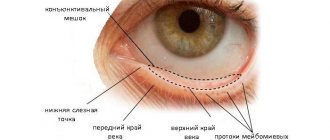
Types of strabismus
There are two forms of strabismus: friendly and paralytic.
In the first case, he squints the left and right eye in turn. The size of the deviations from the straight position is approximately identical. The main reason for the appearance of concomitant strabismus is ametropia. The more developed it is, the more it influences the development of strabismus. The causes of the disease also include:
- Pathologies of the organ of vision leading to a sharp drop in eye acuity;
- Uncorrected hypermetropia or myopia;
- Disease of the retina or optic nerve;
- Anomalies of the central nervous system;
- Congenital abnormalities in the anatomical structure of the eyes;
- A condition of the visual apparatus when the acuity of one eye is much lower than the other.
Friendly strabismus is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Possible drop in visual acuity in the squinting eye;
- Alternating deviation from the central axis of the left and right eye;
- When fixating the gaze on a static object, one eye deviates to the side;
- No diplopia
- The mobility of the damaged eye is maintained in all directions;
- Lack of stereoscopic vision.
| In paralytic strabismus, only one eye is squinted. The main manifestation of the disease is limited movement of the eyeball towards the damaged muscles. As a result, patients often complain of split images. |
The reason for the appearance of the anomaly lies in damage to the corresponding nerve endings or disruption of the functionality of the muscles of the organ of vision. Such pathologies are congenital or develop as a result of injury, infection or the formation of neoplasms.
The clinical picture of paralytic strabismus is as follows:
- Limited mobility of the eye towards the damaged muscle or its complete static state;
- Split image;
- Lack of spatial vision;
- Forced tilt of the head in the direction where the muscles are changed;
- Regular dizziness.
Strabismus is also divided into three forms:
- Convergent (eyes directed towards the bridge of the nose). The disease is often accompanied by hypermetropia;
- Divergent (the organ of vision is deviated towards the temple). In parallel, the development of myopia is possible;
- Vertical. The eye squints up or down.
The benefits and harms of stereo images
A stereo image is a special type of graphics that uses two separate images. They use a combination of different forms. These can be dots, patterns, shapes, etc., in combination of which, with the required viewing angle and focusing, you can see an encrypted 3D pattern.
The benefits of stereo images for the eyes are undeniable. This is felt by people whose eyes are exposed to regular radiation from a computer monitor or phone screen. Some users even set stereo images to their desktop wallpaper to switch when they get tired and train their eyes, while at the same time getting effects such as:
- improving blood circulation in the eye muscles;
- improving the operation of the adaptation and focusing apparatus;
- improvement of nerve fiber conductivity;
- saturation of the tissues of the eyeball with oxygen.
In addition, ophthalmologists have noticed that looking at stereo images helps improve blood circulation inside the eyeball, and also trains the ability to more accurately focus vision on arbitrary objects.
Since the user remains at the same distance from the monitor for a long time, focusing on one point, the eye muscles are in a state of inaction. However, intense viewing of stereo images causes these muscles to contract. When the gaze is focused on such a picture, the ciliary muscle, which controls the lens, first tenses and then relaxes. A similar effect is achieved by looking into the distance.
Viewing stereo images is a kind of physical exercise for the eyes, which means it can help with myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism without impairing vision. Ophthalmologists recommend that people with myopia look at stereo images without glasses or lenses.
In addition to bringing a healing effect on eye health, stereo images help you relax and immerse yourself in your own thoughts, which leads to a meditative-like state because they:
- influence consciousness and subconsciousness;
- affect brain activity;
- help to come to the necessary decision, choice;
- contribute to the development of concentration.
It has been proven that exercises with stereo images do not harm vision in any way, provided that you use a high-quality monitor that does not distort the depicted objects.
The concept of stereoscopic vision and why it is needed
This mechanism allows a person to see images in volume. Provided the organs of vision are functioning normally, a person can see the depth of space. Binocular vision is a functional feature of the visual apparatus. Using it, you can distinguish the shape of objects and their scale in several planes.
Every healthy person has this ability. The depth of space can be determined using a number of mechanisms. Comparing the angular value makes it possible to determine which object is closer to the person and which is more distant.
Having stereoscopic vision helps you navigate. Without it, it is impossible to work in some areas or play most sports. The formation of binocular vision occurs in the first years of life, when the child begins to perceive the world in three dimensions.
Deviations
Humans have several mechanisms for assessing depth. If any of the mechanisms does not work, then this is a deviation from the norm, leading to various limitations in assessing the distance of objects and orientation in space. The most important mechanism for depth perception is stereopsis.
Stereopsis
Stereopsis depends on the joint use of both eyes. When viewing any three-dimensional scene, both eyes form different images on the retina. You can verify this by looking straight ahead and quickly moving your head from side to side or quickly closing one eye or the other. If you have a flat object in front of you, you won't notice much of a difference. However, if objects are at different distances from you, then you will notice significant changes in the picture. During stereopsis, the brain compares images of the same scene on two retinas and estimates their depth with relative accuracy.
Manifestation of stereopsis
Disparity
This is the name for the deviation from the position of the corresponding points on the retinas of the right and left eyes, in which the same image is recorded. If the deviation does not exceed 2° in the horizontal direction, and no more than several arc minutes in the vertical direction, then a person will visually perceive a single point in space as being located closer than the fixation point itself. If the distance between the projections of a point is less than between the corresponding points, then it will seem to the person that it is located further than the point of fixation.
The third option involves a deviation of more than 2°. If the vertical direction exceeds a few arcminutes, then we will be able to see 2 separate points that will appear closer or further from the fixation point. This experiment underlies the creation of a series of stereoscopic instruments (Wheatstone stereoscope, stereo television, stereo range finders, etc.).
What is stereopsis?
La binocular vision or relief vision is the process by which we can perceive what surrounds us in three dimensions, experiencing a sensation of depth, distance or proximity of each of the objects. This process occurs through a mechanism called retinal image disparity, which occurs when, thanks to the two slightly different images that are projected in each of the retinas in our eyes, the brain manages to combine both to form a three-dimensional vision.
Enhanced binocular vision, or stereopsis, is key to many activities of daily living, especially for everyday tasks such as driving a car. However, it is estimated that more than 5% of the population have light or depth vision problems, diagnosis of which is essential to ensure good vision.
Retinal Imbalance Diagram and Stereopsis
What are they for?
Stereo pictures are a collection of dots, various patterns, geometric shapes and backgrounds, with the help of which a three-dimensional image is encrypted. To see it, you need to focus your eyes on such a picture and then relax it. After this, a 3D drawing appears before the person’s gaze.
Sometimes stereo images do not consist of geometric shapes, but of other small images that the human brain can compile into a single whole.
Stereo pictures come from Russia. The first experiments with stereoscopic images began to be carried out by Russian photographer Ivan Aleksandrovsky in the mid-19th century. She superimposed several photographs taken from different angles on top of each other, which made it possible to see a three-dimensional image. Of course, Aleksandrovsky did not create the stereo images we are talking about, but the principle underlying them was discovered by him. And similar images in their modern form appeared in 1979. Their creators were Christopher Tyler and Maureen Clarke, who encrypted a three-dimensional object using a large number of multi-colored dots they typed on the Apple 2 computer.
The principle of how stereo images work is that if one eye receives one image, and the other - another, the brain is able to combine them into a single whole. Three-dimensional pictures contain just two layers of images, which, when the eye muscles relax and vision defocuses, enter each eye separately and are then processed by the brain. This is why a person viewing a stereo image begins to see a 3D drawing at the end of the process.
Such pictures are not only great entertainment, but also quite useful for the eyesight. To understand why stereo images are needed and how they can have a beneficial effect on vision, you first need to understand what actually causes your eyes to get tired, and how disorders associated with this occur.
Again about online application generators
In the previous article in this series, we discussed creating applications for the Android platform using Java and Android Development Tools (ADT). Today we will continue this topic by getting acquainted with a new product from Embarcadero - RAD Studio XE 5. Essentially, this product is a modern incarnation of Delphi, a Windows application development tool that has been incredibly popular in our country for many years, starting from the first 16 bit version, which appeared in the second half of the 1990s. But, unlike Delphi of the late 1990s and early 2000s, RAD Studio XE 5 is a tool that allows you to create applications not only for Windows, but also for Mac OS, Android, iOS, and, importantly, based on one and the same source code and resources - having created an application project, you can simply compile the executable code for any of the named platforms. Development of mobile applications is possible using the Architect, Ultimate, Enterprise editions, as well as the Professional edition, provided that the Mobile Add-On Pack extension module is purchased with it. The development environment itself is available only for the Windows platform. If desired, in RAD Studio XE 5 you can develop in C++Builder, as well as create HTML-5 applications.
This publication cannot be considered a traditional product review - like all articles in this series, it gives an idea of the tool by describing the process of creating a mobile application with minimal effort.
You can get started with RAD Studio XE 5 by downloading a 30-day trial from Embarcadero (available for various versions of Windows). The product installation process is carried out directly from the manufacturer’s website, so it is worth doing this by ensuring that you have a reliable and not too slow Internet connection.
After installing RAD Studio XE 5 itself, you should take care of installing support tools for the platforms for which you intend to create the application. So, to develop applications for the Android platform, we need the Android SDK, already familiar to us from the previous article, with support for selected versions of the platform - it can be installed by launching the Android Tools application included with RAD Studio XE 5 (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Selecting an application for modification
If the application is to be tested on a real device, its driver should be installed on the computer with the development environment (usually it can be found either on the device manufacturer’s website or on the Google website). On the device itself, you should enable remote debugging of applications in the settings.
To develop iOS applications, you will need a computer running Mac OS X to run the emulator. If you don’t have the latter, you can use Embarcadero’s MacinCloud cloud service, which also has a trial period of 24 hours. To test iOS applications on mobile devices and then upload them to the AppStore, you should also join the Apple iOS Developer Program or a similar program for universities or corporate clients.
The development environment itself looks quite traditional (Fig. 2) - a project manager (Project Manager, top right), a component palette with groups of interface elements and so-called non-visual components (Tool Palette, bottom right), a tree with the structure of form components (Structure, left top), Object Inspector (bottom left), form and code editor (center).
Rice. 2. Replacing the application logo
We will begin creating our very first application (as always, dedicated to introducing ComputerPress magazine) by using a ready-made template. To do this, in the main menu of the development environment, select the item File->New->FireMonkey Mobile Application and, among the proposed application templates, select the element Tabbed with Navigation (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Editing buttons
As a result, an application project will be generated, similar to the one the creation of which was described in the previous article of this series, and which is a notepad with four tabs, on each of which you can further place interface elements (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Setting the functionality of the buttons
By selecting a potential platform for running an application in the upper right corner of the form editor, you can see how it will look when executed on a particular platform.
Next, by selecting interface elements with the mouse (in our case, labels and tab titles), we can change the labels on them using the Text property in the object inspector.
For iOS applications, using the StyleLookup property, you can also select icons placed on notepad shortcuts (Fig. 5).
Fig.5. Widgets available for selection
The next step in creating our application is to add interface elements to the notepad tabs. To do this, click on the “About the Journal” tab, select the TMemo component in the Standard group on the component palette (Delphi users are familiar with it, but for beginners I’ll tell you that it’s just a multi-line text editor) and place it on the form. Let's find the Strings property in the object inspector, click on the button with the ellipsis and copy the brief information about our journal borrowed from our website www.compress.ru into the property editor that opens. From the list of possible values for the Align property of our Memo1 component, we select the value alClient - in this case, our text editor will occupy the entire area of the screen between the title and labels. And finally, we will set the Enabled property of this component to False so that the user of our application cannot edit the text (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Publish the application for testing
Let’s repeat all the same steps with the “Categories” tab, placing in the created Memo2 component the text borrowed from the same website about the magazine’s headings.
Next, let's give our application some variety - on the next two tabs we will place not a text editor, but a browser - the TWebBrowser component (it can be found in the Internet group of the component palette). Let's change the Align property of these components to the alClient value. Next, fill in their URL properties. For the component on the “Our Site” tab, enter https://www.compress.ru as the value of this property, and for the TWebBrowser component on the “Coordinates” tab, enter a link to the Yandex.Maps server, which will indicate the search result for the building editorial office on the map of Moscow. Then save the project.
So far, our application has certain disadvantages: for example, it does not have the ability to return to the previous page in browsers on the third and fourth tabs. Let's correct this shortcoming. To do this, at the top of one of the browser tabs, we will place two TSpeedButton buttons, linking one of them to the upper left and the other to the upper right corner by selecting the options akTop, akLeft, akRight of the Anchors property of each button and adding arrow images to them using the already familiar StyleLookup property (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7. Finished application - iPhone 5 screenshots
Let's double-click on each of the buttons, after which empty event handlers associated with clicking on them will be generated. Let's add one line of code to them (highlighted in bold):
procedure TTabbedwithNavigationForm.SpeedButton1Click(Sender: TObject);
begin
WebBrowser1.GoForward;
end;
procedure TTabbedwithNavigationForm.SpeedButton2Click(Sender: TObject);
begin
WebBrowser1.GoBack;
end;
These two lines of code mean that when you click on one of the buttons, you move to the previous page that opened in the browser, and when you click on the second button, you move to the next one.
And finally, select both buttons, copy them to the clipboard, go to the tab with the second browser and remove them from the clipboard. If you do this carefully, the buttons will be copied along with their properties and event handlers. Let's save the project.
Actually, this will complete the creation of the application. Now it can be compiled and tested. Let's start by compiling the application for the iOS platform. First, you need to connect to a computer with Mac OS X, located on the same network as the Windows computer on which development is carried out, or to the MacinCloud service. In the first case, you also need to install the Platform Assistant console application on a computer running Mac OS X and launch it, and then enter a password to access it in the RAD Studio XE 5 development environment. Then you should describe the connection to this computer by selecting the option in the main menu of the development environment Tools->Options. The Connection Profile Manager section of the Options dialog panel contains a list of connection profiles to which you can add a new profile by specifying the computer name and password to access the running instance of the Platform Assistant application (Figure 8).
Rice. 8. E-book created using the appropriate template
You can test the connection using the Test Connection button. If problems arise, it is worth checking whether the computer running the Platform Assistant application is accessible on the network and whether the port through which the connection between computers is made is open.
After successfully connecting to the Platform Assistant application, in the project manager, select the appropriate platform and the configured connection profile with a computer running Mac OS (Fig. 9).
Rice. 9. Create an iPad application
Select the main menu option Run->Run or press the F9 key. We wait for a while and an iPhone emulator with our application will appear on the screen of a computer running Mac OS X.
Now let's try to compile the same application to run on the Android platform. Let's connect the device used for testing, select the device and platform in the Target Platforms section of the project manager and run the application again using the F9 key.
After a relatively short period of time, our application will launch on the connected device.
So, we have created a cross-platform application that can run on both iOS and Android. At the same time, we did not need to use any special execution environments or code generation with subsequent compilation in development environments like Xcode or Eclipse + ADT - RAD Studio XE 5 creates so-called native applications. This means that the performance of such applications should be comparable to the performance of applications created, for example, using Xcode or ADT.
Miracles, of course, do not happen - the size of executable files created using RAD Studio XE 5 will probably be larger than when using Xcode or ADT. But space on mobile devices, you see, is not the most expensive resource today - investments in the knowledge and skills of mobile application developers will cost much more. And here RAD Studio XE 5 is still out of competition - supporting two of the most popular mobile platforms at once means that there is no need to have separate development teams for iOS and Android. It is also important that companies that decide to implement RAD Studio XE 5 have access to a huge number of Delphi and C++Builder experts of all ages and with a wide variety of experience on the Russian labor market - after all, this tool is, after all, almost 20 years old.
In conclusion, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that the Embarcadero website has a huge amount of educational materials on developing mobile applications using RAD Studio XE 5, and this collection of materials is constantly growing. Therefore, mastering this tool will not be too difficult even for beginners.
The previous two articles in this series were devoted to a brief introduction to professional application development tools using the Android Development Toolkit and a new product from Embarcadero - RAD Studio XE 5. We conclude the topic of professional tools for creating mobile applications, and today we will return to online application generation services , the use of which, as we already know, in some cases can be more effective than independent development using professional tools.
The service that today's article is devoted to is called iBuildApp and is an online application builder for smartphones that does not require any programming skills from the user. It belongs to the American company of the same name with a Russian representative office in Vladimir.
You can create applications using the iBuildApp service for free, and you can (but not necessarily) publish them in online application stores on your own. At the same time, the owners of the service provide users with a number of paid services, such as publishing applications in online stores for those who are not ready to publish on their own, assistance in monetizing applications (that is, making a profit by placing advertising in them), sending push and GPS messages -notifications to application users, 24/7 email support. Payment for services is possible on a monthly basis in accordance with various tariff plans, differing in the number of application downloads and the availability of the services listed above. Moreover, all tariff plans, including the free one, include access to ready-made application templates (including free and paid ones) and built-in components (widgets), technical support, the ability to see application performance statistics and downloads.
Special mention should be made of application templates and ready-made widgets - this service has a lot of them. Templates are available for different types of companies, types of activities, application categories, and you can change design options for a ready-made template and add widgets to it. If you wish, you can create your own templates and widgets and place them in the iBuildApp tools catalog, or order the development of a widget or even an entire application from the owners of this service.
Let's take a look at what you can create with the free plan. Let's start with the ComputerPress application, traditional for our cycle, with information about our magazine. To do this, you need to choose either a template or an almost finished application that can be modified.
From the ready-made applications, we will choose “Small Business” - the editorial offices of magazines for the most part belong to this category of companies (Fig. 1).
After making the selection, we will find ourselves in the application editor, in which, by opening the elements of the list of possible actions sequentially or in random order, we can customize its appearance or functionality, for example, replace the background or logo (Fig. 2).
I would like to draw attention to the support for the Russian application interface and the presence of a Russian interface in the online application editor - now not all such services have even the first of these features.
Next, you can make changes to the number and appearance of buttons, and you can choose your own graphic images for them (Fig. 3).
The button functionality available by default can also be replaced with the desired one. In particular, it is possible to select the necessary widgets from a fairly extensive list and configure their parameters, for example, entering text and pictures in the case of a widget displaying a static HTML document (Fig. 4).
Among the widgets available today are widgets for displaying RSS feeds, HTML documents, interfaces with Twitter and Facebook, video lists from YouTube and Vimeo, interfaces with the phone, email client, Google Map mapping services, contact management tool, calculator, camera, photo gallery, an electronic book, a QR code scanner, free-form input with user-selectable interface elements and many others (Fig. 5).
Users also have the ability to create their own widgets and templates to use in their applications.
Once you have finished building the functionality, you can make the application available for download in accordance with your tariff plan. The free plan offers two ways to publish an app: creating a package for download on an Android device (which means we don't have to publish the app to the Google Play store) and creating an HTML5 app (which means we can test it on a device running iOS, without publishing the application in the AppStore and without purchasing an iOS developer license - Fig. 6).
In Fig. 7 shows screenshots of an iPhone 5 running a ready-made application downloaded from the link above.
Because we're using the free plan, the app includes an iBuildApp splash screen ad that appears when the app loads, an ad line on the title page, and banner ads that appear at the top of other pages when you open them (they can, however, be closed).
“Small Business” is not the only type of application available to users of the iBuildApp service. The range of potential consumers of ready-made applications and templates for this service is very diverse - from cafes and restaurants to religious organizations. For example, an e-book created from the appropriate template looks very good (Fig. 8).
In addition to applications for smartphones, the iBuildApp service also allows you to create applications for iPad. The choice of templates for this type of application is still small, and the finished application can only be tested in a browser (Fig. 9).
In addition to creating applications, the user of the service can create their own application templates (for this there is an online template editor that supports drag-and-drop operations) and sell them, as well as create their own widgets using XCode or Android SDK. But if you don’t want to deal with the issues of form design, purchasing a developer license and using development tools, you can get by with ready-made templates and widgets.
This concludes our acquaintance with the iBuildApp service for quickly generating mobile applications. It differs from similar services in the large number of templates and ready-made applications available for use, full support for the Russian language, not only in the applications created, but also in the online application editor, a very flexible pricing policy and a wide range of features available for free or for a nominal fee. Potential consumers of such a service can be companies and organizations of various profiles: cafes, restaurants, medical institutions, fitness clubs, retail enterprises, electronic stores, educational institutions, publishing houses, online stores, clubs. If such a consumer has a need for a Russian-language mobile application with more or less standard functionality, he should pay attention to this service - its use is highly likely to be much more effective than implementing or ordering individual development.
ComputerPress 12'2013
Diploptics as a type of treatment for strabismus
The therapy in question is considered the final stage in the treatment of strabismus. It is allowed to be performed on patients who have reached the age of two years.
A prismatic glass is placed in front of the eyes, which actually produces double vision. When it is removed, vision is slowly restored. During therapy, the prisms are changed.
The final stage of restoring binocular vision is therapeutic exercises aimed at increasing the mobility of the eyeballs. This is done using the convergence trainer.
Important! How to treat strabismus must be decided by the doctor. In most cases, several therapeutic procedures are sufficient, and sometimes major surgery is necessary, during which one or both eyes are operated on
However, strabismus can be treated at home, following all the doctor’s recommendations. Wearing glasses, performing special exercises and procedures - all this allows you to completely restore the balance between your eyes.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you that strabismus does not go away with age, therefore, at the first signs of pathology in yourself or your loved ones, it is necessary to carry out vision correction.
As for the prevention of binocular vision disorders, the following measures must be taken starting from an early age:
- When hanging toys above your child's crib, make sure that their location changes several times a week. In addition, place them at least 50 cm from the child’s face and on different sides. The baby's gaze should not focus on one point.
- If your child draws and looks at pictures with his head in a book, then you should definitely show him to an ophthalmologist.
Vision System Components
Machine vision focuses on primarily industrial applications, such as autonomous robots and visual inspection and measurement systems. This means that image sensor technology and control theory are associated with processing video data to control the robot, and real-time processing of the resulting data is carried out in software or hardware. Image processing and image analysis mainly focus on working with 2D images, i.e. how to convert one image to another. For example, pixel-by-pixel operations to increase contrast, operations to highlight edges, remove noise, or geometric transformations such as image rotation. These operations assume that image processing/analysis operates independently of the content of the images themselves.
Computer vision focuses on processing three-dimensional scenes projected onto one or more images. For example, by restoring the structure or other information about a 3D scene from one or more images. Computer vision often depends on more or less complex assumptions about what is represented in images.
There is also a field called visualization, which was originally associated with the process of creating images, but sometimes dealt with processing and analysis. For example, radiography works with the analysis of video data for medical applications.
Finally, pattern recognition is a field that uses various methods to extract information from video data, mainly based on a statistical approach. Much of this field is devoted to the practical application of these methods.
Thus, we can conclude that the concept of “machine vision” today includes: computer vision, visual pattern recognition, image analysis and processing, etc.
Fish
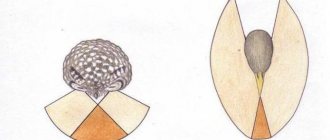
As you know, the vast majority of fish species have eyes located on both sides of the head. They have monocular vision. The exception is predatory fish, especially hammerhead sharks. For many centuries, people have been interested in the question of why this fish needs such a head shape. American scientists have found a possible solution. They put forward the version that the hammerhead fish sees a three-dimensional image, i.e. she is endowed with stereoscopic vision.
To confirm their theory, scientists conducted an experiment. To do this, sensors were placed on the heads of several species of sharks, with the help of which the brain activity of the fish was measured when exposed to bright light. The subjects were then placed in an aquarium. As a result of this experiment, it became known that the hammerhead fish is endowed with stereoscopic vision. Moreover, the greater the distance between the eyes of this type of shark, the greater the accuracy of determining the distance to an object.
In addition, it became known that the hammerhead fish's eyes rotate, which allows it to fully see its surroundings. This gives it a significant advantage over other predators.
Moving stereo pictures
Answer: Rolling bun
Answer: Running clock
Moving stereo pictures for the eyes are animated pictures. The only point is that this animation itself is not visible at first glance, that is, the task of the beholder is to see this animation. Not everything in the picture moves, only some individual element, for example, a person needs to see how it rains or a star falls. Animated stereo pictures are divided into simple and complex. It’s very easy to see animations in simple pictures, but not everyone can do complex animated stereo pictures.
Why is it important to have good stereoscopic vision?
La visión estereoscópica es fundamental en muchas actividades cotidianas como jugar a la pelota, realizar ciertos deportes, actividades que requieran visual acuity, the use of video games and even our ability to applaud correctly.
However, one task where the ability to perceive depth and distance is more relevant is in driving. binocular vision Relief is fundamental to calculating distances when overtaking or when we draw a curve.
Poor stereopsis can also affect daily work, especially in those professions that require good attention, such as surgeons or those who work with precision machinery, with special attention to those that can cause hand injuries.
Basic properties of vision[edit]
Light sensitivity of the human eye
Light sensitivity is assessed by the threshold value of the light stimulus.
A person with good eyesight can see the light from a candle at a distance of several kilometers at night. However, the light sensitivity of vision of many nocturnal animals (owls, rodents) is much higher.
Maximum light sensitivity is achieved after a sufficiently long dark adaptation. It is determined under the influence of light flux in a solid angle of 50° at a wavelength of 500 nm (maximum sensitivity of the eye). Under these conditions, the threshold light energy is about 109 erg/s, which is equivalent to several quanta.
The sensitivity of the eye depends on the completeness of adaptation, on the intensity of the light source, the wavelength and angular dimensions of the source, as well as on the duration of the stimulus. The sensitivity of the eye decreases with age due to the deterioration of the optical properties of the sclera and pupil, as well as the receptor component of perception.
The entire range of brightness that our visual mechanism is capable of perceiving is enormous: from 10−6 cd*m² for an eye completely adapted to darkness, to 106 cd*m² for an eye completely adapted to light, or 12 orders of magnitude brightness!. The mechanism for such a wide range of sensitivity lies in the decomposition and restoration of photosensitive pigments in the retinal photoreceptors - cones and rods.
Accommodation and visual acuity
Main article
:Accommodation of the eye
The ability of different people to see larger or smaller details of an object from the same distance with the same shape of the eyeball and the same refractive power of the dioptric eye system is determined by the difference in the distance between the sensitive elements of the retina and is called visual acuity.
Binocularity and stereoscopy
Main article
:Stereoscopy
Looking at an object with both eyes, we see it only when the axes of vision of the eyes form such an angle of convergence (convergence), at which symmetrical, clear images on the retinas are obtained in certain corresponding places of the sensitive macula (fovea centralis). Thanks to this binocular vision, we not only judge the relative position and distance of objects, but also perceive impressions of relief and volume.
Binocularity may be impaired with strabismus and some other eye diseases. If you are very tired, you may experience temporary strabismus caused by the non-dominant eye switching off.
See also Binocular, Stereoscope.
Contrast sensitivity
Contrast sensitivity is a person’s ability to see objects that differ slightly in brightness from the background. Contrast sensitivity is assessed using sinusoidal gratings. An increase in the contrast sensitivity threshold can be a sign of a number of eye diseases, and therefore its study can be used in diagnosis.
Vision adaptation
Main article
:Eye adaptation
The above properties of vision are closely related to the ability of the eye to adapt. Adaptation occurs to changes in illumination (see dark adaptation), color characteristics of lighting (the ability to perceive white objects as white even with a significant change in the spectrum of incident light, see also White balance).
Adaptation is also manifested in the ability of vision to partially compensate for defects in the visual apparatus itself (optical defects of the lens, retinal defects, scotomas, etc.)
Perception of polarized light
Main article
:Haidinger phenomenon
The human eye, to a certain, albeit small extent, is capable of perceiving differences in the polarization of light.
Leading eye
Human eyes are slightly different, so there is a leading and trailing eye.
Determining the dominant eye is important for hunters, videographers and other professions. If you look through a hole in an opaque screen (a hole in a sheet of paper at a distance of 20-30 cm) at a distant object, and then, without moving your head, alternately close your right and left eyes, then for the dominant eye the image will not shift
Correct techniques for drivers
Both those who are just getting a driver’s license and those who are improving their qualifications undergo testing to identify the presence or absence of ocular abnormalities.
The first test for drivers is the well-known visual acuity test. The first line is large and clear letters “Ш” and “Б”. The lower you go, the smaller the letters become. The very last row above the line will be read by a person with visual acuity equal to 1.
Medical driving correction takes into account the correction; the future driver takes the test wearing glasses or contact lenses with a power of no more than 8 diopters. More serious restrictions exist for drivers suffering from astigmatism. Many, fearing not to pass the medical examination, learn the table by heart
But besides Sivtsev’s table, there is Golovin’s table, which is a series of broken semicircles. It is much more difficult to learn, you need to see in which direction the broken rings are turned
Many, fearing not to pass the medical examination, learn the table by heart. But besides Sivtsev’s table, there is Golovin’s table, which is a series of broken semicircles. It is much more difficult to learn; you need to see in which direction the broken rings are turned.
The second test is a test for drivers for color blindness and color perception. The tables of Ishihara or Rabkin are taken as a basis. Such a table consists of many colored dots, among which images of figures or numbers are “hidden”.
An applicant with impaired color vision will not be able to correctly name the hidden number or figure. It is impossible to learn the test by heart - the tablets are offered randomly by the doctor, and the images may change. Applicants with a mild form of color blindness who are able to distinguish primary colors are allowed to drive.
Neurophysiology of stereoscopic vision
Thanks to research in the field of neurophysiology of stereoscopic vision, it was possible to identify specific cells in the primary visual cortex that are tuned to disparity. They exist in two types:
- cells of the first type react only when the stimuli precisely fall on the corresponding areas of both retinas;
- the second type of cells responds only when the object is located further than the fixation point;
- There are also cells that respond when the stimulus is closer to the fixation point.
All these cells have the property of orientation selectivity. They have good responses to line ends and moving stimuli. Some binocular stimuli are processed in the cerebral cortex in ways that are unclear. There is also a struggle between visual fields. In the case when images are created on the retinas of both eyes that are very different from each other, then often one of them ceases to be perceived at all. This phenomenon means that if the visual system is unable to combine the images on the two retinas, it will completely or partially reject one of the images.
For normal stereoscopic vision, the following conditions are necessary:
- adequate functioning of the oculomotor system of the eyeballs;
- sufficient visual acuity;
- minimal difference in visual acuity of both eyes;
- strong connection between accommodation, fusion and convergence;
- slight difference in the scale of images in both eyes.
If on the retina of the left and right eyes, when viewing the same object, the image has different sizes or is not the same scale, this is called aniseikonia. It is one of the many reasons why stereoscopic vision becomes unstable or completely absent. Aniseikonia most often develops in the presence of anisometropia (different eye refraction). If it does not exceed 2 - 2.5%, then correction can be carried out with conventional stigmatic lenses. For higher levels of aniseikonia, aniseikonic glasses must be used.
One of the reasons for the appearance of strabismus is a disruption of the connection between convergence and accommodation. With obvious strabismus, there is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a decrease in the visual acuity of the squinting eye. He may completely switch off from the process of perceiving images. In the case of hidden strabismus, or heterophoria, there is no cosmetic defect, but it can interfere with stereopsis. Persons with heterophoria exceeding 3° are not able to work with binocular devices.
The threshold for stereoscopic vision depends on various factors:
- on background brightness;
- contrast of objects;
- duration of observation.
Under optimal viewing conditions, the depth perception threshold is in the range of 10 – 12 to 5″.
Stereoscopic vision can be assessed, determined and examined using several methods:
- using a stereoscope according to Pulfrich’s tables (in this case, the minimum threshold for stereoscopic perception is 15″);
- various types of stereoscopes with a set of more accurate tables (measurement range - from 10 to 90″);
- using a device that uses a randomized background, which excludes monocular observation of objects (the permissible measurement error is 1 - 2″).
Development of stereoscopic vision in a child
For several weeks after birth, the child is not yet able to fix his gaze on an object, since his eye muscles are misaligned and cannot make synchronous movements. Because of this, we observe infantile strabismus. The nature of vision after birth is monocular - the baby sees with only one eye, and then monocular alternating - either with the left or right eye.
But by two months of life, the reflex of fixing an object should be formed. During this period, light excitations are already transmitted to the cerebral cortex, a connection arises between the yellow spots of the retina and two images merge into one - the fusion reflex is triggered, without which stereoscopic binocular vision is impossible.
At two to three months, the baby actively masters the near space - an important stage for the formation of binocular vision. At this time, he does not yet have “stereo” vision and sees objects only in two dimensions - width and height, and can only get an idea of depth by touch. This is how he gets his first idea of the volume of objects.
After six months, the stage of active exploration of distant space begins, when the baby begins to actively crawl. At the same time, the child already better estimates the distance to the object to which he is heading, and there comes an understanding that he can fall from the edge of the bed. He is able to reach a variety of things, evaluate their size and relief.
By exploring objects of various shapes and materials, the baby forms stereoscopic vision, his own idea of the world around him. The common game of rolling a ball between an adult and a child is an excellent example of how he learns to judge distance, one of the important signs of binocular vision. Stereo vision is fully formed by about eight years of age.
Strabismus is common in children and indicates a clear impairment of stereo vision. Professor R. Sachsenweger, as a result of many years of observations, derived two terms:
- “stereoamaurosis” - complete absence of stereoscopicity;
- “Stereoamblyopia” is the defective development of stereoscopic vision.
The occurrence of strabismus in a child destroys his binocular and stereoscopic vision. It should be noted that it is possible to restore stereo vision only in that part of children with concomitant strabismus; in cases of congenital or early-onset ailment, it is not possible to restore full three-dimensional vision. Restoration of stereoscopicity is carried out at the last stage of strabismus treatment, when fusion reflexes and normal planar binocular vision are developed.
In this case, the final results depend on the visual acuity of both eyes, the difference between them in diopters, and the angle of strabismus. Also, the threshold limit for deep vision is influenced by the timing of the onset of strabismus (it is important at what stage of formation the visual process was) and the degree of aniseikonia - a disorder in which images of different sizes are formed on the retinas of both eyes. If this difference is more than 5%, then the quality of depth vision is very low.
That is why it is so important to carefully observe the process of development of the child’s visual mechanism, to know what he should be able to do at a certain period of life. Developed strabismus and amblyopia can lead to complete loss of binocular vision, including stereo function. Most often, this disease develops before three years of age.
Causes of binocular vision impairment
There are a large number of factors that can lead to the appearance of pathology
It is important to discover the cause in order to find effective treatment. So, deviations in binocularity can be caused by:
- Anisometropia;
- Damage to the muscles of the organ of vision;
- Problems with muscle innervation;
- Pathological processes in the bone mass of the orbit;
- Brain stem diseases;
- Infectious diseases affecting the visual apparatus and surrounding tissues;
- Intoxication of the body;
- Cataract;
- Mechanical injury to the eye;
- Diseases of the retina (rupture, detachment);
- New growths in the brain or eyes.
This is only a minimal list of ailments that can negatively affect stereoscopic vision.
Why does the syndrome occur?
Defocus of vision refers to pathological conditions caused by impaired accommodation. In this case, the lens loses the ability to focus on visual objects, and the brain does not receive a clear image of them. The most common reasons for this are working for a long time at the monitor, reading in poor lighting, students expressly preparing for a session, and other visual stress.
This is why many people over forty begin to develop age-related farsightedness (presbyopia), and by sixty, normal focusing for most is impossible without correction and is almost impossible to treat.
However, blurred vision can take other forms:
Accommodative asthenopia. It occurs in those who suffer from astigmatism and myopia, in the absence of the necessary treatment and corrective glasses or lenses. Disturbance of accommodation is also possible with farsightedness. In these cases, a person always becomes very tired under visual stress - sometimes to the point of nausea, feels a burning sensation and “sand” in the eyes, sees poorly, his eyelids turn red, and suffers from headaches. Spasm of accommodation. Most often it occurs in schoolchildren and students due to intense visual work in preparation for classes. It is caused by severe tension of the ciliary muscle and is characterized by short-term loss of vision, double vision, burning and redness of the organs of vision. Paresis and paralysis of accommodation. These are ailments of a neurogenic nature, that is, caused by dysfunction of the optic nerve, most often due to mechanical damage, infection or intoxication. With paresis, it is impossible to see small objects, and paralysis gives the feeling that the near point of clear vision practically merges with the far one.
In most cases, all types of syndrome in which vision loses focus have common symptoms and require seeking medical help.
Distinctive features of stereoscopic vision
Stereoscopic vision is the ability to see the world around us with two eyes. In other words, the overall picture consists of a fusion of images entering the brain from each eye simultaneously.
With this type of vision, you can correctly estimate not only the distance to a visible object, but also its approximate size and shape.
In addition, stereoscopic vision has another significant advantage - the ability to see through objects. So, if you place, for example, a fountain pen in a vertical position in front of your eyes and look alternately with each eye, then a certain area will be closed in both the first and second cases. But if you look with both eyes at the same time, then the pen ceases to be a hindrance. But this ability to “look through objects” loses its power when the width of such an object is greater than the distance between the eyes.
The peculiarities of this type of vision in various representatives of the globe are presented below.
Problems with binocular vision
In ophthalmology there is a special part that is responsible for the correct joint activity of the two eyes, in particular for binocular vision. Its name is ortopics.
Or rather, with this disease it is absent as such at all. Strabismus occurs when either (or both) eyes deviate in the opposite direction, causing the visual axes to no longer converge on one object.
A person ceases to fully see with both eyes. Restoring stereoscopic vision is practically the main goal in the treatment of this disease.
There are two main forms of the disease - paralytic and concomitant. With the friendly type, one eyeball squints. In this case, either the left or the right can mow. And the deviation of the visual axis will be the same. The main cause of this disorder is ametropia.
Also, such strabismus can be caused by a significant difference in the visual acuity of each eye, with diseases of the optic nerve and/or retina, with clouding of the lens or other eye membranes, as well as with disorders of the central nervous system.
It is worth noting that with this type of strabismus, eye mobility is completely preserved. There may even be no double vision before the eyes. But when focusing on a specific object, the second eye will be deviated to either side.
In paralytic strabismus, one eye will squint steadily. But at the same time, limited rotation of the eyeball, or its complete immobility, will be observed. In this case, part of the eye muscles will be completely affected and paralyzed.
This type of strabismus occurs due to damage to the nerves responsible for the movement of the eyeball or dysfunction of the muscles themselves. This occurs for various reasons - from the penetration of hostile microorganisms and viruses, to injuries, vascular diseases or even the occurrence of tumors.
Of course, no binocular vision can be observed. A person has to additionally rotate his head towards the paralyzed muscle in order to at least somehow observe the world around him. Against this background, patients often experience dizziness.
Paralytic strabismus can occur in people of any age. In this case, strabismus can be either convergent or divergent (the eyes move in different directions), as well as vertical.
If you have problems with stereoscopic vision, it is necessary to carry out thorough checks using specialized equipment.
When abnormalities are detected, the ophthalmologist is required to conduct all additional tests to determine the degree of development of the disorder. Typically, these include almost all of the checks described above.
One of the most common childhood disorders associated with the development of stereo vision is amblyopia. This is the so-called “lazy eye”, when one of the eyes develops more slowly than the other. In this case, over time, one eye generally ceases to participate in creating a joint image.
The brain will begin to receive too different pictures, and will simply “turn off” the one of the organs that “spoils” everything. It usually starts with a slight difference in visual acuity, which is easy to miss at first and not take action to correct immediately.
Amblyopia, like strabismus, occurs in approximately 4-5% of people. Moreover, they are observed even in countries with very developed medicine. It's all about untimely vision testing, the responsibility for which usually lies with the child's parents.
With regular preventive checks, you can easily detect the problem at the very beginning of development, and take all necessary measures to preserve good vision for the child: make a correct diagnosis, determining the exact degree of binocular vision impairment, and prescribing the correct, effective treatment.
And almost all vision problems in the future can be avoided.
The role of binocular vision for humans
This type of vision arose in humans, as well as in some other representatives of the living world, as a result of evolution.
Of course, modern humans do not need to hunt prey. But at the same time, stereoscopic vision plays a significant role in their lives. It is especially important for athletes. Thus, without an accurate calculation of the distance, biathletes will not hit the target, and gymnasts will not be able to perform on the balance beam.
This type of vision is very important for professions that require instant reaction (drivers, hunters, pilots).
And in everyday life you cannot do without stereoscopic vision. For example, it is quite difficult, seeing with one eye, to insert a thread into the eye of a needle. Partial loss of vision is very dangerous for a person. Seeing with only one eye, he will not be able to correctly navigate in space. And the multifaceted world will turn into a flat image.
Obviously, stereoscopic vision is the result of evolution. And only a select few are endowed with it.