Sometimes parents find a small reddish spot on the skin of newborn babies. It could be a hemangioma. Such skin formations often occur in infancy and do not always require radical intervention.
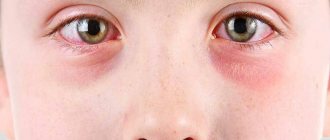
Infantile hemangioma is a benign tumor. It is formed from dilated large and small blood vessels. Often such a formation appears on the head of a newborn, rarely on the back and limbs.
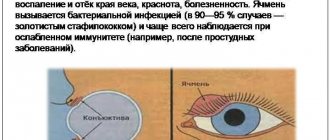
The danger is represented by a tumor that is located on the mucous membrane of the mouth, lip, ears and upper eyelid. Such a location can limit or impair the vital functions of these organs, which will complicate the baby’s life.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing hemangioma is not difficult; to do this, you only need to correctly assess the appearance of the neoplasm.
To accurately determine the type of pathology, there are various manuals, which consist of numerous images of various forms of tumor processes in the eye. Thanks to such reference books, it is possible to accurately determine the nature of the growths present and the location of the lesion.
When diagnosing an eye hemangioma, the child must be registered at the dispensary, since the doctor must monitor the course of the disease. Adequate treatment is also determined, which can be either conservative or surgical.
Medical practice sometimes encounters difficult cases when the lesion is localized in the deep layers of the orbit. In such situations, a visual examination does not make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, so the specialist prescribes the following additional measures:
- X-ray of the eye.
- CT scan.
- Arteriography.
- Venography.
On this topic
Organs of vision
All about ocular sarcoidosis
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- September 3, 2021
Arteriography and venography make it possible to assess the condition of blood vessels.
During the examination, visual acuity is assessed, the presence of strabismus is determined, as well as the presence of other concomitant diseases. Only after carrying out such measures can the doctor determine the most suitable treatment.
In the presence of superficial lesions that do not affect visual acuity, special therapy is not prescribed, but the child should be constantly monitored by a doctor in order to monitor the progression of the pathology.
More often (in 70% of cases), by the age of 7-8 years of life, the neoplasms disappear on their own; in other situations, the use of steroid medications is required or cosmetic surgery is prescribed.
If the presence of the disease negatively affects visual acuity, then removal of the lesion is required. To eliminate the tumor, laser treatment or liquid nitrogen can be used.
The measure of influence is selected depending on the age category of the patient. Often, after removal of the lesion, the doctor prescribes hormonal medications or radiation exposure (prescribed only as a last resort).
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is determined after a visual examination; additional studies are performed to clarify the structure and depth of the tumor: biomicroscopy, sonography, CT or MRI of the orbits, angiography. If necessary, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed.
Treatment of the disease depends on the location, clinical manifestations and extent of the tumor process. Vascular growths are removed surgically, using cryodestruction or electrocoagulation methods. Plastic surgery is used to replace cosmetic defects. In some cases, a course of radiation treatment is carried out.
Modern methods of treatment
Depending on the growth rate of the tumor, its location and other nuances, the child may be prescribed either conservative or surgical treatment. Most often, when indicated, hemangioma is eliminated at the age of 1-3 years.
Surgical
During the operation, under general or local anesthesia, the tumor is partially or completely excised with a scalpel.
Such treatment is not carried out in the first month of life and is often prescribed when the hemangioma is rapidly enlarging or located in an unfavorable location. In this case, the operation should not disrupt the functioning of organs or cause a serious cosmetic defect.
Sclerosing
This treatment helps eliminate cavernous hemangioma. A substance is injected into the tumor, causing it to die due to “sealing” the vessels from the inside.
The disadvantage of this treatment is pain. In addition, sclerosis of large hemangiomas with a large number of vessels is a long process (it lasts 2-4 weeks).
Laser
The tumor is excised with a laser beam. The advantages of this type of coagulation are painlessness and the disappearance of the formation without a trace (no scars or other traces remain).
The disadvantages include the rather high cost and the need in some cases to repeat the procedure.
Radial
This treatment option is used for large flat hemangiomas and cavernous subcutaneous formations. Radiation therapy is also used to eliminate hemangiomas in the brain or eye area.
A child older than 6 months is irradiated several times, performing sessions with a pause of two weeks to six months.
Cryotherapy
Similar treatment is prescribed for small superficial hemangiomas that are not located on the face.
The tumor tissue is exposed to liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide. As a result, frostbite and swelling are caused, after which new skin begins to form at the site of the hemangioma, initially covered with a crust. Sometimes cryotherapy leaves a small scar.
For information on treatment methods for hemangioma, watch the video.
Electrocoagulation
Hemangioma tissue is destroyed by electric current. This treatment is prescribed for tumor diameters less than 3-5 mm. Electrocoagulation is also used in situations where the hemangioma has not been completely removed by other procedures (small parts remain).
Medication
Hormonal therapy using prednisone is used to treat large simple hemangiomas.
Injections are administered into the tissues of the formation according to a specially calculated scheme, supplemented by taking hormones in tablets. The tumor gradually turns pale and subsides, after which it disappears in 80% of cases. Propranolol is also used for drug therapy of hemangiomas.
Symptoms of hemangioma in newborns
Hemangioma appears as a red or bluish spot located on the surface of the skin. It can grow upward and in depth, be single or multiple, have a small size or occupy large areas. Although the tumor is not painful, the temperature at the site of formation and the surrounding tissues is noticeably higher than in other parts of the body.
Infantile hemangioma is localized on the following parts of the body: neck, limbs, abdomen, face, head (especially the back of the head). Less commonly, tumor-like formations are found on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and internal organs. According to statistics, the predominant number of diseases is recorded in girls.
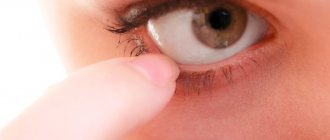
It is important for parents to know that a hemangioma differs from a mole in that when pressure is applied to its surface, it turns pale, and when released, it becomes intensely colored. The mole does not change when exposed to it. Crying or coughing in a child causes hemangiomas to darken, as tension promotes blood flow to the vessels.
The tumor forms in a baby in the first days and months of life. Over the course of six months, it develops at a rapid pace. By the age of one year, tumor growth stops and the reverse process begins. The stain becomes more colorless and invisible.
Most infant hemangiomas disappear on their own by the age of 5-7 years (50-70%), and the rest resolve at the age of 9-12 years (95%).
Treatment
Hemangioma of the eyelid differs from tumors localized in other places in that it more often requires medical intervention. Vascular formations resolve spontaneously in half of children over 5 years of age. But the pathology of the eyelid has to be treated, since its rapid growth poses a danger to vision. In addition, the tumor interferes with the child and is often injured.
Taking into account the growth rate of the hemangioma and the possible risks, the doctor decides whether therapeutic procedures are sufficient or whether surgical intervention is required. It is unlikely to do without radical measures if the tumor has reached a large size and penetrated deep into the tissue.
Doctors have various methods of treating eyelid hemangioma in their arsenal:
- drug therapy;
- ligation of the vessel;
- electrocoagulation;
- sclerosis;
- laser or radiation therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- surgical intervention.
A positive result in treatment is achieved through the use of a set of measures. The doctor decides which methods are best to use in each specific case.
Drug therapy
Taking medications is recommended if a child has a large hemangioma of the eyelid. To treat it, glucocorticosteroids, interferons, propranolol, vincristine are used, which blocks cell division and stops tumor growth.
Ligation of the vessel
This method is used when the hemangioma begins to grow rapidly. Ligation of the vessel that feeds the tumor stops the flow of blood. Thanks to this, the size of the tumor is significantly reduced.
Electrocoagulation
The essence of the method is that the area of the hemangioma is injected with a current of the required strength. This method is used as an independent treatment or additional during surgery. The therapy is long-term, but after it there are no scars.
Sclerosis
To reduce the volume of the hemangioma, the formation itself and the surface around it are injected with ethyl alcohol, a solution of betamethasone or quinine. Injection of corticosteroids into the tumor is also practiced. The procedure requires anesthesia; for this, an anesthetic is first injected.
Laser treatment
Laser tumor removal has no age restrictions. The number of procedures required varies depending on the type and size of the tumor. After treatment there are no scars or crusts left.
Cryodestruction
The procedure involves freezing the hemangioma with liquid nitrogen.
For the treatment of neoplasms on the eyelid, it is used with caution, since small scars remain. The advantage of the method is that a small tumor can be removed in one session
Surgical intervention
In world practice, there is a tendency to refuse operations to remove hemangioma. This is due to the danger of using anesthesia in infants, a long period of rehabilitation and possible tumor relapses.
Surgery is resorted to in extreme cases when the tumor threatens the patient’s health. Hemangiomas can be removed from children no younger than six months old.
Treatment of ocular hemangioma
Treatment of eye hemangioma is not carried out in all situations. It is important to remove the tumor in the following cases:
- amblyopia;
- compression of the optic nerve;
- exposure keratopathy;
- aesthetic discomfort;
- infection.
For ocular hemangioma, the doctor will prescribe steroid medications.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment includes the following methods:
- Local use of steroid drugs. It is used if the neoplasm is at the initial stage of development and is located under the skin. The method has disadvantages:
- the likelihood of the product entering the retinal artery;
- necrosis;
- atrophy of fatty tissue.
- Administration of steroid drugs in a course manner. They resort if the hemangioma is located in the orbit of the eye.
Removal of an eye tumor
Removal of hemangioma on the eye is carried out using the following methods:
| Name | Description |
| Surgical intervention | The operation is performed by a surgeon using a scalpel, with which he makes an incision and excises the hemangioma. This method of getting rid of formations is used if the growth rapidly increases in size and compresses nearby blood vessels. Surgery is also used when a person experiences pain when touching the growth. The location of the formation on the eyelid and its rapid growth are also indications for removing the hemangioma through surgery. This is due to the fact that sometimes such localization leads to loss of vision. Before the intervention, the patient is given general or local anesthesia. The choice depends on the location and size of the tumor. The disadvantage of surgery is that recovery takes a long period. |
| Sclerosis of blood vessels | A special drug, a sclerosant, is injected into the site of the tumor, which acts on the blood vessels and kills them. The procedure is used to get rid of small hemangiomas. |
| Laser therapy | Often they use a laser device that emits green or yellow light. Small formations are removed. In rare cases, it is used to remove large hemangiomas, but in this case, 2 or 3 sessions will be required, with a break between them. Its duration is determined by the attending physician. |
| Electrocoagulation | Used to get rid of tumors of any size. During the manipulation process, an electric current is applied to the ocular hemangioma. |
Symptoms
The formation of eye hemangioma occurs in stages. The initial stages are characterized by small tumor sizes; a slight swelling is observed in the lesion, in which a network of capillaries is clearly visible.
On this topic
Organs of vision
What symptoms can be used to recognize optic nerve glioma?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- September 3, 2021
When mechanical impact is applied to the location of the tumor, painful sensations appear.
Capillary and cavernous neoplasms have some differences between themselves:
- Cavernous form - characterized by the fact that the tumor protrudes above the skin level, the capillary network is clearly visible, and cavities filled with blood are also visible.
- Capillary form - characterized by the appearance of a dark red spot, which consists of thin, intertwined vessels.
In addition, there is an internal form of pathology - this is choroidal hemangioma. Rarely diagnosed in patients, it is a tumor process affecting the orbit of the eye. In the future, if left untreated, it leads to strabismus and vision impairment.
If large hemangiomas are observed, the doctor will prescribe an additional study, which is aimed at diagnosing cardiovascular diseases; also in such situations, a disease such as chondropathy of the upper or lower extremities is often associated.
Diagnostics
If parents suspect such a formation, then they should show the baby to the doctor.
If a hemangioma is detected, it is necessary to show the newborn to a pediatrician or dermatologist. The doctor examines the affected area. To determine the extent and danger of a tumor, the following basic examinations are used:
- General blood analysis. Shows the state of the body and the hematopoietic system as a whole.
- Coagulogram is a study of blood clotting.
- Dermatoscopy is an examination of the tumor structure with a device that provides multiple magnification.
- Thermometry is the measurement of the temperature difference between healthy skin and the surface of the hemangioma.
- Thermography is the recording of thermal radiation from the skin, which determines the depth and boundaries of the tumor.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) is a study of the size, structure, size and depth of a neoplasm.
- Angiography - determination of blood circulation rate, size of hemangioma and spread to neighboring tissues using an injected contrast agent.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a cross-sectional scan of the affected area.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - detailed layer-by-layer visualization of the hemangioma and surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy is the removal of a sample of tumor tissue for microscopic examination.
- Histology - examination of the cells and structure of the tumor.
Treatment methods
If a hemangioma begins to form on the upper eyelid, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately. The tumor grows in size very quickly, and if it is not eliminated in a timely manner using conservative methods, the tumor will have to be removed surgically. Only in 2% of all cases the tumor goes away on its own.
Treatment of pathology includes three main methods:
- medicinal;
- surgical;
- physical.
The drug method has been applied to the treatment of hemangiomas relatively recently. Taking certain drugs reduces the growth of tumor formations and also contributes to their reverse development. But using this method alone is ineffective. With the help of medications, it is possible to get rid of a hemangiosal tumor only in 2% of cases.
Treatment should only be prescribed by the attending physician.
In order to reduce the growth of pathological formations, the following medications are used:
- Propranolol has a vasoconstrictor effect, activates the process of destruction of capillaries in the affected area and replaces them with scar tissue;
- Prednisolone is a hormonal drug that promotes tissue scarring and compression of capillaries, due to which blood circulation in them decreases, due to which the growth of hemangioma stops;
- Vincristine blocks the process of cell division, which leads to the cessation of tumor development.
Each of the listed drugs has side effects and contraindications, so the dosage and duration of therapy should be prescribed only by the attending physician.
Physical methods act directly on hemangioma tissue, destroy them and help eliminate tumor formation. The most popular methods in this group include:
- irradiation with laser beams;
- electrocoagulation;
- sclerosing therapy;
- X-ray therapy;
- treatment with drops if the internal tissues of the eye are affected.
The laser can remove tumor formations no larger than 2 cm. Tissues exposed to irradiation become charred and evaporate. A crust forms in the area where the treatment was carried out, which disappears after three weeks.
Hemangioma can be removed with a laser.
The electrocoagulation method is based on the action of high frequency electric current on problem areas. The current chars and destroys tissue, which subsequently heals itself.
Large hemangiomas are eliminated using sclerotherapy. The effect in this case is aimed at cauterizing the chemical elements that make up the hemangioma, leading to the destruction of capillaries and cavities. The procedure must be carried out more than once. In treatment, 70% alcohol is used, it is injected into the hemangioma.
The tumor can be exposed to X-rays; this method also leads to tissue destruction. Most often, this procedure is used during preparation for surgery to reduce the affected tissue in order to reduce the volume of the tumor being operated on.
Surgical intervention is used extremely rarely, only when the disease progresses rapidly and carries a risk of complications. This option is not suitable for newborns.
A child has a growing hemangioma - what to do?
As noted earlier, tumor growth in the first 6 to 12 months after appearance is the norm. Watchful waiting is not used if the hemangioma is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Excessive and prolonged growth. Parents can monitor this parameter themselves by periodically photographing the tumor and measuring its size. The indication for treatment is tumor growth after the child is two years old.
- Development of hemangioma on the eyelids, near physiological openings, in traumatic places.
- Formation of hemangioma on internal organs and bones. Such a tumor does not allow the child’s organs to develop normally.
- Large tumor sizes, creating a significant cosmetic defect.
Capillary hemangioma on the face requiring surgical treatment
What is hemangioma
Having discovered a hemangioma on the eyelid of a newborn, parents should go to the hospital to clarify the diagnosis and receive specialist advice on the need for treatment.
On this topic
- Skin covering
Tumor on the face
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 10, 2021
The tumor is formed as a result of a plexus of superficial blood vessels surrounded by fat cells. This neoplasm of vascular tissue is benign. Hemangioma tends to actively grow in the first months of a child’s life, sometimes expanding not only in breadth, but also deep into the tissue.
The tumor not only spoils the appearance, but also impedes the normal vital functions of the eye. There are several types of pathology:
- capillary (simple);
- cavernous;
- mixed.
The neoplasm comes in different shapes, differs in size and color - reddish, cherry, with a bluish tint. A cavernous type tumor affects the deeper layers of the skin and even occurs on internal organs.
Treatment of hemangiomas in children
First of all, a complete examination of the child is carried out, the purpose of which is to determine the type of tumor, its structure, size and potential dangers during its further development. For this purpose, a set of laboratory and instrumental studies is prescribed:
- A general blood test to check for a decrease in the level of platelets and hemoglobin in the blood circulating through the vessels of the tumor
- Ultrasound - to determine the type of hemangioma
- CT, MRI, thermography - to establish the true size of the hemangioma
- Angiography is a study using a contrast agent injected into the vessels, which determines the degree of involvement of tissues of other organs in the growth of hemangioma; used in complex cases when surgery is required, for example, on the bones of the skull.
Multiple liver hemangiomas (ultrasound)
Cavernous hemangioma of the left frontal lobe of the brain (MRI)
Based on the research results, the doctor chooses wait-and-see or surgical treatment tactics. In modern medicine, the following methods are used to combat hemangiomas in children:
- Cryodestruction is the freezing of a tumor with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser exposure - destruction of tumor vessels with a laser.
- Electrocoagulation is cauterization using electric current. Can be used for any type of superficial hemangioma.
- Sclerosis is the administration of injections with a special composition that clogs blood vessels.
- Radiation therapy is the removal of a tumor using targeted X-rays. It is used in the case of hemangiomas of internal organs, bones, or when it is impossible to use another method (for example, if the tumor is located in the orbit).
- The operation is an ineffective and traumatic method, in which the development of hemangiomas in neighboring areas is often observed. Used only in extreme cases.
- Drug therapy - treatment with drugs containing timolol, propranolol, hormones.
Types of benign vascular pathologies
Three selected types:
- Capillary - a cluster of small blood vessels in the upper layer of the skin. This type of hemangioma is also called the simplest and most harmless. When pressed, it fades, but returns color when the physical impact ends. Usually, the spider veins disappear as suddenly as they appear.
- Cavernous is a nodular accumulation of small and enlarged vessels in the subcutaneous space. Soft and elastic to the touch. Under the skin of normal color, edematous cyanosis is visible. It increases under stress and grows with the child. It is dangerous because it is located on the face and internal organs.
- Combined – a mix of simple and cavernous hemangiomas. Characterized by deep germination in tissue. Insidious, requires careful observation.
Benign tumor hemangioma in a child
The presence of a “red mark” in children suggests contacting a doctor. The doctor will determine the need for further examination and treatment. The urgency of medical measures depends on the location of the tumor and its phase.
Causes
It is difficult to unambiguously determine the reasons that provoke the formation of hemangioma. Only certain factors are identified that cause such a disorder in the blood vessels.
On this topic
Organs of vision
How to get rid of wen on the eyelid
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- February 27, 2021
Most often, the following conditions contribute to the development of hemangiomas in young children:
- Diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
- Premature birth.
- "Late" pregnancy.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Development or exacerbation of a chronic form of the disease associated with the thyroid gland in the expectant mother.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions during pregnancy.
- Transferred viral pathology in the initial stages of pregnancy (immediately at the time when the circulatory system of the fetus is formed).
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Hormonal disturbances during pregnancy.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Incompatibility of mother and child by Rh factor.
- Abuse of alcohol and tobacco products while pregnant.
The exclusion of all provoking factors can be considered preventive measures against the manifestation of pathology in the unborn child.
We must not forget that an adult is also not immune from the manifestation of the disease. In such phenomena, the provoking factor is often various eye injuries or thrombus formation processes.
Medical scientists put forward several theories describing the mechanisms of disease formation, but even this does not fully explain all aspects of the development of the disease.
Causes of pathology
Intrauterine disruption of the formation of the vascular system leads to the appearance of hemangiomas after birth.
Dilated blood vessels group together and form a defect on the skin of the baby's eyelid. Main causes of the disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- Rh conflict - incompatibility of the blood of the mother and the embryo;
- multiple pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalances in the child or mother;
- viral diseases in early pregnancy;
- endocrinological pathologies of acute or chronic course;
- severe toxicosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- early delivery;
- Prematurity or underweight baby.
Unfavorable factors contributing to the manifestation of hemangioma:
Late pregnancy can provoke the formation of pathology in the baby.
- pregnancy at an older age;
- exposure to medications;
- environmentally unfavorable location;
- non-compliance with healthy lifestyle standards;
- unstable emotional state, increased nervousness.
In children
A tumor on the eye of a newborn has the ability to grow quickly, which is why such children are under constant medical supervision. Even the smallest formations should be observed. Pediatricians believe that parents should remain calm in this situation. The main thing is to contact a doctor in a timely manner to eliminate the problem and possible complications.
In almost 90% of small children, the formation on the eye is not treated, since it has the ability to disappear with age, but not always.
According to statistics, education disappears between the ages of 5 and 9 years.
In a situation where rapid tumor growth is noted, it is necessary to begin emergency treatment, since in addition to a cosmetic defect, this can lead to loss of vision. Surgical intervention is performed as a last resort and only after the child reaches 4 months of age.
Hemangioma in a child: signs and causes
To correctly diagnose hemangioma, a combination of all characteristic signs is necessary:
- At first, the tumor develops quite quickly and increases in size, thanks to which it is possible to distinguish a hemangioma from, for example, a birthmark.
- Due to the large flow of blood in the vessels of the hemangioma, it is hotter than the surrounding tissue.
- When pressed, the tumor turns pale, and after cessation of exposure it quickly restores its original color.
Combined hemangioma in the breast area
Most often, hemangiomas are located:
- on the scalp (eyelids, cheeks, nose, scalp, back of the head)
- on the skin of the extremities (hands, soles of feet, buttocks)
- on the body (stomach, back)
- on mucous membranes (nasal passages, oral cavity, genitals)
- on internal organs (liver, spleen)
- on the organs of the musculoskeletal system (pelvic bones, skull).
Since in the vast majority of cases, hemangioma appears in a child from birth or in infancy up to one year, it is generally accepted that the main cause is abnormalities in the development of the vascular system in the embryonic period. At the same time, experts also note a dependence on the sex of the baby, since in 80% of cases hemangiomas occur in girls.
Multiple hemangiomas on the leg and body of a newborn
Other probable causes that increase the risk of developing hemangioma in children:
- viral diseases suffered during pregnancy
- heredity
- unfavorable environmental situation
- mature age of mother
- alcohol abuse, smoking
Hemangioma in children and newborns: photos, causes, treatment, laser and surgical removal
Benign neoplasms such as hemangiomas, which are formed from vascular tissues, often appear in newborns and older children. As a rule, the cause of hemangioma is anomalies in the embryonic development of the vascular system.
Externally, the tumor appears bluish or purplish-red, slightly raised above the skin, or as a flat spot. Such tumors tend to bleed and actively increase in size.
According to statistics, hemangiosal formations are diagnosed in 1-3% of newborn babies and in every 10 children in the first 12 months of life, and girls are the owners of such formations two to three times more often than boys.
Although the tumor is not malignant, it can grow deeper, damaging surrounding organs, which can have dysfunctional consequences for the child’s respiratory, visual and auditory systems.
Classification
All hemangiosal tumors are divided into 4 types:
- Capillary or simple hemangioma - it consists of a cluster of tiny capillary vessels and is localized mainly on the skin surface. Detected in 95% of cases;
Photo of capillary hemangioma on the lower eyelid of a newborn
- Cavernous - localized subcutaneously and consists of many cavities filled with blood content;
The photo clearly shows what a cavernous hemangioma looks like on a child’s face
- Combined - such a tumor has the characteristics of a simple and cavernous hemangioma, while simultaneously being localized in the subcutaneous layers and on the skin;
The photo clearly shows what combined hemangioma looks like in children
- Mixed hemangiosal tumor has a multi-tissue structure and consists of lymphatic, nervous, vascular and connective tissue.
In addition, a hemangioma can be present at birth - a congenital tumor, or it can form later - an infantile hemangioma.
Hemangiovascular formations appear in infants and children for many reasons:
- Late motherhood, when a woman gives birth at a fairly mature age;
- Pathologies during pregnancy;
- Carrying twins, triplets, etc.;
- The birth of a child before the due date;
- Aggressive or unfavorable environmental environment of the pregnant woman;
- Relapse or exacerbation of an endocrine pathology in a pregnant woman;
- If in the first 6 months of bearing the baby the mother suffered from a viral infection;
- Abuse of certain medications.
How can you understand that a child has a hemangioma?
Sometimes, in terms of external signs, a hemangiosal tumor resembles a mole. Therefore, it is important to distinguish between such neoplasms. As reported above, hemangiosal tumors are detected immediately after birth or in the first six months of a baby’s life. Typically in children, hemangiosal tumors are located:
- On the scalp, mainly on the back of the head and neck;
- On the face, eye, eyelids, forehead, nose, lip and cheeks;
- On the limbs of the arms and legs, as well as on the butt, stomach and back;
- On the mucous tissues of the tongue, lips, genitals or anus;
- On bone vertebral and cranial tissues;
- On intraorganic surfaces, such as the liver.
Photo of a flat (capillary) hemangioma on the nose of a newborn
Hemangiomas in children are characterized by two stages of development:
- Proliferative is the growth stage, it can last up to six months, during which time the tumor practically grows to its final parameters.
- Involutional is a stage of reverse development; in half of the cases it comes to an end at the age of five. By the age of 9, 90% of children experience the end of the involutionary period. By the end of involution, the area where the hemangioma was previously located will not always be indistinguishable from healthy tissue. Sometimes small marks and scars remain in these areas.
Hemangiosal formations may rise slightly above the epithelial surface or be flush with it. The sizes of such tumors vary from 0.1 to 15 cm. When touched, they feel somewhat hotter than the surrounding surfaces.
Characteristics of education
Types of hemangiomas differ not only in structure, but also in external characteristics:
- A simple hemangioma looks like a flat, sometimes lumpy, clearly defined spot of a bluish-red hue; when you press on the capillary tumor, its color will turn pale, but will quickly return to its previous saturation after the pressure is removed;
- Cavernous varieties of hemangiomas are distinguished by their typical slightly bluish tint. With tension in the surrounding tissues or during strong crying, such a hemangioma will become brighter and a little larger, but then will again acquire its original shades and sizes;
- Combined formations combine the features of cavernous and simple hemangiomas;
- Mixed hemangiosal tumors appear depending on the predominance of a particular type of tissue.
Causes
The number of newborns with congenital pathology is increasing every year. According to statistics, every 10th baby has at least one small tumor. Why do they appear?
Scientists cannot yet give a definite answer about the reasons for the appearance of neoplasms. Most experts agree that their formation is associated with viral-infectious diseases suffered during the period of intrauterine development. Underweight babies and premature babies are at greater risk of getting such a tumor. There are 4 times more cases of the disease in girls than in boys.
According to experts, hemangiomas are the body’s reaction to problems in intrauterine development
Also among the reasons are the following factors:
- mother's use of medications during pregnancy;
- viral diseases suffered by the mother in the 1st and 2nd trimester;
- development of diseases of the endocrine system or their exacerbation during pregnancy;
- poor ecology in the mother’s place of residence;
- diseases that prevent the birth of a full-term baby;
- multiple pregnancy;
- various types of pathologies (placenta previa, preeclampsia);
- mature age of the woman in labor (over 35 years).
Hemangioma can also appear in adolescence. What is this connected with? In most cases, there is a hormonal imbalance, as well as liver disease, against which a tumor subsequently develops.
The appearance of hemangioma in adolescence and adulthood is most often associated with changes in hormonal levels
In the first weeks, the newborn develops a small red spot that rises slightly above the skin. During the first three months, the tumor increases significantly in diameter. A characteristic sign is that when you press on the hemangioma, it turns pale, but then turns red again. This is due to the outflow of blood. In a crying or coughing child, the tumor becomes more saturated and larger, which is due to active blood flow.
Sometimes with hemangioma there is a difference in temperature between the formation and the tissues nearby, i.e. hemangioma is hotter. About 80% of all cases in infants end safely. They do not develop into malignant tumors and most often they regress on their own, i.e. disappear without a trace within 3-5 years. This outcome is most typical for simple hemangiomas that are small in size.
Depending on how the vessels in the hemangioma are built, there will be differences in the appearance of the tumor. You can see a photo of what each form looks like on the Internet:
- Capillary hemangioma. It looks and feels flat or lumpy. It is characterized by the presence of clear boundaries, as well as a reddish or bluish tint. You can distinguish the capillary shape by pressing: after pressing on the spot, it turns pale, after which it regains its previous color. It can be on the lips, on the nose, on the back of the head, on the fontanelle, on the butt, on the shoulder and on other parts of the body.
- Cavernous hemangioma. To the touch, the neoplasm has a soft surface, covered with bluish skin on top. This form of tumor increases in size when crying or coughing. When pressed, the swelling disappears and the skin becomes pale.
Cavernous hemangioma turns red and fills when the child is active
- Combined hemangioma includes the characteristics of the first two types.
- A mixed hemangioma will have a different appearance, depending on the type of tissue included in the tumor process.
- As bone hemangioma grows, it is characterized by bone pain associated with compression of nerve endings and blood vessels.
Hemangioma
Ulcer
11720 20 January
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Hemangioma: causes of appearance, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Hemangioma is called vascular hyperplasia (proliferation of cells in the vascular wall) - a disease that is classified as a benign tumor (benign neoplasm) and can be either congenital or appear within a few months after the birth of the child.
Skin hemangioma occurs in adults, but not often, since most tumors resolve on their own in childhood. If a similar tumor appears on the skin of an adult, where there were no surface defects before, then such a tumor requires careful diagnosis.
If in childhood the hemangioma is weakly expressed (in the form of an abrasion or a small spot), then in adulthood under the influence of certain factors it can grow and enlarge.
Hemangiomas form, as a rule, on the scalp, face, neck and, less commonly, on the torso and limbs. Favorite locations on internal organs are the liver, bones, and lungs.
Skin hemangiomas are most often single neoplasms, but there are exceptions. It has been noticed that if there are more than five hemangiomas in visible areas of the body, there is a high probability that there is also a hemangioma of internal organs.
Causes of hemangiomas
The causes of hemangiomas are not fully understood. One theory is that the overgrown endothelial cells may be residual embryonic cells. Another assumption is that the hemangioma begins to grow in utero under conditions of chronic lack of oxygen. It is possible that the formation of a tumor can be provoked by acute infections, including respiratory viral infections, if the mother had any in the first trimester of pregnancy. This is only a theory, because hemangiomas also occur in children born to mothers with normal pregnancies.
It has been noted that hemangiomas are more common in premature babies and in multiple pregnancies.
Threats of miscarriage, placenta previa (a very low location of the placenta in the uterus, making natural childbirth difficult), abruption and inflammation of the placenta, entanglement of the umbilical cord, preeclampsia (a set of symptoms including edema, increased blood pressure and detection of protein in a urine test), maternal age (over 38 years) are also risk factors.
Classification of the disease
Hemangiomas of childhood are divided into congenital and infantile (infantile).
Congenital hemangiomas appear, grow and reach their maximum size in utero.
Often large hemangiomas can be seen during ultrasound screening. A newborn appears with a hemangioma, which can subsequently decrease in size and disappear on its own within a year and a half (rapidly involuting), decrease but not completely disappear (partially involuting) or not change at all (not involuting). If a congenital hemangioma grows, it grows only in proportion to the child’s growth. It occurs with equal frequency in both boys and girls.
Infantile (baby) hemangiomas appear during the first weeks of life.
Infantile hemangioma
This hemangioma is preceded by an area of changed skin or a red spot. The growth of hemangioma can continue up to six months of the child’s life. Then comes a period of growth cessation, which lasts on average two months, and then there is a phase of slow reduction of the tumor, which can last up to ten years.
Infantile hemangioma occurs five times more often in girls than in boys.
Infantile hemangiomas can be located on the skin (simple capillary hemangiomas), under the skin (venous and cavernous hemangiomas) and be combined.
Depending on the histological structure and the caliber of the vessels, hemangiomas are divided into:
- to capillary
- venous,
- cavernous,
- combined.
Capillary or superficial hemangioma of the skin (port-wine stain).
It is located on the surface of the skin and is a dense network of closely intertwined capillaries lined with endothelial cells. This form occurs in 90-96% of cases, is characterized by intensive proliferation of new vessels and is considered the initial stage of development of the formation.
Venous hemangiomas.
The formations are represented by veins of small and medium caliber. Such hemangiomas tend to grow deep into the skin and above its surface.
Cavernous or cavernous hemangiomas.
Cavernous formation is considered the next stage in the development of the venous form of hemangioma. It consists of cavities bounded by the endothelial layer of blood vessels and separated by septa. Such a hemangioma is formed as a result of the overflow of defective capillaries with blood and rupture of their walls with the formation of cavities (cavities) and hemorrhages (hematomas). The blood in these cavities forms small clots due to increased coagulation properties.
Combined hemangiomas.
This type of hemangiomas includes formations that have signs of several forms of varying severity.
Symptoms of hemangioma
- Capillary or superficial hemangioma of the skin (port-wine stain) is prone to growing into surrounding tissues and is a voluminous elastic formation from pale pink to deep red or burgundy, with uneven outlines, slightly rising above the surface of the skin.
When pressed, the hemangioma turns pale, but then quickly returns to its original appearance. When localized on the back of the head it is called “stork bite”, when localized on the forehead it is called “angel’s kiss”. The edges of the hemangioma indicate the stage of its development: a smooth, defined edge is observed in the growth arrest phase and the tumor shrinkage phase. During active growth, the edges are blurred. - Venous hemangiomas are dark red in color with a blue or purple tint. They are not found often, but they are quite large in area.
- Cavernous or cavernous hemangiomas have the appearance of a soft bluish-purple or purple elastic subcutaneous formation with outlines clearly demarcated from the surrounding tissues and a rough surface through which small vessels are visible. A small part of the formation rises above the surface of the skin, the rest is located deep in the tissue and can penetrate not only into the subcutaneous tissue, but also into the muscles. When pressure is applied for several seconds, the tumor shrinks, its volume and color intensity decrease, which quickly recover after the pressure is removed.
- Combined hemangiomas combine the features of the superficial and subcutaneous forms, with the subcutaneous part occupying a larger volume.
- Hemangiomas of internal organs.
Small hemangiomas of internal organs often do not manifest themselves and are accidentally detected during studies related to other diseases.
In order for a liver hemangioma to cause pain, it must reach an impressive size - 5–10 cm. A hemangioma of the spine does not cause any symptoms if it is located inside a vertebra. Once it affects the periosteum (the membrane covering the bone) or ligaments, constant pain occurs. A tumor that compresses the roots of the spinal nerves can lead to various sensory disturbances in the limbs.
Some hemangiomas immediately cause symptoms, this is explained by the peculiarity of their location. As they grow, they quickly disrupt the function of the organ. These include hemangiomas of the larynx, trachea, and eye tumors.
Diagnosis of hemangioma
Diagnosis of hemangioma begins with asking the patient and/or his representatives about the course of the disease, the first manifestations, and the dynamics of events. Then a detailed examination of the vascular formation is carried out. Depending on the symptoms and location of the hemangioma, an in-depth examination by a specialist (ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, etc.) may be required.
To clarify the size, depth, and structure of the neoplasm, an ultrasound examination with the study of blood flow is indicated. However, in some hemangiomas it may not be informative.