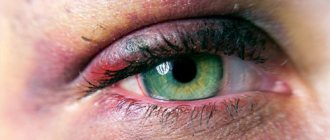
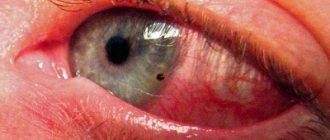
What are the dangers of acetic acid?
Vinegar is a carboxylic acid. It is colorless and has a pungent odor. If the concentration is low - sour taste. When it gets on the skin or mucous membrane, it destroys proteins and soft tissue cells. Necrosis, that is, cell death, occurs instantly.
The reaction is characterized by the release of water. The degree of chemical burn to tissue encountered by this caustic substance depends on the concentration. The most severe vinegar burn can be obtained from vinegar essence, the concentration of which exceeds 30%.
A weak solution will take some time. If acetic acid gets on clothing and the victim does not notice it immediately, the resulting burn can be severe. Every minute matters.
Causes of damage
Acetic acid belongs to the carboxylic group and is considered one of its most typical representatives, exhibiting all the characteristic properties.
It is colorless, volatile, has a pungent odor, has a sour taste in low concentrations and easily dissolves in water. Upon contact with the skin and mucous surfaces, the acid destroys their cells, “burning” water out of them, causing protein denaturation, resulting in tissue necrosis, and with prolonged exposure, deep and extremely severe injuries occur.
Unintentional burns from acetic acid occur:
- in case of careless handling - for example, opening the cork with hands without gloves or, which is strictly prohibited, with teeth;
- if storage rules are violated: a loose lid, location on the edge of a shelf, which increases the risk of accidentally touching, breaking the container and dousing the contents;
- if a bottle of acid is found by people who, due to their age, are not aware of what they are dealing with (children, old people). They may accidentally swallow vinegar essence, resulting in severe burns to the esophagus and larynx.
Types and degrees of damage
If you neglect the rules for handling acids and caustic solutions, you can get burned by vinegar. They are usually divided into 2 types:
- Internal - the effect of the solution on the larynx, stomach, esophagus. Contact is dangerous because acetic acid that enters the stomach instantly reacts with hydrochloric acid from the stomach. Even a small volume and low concentration are dangerous due to the consequences of gastrointestinal disorders.
- External - affects the skin or mucous membranes. Prolonged contact with the active components of the acid causes severe damage. Moreover, the higher the concentration of the solution (5%, 10%, 70%), the more severe the consequences will be. If the wound is large, then you should not put off visiting a doctor.
Regardless of the type of injury received, there are 4 degrees of severity. Only a doctor can determine them:
- the first one is the easiest. It is characterized by redness of the skin, soreness, and slight swelling. Complete healing occurs in 3–4 days. It should be noted that there will be no trace left on the body that could remind of the unpleasant incident.
- in the second degree, 2 layers of the epidermis are affected: the stratum corneum and the germ layer. The wound, as in the first case, does not leave behind scars, but regeneration of skin cells and healing will take about 2-3 weeks.
- the third and fourth degrees are characterized by the formation of black or brown crusts and scabs. At stage 3, the skin is affected down to the sweat, sebaceous glands, and blood vessels.
Grade 4 injury reaches the fatty tissue. You can get such a serious wound with vinegar of the highest concentration.
Chemical burn to the eye: first aid and treatment at home
Eye burns are not uncommon. They may be different. But the most dangerous type is a chemical burn to the eye. What is it, what causes it, how can I help a person with burns of varying severity? Let's try to answer these questions.
Main characteristics of injury
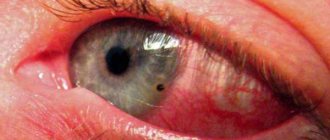
A chemical burn is an injury to the eye caused by exposure to aggressive chemicals.
First of all, there is damage to the conjunctiva - a thin connective membrane that covers the outer surface of the eye and the back surface of the eyelid.
It performs an important function because it releases a special liquid that lubricates the eye and prevents it from drying out. Its damage often leads to impairment and even loss of vision.
Damaging substances
Chemical burns of the conjunctiva are not uncommon these days. According to statistics, 10% of all eye burns are of chemical origin. Most often, damage occurs when aggressive substances come into contact with the ocular surface. Among them are:
- Acids. Most often, burns occur with the following acids:
- hydrochloric acid (HCl);
- acetic (HC, COOH);
- hydrofluoric(HF).
sulfuric (H2SO4);
An acid burn is similar to a thermal burn. It affects the conjunctiva and cornea without spreading into the eyeball. The degree of damage is influenced by the concentration of acids and the duration of their exposure.
At the site of acid entry, a necrotic area appears, which is separated from healthy tissue (coagulation). In this case, a very strong pain syndrome appears, since the optic nerves are irritated.
- ammonia (ammonium hydroxide);
caustic soda (sodium hydroxide);
Burns from alkaline substances are considered more dangerous because the damage extends deep into the eye, from where it is not easy to remove. At the same time, the time of negative impact increases.
This occurs due to the fact that alkali provokes liquefaction necrosis in the proteins, which leads to their melting (myomalacia) and spreading throughout the eye. In this case, the optic nerves are damaged by alkali, which leads to their loss of sensitivity. That is why a person with alkaline burns practically does not feel pain. This often leads to underestimation of damage.
How does it manifest?
The severity of a chemical burn depends on many factors. Among them are:
- type of chemical (acid, alkali, etc.);
- the amount of substance that has reached the surface of the eyes;
- concentration of the chemical (the more diluted it is, the less harm the burn will cause);
- temperature of the substance (the higher it is, the more complex the consequences);
- duration of exposure to the eyes.
The favorable outcome of treatment is also influenced by the patient’s age (the younger the person, the faster the recovery), as well as how timely and high-quality first aid was provided.
There are several degrees of eye damage from chemicals, which differ in the severity of the damage and are manifested by specific symptoms. There are 4 degrees of chemical burns:
- The first is considered the mildest degree of burn. Its main symptoms are: sudden onset of pain;
- cloudiness in the eyes (vision problems);
- the appearance of red blood vessels in the whites of the eyes (hyperemia);
- conjunctival edema (chemosis);
- cloudiness of the fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye.
- the pain becomes constant (pain syndrome), but with an alkaline lesion it subsides;
vision is significantly weakened;
Most often, grade 3 and 4 lesions do not go away without complications. The most unpleasant of them are the formation of ulcers and scars on the skin of the eyelids, the connective membrane and the cornea (cataract), fusion of the conjunctivae of the eyelids and eyes, inflammatory processes, and increased intraocular pressure. All this can lead to a decrease in visual acuity, and sometimes to its complete loss.
Healing procedures
For a chemical burn to the eye, first aid involves a set of certain actions. It must be provided on an emergency basis. It’s good if there is a person nearby with a medical education or basic knowledge in this area. But even an ordinary person can help.
Further therapy
Medical centers offer these procedures to treat eyes damaged by chemicals. First of all, medications are used. Among them:
- local anesthesia for the purpose of carrying out manipulations to remove aggressive substances (Lidocaine);
- antitetanus serum;
- antibiotics to prevent infection (drops containing ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin eye ointment);
- cycloplegic drugs that reduce pain and prevent scarring (atropine sulfate solution);
- tear fluid substitutes (Lakrisin);
- drugs that reduce intraocular pressure (Timolol, acetazolamide solution);
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) are prescribed when inflammation occurs.
Additionally, citrates (citric acid salts) or ascorbic acid are prescribed, which improve calcium metabolism in the affected area.
If extensive damage to the eyeball is observed (with burns of 3 or 4 degrees of severity, when defective conditions occur), then surgical intervention may be required:
- tarsography (suturing the skin of the eyelids during healing);
- tissue transplantation;
- autotransplantation;
- keratoplasty (to remove scars);
- prompt correction of the consequences of burns (glaucoma, cataracts).
In some conditions (subatrophy - slow death of the damaged eye), keratoprosthesis may be required - replacing the cloudy cornea with an artificial optical device.
Eye burns of chemical origin are common. Most often they are caused by acids and alkalis that enter the eye due to carelessness or failure to follow safety rules when in contact with aggressive chemicals. Such burns should be treated by a qualified physician.
Loading…
Source: https://doloypsoriaz.ru/ozhogi/vidy-04/ximicheskij-ozhog-glaza.html
First aid for injuries to different parts of the body
If you realize you have been burned by acetic acid, remain calm. This will allow you to carefully plan all actions and avoid serious consequences. First of all, it is necessary to stop the contact of the acid with the skin or mucous membranes. The first aid technique depends on the affected area.
Vinegar burn to esophagus
This type of injury can be considered the most dangerous to life and health. 50 ml of 70% vinegar essence is considered a lethal dose for an adult. For a child, this dose is reduced several times, which is why it is recommended to hide the acid from children and the elderly.
The victim must be immediately taken to the nearest medical facility. First aid consists of taking a soda solution and drinking plenty of warm boiled water. The larger the volume of water the esophagus and stomach are washed, the lower the risk of complications.
In most cases, the patient will be offered hospital treatment. You will have to stop eating for the next few days.
Vinegar burn to the respiratory tract
Receiving such an injury in a domestic environment is almost impossible. A burn to the respiratory tract can be caused by prolonged inhalation of vapors or by accidental inhalation of vapors from a 70% solution. Not only the upper sections are damaged, but sometimes even the bronchi.
Providing first aid consists of washing the accessible parts as much as possible and ingesting a bicarbonate solution. For an adult, the dosage is 0.5 liters. You can also neutralize the effect of vapors with a soda solution.
Treatment can only be provided by medical professionals. The victim is picked up by an ambulance and taken to the nearest hospital. The patient is prescribed:
- antihistamines;
- painkillers;
- moisturizing inhalations;
- antibiotics to prevent the development of pathogenic microflora.
Treatment is usually long-term and can last for several months.
Vinegar burn to mouth
When acid enters the oral cavity, it immediately reacts. The degree and complexity of the injury depends on the timeliness of preventive measures. It is necessary to rinse the affected area thoroughly and in large quantities.
It is acceptable to prepare an alkaline solution (water with soda). The duration of the manipulations is at least 15–20 minutes. At this time, you need to call an ambulance so that doctors can assess the extent of the damage, the need for surgical intervention, and hospital treatment.
Burn of the larynx
The victim must immediately begin gargling and gastric lavage with an alkaline solution. Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
Attention! Self-medication for this type of injury is unacceptable. The patient needs to be admitted to the hospital, where he will be offered lavage of the larynx and stomach with saline solution to neutralize the acid.
Further, the victims are prescribed antihistamines, medications to stabilize the heart rhythm, and painkillers.
Skin burn
Skin burns from vinegar are a common injury in everyday life. If acid gets on the skin, it should be thoroughly washed off the affected area under running water. To neutralize the residual effect of the acid, the burn site is treated with alkali.
To do this, use regular soap or baking soda. The treated area is washed again with water, and then an anti-inflammatory ointment and a sterile bandage are applied.
If drops of acetic acid get on clothing, the burn does not appear immediately. Itching and burning can be felt after two hours. The first aid action plan remains the same. It is important not to forget to change your clothes.
Burn of the mucous membrane of the eyes
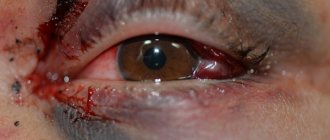
Acid that gets into the eyes entails the most unexpected, unpleasant consequences. The victim feels acute pain and burning. The burn is accompanied by profuse lacrimation. Scars may remain on the surface of the mucosa, which has a detrimental effect on visual acuity. The damage can be so extensive and severe that the person loses vision.
Help lies in long-term washing. It should be noted that the eyes need to be opened in the water in order to quickly wash away any remaining caustic liquid. The duration of rinsing is about 20–30 minutes.
For convenience, you can replace washing with a bath of water, where the victim lowers his face and opens his eyes. When first aid has been provided, you need to visit an ophthalmologist. The specialist will prescribe restorative eye drops and a disinfectant healing gel.
Causes and symptoms of vinegar burns
Everyone has been burned at home at least once. The initial pain and inflammation will take a long time to subside, and a scar may remain that is difficult to remove. Esophageal lesions are even more dangerous; internal organs react painfully to the negative effects of chemicals.
Common causes of lesions include:
- Careless handling of vinegar during cooking.
- Small children may drink or pour it on themselves. Sometimes adults confuse vinegar with water and take it orally.
- Inhalation of hot acetic acid vapor.
If the substance gets on the skin, the main symptom will be the appearance of a white spot. A person is bothered by intense, burning pain, which intensifies over time. When the essence gets inside, the patient complains of:
- burning pain in the mouth, along the esophagus and in the stomach;
- it is impossible to swallow due to pain;
- salivation;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
The consequences of inhaling steam can manifest as mental disorders when acetic acid affects the brain.
What you should absolutely not do if you have a vinegar burn
Every person's first aid kit probably contains a variety of antiseptics and medications for treating wounds. The most popular include iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate, and hydrogen peroxide. It is strictly forbidden to treat wounds with vinegar burns with these solutions. Not only will they not produce results, but they may even make the situation worse.
Badger and bear fat have long been popular among adherents of alternative medicine. But treating wounds with fat is also prohibited. They create an invisible film. Under the dense layer, an ideal environment is formed for the development and reproduction of pathogenic microflora. After a few days of such self-medication, the wound may begin to fester.
It should be noted! A chemical burn is a fairly serious injury, the consequences of which are unpredictable. If even the slightest doubt arises, it is recommended to contact the trauma department at the nearest medical facility.
An adult is responsible for his body and health independently, but if we are talking about a child, it is better to spend a couple of hours consulting a specialist who will competently plan treatment.
Treatment prognosis
For first-degree burns, the treatment period does not exceed one week. Burnt tissue cells dry out and peel off. No scars appear at the site of damage.
There are no scars left with 2nd degree burns. Timely first aid and a well-designed treatment plan will reduce the healing time to 2-3 weeks.
With more severe burns, adhesions, scars, and scars may remain. This result is most often typical for areas of the body with delicate skin and mucous membranes. For 3rd and 4th degree burns, consultation with a surgeon or even surgical intervention is required. The treatment period may take several months.
Vinegar is a fairly common acid that requires careful handling and compliance with safety precautions. Children and old people are at risk: the former are interested in a bottle with a bright picture, while the latter, due to inattention, may confuse it with other solutions.
Try to hide the vinegar essence away from the eyes of a child and an inattentive elderly person, and an adult should familiarize themselves with the rules of what to do in case of a burn with acetic acid.
source
Symptoms of the lesion
With an external acetic acid burn, the symptoms are obvious. Firstly, the place where the acid enters turns white, and after a few minutes it turns gray. Secondly, the victim feels severe pain and burning.
Symptoms of injury from an internal burn:
- pain and burning in the throat area;
- it is painful for the victim to swallow;
- Nausea and then vomiting may occur;
- pain in the area of the lymph nodes;
- high body temperature;
- abundance of saliva.
Symptoms after contact with eyes
Vinegar essence is especially dangerous, as it burns the retina and melts the cornea. If a chemical gets into your eye, you should immediately call an ambulance.
The degree of injury from contact with mucous membranes varies depending on the concentration of the product. Malic, grape and acetic acid up to 9%, the most commonly used in everyday life, can cause a chemical burn to the skin of the eyelids and retina, which will lead to disruption of blood supply. High concentrations can completely melt the cornea and cause the formation of a cataract that cannot be cured. Unpleasant symptoms include the following:
- burning and itching;
- increased lacrimation;
- blurred vision;
- redness of the skin of the eyelids;
- acute pain;
- dizziness.
Return to contents
Getting vinegar into your eyes. First aid for adults and children
Housewives usually store vinegar in their kitchen . And curious children can easily knock the bottle over themselves and get serious chemical burns.
It’s even worse if a drop of the substance gets into your eyes: it immediately causes a burn to the retina, which can lead to loss of vision .
Due to carelessness, an adult can also receive such an injury.
Symptoms of a chemical burn depend on the concentration of the substance.
If an accident occurs with acid up to 9%, which is most often used in everyday life, you can hope for a favorable outcome.
But 70% vinegar can completely melt the cornea and lead to the formation of a cataract, which cannot be treated.
If vinegar gets on the cornea, a person experiences:
- severe burning and pain;
- tearfulness;
- itching;
- dizziness.
These symptoms include blurred vision and redness of the eyes and eyelids.
First aid at home
But first aid is necessary to reduce pain and prevent the substance from penetrating into the deep tissues of the eye.
For an adult
An adult needs to rinse the eyes for 15-20 minutes or until the burning sensation completely disappears .
To do this, you need to either place your open eye under running water, or fill a basin with cool water, lower your face there and blink quickly.
The colder the water, the stronger the analgesic effect.
Then you can do the same procedure, but pour a little soda into a bowl of water . The concentration should be 1 teaspoon of soda per 1 glass of water.
A cold compress is then applied to the eye . You can keep it until your appointment with the doctor.
The procedure for providing first aid to a child is practically no different from that for an adult.
just need to rinse your eyes with a syringe without a needle : pour cold water into it and rinse the eye, slightly pulling back the lower eyelid.
The child must be positioned in such a way that the water flows down, for example, over a basin or sink.
Do not wipe your eyes with a towel or allow your child to rub them with their hands.
Then the syringe is filled with a weak soda solution to wash the eyes.
The washing procedure can be repeated several times.
When should you see a doctor?
If vinegar gets into your eyes, medical attention is required in any case, regardless of the degree of damage and the age of the victim .
The doctor must make sure that the reagent does not enter the deep structures of the eye and will not lead to loss of vision.
Consequences
Even a small amount of vinegar that gets on the cornea does not pose a direct threat to the health of the victim .
A chemical can cause damage to the eye even without symptoms: this is the insidiousness of a burn.
In severe cases, the acid burns through the cornea to the sclera , resulting in the formation of a fairly large white spot.
Because of it, vision becomes blurred or almost completely lost .
Complete or partial clouding of the lens leads to irreversible pathological changes in the ocular structures.
Their consequence is complete loss of vision.
The most harmless consequence of a vinegar burn is infection of the mucous membranes . In this case, a course of antibacterial treatment will be required.
Treatment
Immediately after an injury, cold compresses and lotions allowed .
In the evening of the same day, Cyclomed or Hydrocortisone ointment is applied . This should be done immediately before bed.
Then the doctor may prescribe eye drops , which need to be instilled 3-5 times a day, 1-2 drops.
These can be solutions of Balarpan, Levomycetin, Solcoseryl, Interferon , Albucid, Tsipromed, Oftan Dexomethasone.
Albucid 30% drops should not be instilled into a child without consulting a doctor.
For 2-3 days after the injury, you are allowed to rinse your eyes with a cool decoction of chamomile or calendula.
Conclusions and Conclusion
- Getting vinegar into your eyes almost never goes away without leaving a trace. But this injury can be prevented by following safety precautions.
- If a drop of acid does get on your eyes, you should immediately rinse them with running water until the burning sensation stops completely. Then you need to apply a cold compress and go to the hospital.
- Rubbing your eyes with your hands and using folk remedies and medications without a doctor’s prescription is strictly prohibited.
From this video you will learn how to provide first aid for a chemical burn:
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material and the author!
( 2 5.00
Source: https://zrenie1.com/bolezni/simptomy/uksus-popal-v-glaza.html
What complications can there be?
Although acid is less dangerous than alkali, exposure to the eye can lead to complete loss of vision. In severe cases, the acid completely burns through the cornea to the sclera and causes the formation of a white spot. Another complication is complete or partial clouding of the eye lens, which will also lead to irreversible pathological processes that can lead to blindness in the affected eye. Therefore, even if the unpleasant first symptoms were managed to stop, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist. The destructive influence can occur unnoticed. Another possible cause of discomfort in the eye, which does not go away for 2-3 days, is infection of the mucous membranes. In this case, the ophthalmologist may prescribe a course of antibiotics.
First aid: what to do?
As soon as the acid gets on the mucous membranes, it is necessary to rinse the eye with cool running water. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. Since a quick wash will not completely remove the remaining reagent. If vinegar gets into a small child's eyes, you can fill a syringe with water and inject it directly into the eyeball. The colder the liquid, the stronger the analgesic effect. Afterwards, washing with a weak soda solution at a concentration of 1 tsp is indicated. for 1 glass. It is also recommended to fill a large container with cool water and put your face in it. You need to keep your eyes open. The procedure should be repeated 3-4 times or until the severe burning sensation disappears.
First aid rules
If acid gets on clothing, it must be removed immediately, even if the strength of the composition is low. With prolonged contact with the skin, table vinegar also injures the surface.
The affected area should be washed with plenty of running water for at least 15 minutes. This will help relieve pain and clean the surface. Then, to stop the effects of the acid, apply a weak solution of soda to the burn (1 teaspoon per glass of water) or wash it several times with laundry soap.
In case of any injury, it is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible or take the victim to the hospital.
Necessary actions in case of external and internal burns
Vinegar burns are classified as chemical injuries. It occurs when acid gets on the skin or inside the body. Moreover, the higher the concentration of vinegar, the more dangerous the burn.
The location and severity of the injury is of great importance. There are 2 types of vinegar damage - external and internal. In both cases, in order to neutralize the effect of the acid, it is necessary to rinse and transport the patient to a medical facility. However, the algorithm for providing first aid for external and internal burns is different.
What to do if the skin and mucous membrane of the eye is burned with vinegar
In case of external injuries, vinegar gets on the skin or mucous membrane of the eyes. In the latter case, particularly severe pain occurs.
First aid for burns with vinegar or its derivatives of the skin and mucous membrane of the eyes:
- Remove clothing that has been exposed to aggressive acid (if the skin is damaged), as well as jewelry;
- Rinse the damaged area with tap water. Keep the affected part of the body under the stream for 20 minutes or more. This is an important measure that will help wash the vinegar from the skin and reduce the intensity of the pain;
- To neutralize the effect of the acid, prepare an alkaline solution from soap or soda. It’s great if the victim has a loved one with him who will prepare such a solution while he washes the burn site. If there is no one nearby, then you need to prepare the neutralizer yourself after the first rinse. In this way, rinsing is carried out when acid comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of the eyes;
- Then a wet compress is applied to the affected area , which will further reduce the negative effects of vinegar;
- Then the burn site is treated with antiseptics in the form of creams, ointments or gels. These medications will help reduce inflammation and pain;
- Then you need to transport the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance, especially if the injury is severe.
Doctors will assess the extent of the damage, treat the damaged area with special medications and formulate a treatment strategy.
Necessary measures for burns of the digestive tract and respiratory tract
An internal burn with vinegar is dangerous not only to health, but also to human life. The fact is that acid burns the walls of all internal organs through which it passes. To avoid dangerous consequences, you need to provide first aid to the victim as quickly as possible :
- The first thing to do if you or someone close to you has swallowed vinegar is to call doctors or transport the patient to a medical facility yourself. Only specialists will be able to correctly assess the condition of the victim and take the necessary measures;
- While waiting for the ambulance, you need to rinse your stomach with regular boiled water, then with a weak solution of baking soda, and then again with water. This will help neutralize the acid.
Further assistance is carried out by doctors.
Otherwise, complications may arise that are incompatible with life. Then only doctors can help, the main thing is to take the victim to the hospital without delay.
Unfortunately, the process of tissue destruction of the digestive organs does not stop even after the source of the burn is eliminated. That is, in the first hours, and sometimes days, it is difficult to determine the exact degree of damage. The exact diagnosis will be known 7–10 days after instrumental studies.
Chemical burn to the eye: symptoms, risk factors, first aid measures, prohibited actions, treatment
Eye injuries are a common injury that causes vision impairment and can lead to blindness. A chemical burn to the eye poses a great danger. It can easily be obtained by careless handling of toxic substances. If you find yourself in such a situation, you need to know how to provide first aid. Correct actions reduce the damaging effects of chemicals and can preserve vision.
Description of injury
According to statistics, about 10% of damage to the visual organ is caused by chemicals. Most often, local damage occurs upon contact with acid and alkali. The degree of severity directly depends on the number of aggressive agents that have reached the mucous membrane and on the duration of the dangerous influence.
Penetrating into the eye, liquid chemicals immediately mix with tears and act more slowly. Solid agents quickly dissolve, forming a concentrate that destroys the structure of the organ.
Acid
An acid burn is similar to a thermal injury. It injures the cornea and creates coagulative necrosis. A film of dead tissue prevents the substance from penetrating deep into the eyeball. The following acids pose a serious danger:
- vinegar, salt;
- chlorine, nitrogen;
- sulfuric, hydrogen fluoride.
Under the influence of acids, nerve endings are irritated, so a person feels acute pain.
Alkali
Alkali burns pose a serious threat. The substance tends to penetrate deep into the eye and continue its destructive effect for a long time. If the chemical is not removed immediately, the burn will worsen and may cause blindness. Large-scale damage is caused by concentrated hot alkaline solutions. Common substances that can burn the eye:
- caustic soda;
- caustic potassium;
- slaked and quicklime;
- ammonium hydroxide;
- ammonia;
- Magnesium hydroxide.
Symptoms of damage by various substances
The main signs of a chemical burn of the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye are:
- burning;
- lacrimation;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling;
- blurred vision.
When exposed to acids, the color of the conjunctiva changes. Chromium provokes the appearance of a brown tint, nitrogen - yellow. A substance in the eye promotes excessive tear production. It becomes difficult to open the eyelids, they hurt, vision becomes blurred, and a feeling of a foreign body appears.
Characteristic symptoms of an alkaline burn are photophobia, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. The chemicals destroy nerve fibers, so the victim rarely feels severe pain. Sometimes this causes a person to underestimate the injury.
Acid and alkali burn the skin around the eyes. It becomes inflamed, red, and blisters form.
Risk factors
If safety rules are violated or as a result of an accident, dangerous reagents penetrate into the eye, cause the death of the conjunctiva and gradually penetrate deeper into the eyeball. Injury can occur at work, at home, and even in a beauty salon after unsuccessful eyelash extensions. At risk are people working:
- builders;
- pharmacists;
- mechanics;
- laboratory assistants.
Accidents occur during chemical experiments and in everyday life due to the careless use of lime, ammonia, and bleach. Incorrect actions by a cosmetologist can lead to synthetic glue getting into the eye during eyelash extensions. Symptoms of an unpleasant incident are:
- painful sensations;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- redness and foreign body sensation;
- copious tears.
The tendency to drink alcohol increases the possibility of burns. Alcohol makes a person irresponsible and forces them to neglect safety rules when working with hazardous substances .
Emergency help
There are 4 degrees of damage for chemical burns of the eye with acid and alkali. Help needs to be provided as quickly as possible. This will minimize damage and improve the prognosis for recovery.
- First of all, you need to rinse the affected area. This must be done no later than half an hour after injury.
- You will need saline solution, potassium permanganate slightly diluted in water, or 0.9% sodium chloride solution. You can use regular cool water.
- The procedure should be carried out for 20 minutes, washing the mucous membrane from the inner corner of the eye to the outer.
- If the cause of the burn is a solid substance, you must first remove it with tweezers or a sterile cloth..
- To provide qualified emergency care, it is important to find out what exactly caused the injury, because the effect of chemicals can be neutralized.
- When alkali gets into the eye, rinsing should be done with a three percent acetic solution or two percent boric acid.
- Acid burns should be washed with a solution of baking soda - 25 g of the substance is dissolved in 0.5 liters of water.
To prevent the development of infection, you can instill a solution of Furacilin. Then you should cover the eye with sterile gauze, secure it with a bandage and go to the hospital. It is advisable to take with you a bottle of the reagent that caused the injury. Studying the contents will help doctors prescribe the right therapy.
What not to do
Chemical eye damage should not be treated independently. You should definitely contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
In order not to aggravate the situation, first aid should be carried out in strict compliance with hygiene rules.
Forbidden:
- rub your eyelids;
- leave solid chemicals on the mucous membrane;
- try to reach particles of the aggressive substance with your fingers;
- apply warm compresses;
- use medications without a doctor's permission.
Therapy
The specialist prescribes a treatment regimen on an individual basis after studying the clinical picture. Deep burns require urgent hospitalization. Restorative therapy is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- relieving inflammation;
- prevention of infection;
- pain relief;
- stabilization of intraocular pressure;
- healing of damage;
- prevention of complications.
As painkillers, doctors usually prescribe Novocain 2% and Dicaine 0.25% solution. To eliminate microbes, antibiotics Ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin, Ofloxacin are used.
To remove inflammation of the eyelids and skin around the eyes, the affected areas are lubricated with Tetracycline or Streptocide ointment. Rapid healing of the cornea and conjunctiva is ensured by corticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone. To relax the eye muscles and dilate the pupil, ophthalmic drugs Midrimax and Midriacil are used.
Twice a day you should wash the mucous membrane with a solution of Furacilin or Chlorhexedine and regularly instill eyes with Lacrisin, a substitute for natural tears. To improve the body's resistance, vitamin complexes are prescribed.
With deep extensive lesions, surgical intervention is necessary. It helps reduce the effects of injury and restore the function of the visual organ.
Source: https://ProTravmy.com/ozhogi/glaz-himicheskie
What not to do when providing first aid
When providing assistance after a vinegar burn, people may make common mistakes:
- Treat the burn with oil or other fat-based products. Then a thin film will form on the damaged area and the burn will spread inward;
- Immediately treat the burned area with anti-burn agents, for example, Panthenol, Olazol. First of all, you need to cool the damaged area and neutralize the effect of the acid, and then use pharmaceutical preparations. In addition, external agents can only be used for 1st degree damage;
- Tear off stuck clothing from the burned area. If the fabric is stuck to the wound surface, then there is no need to forcibly tear it off, it is better to thoroughly wet it with water so that it comes off, or entrust it to doctors;
- If acid is swallowed, do not artificially induce vomiting, as repeated exposure to it will intensify the injury. If vomiting occurs on its own, then do not hold it back, just continue to drink water;
- If there is a wound on the burned area , then rinsing it with water is prohibited; apply a bandage and cool it from above.
If the mucous membrane of the eyes is burned, it is strictly forbidden to rub them, otherwise the chemicals will penetrate deep into the tissues of the eye, causing damage. If a burning sensation occurs, immediately rinse the mucous membrane with plenty of water and rush to the doctor.
Symptoms of external and internal burns
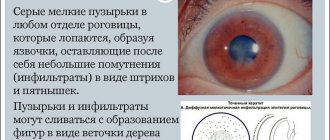
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the concentration of the acid. A weak solution provokes a burn only with prolonged exposure to tissue, while the essence provokes a burn instantly.
After contact with the skin of a highly concentrated solution, it becomes whitish, and later the tissues acquire a gray tint due to tissue necrosis. A dry crust (scab) appears on the affected area, which has clear boundaries. The victim feels a burning sensation, severe pain, and the area around the burn may become red and swollen.
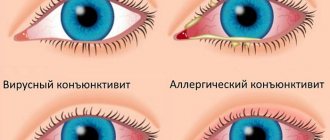
When the eyes are burned with vinegar, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain and burning in the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- Excessive tearing;
- Painful sensitivity to light;
- Decreased vision in the damaged eye.
If a person accidentally swallows acid, a sharp burning pain appears, and the tissues that came into contact with the aggressive substance are instantly deformed. It is painful for the victim to swallow, talk, he feels nausea and the urge to vomit.
Once in the stomach, vinegar reacts with hydrochloric acid. If the concentration of the substance is high, then this interaction ends in the death of the victim. If the substance does not penetrate further than the oral cavity, then the tongue is burned by vinegar, the victim has difficulty distinguishing tastes, swelling of the soft tissues occurs, and a burning sensation occurs.
When the respiratory tract is damaged by vinegar, general intoxication develops. This condition is accompanied by fever, weakness, impaired functionality of the cardiovascular system, hallucinations, etc.
Symptoms
The degree of damage depends on the concentration of the substance. A weak solution can cause harm only with prolonged exposure and appear after some time, while the essence instantly corrodes soft tissue upon contact with them.
You can understand that a person has received such a burn by the signs described below.
When in contact with high concentrations of acetic acid, the affected area becomes whitish, then turns gray due to cell death. A scabby, dry crust with clear boundaries forms on the skin. The victim experiences a strong painful burning sensation. The area around the burn may become red and swollen. After deep damage, scars form on the skin.
If concentrated vinegar gets into the esophagus, severe pain and burning will be obvious symptoms. The tissues of the mucous surface are instantly deformed. The victim has difficulty swallowing and speaking, a feeling of nausea appears, vomiting, chest spasms may occur, the temperature rises and the heart rhythm is lost. In this case, the mucous membranes swell greatly and the person may experience a lack of air and suffocation.
In the stomach, vinegar begins to interact with the hydrochloric acid contained in it. At high concentrations of the substance, their reaction becomes fatal to the patient.
If the acid has not been swallowed, only the oral cavity is affected: the papillae on the tongue are burned, taste buds lose sensitivity, soft tissues swell, a burning sensation appears, and the temperature rises.
If vinegar gets into your eyes, the same thing happens. If the acid is concentrated, it will corrode the cornea, and the person will lose vision without the possibility of restoration. The victim experiences severe pain, cannot be in the light (photophobia develops), and tearing appears.
How to treat a vinegar burn
After first aid is provided, care for the victim passes to the shoulders of doctors. They draw up a treatment plan taking into account the location of the damage, its degree, age and characteristics of the patient’s body.
As part of complex treatment, pharmaceutical products for external and internal use, as well as effective folk remedies, are used. The decision on the choice of medications is made only by the attending physician. Before using traditional recipes, you should also obtain a doctor’s permission.
Use of drugs
The doctor selects medications for the patient. In the hospital, he is injected with drip solutions that help cleanse the blood, neutralize the effect of vinegar, and also remove its breakdown products.
As part of complex therapy, the following are used:
- Analgesics;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Antibacterial agents;
- Medicines that accelerate tissue healing.
If the mucous membrane of the throat is damaged, then oil preparations are used for treatment, which are administered using a syringe. For internal burns, detoxification therapy is carried out using a hemodez or glucose solution.
Drugs with a sedative effect, for example, Valerian, help normalize the psycho-emotional state of the patient. To treat skin burns with vinegar at home, external remedies are prescribed in the form of ointments, gels, and sprays to treat the damaged area.
You can treat a vinegar burn on the skin with the following ointments:
The drugs should be used daily, according to the instructions or recommendations of the doctor. It is also recommended to disinfect the damaged area with antiseptics, for example, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin solution.
Ointments and drops are used to treat damaged eyes. The decision on the choice of medications, the frequency of their use and dosage is made by the ophthalmologist.
Treatment with traditional methods
After providing basic assistance, when the victim’s life is not in danger, treatment can be supplemented with folk remedies. They are not as effective as medications, but have minimal contraindications.
The following folk recipes will help remove vinegar burns on the skin of the face and body:
- Grind peeled raw potatoes using a grater, apply to the damaged area, leave for 10 - 15 minutes, and then rinse. This remedy helps reduce inflammation and swelling;
- Apply a thin layer of sea buckthorn oil to the burn area. Carry out this simple procedure until the tissue is completely healed. This remedy will help restore skin faster after a vinegar burn;
- Lubricate the damaged area with aloe juice until the epidermis is completely restored. This remedy accelerates tissue regeneration;
- Pour 4 tbsp. l. oak bark 660 ml of water , bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for another 10 minutes. Then cool and strain. Dip a piece of gauze of the desired size into the broth, apply it to the burn site, and leave for half an hour. This remedy destroys pathogenic microbes and reduces swelling.
Therapy
If a small area of skin in an adult is injured, then first aid and treatment can be carried out at home.
If the victim is a child or a mucosal burn occurs, then consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Treatment consists of timely provision of first aid, elimination of aggressive acid from the surface of the skin or mucous membrane. Next, wound healing gels or ointments are applied to the affected area. A sterile bandage is applied on top. It should not put pressure on the injured area.
It is also important to do dressings in a timely manner. If blisters appear on the wound, do not open them yourself. Entrust this activity to a traumatologist or surgeon. He will carry out all manipulations under local anesthesia followed by application of an antiseptic solution.
Medicines
Self-prescribing medications is unacceptable. Only a doctor can determine a drug treatment plan.
Drugs that can be used for chemical burns can be divided into 3 main groups:
- Antiseptics for disinfection and permanent treatment of wounds. They prevent the entry of pathogens.
- Painkillers, cooling, anti-burn creams, gels.
- Antibacterial ones do not allow the wound to fester.
If the burn is external and the lesion is not severe, then independent use of Levomekol, Bepanten, Panthenol is acceptable.
If the burns are deep, the doctor may prescribe local antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Baneocin powder is very popular, it dries the top layer, protects against the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, and has wound-healing properties.
Baneocin is a powder that dries the top layer well, protects against the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, and has wound-healing properties.
The antibiotic Cifran works throughout the body as an anti-inflammatory drug, but before taking it, you must consult a doctor.
Folk remedies
If medications are not at hand, and the nearest pharmacy is far away, then traditional methods are often used. Among all the known methods, the most popular for acetic acid burns are the following:
- Sea buckthorn oil. They treat the wound until complete healing.
- Butter and beeswax mixed in a 3:1 ratio. To prepare, both ingredients must be melted in a water bath and mixed thoroughly. The cooled mixture is applied to the affected area and a bandage is applied on top.
- Crushed aloe stem. To prepare it, you need to grind the aloedo leaf into a mushy state and apply it to the skin. A bandage is made from a sterile bandage on top. During the day it can be removed, and the wound is washed with aloe juice.
- Fresh potatoes. Peel the root vegetable and grate it. The paste is applied to the wound and secured with a sterile bandage. It is also permissible to apply a cut of a tuber - the main wound-healing component is the secreted juice.
- You can make wet compresses from strong tea leaves. It is important to change them periodically to cool and relieve acute pain.
- A decoction of chamomile, calendula, oak bark, and St. John's wort will relieve swelling and eliminate pain. To prepare, you need to mix all the ingredients in equal proportions. One tablespoon of herbal mixture will require one liter of boiling water. The decoction is infused for 30 minutes.
A doctor prescribes a treatment regimen for a skin burn. He selects medications depending on the clinical picture of the lesion.
If the therapy takes place in a hospital setting, the patient is given special solutions to purify the blood, neutralize the acid and remove its breakdown products.
For treatment at home, various ointments, gels, sprays for treating the wound surface, means to accelerate tissue regeneration, painkillers, anti-inflammatory tablets, and antibiotics are prescribed.
Medicines
At the injury healing stage, the following is prescribed for external use:
- Bepanten;
- Solcoseryl;
- Radevit;
- Levomekol;
- Rescuer;
- Vishnevsky;
- Dermazin.
Wounds should be smeared regularly, according to the instructions of a particular drug. If necessary, before application, disinfect with antiseptic agents - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin.
Folk remedies
The use of any folk remedies is permissible only at the stage of treating a burn, but not when providing first aid. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.
Among the most effective folk methods are the following:
- Use sea buckthorn oil to lubricate the burn. Carry out the treatment at least 3 times a day.
- Brew oatmeal with a small amount of boiling water to form a liquid porridge-like mass. Let it brew for 20-30 minutes. Drain off excess water. Squeeze out the cereal and use the released mucus to wipe the injured area.
- Grate the potatoes on a fine grater. Squeeze. Apply the paste as a compress for 30 minutes.
- Apply fresh juice from aloe leaf in a thin layer several times a day to the affected area.
- Prepare a decoction of oak bark and coltsfoot, taken in equal proportions. Pour 1 tablespoon of raw material into 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes, strain and cool at room temperature. Soak gauze in the broth and apply as a compress for half an hour, 2-3 times a day.
Surgery is required for extensive and deep injuries. Often there is a need for skin grafting or plastic surgery to remove scars after wound healing.
Surgical treatment of extensive and deep burns
If the external acid burn is extensive and deep, surgery may be necessary. In some cases (especially with severe damage), there is a need for dermoplasty - this is a skin grafting operation.
If the esophagus and stomach are severely damaged by vinegar, the victim may be prescribed an urgent operation to excise the affected areas of the mucous membranes. Surgery is performed for internal hemorrhage that occurs as a result of a rupture of the organ wall.
Possible consequences
External burns with vinegar can cause scarring, especially if the wound is large or deep. If the patient does not follow the rules for caring for the damaged area, the scar will be pronounced, and it will be possible to get rid of it only with the help of plastic surgery.
After an eye burn, vinegar can:
- A fusion between the eyelids will form;
- The cornea becomes cloudy;
- Develop glaucoma (constant increase in intraocular pressure).
When acid is swallowed, not only the walls of the digestive tract are damaged, but other organs that are involved in the process of digesting food and eliminating toxins.
As a result, the liver, gall bladder and its ducts, pancreas, kidneys, and urinary tract suffer from a vinegar burn. In addition, the acid enters the bloodstream through the walls of the digestive organs, causing toxic shock.
After swallowing vinegar, the likelihood of the following diseases increases:
- Gastritis;
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- Stomach ulcer;
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum);
- Pneumonia;
- Functional failure of the liver and kidneys.
The victim loses weight and weakens the immune system. A person is forced to follow a strict diet to reduce the load on damaged gastrointestinal organs.
As you can see, a vinegar burn is a dangerous phenomenon, especially when it comes to internal damage. If the skin is damaged, you need to provide assistance to the victim, and after neutralizing the effect of the acid, send him to a doctor.
If you burn your eyes or accidentally ingest the concentrate, you should urgently call a doctor and rinse the affected area with water and then with an alkaline solution. It is important to follow your doctor's recommendations regarding burn treatment to avoid dangerous (sometimes life-threatening) consequences.
Victor Systemov - expert of the 1Travmpunkt site
source
Was the information helpful? Tell others about us, maybe they need help too.
Complications and consequences
The consequences of a vinegar burn on the skin are scars. If the eyes are injured, then, depending on the extent of the damage, the outcome may be the development of cataracts, partial or complete loss of vision.
If a person swallows an aggressive substance, then not only the walls of the esophagus are burned, but also other internal organs involved in the process of digestion and elimination of toxins: liver, kidneys, intestines, pancreas, gall bladder, urinary system. In addition, the acid is absorbed into the blood and the body experiences toxic shock.
The consequence of a burn is the development of diseases such as:
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity, pancreas;
- pneumonia;
- renal and liver failure.
A person loses significant weight, and the body’s immune defense decreases. In this case, the victim cannot eat fully, as he must constantly follow a strict diet in order to spare the stomach and digestive system.
With serious extensive damage to internal organs, a person dies.