Adenoviral conjunctivitis is a disease that affects the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Characteristic clinical symptoms develop, based on which the doctor suggests a diagnosis.
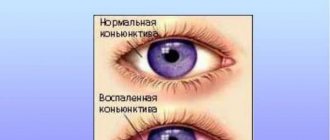
The patient's eyes become very red, tearing, pain, and burning appear. Without treatment, the condition worsens, so it is recommended to consult a doctor in a timely manner and carry out diagnostics. Adenoviral conjunctivitis can be confused with the bacterial form, so laboratory tests are required.
Cause of adenoviral conjunctivitis
The only cause of the disease is adenovirus entering the human body. There are many of its serotypes, which are determined using the PCR method. The pathogen is transmitted from an infected person to another person by the following actions:
- cough, sneezing;
- contaminated hands.
If the virus enters the body of another person, it does not always manifest itself and become active. This requires the following factors:
- malfunction of the immune system;
- exposure to high and extremely low temperatures on the body;
- frequent viral infectious diseases;
- mechanical damage to the eyelids and eyes;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules (lack of hand washing, touching eyes, wearing lenses incorrectly);
- swimming in public places (swimming pool, fountains) and bodies of water (river, pond);
- postoperative complications;
- depression, stress.
If you treat a disease without addressing the root cause, the condition will recur. Complications and the development of chronic conjunctivitis are possible.
Causes of the disease
Already from the name it is clear that the causative agent of this disease is adenoviruses. Basically, these can be adenoviruses 11, 7a and 3 serotypes, less often than other serotypes; infection occurs by coughing and sneezing, that is, by airborne droplets; infection by contact is less common. The average incubation period is a week.
The risk of the disease increases with hypothermia, poor eye hygiene, eye injuries, violation of the rules for using contact lenses, as well as in people who swam in polluted waters, recently suffered a respiratory disease, or are in constant stressful situations.
Risk group
The risk group of patients who most often develop adenovirus infection includes:
- persons whose work involves immersion in untreated water bodies;
- children attending educational institutions (kindergarten, school);
- people who often suffer from viral and infectious diseases;
- patients with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- people who have recently undergone surgery.
The above categories of patients should undergo an annual preventive examination by an ophthalmologist. If signs of the disease appear, therapy should be started immediately with the approval of a physician.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in adults
If a person develops adenoviral conjunctivitis, then it is necessary to immediately seek help from an ophthalmologist. He will prescribe effective treatment.
It should be noted that treating a viral infection is quite difficult. This is due to the fact that there are no drugs in medicine that can destroy viruses. Only the human immune system can kill them. In this case, it is necessary to maintain the body’s defenses so that they can overcome adenoviruses.
Therapy for adenoviral conjunctivitis should be comprehensive , that is, include the following types of treatment:
- Antiviral;
- Antibacterial;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Antihistamine;
- Immunomodulatory and immunostimulating;
- General strengthening.
Let's look at how to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis.
Antiviral treatment
In the treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis, antiviral drops and ointments are used. Drops such as Tebrofen, Interferon, Laferon and others are instilled 6 to 8 times a day in the first few days of the disease. When inflammation subsides, drops are used 3 times a day.
If the inflammation is severe, then the use of anti-inflammatory ointments is indicated: Florenal, Bonafton, Riodoxol ointment, and so on. The ointment is placed behind the lower eyelid in the fold. Before this, you need to rinse your eyes with a solution of Furacilin and chamomile.
Antibacterial treatment
To prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, the use of antibacterial agents in the form of eye drops (Albucid, Tobrex) and ointments (Tetracycline and Erythromycin) is indicated.
Antibacterial nasal drops (Albucid, Polydexa) are also prescribed. This is necessary to prevent the re-development of adenoviral conjunctivitis.
The course of treatment lasts from 1 week to 10 days. it all depends on the form of the disease, the condition of the patient’s body and the severity of pathological symptoms. In the first days of treatment, the drops must be used 6 times, then the frequency of use is reduced. This issue is decided by the attending physician.
Anti-inflammatory treatment
To relieve signs of inflammation and associated inconveniences in treatment as quickly as possible, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets are used. These drugs include: Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Diclofenac and others.
They also relieve pain, which is especially important in the first days of illness.
Similar articles Symptoms and treatment of viral conjunctivitis Causes, symptoms and treatment of allergic conjunctivitis Symptoms and treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in adults and children Symptoms and treatment of conjunctivitis in adults
Antihistamine treatment
To get rid of swelling and itching with adenoviral conjunctivitis, it is necessary to use antihistamines (tablets and drops for oral administration). Sometimes patients, especially children, experience very severe itching. If you start rubbing and scratching your eyes, the swelling and soreness will only increase. It is also possible that a secondary infection may occur. That is why the ophthalmologist will necessarily prescribe antiallergic drugs: Zodak, Fenistil, Zyrtec.
General strengthening and immunomodulatory treatment
To support immunity, it is necessary to take a special group of drugs: immunostimulants and immunomodulators. They will boost the immune system and help it fight adenoviruses.
However, it is possible to strengthen the body’s defenses with the help of general strengthening therapy, which includes:
- Taking vitamins;
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals;
- Compliance with the drinking regime (this is very important when inflammation develops and body temperature rises);
- Maintaining bed rest.
Also in the later stages of the disease, the use of eye drops that resemble tears in composition (for example, Artificial tears) is indicated. This is necessary to prevent dry eyes.
Classification of viral conjunctivitis
Depending on the prevalence of the pathogen, the disease is divided into several forms.
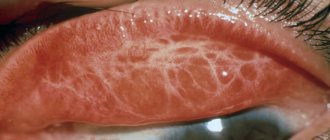
- Catarrhal. As a result of the spread of the virus through the mucous membrane, slight swelling and redness occurs. The effect of the pathogen is eliminated in 7-10 days. Clinical symptoms disappear quickly.
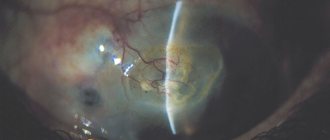
- Follicular. This form is characterized by the appearance of bubbles, which contain transparent contents filled with the virus. They spread throughout the mucous membrane, in the corners of the eye. This negatively affects the patient’s condition; treatment requires a cauterization technique. If therapy is not completed on time, a person experiences constant dry eyes, the cornea becomes cloudy, and visual acuity decreases.
- Membranous. Typical for people suffering from immunodeficiency. When the disease occurs, a whitish film forms on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyes, which cannot be removed independently. This can only be done by a doctor, but after the manipulations, slight redness and bleeding occur on the surface structures. After removing the films, scars remain that can reduce visual acuity. When sick, the patient's body temperature always rises above 39 degrees. Fever can last up to 10 days.
The doctor is obliged to determine the form of the disease, since the treatment depends on it.
Diagnostics
It is possible to assume pharyngo-conjunctival fever in a patient if there is a history indicating contact with a patient suffering from this disease. During the examination, attention is paid to the combination of signs of conjunctivitis with regional lymphadenopathy and inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out by virological, cytological and serological research methods. For early diagnosis of the disease, an immunofluorescent method is used, which makes it possible to detect specific viral antigens in the mucous membrane of the eye.
Adenovirus DNA can be detected in scrapings from the conjunctiva using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is highly informative. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and complement fixation reaction (FFR) allow us to determine the content of antibodies to adenoviruses in blood serum. For adenoviral conjunctivitis, the diagnostic criterion is an increase in the concentration of antibodies by at least 4 times.
ELISA for adenoviral conjunctivitis reveals an increase in antibodies to adenoviruses by more than 4 times
To isolate and identify adenoviruses in cell culture, a virological study of discharge from the conjunctiva is performed.
Sporadic cases of adenoviral conjunctivitis are most often caused by adenovirus types IV, VI, VII and X. Epidemic cases are usually caused by adenoviruses III, VIIa and XI types.
In the follicular form of adenoviral conjunctivitis, differential diagnosis is carried out with trachoma. With trachoma, the follicles are localized in the upper eyelid, and in addition, the disease is not accompanied by fever and symptoms of nasopharyngitis. The filmy form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is in some cases mistaken for ocular diphtheria.
Symptoms of viral conjunctivitis
When the disease occurs, the following characteristic clinical symptoms appear:
- severe redness of the mucous membrane;
- increased production of tear fluid, which is replaced by dryness during prolonged illness;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- spasm of the eyelids, not very pronounced;
- sensation of a foreign object under the eyelids;
- discharge of mucus from the nose, cough, which can often be confused with ARVI;
- dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting);
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
The above symptoms appear only in the first few days of the disease. Next, the body temperature rises, the conjunctiva becomes even more inflamed in each eye in turn.
Patients often confuse bacterial and viral forms of conjunctivitis. Unlike the first type, adenovirus does not form suppuration. This condition develops only in the absence of treatment, when complications begin.
The further course of the disease depends on its form. If catarrhal conjunctivitis occurs, the disease is not very pronounced, there is slight redness, the symptoms are quickly eliminated. The follicular form lasts longer, bubbles form, which complicate the patient’s condition. With the membranous type, the most severe condition of the patient is formed, often accompanied by complications.
Symptoms of the disease
Acute adenoviral conjunctivitis does not appear immediately; a person can simply be a carrier of this disease for a long time, but as soon as the immune system fails, for example, due to hypothermia, the infection immediately manifests itself.
In most cases, film conjunctivitis occurs along with upper respiratory tract infections, so the initial symptoms include sore throat, runny nose, fever and inflammation of the tonsils.
The disease first affects one eye, and after a few days symptoms appear in the second eye. Conjunctivitis can occur in both adults and children. In adults, this may be catarrhal or follicular form.
What is adenoviral conjunctivitis
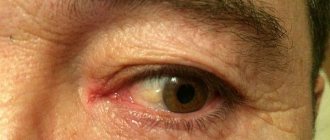
The catarrhal form of adenoviral conjunctivitis has the following symptoms:
- eyes become red and swollen;
- there is itching and the presence of a foreign body in the eyes;
- tear production increases, often to such an extent that a person cannot see anything because of the tears;
- photophobia appears;
- the palpebral fissure closes partially or completely.
The follicular form has slightly different manifestations:
- the conjunctiva of the eyes turns red;
- purulent discharge appears;
- Many follicles appear on the mucous membrane, they can be of different sizes.
Both stages of adenoviral conjunctivitis are characterized by headache, fever, and signs of acute runny nose and pharyngitis may appear.
In addition, sometimes the lymph nodes become enlarged and dyspeptic disorders appear. After some time, the temperature returns to normal, and the symptoms already described above appear in the eyes.
Symptoms and forms of pathology
In some cases, with pharyngo-conjunctival fever, a grayish film may appear, which is why the pathology is also called film conjunctivitis. This plaque can be removed independently, but in extremely rare cases it grows tightly together with the mucous membrane.
Diagnosis of viral conjunctivitis
When patients with clear signs of conjunctivitis come to the ophthalmologist, the doctor does not immediately make a diagnosis, since there are various forms of the disease. 1-2 diagnostic tests are carried out, on the basis of which treatment is carried out:
- Anamnesis collection. These are the patient's complaints that worry him most.
- General inspection. The doctor detects acute redness of the conjunctiva. There may be no discharge from the eyes, and clear mucus rarely forms. If the disease is acute, the doctor will identify symptoms of rhinitis (runny nose).
- Bacterial culture. The analysis reveals a large number of pathogenic microorganisms. The laboratory assistant determines the normal microflora. If the condition becomes complicated and a bacterial infection occurs, a microorganism will be detected that contributes to the secretion of pus. Additionally, the doctor conducts testing to determine the antibiotics to which the bacteria is sensitive.
- PCR. Using the technique, the RNA of the pathogen is determined, and the adenovirus is determined.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor begins treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
The attending physician first makes a conclusion about the disease based on the medical history and clinical picture. Many experts believe that there are no special clinical manifestations that can help in diagnosing and distinguishing the adenoviral nature of the disease from an allergic or bacterial nature. Laboratory research methods can determine the exact cause of the disease.
The pathogen can be determined by scraping; if it is a viral infection, then in the affected cells the viruses will turn green during immunofluorescence; extracellular viruses will have a bright green color.
Diagnosis of the disease
There is also a cytological research method, which can also provide a lot of useful information to the doctor to clarify the etiology of the disease. A serological blood test, which is carried out at the onset of the disease and in its final stages, can confirm the correctness of the diagnosis.
With a bacteriological examination, the doctor can identify the microflora that accompanies the disease, as well as determine its sensitivity to certain antibiotics, which allows for antibacterial therapy.
At the moment, a method for determining immunoglobulins in the tears of patients with adenoviral eye infection is being actively researched and developed, and the question of whether this method can be used to make a diagnosis is being discussed.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Treatment of the disease depends on the complexity of the patient's condition. Comprehensive treatment is carried out to prevent the development of complications:
- A systemic antiviral agent to which adenovirus is sensitive.
- Local antiviral agents used in the form of ointment (Florenal).
- Drugs that stimulate local immunity, which are used in the form of drops (Interferon).
- Antibacterial therapy is not always used, only if the patient is predisposed to developing complications or the clinical symptoms of the disease are severe. They are used in the form of drops or ointments (Tobrex, Vigamox, Erythromycin).
- Antihistamines to relieve swelling. Suprastin and Zodak are used.
- Eye moisturizing drops. Slezin and Hyphenlez are used. They are necessary to prevent damage to the cornea due to the formation of increased dry eyes.
If the patient has a follicular form, cauterization is used to eliminate the blisters. In the filmy type, the doctor uses special instruments to remove the film on the cornea.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. It is difficult to say exactly how long adenoviral conjunctivitis is treated. Local medications are prescribed for 2 weeks. Ophthalmologists prescribe interferon instillations and the use of drops with anti-inflammatory and antipruritic properties. To suppress the infectious process, antiviral drugs are prescribed, which are available in tablets and ointments.
Antibacterial agents are used when the risk of secondary infection increases. But self-prescribing antibiotics is prohibited. First, it is necessary to determine the type of pathogen, make an accurate diagnosis, and only then begin drug therapy. Antiviral ointments are placed behind the eyelids daily. It is better to do this at night so that the maximum amount of the product gets into the conjunctiva and has a healing effect.
To get rid of itching and local inflammatory reaction, antihistamines are prescribed. Preference is given to the latest generation drugs that do not cause drowsiness or other adverse reactions.
Complications
If the patient is immunodeficient or does not undergo treatment, the following complications arise:
- an increase in opportunistic microorganisms, which leads to bacterial infection;
- formation of allergic conjunctivitis;
- redness of the surface structures of the eye, which leads to the formation of microtraumas and cracks in the cornea;
- inflammation of the cornea;
- small hemorrhages on the cornea;
- inflammatory diseases of the outer or inner ear;
- exacerbation of adenoiditis;
- exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor, conduct diagnostic tests and treatment.
Complications and prognosis
Late or improper treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis can lead to the development of quite severe complications, namely:
- development of chronic recurrent conjunctivitis;
- keratoconjunctivitis (spread of inflammation to the cornea);
- addition of a secondary (bacterial) infection;
- development of dry eye syndrome;
- iridocyclitis (damage to the iris and ciliary body of the eye).
The prognosis is favorable: usually the disease ends with complete clinical recovery in 2-4 weeks. When dry eye syndrome develops, long-term use of tear substitutes is required.
Prevention
To prevent the development of viral conjunctivitis, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- compliance with hygiene rules (washing hands and face, wearing contact lenses according to the rules);
- It is prohibited to swim in public bodies of water;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases;
- annual preventive examination by an ophthalmologist, especially if the patient has a chronic eye disease;
- Seeing a doctor in the early stages of the disease.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is easily treatable if detected early. To avoid complications, all therapeutic procedures must be agreed with a doctor. The adenoviral form is easily confused with the bacterial one. For recognition, diagnostic tests are performed.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Treatment of film conjunctivitis
In case of illness, treatment can only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist; only a doctor can give recommendations on how to treat the disease and what medications to use. Adenoviral conjunctivitis is mainly treated on an outpatient basis.
In this case, antiviral therapy is used - these can be bonaftone, florenal, riodoxole and other ointments. Local instillations of interferon and deoxyrionuclease are required. Antihistamines and, if necessary, antibacterial drugs, corticosteroids and artificial tear substitutes are also indicated.
The patient must have his own pillow, towel, soap and dishes. Before and after treating the eyes, hands must be washed very thoroughly, otherwise they will remain infected, which can be transmitted through contact with other people.
The virus dies at very high temperatures, so the dishes, ointment stick and pipette must be boiled to avoid re-infection. The room where the patient is located should be regularly ventilated and it is advisable to darken the windows so as not to irritate the eyes with bright light.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
Drops prescribed by an ophthalmologist should be instilled up to 8 times a day in the first week of treatment, then the frequency decreases to 2-3 times. If there is purulent discharge, it is imperative to use drops that have antibacterial properties to reduce the risk of re-infection.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis can be cured in 10 days. Treatment has a favorable prognosis only if it is supervised by a doctor and the patient strictly follows all recommendations received. Self-medication of conjunctivitis is unacceptable!
Types of bacterial conjunctivitis
The cause of its occurrence is bacteria. They cause acute inflammation, the symptoms of which develop very quickly. Within 1-2 days after infection, a person begins to experience severe itching and burning in the eye.
A characteristic symptom of all bacterial conjunctivitis is purulent discharge. Initially, they may be mucous, but later pus appears. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by this symptom from the very beginning. In addition to the listed symptoms, with bacterial conjunctivitis the following are observed:
- tearfulness;
- blepharospasm;
- photophobia;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- swelling;
- gluing of eyelashes and formation of crusts along the edges of the eyelids;
- pain in the eye.
Bacterial infection in childhood is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. In adults, this symptom usually occurs only with viral conjunctivitis. There are many types of bacteria. Each of them leads to the development of different types of disease:
- Streptococcal conjunctivitis. In the first days of the disease, patients complain of dry eyes, which causes uncontrollable lacrimation. After a day or two, purulent discharge appears. If the disease is not treated, the infection will spread to the upper respiratory tract.
- Staphylococcal conjunctivitis. Its symptoms appear a day after infection. The patient is bothered by itching in the eye, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in it. The disease is accompanied by copious secretion of mucus, pus and the formation of purulent crusts.
- Gonococcal conjunctivitis. Gonococci are especially dangerous for newborns, who can become infected from a mother with gonorrhea. Without treatment, the child may go blind. A characteristic sign of this type of inflammation is a large amount of pus. The eyelids swell so much that the baby's eyes close completely. When you open them with your hands, the discharge splashes out in a stream.
- Pneumococcal conjunctivitis. It is also more often diagnosed in children. Pneumococci spread rapidly. The disease often takes on the character of an epidemic. A distinctive sign of the disease is the presence of pinpoint hemorrhages on the connective membrane. Sometimes grayish films form on it.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa conjunctivitis is a rare form of the pathology in question. The risk group includes people who use scheduled replacement contact optics for correction. Typical signs of inflammation caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa are photophobia and severe swelling. Cloudy white pus is discharged from the eyes.
- Diphtheritic conjunctivitis. It occurs against the background of diphtheria, an infectious disease caused by Loeffler's bacillus, or diphtheria bacillus. The patient has cyanosis of the eyelids and swelling. The separated exudate contains white flakes. When the eyelids are lifted, pus flows out. Films form on the conjunctiva, which over time grow tightly together with it. Removing them leads to bleeding followed by tissue scarring.
Bacterial conjunctivitis: treatment
For diseases caused by bacteria, antibiotics are prescribed. Antibacterial drugs are also used - drops and eye ointments. For conjunctivitis, almost all medications are topical.
The eyelids and conjunctiva are washed with Furacilin solution. This procedure should be carried out in the morning, in the evening and each time before instilling solutions and applying ointment. Elimination of symptoms - itching, burning, redness - is carried out using drops based on natural tears - “Systane”, “Oxial”, “Artificial tear”. Medicines of this type are prescribed for almost all types and forms of conjunctivitis.
Features of symptoms and treatment in children
It should be noted that any viral disease in children is more severe than in adults. The child’s general condition suffers significantly:
- He becomes lethargic;
- Is capricious, infants cry a lot and may refuse to breastfeed;
- Body aches;
- Increased body temperature.
In infants and children, a film form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is most often observed. This is the most complex form of the disease. Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis in children:
- Body temperature rises to high numbers (39 degrees). Such values last for 7 – 10 days;
- Fibrous films form on the mucous membrane of the eyes. They can be single or multiple. As a rule, these films are easily removed. However, in severe cases, they are firmly connected to the mucosa. When they are separated, mucosal bleeding and pain are noted;
- Decreased or complete absence of appetite in the child.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in children
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal antiviral drug – Nurofen in the form of syrup. It can be used from 3 months of a child's life. It will reduce pain and help reduce fever;
- Antiviral eye drops: Actipol, Oftalmoferon;
- Antibacterial eye drops. Albucid is the drug of choice for children of all ages. The drug must be dripped into both eyes, even if pathological signs are observed in only one;
- Drops for the treatment of rhinitis (runny nose). Children from birth can be instilled with Nazol Baby and Albucid.
The child must be given water, fruit drinks, and herbal tea. This will help avoid dehydration during hyperthermia.
Rules for caring for a child with adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- Provide the child with separate bed linen and towels;
- Frequently ventilate the room where the patient is;
- Frequent sienna of underwear and bed linen;
- Before treating your eyes, wash your hands thoroughly to avoid re-infection;
- There should not be a bright source of light in the room, as the baby may experience pain;
- Eye treatment should be carried out with sterile gauze swabs. Use 1 tampon per wipe. Its reuse is prohibited!
- Wash your hands after treating your child's eyes. This will help prevent further spread of the infection.
You can read about the treatment of conjunctivitis in children here.