Causes of eyelid inflammation
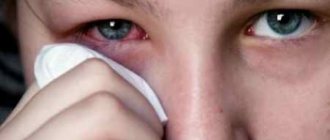
Inflammatory processes are formed as a result of infection with bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and Demodex mites. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply due to insufficiently effective immune defenses. This can happen due to a general weakening of the body, constant stress, and poor nutrition. The development of infections can also provoke mechanical damage to eye tissue and burns. Inflammatory reactions also occur as a result of allergies.
Hormonal ointments
Any hormonal drug should only be prescribed by a doctor, because such active components affect not only allergies, but also organs and systems. Such drugs are strictly contraindicated for children under 14 years of age (only in case of urgent need, but not earlier than 2 years), pregnant and nursing mothers, and people with endocrine organ disorders.
The choice of hormonal ointments against allergies on the face is extensive; they are all highly effective, but can be used for different symptoms. Medicines of this class are divided into 4 groups, differing in the strength of their effect.
First group
Ointments of this group can be used against mild allergies on the face, which are manifested by slight redness, swelling of the eyelids and rash. Their activity is rather weak, so if there is a strong need, they are prescribed to pregnant women and children over 2 years old. The most popular ointments are:
- Hydrocortisone;
- Prednisolone.
Second group
This includes more effective drugs prescribed against facial allergies if ointments from the first group do not help. These remedies are used against severe swelling and redness of the eyelids, the appearance of a profuse itchy rash on the skin of the cheeks, forehead and chin. In the pharmacy such ointments can be found under the names:
Before using them, be sure to consult your doctor; do not apply them to allergies in children, pregnant women, or people with hormonal imbalances.
Third group
Ointments of the third group are used against severe inflammation, general swelling, flaky red spots and other severe manifestations of an allergic reaction. They have a powerful effect, so they quickly relieve dangerous symptoms. Also, these medications are used for eczema around the eyes and on the cheeks, allergic dermatitis and other chronic skin diseases. The list of the third group includes:
Another important property of these ointments is their high speed of action. Within 2-3 days after use, there will be no traces of an allergic reaction on the skin. These drugs cannot be used independently; if the dosage or selection of the drug is incorrect, they negatively affect the pancreas and liver.
Fourth group
These anti-allergy ointments are prescribed only in cases of severe need, exclusively by a doctor. Drugs of the fourth group have a high concentration of active ingredients and a very powerful effect, so dosage is important when using them.
These ointments are used against severe skin rashes, the appearance of weeping wounds that become crusty, and inflamed flaky areas. The active substances of these drugs penetrate as deeply as possible and have a very quick effect. This group includes:
Types of eye ointments for inflammation of the eyelids
It is recommended to use drugs based on their pharmacological properties. That is, you should not use antibacterial ointment to treat, for example, herpes. Conversely, an antiviral agent will not be effective in treating bacterial diseases.
Antibacterial
Quite often, inflammation is caused by pathogenic bacteria, which are always present on the eyelids. If the growth of the population of these microorganisms is not restrained by the immune system, then the disease begins to develop. The effect of antibacterial ointments is to suppress the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria that cause diseases such as infectious conjunctivitis, blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, and barley.
Tetracycline eye ointment 1%
Available in tubes (3, 7, 10 g). Used for conjunctivitis, blepharitis. Contraindication is hypersensitivity. The ointment is placed behind the eyelid several times a day. The duration of therapy with Tetracycline ointment is determined by the doctor.
Erythromycin ointment
Used for bacterial eye infections. Well tolerated, rarely causes allergies.
The downside of this drug is that microorganisms quickly develop immunity to erythromycin, so if there is no therapeutic effect, the drug should be changed.
Tobradex eye ointment
The combined drug contains the synthetic glucocorticosteroid dexamethasone, which has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect, as well as the antibiotic tobramycin. It is used for bacterial eye pathologies and for the prevention of postoperative infectious complications.
The drug is contraindicated for viral and fungal eye diseases, as well as for traumatic damage to the cornea. With long-term use of Tobradex, it is possible to develop a fungal infection in the form of ulcers on the cornea, as a result of the action of dexamethasone.
May suppress natural immunity and cause irritation to the mucous membranes of the eyes. Uncontrolled long-term use of this product is not recommended.
Phloxal ointment
Contains ofloxacin 3 mg. Indications for use are infectious and inflammatory eye pathologies caused by microorganisms sensitive to ofloxacin:
- blepharitis;
- barley;
- dacryocystitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- chlamydial infections.
Contraindications:
- hypersensitivity;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Side effects include allergic reactions and photophobia.
It is not recommended to use the ointment for more than 2 weeks.
Antiviral
The most common viral eyelid disease is herpes. In case of deep forms of herpes infection, as well as in cases of relapse, combined treatment with ointments and antiviral tablets is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. For example, the simultaneous use of Acyclovir ointment and tablets of the same name is allowed.
Acyclovir eye ointment 3%
Available in 5 gram tubes. The drug is active against herpes viruses types 1 and 2. Used for herpes infection of the eyelids. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is better to avoid Acyclovir.
The ointment is applied immediately after the first signs of herpes are detected, as soon as redness and itching appear, at intervals of approximately 4 hours. A side effect is a burning sensation in the mucous membranes, which goes away on its own.
Zovirax
Contains micronized acyclovir 3%. An analogue of the ointment of the same name. Used for inflammatory processes caused by the herpes virus, including in newborns. When used, there may be a slight burning sensation in the eyes. During treatment, you should temporarily stop wearing contact lenses. After recovery, continue to apply Zovirax for 3 days.
Bonafton eye ointment 0.05%
Contains bromonaphthoquinone. Disturbs the process of protein synthesis in viral cells. Bonafton is used for various forms of ophthalmoherpes and adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis. A burning sensation in the eye may occur after applying the ointment; it goes away on its own within 5-10 minutes, applied 3-4 times a day.
Antihistamines and anti-inflammatory
This group of eye ointments includes hormonal (steroid) agents. They have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, but at the same time they can suppress natural immunity, have side effects and contraindications. Therefore, they should be used as prescribed by a doctor, especially during pregnancy and lactation. Hydrocortisone and Prednisolone are contraindicated for use in bacterial, fungal, and viral infections of the eyelids, as well as in cases of corneal damage.
Hydrocortisone eye ointment
Available with different concentrations of the active substance - hydrocortisone acetate - 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%. Hydrocortisone is an active hormone of the adrenal cortex that has a strong anti-inflammatory effect.
Suppresses the secretion of histamine, due to which it exhibits antihistamine properties, i.e. antiallergic properties.
It is used for the following pathologies:
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- eyelid dermatitis;
- blepharitis;
- eyelid burns, etc.
Side effects:
- burning;
- steroid glaucoma (with long-term use);
- corneal perforation (if the integrity of the cornea has been compromised);
- re-infection due to immunosuppression by glucocorticosteroids.
The ointment is applied behind the eyelid 2-3 times a day. With long-term treatment, monitoring of intraocular pressure is necessary.
Prednisolone ointment 0.5%
Hormonal drug. Has pronounced antiallergic properties. Actively suppresses immune reactions, reduces inflammation. It is used externally for eyelid lesions of an allergic nature.
Antiparasitic
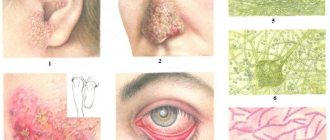
Inflammatory processes in the eyelids can occur against the background of demodectic blepharitis, caused by parasitic Demodex mites, as well as other pathogenic microorganisms.
Sulfuric ointment
A product proven over the years for the treatment of skin diseases. Has antimicrobial and antiparasitic effect. Apply externally to the eyelids.
To enhance the therapeutic effect, the affected skin of the eyelids can be pre-treated with an aqueous or diluted alcohol solution of medicinal plants with anti-inflammatory effects, such as calendula, chamomile, string, eyebright, eucalyptus.
Demalan for eyelids
Contains chamomile extract, olive oil. Eliminates itching, rashes, reduces inflammation and discomfort in the eyes. Demalan is applied to the edges of the eyelids affected by demodicosis.
Antifungal
If the immune system is severely weakened, the eyelids may be damaged by pathogenic fungi. Candidiasis of the eyelids and dermatomycosis require an integrated approach to treatment and identification of the causes of insufficient immunity. Fungal infections also occur as a result of long-term antibiotic treatment.
Clotrimazole
It is used for skin and mucous membranes affected by pathogenic fungi. Apply to eyelids 3 times a day until symptoms disappear, then for another 2 weeks.
Pimafucin 2%
Antifungal agent with a wide range of applications. Contains natamycin. Burning of the eyelids may occur as a side effect. Apply externally.
Classification of antibacterial eye ointments
In medical practice, broad-spectrum ointments are more often used. Based on the name of the active substance, they are usually classified as follows:
- Macrolides. They give a bacteriostatic effect, preventing the reproduction and growth of bacteria. Drugs of semi-synthetic or natural origin are less toxic than the quinolone group. Due to the minimal list of contraindications, antibiotics of this group are more often prescribed to pregnant women and children.
- Fluoroquinolones, quinolones. Antibiotics for eye inflammation, inhibiting the growth of bacteria. They contain synthetic active ingredients - DNA gyrase inhibitors, which are introduced into the DNA structure of the pathogen and lead to its death.
- Aminoglycosides. The first group is least effective. Modern aminoglycosides, which belong to the third generation, act quickly, give a minimum of side effects and cope even with multi-resistant microflora.
- Levomycetins. Popular and cheap antibiotics of synthetic origin. RNA and DNA penetrate into cells and inhibit protein synthesis, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of bacteria.
In ophthalmological practice, topical medications are prescribed not only for inflammation, but also for thermal and chemical burns and injuries.
Ointments for inflammation of the eyelids for children
Up to 3 years of age, eye drops are used predominantly; ointments are used less frequently. For eye diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria, Erythromycin ointment 1% is prescribed. Tetracycline ointment is recommended for use in children over 8 years of age. It should not be used for a long time.
Zovirax and Acyclovir are used as antiviral agents in pediatric practice. Accelerates regeneration and healing Bepanten.
Treatment of ophthalmological diseases in children is carried out under medical supervision.
List of the best ointments
Local medications for purulent, infectious or inflammatory damage to the organs of vision are prescribed by the doctor after examination. Ointments are often recommended to be combined with eye drops for eye inflammation with an antibiotic, which allows you to quickly get rid of symptoms and speed up recovery.
Popular titles:
- Tsiprolet . Thick ointment is used to treat keratitis, conjunctivitis, bacterial corneal ulcers, barley, blepharitis. Belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones and has an antimicrobial effect. Not approved for use in children under 2 years of age.
- Tobradex . Contains aminoglycosides and glucocorticosteroid dexamethasone. Combined drug with a wide spectrum of action. It is used to treat keratitis, iridocyclitis, blepharitis, to prevent inflammation and after surgery. Approved for use by adults only.
- Erythromycin ointment . The cheap product includes antibiotics from the macrolide group, effective against staphylococci, streptococci, corynobacteria and more than 20 types of pathogens. Used in the treatment of keratitis, conjunctivitis and corneal ulceration.
- Phloxal . Antimicrobial agent for external use of the fluoroquinolone group. Effective against gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. Suitable for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory lesions of the anterior parts of the eyes. Approved for use in children.
- Tetracycline ointment . A budget pharmaceutical product containing tetracycline hydrochloride, which has a wide spectrum of bacteriostatic effects. It is used mainly for the treatment of streptococcal and staphylococcal lesions of the cornea and conjunctiva.
- Neladex . The combination of an antibiotic and dexamethasone has antiallergic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Used in the treatment of iridocyclitis, keratitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, as well as for the treatment of otitis media. Do not use for children, women during lactation and pregnancy.
- Eubetal . Contains the antibiotic chloramphenicol and glucocorticosteroids. Can be used in pediatric practice, in women during pregnancy, but under the supervision of a physician. It is a gentle product and has a minimum of contraindications.
- Fucithalmic . An antimicrobial drug in the form of a thick and viscous suspension, belongs to the fusidine group. Allowed for newborns.
The combination of an antibiotic and glucocorticosteroids, mainly dexamethasone, in the ointment makes it possible to expand the range of therapeutic effects. GCS have antiexudative, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory properties - they reduce redness, hyperemia, and accelerate tissue restoration.
Doctors' recommendations
Anti-inflammatory eye ointments are placed behind the eyelid and on the skin of the eyelids (externally). It is not recommended to use these products in case of profuse lacrimation and severe suppuration. The duration of treatment is determined by specialists. When used simultaneously with drops, the ointment should be used last - 5-10 minutes after the drops are absorbed. It is advisable to avoid contact lenses during treatment to avoid unnecessary irritation of the eye mucosa, which can slow down recovery.
Application rules
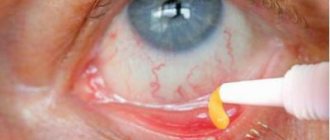
The eye ointment is stored in the refrigerator and must be warmed before use. Before use, wash your hands thoroughly with soap. It is not advisable to apply the product with your finger; it is better to use special glass eye or clean ear sticks.
If the ointment is applied directly from the tube, then it must be individual. Approximately 1 cm of product is squeezed out and applied along the entire length of the eyelid or in the central part. In this case, the lower eyelid is pulled down and the gaze is pulled up. Then you should lightly massage the skin and roll your eyes so that the ointment is distributed evenly. After the procedure, you should wash your hands again with soap or better disinfect them with special solutions. Sterile medical gloves can be used.
Types of ointments for allergies according to action
If symptoms appear, you should seek medical help.
After diagnosis, the doctor will offer an ointment, the effect of which depends on the cause that caused the mucocutaneous reaction.
The drugs come in two forms: some can be applied to the skin of the eyelids, others can be placed on the inner lower eyelid, and can be purchased at any pharmacy. The primary goal of treatment will be to relieve discomfort, pain in the eye area, reduce itching, and swelling. Therapy can be supplemented by taking antihistamines orally or by injections according to the scheme.
Hormonal
Creams containing hormones are prescribed as quick help to relieve severe allergies. The course of treatment is short: it can be completed in a few days or a week.
In the first days, a hormone-containing cream is applied in a thin layer to the area near or inside the eyelids up to 6 times a day. When inflammation decreases, they switch to twice-daily treatment. The products require a doctor’s prescription, there are many restrictions on use and contraindications: childhood, pregnancy, lactation.
Possible side effects of hormonal ointments during treatment:
- manifestation of spider veins;
- transient skin discoloration;
- withdrawal syndrome after long-term use.
The patient must be notified that the medicine relieves external signs of allergy and does not act on the root cause of the body's reaction.
Non-hormonal
Non-hormonal ointments and eyelid creams are prescribed to all categories of patients and children in the first year of life. The products take effect after some time.
Benefits of eye ointment therapy for non-hormonal allergies:
- eliminates itching;
- additionally has an antimycotic and antibacterial effect.
Moisturizing ointments
Prescribed when dry eye syndrome occurs. Causes:
- windy weather;
- working on a computer, TV, telephone;
- small activities;
- wearing lenses.
Symptoms of the syndrome:
- redness of the eyes;
- itching, burning;
- irritation;
- pain;
- acute reaction to light;
- profuse lacrimation.
Ointments relieve symptoms and moisturize the visual apparatus.
Oftagel
The medicine “puts” a film on the eye that lubricates and moisturizes the cornea. Oftagel protects the eye from drying out and prevents visual fatigue. The drug does not penetrate into tissues. Overdose of the drug and side effects are unknown. Cost – from 300 rubles.
Antibacterial drugs for eyes
Antibacterial eye ointments will help relieve bacterial inflammation in conjunctivitis and a number of other eye diseases, but drugs in this group have a number of side effects and do not act on viruses.
Antibiotic ointments are used for placing in the conjunctival sac for diseases of the cornea and other structures of the eye (bacterial conjunctivitis and corneal lesions, burns, trachoma, blepharitis) as well as for diseases of the eyelids (styree, meibomitis, dacryocystitis)
Among the most famous eye ointments in this group are the following.
- Tetracycline eye ointment, its use is widely practiced, since the active substance actively fights most known bacterial infections of the eye. It is used for infected burns and bacterial infections of the cornea, conjunctivitis with purulent discharge. However, before using tetracycline eye ointment, the instructions for use advise you to consult a specialist. Many microorganisms are resistant to this antibiotic; the drug has a significant number of contraindications and is not used for treatment during pregnancy and lactation.
- Oflaxacin, Floxal are indicated for bacterial diseases of the sclera, conjunctiva, eyelids, and chlamydial infections.
- Gentamicin is prescribed for blepharitis, dacryocystitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, keratitis and meibomitis.
- Erythromycin. The drug is effective against a wide range of bacteria, but has been used for several decades, so in some cases it is ineffective.
- Tobrex (aminoglycoside), ointment is usually prescribed in combination with drops, Tobrex drops are prescribed for the day, and ointment is prescribed at night.
One of the important characteristics of antibiotics is their selective effect on microorganisms. Therefore, in one case the instructions recommend the use of tetracycline eye ointment, but in another it does not. And this applies to all drugs in this series. For treatment to be effective, it will be necessary to conduct special studies on the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics (bacteria culture). Along with bacterial ointments, doctors always prescribe antibacterial drops (Tobradex, Tobrex, Levomycetin, Tsipromed, etc.).
Antiviral ointments
Prescribed for viral damage to the visual apparatus. These include:
- uveitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- keratitis – inflammation of the cornea;
- conjunctivitis - damage to the eyelids and eyeball;
- adenovirus – damage to the mucous membrane;
- herpes.
Antiviral ointments are safe. Therefore, they are dispensed without a doctor's prescription.
Acyclovir
An effective drug. The effect is noticeable after several placements in the conjunctival (eye) sac. Not recommended for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Children are allowed to use the ointment, but only after a doctor’s prescription and in full compliance with the dosage.
After application, a short-term burning sensation occurs. This kind of reaction is normal. There is no need to stop using the ointment. The use of Acyclovir does not affect visual acuity. Therefore, after use, you can drive and engage in minor activities. Cost – 100 rubles and more.
Antiviral eye products
These ointments are used to treat viral infections of the skin of the eyelids and conjunctiva. Among them, the most commonly used drugs are the following.
- Oftocipro (active ingredient ciprofloxacin) is used for viral infections of the eye structures (acute conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratoconjunctivitis, bacterial ulcers and infected wounds).
- Acyclovir, Zovirax, Virolex, Zirgan are ointments based on acyclovir. The drugs effectively cope with viral eye diseases and suppress the herpes virus.
These products differ in the method of application and require careful study of the instructions for use.
In some cases, patients independently prescribe a drug such as Polycarpine. However, it is used in the treatment of eye diseases in dogs and is not used for humans.
Antiparasitic ointments
Their use is usually associated with the detection of Demodex mites on the eyelash margin. In this case, a number of characteristic symptoms arise (redness of the eyelid, peeling, swelling, itching), which can be eliminated through treatment with antiparasitic ointments. You can buy the following products in pharmacies.
- Demalan (metronidazole in combination with chamomile extract) relieves inflammation, eliminates swelling and redness, and removes rashes caused by demodicosis.
- Demazol is a special cream for the treatment of demodectic rash on the eyelids.
The use of these ointments is exclusively for the skin of the eyelids; the drug should not come into contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Healing ointments
Healing drugs are prescribed to treat the eye after various injuries (mechanical, burns). They accelerate cell regeneration, relieve pain and have a healing effect on affected tissues.
Actovegin
The drug is prescribed for therapeutic and preventive treatment. Actovegin is often prescribed when wearing lenses to prevent injury. It does not penetrate into the blood, so it does not affect the functioning of the body. Actovegin has virtually no contraindications. It is not recommended for use only in patients with hypersensitivity to the elements of the composition. Cost – from 120 rubles.
Korneregel
Relieves redness and has an analgesic effect. There are practically no contraindications, which makes Korneregel a popular ointment. After applying the ointment, a short burning sensation occurs (1-2 minutes). There is no need to stop taking the medicine. Cost – 350 rubles.