of modern technologies, MGC guarantees the best treatment results and the return of vision. By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, you can be sure of quick and accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Prices
At the Moscow Eye Clinic you can undergo a full diagnostic examination and receive recommendations on the most effective treatment methods. A comprehensive examination of the patient (including methods such as testing visual acuity, biomicroscopy, autorefractometry, small-pupil ophthalmoscopy, pneumotonometry) costs 3,500 rubles.
The final cost of treatment is determined in each case individually and depends on the specific diagnosis, stage of the disease, available tests, etc.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling in Moscow 8(499)322-36-36 or number 8(800)777-38-81 (free for all phones in the Russian Federation). You can contact our specialist online using the appropriate form on the website, you can also familiarize yourself with the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
Mironova Irina Sergeevna