There are so many bruises we have to deal with in everyday life. Due to the inexorable pace of modern life, people often lose their vigilance and get injured in various parts of the body due to negligence. When it comes to an injury such as an eye injury, many do not understand what it means.
In fact, an eye contusion should be understood as a blow to the eyeball with a blunt object. You can get injured as a result of a blow, for example, with a stick or stone, as well as during a fight with your fist.
Causes of eye injury
The causes of eye injury are different, but the main ones are the impact of a foreign object on the organ. You can get a bruise to the eyeball due to a blow:
- hands;
- branches;
- ball;
- stone;
- when falling, etc.
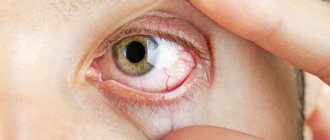
The degree of damage depends on the force of the impact. In case of injury, the sclera, cornea, lens, blood vessels, optic nerve, retina and lacrimal system may be damaged.
The eye area is surrounded by tissue that has a small subcutaneous fat layer and many blood vessels. Eye injury is accompanied by hemorrhage and rupture of dense tissue. In the professional sphere, an eye injury is called a concussion.
Mechanism and causes of injury
At the moment of receiving a blunt injury to the eye, significant changes occur in its structure - displacement of the eye, its deformation (compression in one direction, and stretching in the other). Anatomical features determine the transmission of impact force through the gel-like vitreous body to the remaining structures of the eyeball. As a result, a sharp spasm of the blood vessels in the eye occurs, and then their expansion, which causes a change in intraocular pressure.
Eye bruises most often occur during sports or active recreation, accidents at home and at work, in fights, car accidents . Sports head injuries often result in eye contusion. Damage may occur as a result of being hit by a football or tennis ball during a boxing match.
In everyday life, this type of injury occurs as a result of falling face down and hitting the eye on the corner of furniture. Eye bruising also often occurs as a result of blows with a fist, elbow, stick and other violent actions.
Symptoms of an eye injury
The main symptoms are:
- pain;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
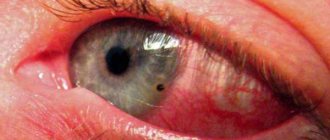
- hemorrhage or bleeding;
- partial loss of vision;
- involuntary closing of the eyelids;
- headache;
- loss of consciousness, dizziness;
- edema.
If an eye injury occurs without a combination with a penetrating wound or damage to the eyeball, then when the pain disappears, the injury is not given much importance, but the consequence may be deterioration of vision. This process occurs due to hemorrhage in the internal areas, the formation of a clot and the formation of connective tissue, which affects the functioning of the lens and provokes retinal detachment or the development of cataracts and glaucoma.
Eye contusion is classified as direct or indirect. Direct injury occurs when an object hits the eye. Indirect – when the face or head is damaged.
Symptoms and signs
The first signs of an eye injury:
- severe pain in the area of injury;
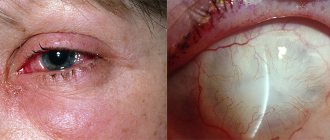
- hematoma of the eyelid and orbital tissues;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- decreased or complete loss of vision in the injured eye;
- diplopia (double vision);
- blepharospasm (involuntary closure of the eyelid);
- hemorrhage in the space around the iris.
With a strong indirect impact, pronounced swelling of the orbital tissues and exophthalmos occur - protrusion of the eye forward.
Note! As a result of excessive application of force exceeding the strength of the skull bones, damage to the bony walls of the eye orbit and air sinuses may occur. This phenomenon is accompanied by the formation of subcutaneous emphysema, sunken eyes, and crepitus (crunching) of bone fragments upon palpation.
First aid
If you receive an eye injury, pre-medical measures are taken, followed by mandatory seeking help from a specialist.
First aid for an eye injury should be performed with clean, washed or antiseptic hands.
Under no circumstances should you:
- use cotton wool;
- use alcohol-containing solutions;
- independently remove foreign objects from the damaged area;
- press and rub your eyes.
If you receive an injury, many can provide first aid, they know the basics of healing and rehabilitation methods, but still, not everyone knows what to do if they bruise their eyes.
The complex of first aid measures for eye injury includes:
- applying a bandage to protect from light;
- exclusion of physical activity;
- for the purpose of prevention, it is possible to instill Albucid into the eyes;
- stopping bleeding;
- use of anesthetic.
The injured person must take a horizontal position and apply ice wrapped in cloth to the bruised area.
If an alarming state occurs, the victim must be given a sedative and taken to a medical facility for professional assistance.
What happens to the eye after a blow?
An eye injury can occur as a result of a domestic accident, a blow with a fist, a ball or snowball, or a fall. Changes in the organ of vision and their degree depend on the cause, strength and location of the impact (lens, eyeball or other part), and the speed of the moving object.
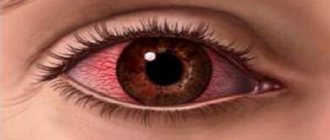
If there is a blow to the eye, the patient experiences discomfort, pain of varying strength, photophobia and redness, blurred vision and blurred vision.
When an injury occurs, hemorrhage occurs. It can be localized in various parts of the organ of vision (hemophthalmos, hyphema).
The structures of the eye temporarily shift back, the fibrous capsule rapidly increases in width. This leads to flattening of the cornea and its deflection inward, increasing intraocular pressure. Swelling may occur.
If intraocular pressure increases, this leads to pupil dilation and tearing. Detachment of the iris and retina is possible.
When the lens gets into the area, it becomes displaced and subluxated. This provokes rupture of the lens and the development of cataracts.
With excessively strong impacts, there may be a fracture of the optic canal or orbital walls.
Diagnostics
At the ophthalmic trauma center, a medical history of the injury will be taken, initial measures will be taken to treat the damaged area and, if necessary, the foreign body will be removed from the injured eye.
By contacting a specialized institution, you will receive a full range of examinations, consisting of:
- ophthalmochromoscopy,
- tonography;
- rheography;
- ultrasound examination;
- X-ray diagnostics.
After diagnostic measures are carried out, a diagnosis is established and treatment is prescribed.
After the blow the eye sees blurredly
Eye injury can lead to irreparable consequences: cloudiness, blurred vision, discomfort, hemorrhage, retinal detachment and even blindness.
If the organ of vision is affected, you should not self-medicate and look for the cause without a specialist.
A suitable place to go is an ophthalmology clinic; an emergency room is not suitable in this case.
If a stroke occurs, it is important to visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to determine the changes that have occurred, their cause, conduct a full diagnosis and prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Treatment
Eye injury is divided into types:
- superficial damage;
- penetrating;
- stupid;
- burns
Superficial injury occurs due to the introduction of a foreign object into the mucous membrane - soil, metal particles or stone.
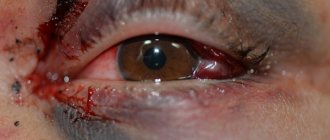
Superficial damage may result in insect entry. Acute pain, tearing and photophobia occurs, irritation and hyperemia of the mucous membrane occurs. With this type of injury, the foreign body is removed and a bandage with an antiseptic is applied. Penetrating eye injury occurs due to disruption of the integrity of the eye by cutting or piercing objects, as a result of which the eyeball suffers. Characteristic symptoms are severe pain, decreased or loss of vision. In this case, hospitalization is prescribed.
Blunt trauma occurs when the eye is exposed to a blunt object: a hand, a stick, etc. This type of injury occurs without visible damage to the eye and failure to promptly seek qualified help can lead to deterioration of vision. It is accompanied by painful sensations and “bloating” of the eye.
An eye burn occurs when the mucous membrane is exposed to chemical, thermal or radiation irritants. In case of a chemical burn to the eye, rinse with water and seek medical help.
In case of complex damage, hospitalization and, in some cases, surgery are prescribed. If a minor injury occurs, dispensary treatment is carried out under the supervision of specialists, which will quickly restore the injured organ.
The complex of eye treatment includes the use of:
- compresses of cold water, hydrogen peroxide;
- antibacterial and anti-inflammatory ointments;
- antibiotics;
- drugs that reduce eye pressure and restore blood vessels.
Drug treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Diagnosis of severe bruises
The damaged eye is examined by an ophthalmologist. It establishes the degree of injury and determines which elements of a given organ were damaged. Methods for diagnosing a bruise are as follows:
- Examination with an ophthalmoscope. It is used to study the fundus of the eyeball and is effective in the presence of obvious retinal injuries. This method is inaccurate, so it is better to dilate the pupil first. Otherwise, more than sixty percent of the retina may not be visible.
- Examination using a Goldmann lens. Allows a more thorough examination of damage in difficult-to-reach areas of the eye. A device with this lens is available in specialized and private clinics.
- Eyesight check. The standard procedure is carried out using a table with letters. A surefire method that will show whether vision loss is due to a bruise or not.
- Gonioscopy. Examine the anterior chamber of the eye. The procedure is quite painful; painkillers are used.
- Perimetry. The visual field is examined using a computer, since injuries of this nature can lead to its impairment.
- Ultrasound. Allows you to determine the clinical picture of a clouded state of the cornea and lens.
- Tomography. Maybe computer, or maybe magnetic resonance. In the first case, the eyeball and intracranial area are examined. In the second, defects in the optic nerves and muscles are examined, and motor abilities are tested.
Traditional medicine recipes
At home, it is also possible to treat with traditional methods that remain relevant in modern life:
- a compress of calendula infusion (1 tablespoon of calendula per 100 ml of water) will relieve swelling and inflammation;
- Applying burdock leaves to the damaged area will relieve pain. The pre-washed sheet is applied with the back side and covered with polyethylene and a warm cloth;
- To improve blood supply to the affected area and in the absence of bleeding, a paste of ginger and turmeric is used (0.5 teaspoons of turmeric and ginger and 1 teaspoon of water). The product is applied to the fabric, applied to the closed eye, polyethylene and a scarf are placed on top;
- for pain, onion gruel with the addition of a small amount of sugar will help;
- A compress of cabbage leaves will remove bruises. First mash the leaves until the juice is released and apply for 2 hours once a day;
- To eliminate hematomas and relieve inflammation, a 10% salt solution is used in the form of lotions;
- Iodine mesh is applied to the closed eyelid to restore blood circulation and healing. The mesh must be applied carefully so that the solution does not get into the eye;
- A poultice of cabbage leaves will help get rid of bruises. The leaves are poured with boiling water and heated. After heat treatment, they are kneaded and applied to the damaged area;
- Using masks made from sour cream and chopped parsley (1:2), tomato puree with a small amount of lemon juice, lentil flour and turmeric will help remove bruises. Masks are applied around the eyes.
It is impossible to treat an eye injury using folk remedies alone. Strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and at the same time apply the experience acquired by the people.
Damage to the organs of vision: main symptoms
A severe bruise of the eyelid is accompanied by severe symptoms that do not go away for a long time. If an adult is hit on the head and hit in the eye with a fist, the first thing the victim feels is severe pain. Next, swelling of the eye forms, the bruised organ waters, does not open, and over time a bruise appears. When hit hard with a stick, the head often hurts, visual functions are disrupted, photophobia appears, and an eye hematoma occurs.
If a baby or older child hits his eyebrow on the corner of a table or door, swelling will form near the damaged area after the impact, and after a while a bruise will form. In this situation, it is necessary to monitor the baby. If the broken eye becomes very red, swollen, looks unnatural, and also has a headache, the child should definitely be seen by a doctor to rule out damage to the bones of the skull.
Eye injuries in children
Particular attention should be paid to eye injury in a child.
Children cannot always determine the location of pain and often spread the infection throughout the body. If you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, treatment can be protracted and complex. Any deviations from the norm (redness, blurred vision, rolling eyes, frequent blinking) should cause concern and immediately consult a doctor. Children should be examined regularly (once a year) by an ophthalmologist to avoid deterioration or loss of vision. If you injure your eye, immediately consult a doctor and follow all his instructions. Do not forget that delay can lead to irreversible processes. Vision is an indispensable source of information about the world around us.
Symptoms: numbness, pain, hematoma of the cheeks, cheekbones, lips, double vision
Do you have complaints about a constant aching dull pain in the left or right infraorbital region, which intensifies when opening the mouth and eating, swelling and hematoma in the left or right infraorbital region, double vision in the left or right eye (“the picture is floating”)?
You need to contact a maxillofacial surgeon in a hospital. You most likely have a fracture of the zygomatic bone. The diagnosis is confirmed by examination and x-ray examination. When palpating the lower orbital edge, a characteristic step is determined. X-rays show displacement of fragments of the zygomatic bone.
How are traumatic injuries diagnosed?
Parents themselves will not be able to assess all possible vision problems after an impact, so even with a minor injury it is worth contacting an ophthalmologist. The doctor will conduct an external examination and additional research techniques necessary in a given situation, initially assessing the method of injury. The use of ophthalmoscopy or ophthalmochromoscopy, ultrasound of the eye and tonometry is indicated; if necessary, radiography of the orbits and additional methods for assessing vision are performed.
In many cases of minor injuries, the doctor will only examine the environment of the eye and external damage to the eyelids and tissues, prescribing appropriate treatment.
Complications and consequences
In addition to these symptoms, severe injuries can also cause very serious consequences:
- Disturbances in the structure of the retina or its detachment. It occurs when the capillaries cannot withstand the force of the impact and rupture. The risk group includes people with retinal dystrophy and other pathologies.
- Problems with the cornea. Traumatic cataracts, clouding or even destruction of the lens may develop.
- Ligament rupture. When they are damaged, the lens is the first to suffer and loses its transparency.
- A rupture of the iris leads to the fact that the pupil loses its functions of constriction and dilation, that is, it stops responding to light. This indicates damage to the nerve endings.
- Bleeding inside the eye - indicates the likelihood of retinal detachment and further deterioration of visual functions; it appears a minute after receiving a blow.
Retinal detachment is a consequence of untimely assistance to a person after an injury.
- damage to the anterior chamber or cornea of the eye;
- intraocular bleeding;
- retinal dissection;
- rupture of the ligaments that support the lens;
- damage to the iris.
The consequences of an eye injury are fraught with possible complications:
- untimely treatment of wounds can lead to purulent inflammation, as a result of which the visual organ can be removed;
- penetration of a staphylococcal infection into the ocular membrane can lead to complete loss of vision and death;
- inflammation of the cornea of the eye (keratitis), which leads to decreased visual function;
- some time after an eye injury, a prolonged inflammatory process without suppuration may be observed (sympathetic ophthalmia);
- development of optical displacement of the visual organ;
- As a result of infection, blood poisoning is possible;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- brain abscess.
Prevention
To prevent the development of complications after a blow to the eye, you must adhere to the following recommendations. They constitute first aid for injury:
- To reduce swelling and resolution of the hematoma, it is recommended to sleep half-sitting.
- After the blow, apply cold to the eye every hour for two days, wrapped in a cotton cloth. After this period, replace the cold with heat and massage the tissues around the hematoma.
- Regardless of the degree of the blow, its manifestations, consult an ophthalmologist to clarify the consequences and possible complications.
If there are no changes in the eyeball, symptoms after a blow to the eye disappear within 2-3 weeks. If they do not go away or get worse after this period, you should consult an ophthalmologist.