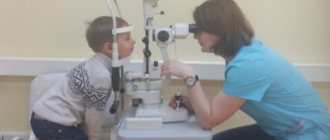
An allergy occurs due to an inadequate response of the immune system to a certain substance. Conjunctivitis is one of the options for this effect of allergens. The mucous membrane of the eyeball and eyelid becomes inflamed, swollen, and itchy. If a child has symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis, you should contact an ophthalmologist and an allergist, who will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Causes
Most often, the disease occurs in children due to the development of the following factors:
- exposure of the child to allergens (flowering plants, house dust, animal hair, bird feathers, chemicals, household products);
- if a child is allergic to any herbal remedy, he may develop a cross-reaction with related plants;
- use of medications;
- exposure to viruses or infections that are foreign to the body, because of which the immune system begins to activate, releasing cells and mediators;
- wearing contact lenses, inside of which pathogenic microorganisms are concentrated, and in children with hypersensitive eyes, the optical medium may be considered foreign;
- in chronic allergic conjunctivitis, any surrounding substances that come into contact with the eyes can cause a reaction.
Allergic manifestations are dangerous because initially they can form only in the eyes, but then spread systemically to the entire body, as a result of which atopic dermatitis, urticaria, and asthma may appear.
Complications and preventive measures
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis in a child in time and start treatment too late, the disease may become more complicated.
The inflammatory process covers the cornea and other tissues of the eye, which leads to a decrease in visual acuity and provokes the occurrence of other intractable ailments (corneal ulcer, keratitis). There are no specific preventive measures for this disease. Parents should strengthen the child’s immunity, monitor his nutrition, and maintain hygiene in the house. If there are known negative reactions to certain substances, it is recommended to avoid contact with them. Allergic conjunctivitis in children causes severe discomfort and can lead to vision impairment. At the first suspicion, you should immediately consult a doctor: pediatrician, ophthalmologist, allergist. Only a specialist can make a diagnosis, identify the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment.
Author of the article: Mager Irina Yuryevna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Risk group
Allergic conjunctivitis most often occurs in the following categories of patients:
- often suffering from viral and infectious diseases;
- having a history of autoimmune diseases, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, that is, their immune system is constantly activated;
- children who wear contact lenses to improve vision function, but suffer from increased eye sensitivity;
- patients who have a history of allergies to various household substances, plants, animals and birds.
The above categories of patients should be periodically examined by specialist doctors in order to detect pathology in a timely manner.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis
Therapy for bacterial conjunctivitis may include the use of drugs such as Albucid, Levomycetin, Furacilin, Futsitalmic. As for ointments, doctors usually recommend using tetracycline or erythromycin. Antibacterial drops "Albucid" affect most bacteria, including staphylococci and streptococci. This drug is even used in the treatment of infants. Levomycetin eye drops are often prescribed for purulent discharge.
Furacilin solution is used to wash the eyes. It is diluted with water. The product can replace a pale pink solution of manganese or a weak infusion of chamomile. Acute bacterial conjunctivitis is not always treatable with ointments and drops alone. Sometimes antibiotics are required.
Forms of allergic conjunctivitis
There are different forms of the disease, each of which requires different treatment.
- Seasonal. This type of conjunctivitis is called hay fever. It is formed as a result of human exposure to flowering herbs, cereals, and various trees. It manifests itself seasonally, from spring to autumn.
- Spring. This form is formed spontaneously, most often the activating factor is flowering plants. But doctors also suggest a certain role for the endocrine glands in the human body.
- Large papillary. It develops due to the presence of a foreign body on the mucous membrane of the eyes. This could be a suture after surgery, contact lenses, eye prostheses, or deposits of various substances. An inflammatory reaction is formed, which leads to the appearance of large papillae on the mucous membrane.
- Drug. Formed as a result of the patient's use of any medicine. Most often, such patients self-medicate without resorting to doctor’s recommendations. But there may also be individual cases when the drug was prescribed by a doctor, but the child developed an individual intolerance.
- Chronic. Minimal eye irritation develops when a person experiences severe inflammation and irritation. The cause may be cosmetics, perfumes, feathers, food products. Patients often have bronchial asthma.
- Atopic keratoconjunctivitis. It develops due to excessive activity of the human immune system. Most often it occurs against the background of a systemic disease, for example, urticaria, asthma.
It is necessary to classify the disease, since there is a separate treatment for each form. This can only be the use of medicinal drops or complex therapy.
Classification
Allergic conjunctivitis is classified according to the types of causes that caused it. The following forms of the disease occur:
- Spring catarrh - the disease is chronic, worsening in the warm season, when there are many sunny days. It is more common in boys aged 5 to 12 years.
Drug-induced conjunctivitis - appears when using eye drops. An allergy occurs to the active ingredient of the drug or preservatives in it. Anesthetics and antibacterial agents are often irritants.- Hay fever (hay fever) - a reaction appears to plant pollen. This is a seasonal conjunctivitis that occurs during the flowering period. Usually accompanied by other forms of allergies (Quincke's edema, urticaria, asthmatic bronchitis, dermatitis).
- Infectious-allergic conjunctivitis in children occurs with increased sensitivity to viruses, bacteria, and fungi. The microbes themselves are not found in the conjunctiva.
Hyperpapillary (large-papillary) conjunctivitis – causes the presence of a foreign body in the eyes (contact lenses, sutures). During examination, a proliferation of papillae measuring 1 mm in size is detected on the inner surface of the eyelid.- Tuberculosis-allergic conjunctivitis is provoked by waste products of tuberculosis microbacteria present in the body. With this form, the cornea and conjunctiva are simultaneously affected.
Some symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis in children help to identify the pathogen and prescribe the correct treatment. Concomitant pathologies require an integrated approach for complete recovery.
Symptoms
With allergic conjunctivitis, the patient develops the following characteristic clinical symptoms:
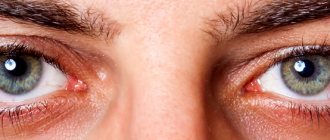
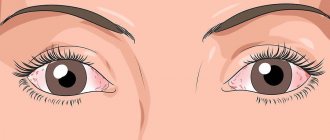
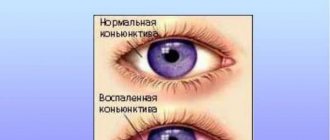
- severe redness of the eyes;
- irritation of the mucous membrane, due to which the cornea may be involved in the process, small hemorrhages appear on it, which subsequently resolve on their own;
- swelling of the tissues of the eyelid, sometimes the patient’s eyeball is completely invisible;
- increased production of tear fluid, often this condition is replaced by chronic dry eyes, due to which microscopic damage forms on the cornea;
- discomfort in the eyes: itching, burning, pain;
- sensation of a foreign body under the eyelid that is not actually there;
- severe spasm of the eyelids, due to which the child cannot open his eyes;
- increased sensitivity to the effects of bright artificial or natural lighting, which causes eyelid spasm and lacrimation;
- a child may often rub his eyes due to discomfort, which further irritates them and leads to the formation of papillae and follicles on the mucous membrane;
- a transparent mucous formation appears from the nose;
- if the patient’s condition is complicated by a bacterial infection, suppuration of the inner corner appears, which sticks the eyelashes together in the morning;
- Systemic manifestations may occur, for example, rash and redness on the skin, bronchial asthma, edema, anaphylactic shock.
Each patient's allergic condition is individual. It may manifest itself insignificantly if it is in a chronic form. If the disease worsens, most of the above symptoms may occur.
Causes of the disease
For the first time, symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis in children are usually observed at 3-4 years of age. The course of the disease is often accompanied by other manifestations of allergies: rhinitis, dermatitis, bronchial asthma. The cause of the development of the disease is individual hypersensitivity to certain substances. Allergens are divided into the following types:
- pollen;
- medicinal;
- household;
- food;
- epidermal.
Sometimes the disease is provoked by the entry of a foreign body into the eyes, or viruses, parasites, fungi, or bacteria. Predisposition to allergies is transmitted genetically. Its development is facilitated by the conditions in which the child lives: infrequent cleaning, dry air in the house, excess household chemicals, early introduction of potential allergens into the diet.
Diagnostics
Initially, the doctor examines the patient and determines the characteristic clinical symptoms. They can be used to identify conjunctivitis, but in order to find out the exact form, laboratory testing is necessary.
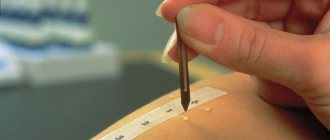
The main diagnostic method for allergic conjunctivitis is an allergy test. It is performed in the autumn-winter period. Substances to which there may be a reaction are sequentially applied to the child’s hand. If redness or inflammation is observed in any area of the skin, this means that the baby is developing a reaction to this particular substance.
For differential diagnosis, PCR may be prescribed to determine the virus that causes conjunctivitis. This is due to the fact that the symptoms are similar. The doctor may also prescribe a bacteriological culture if pus appears from the inner corner of the eyes. Allergic conjunctivitis is often complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection.
Features of the disease
Experts say that allergic conjunctivitis is more common among urban residents and occurs in 40% of children suffering from any type of allergy. Often this disease is accompanied simultaneously by rhinitis, bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis. The inflammatory process of the conjunctiva in this pathology leads to excessive filling of the blood vessels of the eye. Therefore, they become visible to the naked eye, and the eyeball acquires a pink or red tint.
Classification of species
Depending on the cause of development and characteristics of the course, the disease is divided into several types:
- Spring uniform. This variety often occurs in boys from the age of 5, and has the ability to disappear with puberty. Moreover, exacerbations of pathology are observed only in the spring and do not appear at all during the rest of the year. The course of the disease of this variety is more acute than others.
- Seasonal and year-round form. These varieties are considered the most common. The seasonal development of the disease is associated with the flowering period of various flowers and trees, and worsens in spring or early autumn. The year-round development of the disease is associated with the body’s reaction to animal hair, bird fluff, dust and other factors that surround the child throughout the year.
- Dosage form. The development of this variety is caused by an allergic reaction of the body to taking various medications. It tends to go away on its own after discontinuation of these medications.
- Infectious-allergic form. The cause of this variety is staphylococci, which may not even come into direct contact with the conjunctiva of the eye. The danger of this species is that it can be transmitted from one child to another in a matter of hours.
- Toxic-allergic form. Often this variety occurs in children under 3 years of age and develops against the background of tuberculosis intoxication of the body. Its danger lies in the fact that the child can open his eyes only with local anesthesia. Due to constantly closed eyes, swelling increases and visual acuity decreases significantly.
- Atopic form. In most cases, its appearance is due to the presence of concomitant pathologies, such as asthma, dermatitis, and urticaria.
Causes
The main reason for the manifestation of allergic conjunctivitis in a child is the individual sensitivity of the body to one or another allergen. This feature may be caused by a hereditary predisposition or due to the child’s immature immune system, which reacts to exposure to allergens.
The most common causes of this disease are:
- Household factors manifest themselves in the form of dust, detergents, pillow fluff, dust mites;
- Epidermal allergens, which are pet fur, as well as bird and animal food;
- Medications due to the child’s individual intolerance;
- Flower pollen;
- Food components found in products;
- Various types of infections that cause the occurrence of infectious-allergic forms of the disease.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease
The first signs of the disease begin to appear within a few hours, less often during the first day, and it is noticed that mainly both eyes are affected at the same time. Symptoms of the disease are expressed in the following signs:
- swelling and significant redness of the eyes;
- profuse lacrimation;
- increasing itching, which forces the child to regularly rub his eyes;
- characteristic discharge that accumulates in the corners of the eyelids;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- the appearance of characteristic papillae on the mucous membrane of the eye;
- discomfort from bright light;
- blood-filled eye blood vessels.
In the future, symptoms may change and be expressed in the following signs:
- dry surface of the mucous membrane;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- negative influence of bright light, so there is a desire to close your eyes;
- sensation of pain when moving the eyes;
- decreased quality of vision with severe swelling and lacrimation.
Often, parents can monitor the reaction of the child’s body and point to the allergen that causes conjunctivitis.
Diagnostics
If you suspect allergic conjunctivitis, you will need to consult not only an ophthalmologist, but also an allergist. Based on the results of the examination and research of these two specialists, a diagnosis is determined and appropriate treatment is carried out.
Initially, the doctor interviews the child and parents to determine the cause of the complaints. In the future, based on the identified reasons, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations and tests:
- A general blood test is performed.
- Eye secretions are taken for analysis to identify eosinophils in them, which must be present in the allergic form of the pathology.
- Skin tests are performed to determine a possible allergic reaction in the body.
- The function of the gastrointestinal tract is examined.
- Eye discharge is checked to detect infection if an infectious nature of the disease is suspected.
In difficult cases, the doctor may prescribe an additional provocative test, in which several types of allergens are instilled into the eyes to determine the reaction of the eye mucosa. However, such an examination can contribute to the development of complications, so it is now used extremely rarely. Based on the results of all the tests performed, the doctor makes a diagnosis and determines what to treat.
What danger does it pose?
A timely visit to a doctor eliminates the possibility of complications, and in this case the disease passes painlessly for the child. However, if parents neglect the allergic form of pathology, an infection may develop. Then there is a risk of the following complications:
- blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids);
- keratitis (inflammation of the cornea);
- structural changes in the lens;
- retinal detachment.
Also, in the infectious-allergic form, the disease can be transmitted very quickly, literally within a few hours.
Treatment
After discovering the allergic cause of conjunctivitis, the most important action is to eliminate the substance from the patient’s life to which the patient’s immune system reacts. After this, the doctor prescribes medications:
- systemic antihistamines for oral administration (Cetrin, Suprastin, Claritin);
- antihistamine eye drops (Allergodil, Azelastine);
- antibacterial eye drops if the condition is complicated by a bacterial infection (Levomycetin, Vigamox);
- moisturizing eye drops for dry corneas (Slezin, Defislez);
- eye drops based on corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, dexamethasone) to relieve inflammation, swelling and redness in acute form;
- if the child is still too young for steroid drugs, it is recommended to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of diclofenac-based drops;
- in the autumn-winter period, it is recommended to use immunotherapy, that is, the patient’s body is saturated with small doses of the allergen so that his immune system gets used to it.
The child needs to promptly eliminate allergens around him, and also use only those medications that are suitable for his age.
Traditional medicine for conjunctivitis in children
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in children with folk remedies should be carried out with extreme caution. Parents should first make sure that the child is not allergic to the substances used. The following recipes are used:
- Blueberry infusion strengthens vision and speeds up recovery. 1 tbsp. l. dried berries are poured into a glass of boiling water and drunk after half an hour.
- Aloe has anti-inflammatory properties. Its juice is diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:10 and the eyes are washed with it 4-5 times a day.
If conjunctivitis is complicated by a bacterial infection, use the following remedies:
- Pour a glass of boiling water over 6 dried rose hips and leave for half an hour. The resulting liquid is used as an eye lotion.
- 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the color of calendula and leave for 30 minutes, rinse the conjunctiva with this product 5-6 times a day.
The attending physician decides how to treat allergic conjunctivitis in a child. The use of traditional medicine should be previously agreed with him.