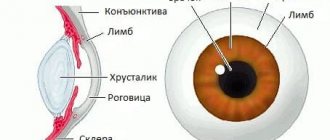
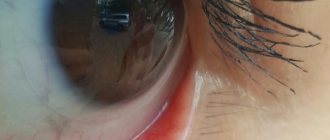
Xanthelasma is a benign formation that occurs on the eyelids. In its structure it resembles a lipoma. The tumor grows slowly and cannot degenerate into malignant, but it will never go away on its own unless you get rid of it. What causes xanthelasma and what are the effective methods of treating it?
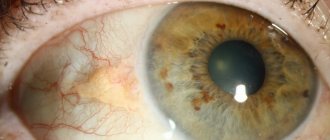
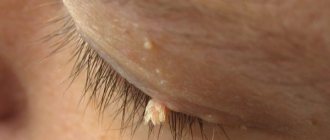
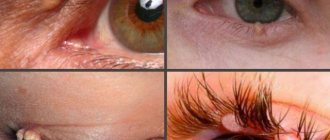
Externally, this benign formation appears as yellowish, flat plaques, varying in size and with uneven borders. Their surface may be smooth or slightly wrinkled. Their size varies from a few millimeters to 4-5 cm. Most often they are located on the upper and lower eyelids, but sometimes they can be observed on other parts of the face: on the tongue or ears. The plaques have a soft consistency, and as they grow, they begin to merge with each other - this phenomenon is called xanthoma. This fusion most often occurs on the lower eyelids. New growths appear suddenly, without any prerequisites. In this case, there are no additional symptoms such as itching or redness.
Why does xanthelasma form on the eyelids?
Doctors have not yet come to a consensus on the exact causes of this skin defect. However, it is believed that in most cases this is facilitated by a violation of fat metabolism - the accumulation of excess fat molecules and a failure of metabolic metabolism in various diseases:
- diabetes;
- disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas;
- diffuse toxic goiter;
- renal tissue dystrophy;
- hypertension;
- obesity.
Most often, xanthelasma occurs in middle-aged and elderly women.
An interesting study by scientists at the University of Copenhagen was recently published. They found that almost 50% of patients with this benign formation have blood cholesterol levels that are within normal limits. Fat deposition on the eyelids in this case can serve as an indicator of developing diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems.
The appearance of xanthelasma on the eyelids indicates the risk of a heart attack or coronary artery disease. The findings of Danish researchers were adopted by doctors. If xanthelasma is detected on the eyelids of patients with normal cholesterol levels, they will be advised to pay special attention to the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Yellow spots on the eyelids as a symptom of the disease
There are several diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of yellow spots on the eyelids and around the eyes:
- Violations of vitamin A metabolism. If there is an excess of it, yellowing of certain areas of the skin may occur.
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder. A very common cause of yellowing of the skin.
- Blood disorders (such as blood cancer or sickle cell disease).
About yellow circles under the eyes >>
In all of the above cases, yellowing of the skin is observed throughout the body or on the mucous membranes. But there is a disease that is characterized by the following symptoms: pronounced straw-colored spots, small in size, with clearly defined contours. If the formation looks exactly like this, then most likely it is xanthelasma. We should talk about it separately.
Xanthelasma
If yellow spots appear on the eyelids, then in most cases, specialists diagnose this particular disease. Xanthelasma is a benign yellow neoplasm, slightly raised above the surface of the skin in the form of a plaque. It is most often located on the upper eyelid, at the inner corner of the eye. On the lower eyelid, xanthelasma looks like a yellow or straw-colored stripe.
How is diagnostics carried out?
If suspicious formations occur, you should contact a dermatologist. He will conduct a visual examination and refer you to an endocrinologist for additional diagnostics. The final diagnosis is formed taking into account the overall clinical picture after collecting the necessary tests. Lipid metabolism is examined and cholesterol levels are determined. In order not to confuse xanthelasma with pseudoxanthoma, syringoma (tumor of the sweat glands) and malignant tumors, differential diagnosis is carried out.
There has not yet been a single case of this benign tumor developing into a malignant one. However, the neoplasm is an unpleasant cosmetic defect.
If left untreated, the plaques will grow and cause psychological discomfort, especially since the vast majority of women suffer from this disease.
Diagnostics
Patients with xanthelasma of the eyelids need to consult not only an ophthalmologist, but also an endocrinologist and a dermatologist. The examination must include a general blood test, a study of lipid metabolism (level of lipoproteins and cholesterol in the blood serum).
The characteristic appearance of the formations usually does not pose any difficulties in making a diagnosis. In addition to xanthelasmas and xanthomas, the patient is often diagnosed with obesity, hypertension, metabolic syndrome or diabetes mellitus. Xanthelasma of the eyelids must be differentiated from other similar skin diseases (syringoma, pseudoxanthoma), incl. malignant tumors.
Traditional methods of treating xanthelasma
These are the folk remedies recommended for xanthelasma. Decoctions of various medicinal plants: dandelion roots, birch buds, immortelle flowers. Also, to remove bile, it is useful to drink juices from raw vegetables and fruits: tomatoes, spinach, beets, celery, citrus fruits. However, you should first make sure that there are no disorders in the biliary tract or kidney stones. Various compresses. This can be baked onions or chestnuts, aloe juice, grated cabbage leaves, sour cream with honey and other ingredients. They are applied to the eyelids for 15-20 minutes, then washed off with water.
Detailed recipes can be found on the Internet, however, it is better to coordinate them with your doctor.
Removing xanthelasma with laser
Today this is the most effective way to get rid of xanthelasma quickly and permanently. The effect occurs using a carbon dioxide laser, which has been successfully used in aesthetic cosmetology for almost three decades. It destroys fatty structures without damaging surrounding tissues. The operation is more expensive than other methods, but has many advantages:
- no mechanical trauma to the skin;
- rapid bleeding stop;
- complete sterility;
- high accuracy of tumor removal;
- absence of scars;
- short rehabilitation period.
Laser treatment is widely used to treat various skin problems. Removal of xanthelasma using a carbon dioxide laser gives good results. The tumor disappears and there are no more relapses.
After surgery, you need to adhere to a special diet for 1-2 weeks, eliminating fats from the diet and minimizing the consumption of carbohydrate foods. In the future, to prevent the disease, you should eat right.
Electrocoagulation
Destruction of xanthelosis plaques using high-frequency electric current. An electrode is placed on them, current is applied, and the tumor is cauterized. Tumor cells are destroyed. At the site of each plaque, a red crust remains, which must be cared for with ointments. The eyelids finally heal in about 10 days. Electrocoagulation is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. The patient can go home on the same day. The method is used for small tumors, since removal of large xanthelasmas that have merged into xanthomas with electric shock can be quite traumatic.
Why do white spots appear under the eyes?
The appearance of any formations on the eyelids may indicate the presence of undetected pathologies. Xanthelasma of the eyelids is a disease in which yellow, white, and sometimes orange plaques appear on the skin of the eyelids.
In parallel with xanthelasma, diabetes mellitus, hypertension or liver problems are diagnosed. In this article we will tell you why white spots form on the eyelids.
Experts still have not figured out the nature of the formation of spots on the eyelid. The main reasons for the appearance of white plaques on the skin of the eyelid include:
- problems with the pancreas;
- liver pathologies;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- metabolic disease;
- lipid metabolism disorder.
Formations can be single or part of a group. As a rule, the disease is located in the corner of the upper eyelid or below.
For information! According to studies, it was found that xanthelasma may indicate a threat of myocardial infarction or the development of atherosclerosis.
In appearance, the plaques have a straw or white color, the surface and contour of the formation are uneven and smooth, and the spot is quite soft to the touch. It is worth noting that xanthelasma is a benign formation that never becomes malignant.
The pathology is more a cosmetic defect than a threat to life.
The size of the spot can be as large as a pea, and in some cases the formation can reach the size of a bean.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of xanthelasma on the eyelid is carried out by external examination using a glass slide.
The plaque area is slightly pressed with a glass slide so that the formation, its color, shape and structure can be clearly seen.
White spots on the eyelids have characteristic features, so to identify them, a blood test is prescribed, which allows you to determine your cholesterol level.
For information! The level of cholesterol in the blood reflects the presence of a malfunction in lipid metabolism.
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist and endocrinologist, their examination consists of identifying:
- the root causes of the formation of a white spot;
- determination of xanthelasma or tumor;
- determining the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus or atherosclerosis.
Treatment methods
Treatment of the disease consists of following a diet, namely limiting the consumption of foods containing animal fats.
The main goal of therapy is aimed at eliminating the pathology that provoked metabolic disorders. The diet helps to correct the internal metabolism in the patient’s body.
If the plaques do not go away with diet, your doctor may prescribe their removal.
For information! The formation of recurrence of white spots on the eyelids after removal is completely excluded.
Plaque removal methods include:
- Electrocoagulation - used together with the surgical method; after removing the white spot, its edges are connected to each other and cauterized with an electrode.
- Surgical excision - performed under local anesthesia, plaques are separated using tweezers and scissors. The edges of the spots are connected and lubricated with a solution of iron sesquichloride. The wounds heal within a week after the procedure.
For information! If the edges of the wound are peeled off, they are cauterized with electric current.
- The radio wave method is an absolutely safe procedure, carried out using high-frequency waves, where the instrument used is heated and tumor cells are evaporated with its help. This procedure is non-contact and painless.
- Cryodestruction - the method involves applying liquid nitrogen to the affected area. The temperature of the substance is -195C degrees, the time of application of nitrogen is determined by the attending physician. The main task of nitrogen is to destroy neoplasm cells.
- Laser therapy - the procedure is a gentle removal of formations without gross traces of intervention and injury to nearby tissues. Laser therapy eliminates infection of wounds, the formation of scars or marks after removal, and also eliminates the postoperative period.
You can prevent relapses by following the following dietary regimen:
- limiting carbohydrates;
- exclusion of products containing natural fats;
- inclusion of dairy and plant products in the diet.
In addition to diet, it is recommended to avoid injury at the site of formation of white spots, because It is in previously affected areas that new nodules or tumor-like nodules can form.
For information! Patients suffering from xanthelasma of the eyelid are advised to avoid physical activity.
As a rule, such patients are observed by a therapist to quickly detect the development of early atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and heart attack. If the xanthomatous white formations on the eyelids are quite dense and have a large area of epidermal damage, the patient is recommended to continue treatment with an ophthalmologist.
The presence of white spots on the skin of the eyelids may indicate serious internal problems. When formations are first detected, it is recommended to undergo an initial examination by your attending physician and undergo the necessary tests.
It is important not to try to cope with it using home methods.
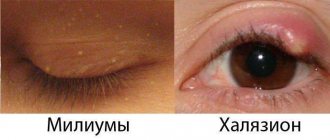
White spots under the eyes, and sometimes on the upper eyelids and other areas of the face, are called milia. Their popular name is millet, due to their external resemblance to millet grains. To the touch, these are dense small formations, small bumps, not painful, but causing aesthetic discomfort. Why do they occur and how can they be removed?
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Endoscopic midface lift
The distribution area of milia is the area under the lower eyelid, but they can also appear around the nose, on the upper eyelids, under the lower lip. They do not change in size, but they do not go away naturally, even if you try to squeeze them out.
White spots under the eyes, similar to pimples, are small subcutaneous formations of white or yellowish color, filled with layered keratin accumulations (keratinized epithelial cells). Their size varies from 0.5 to 2-3 mm, and the points are located in small groups or in the form of separate elements, but never merge with each other.
Of course, you want to get rid of them as quickly as possible, but you need to do this not on your own, but by turning to the services of specialists. Let's talk about the reasons for the formation of milia and methods of removal.
Why do white spots appear under the eyes?
The main reason for the appearance of white dots under the eyes is a violation of the mechanism of exfoliation of dead skin particles.
When this process fails, they accumulate on the surface of the skin, clogging the ducts of the sebaceous glands, which become clogged, and milia appear.
Also, the cause may be excessive activity of the sebaceous glands - owners of excessively oily skin are well aware of this, when excess sebum does not have time to be eliminated.
Other factors that cause millet grains are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Often milia are a consequence of hormonal changes in the body - for example, during puberty, pregnancy or menopause. Another version of the appearance of white spots on the skin around the eyes is exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Millet is often observed in newborns in approximately 40-50% of cases. In this case, white dots can appear not only on the face, but throughout the body. In infants they disappear in the first 1-3 months of life. The cause is usually a blockage of the sebaceous glands; the child’s body adapts to a new, unusual environment for him.
Cryodestruction
This is a method of removing skin lesions - xanthelasmas, warts, papillomas - by freezing with liquid nitrogen. The procedure gives a good cosmetic effect. The fatty plaque is frozen at an ultra-low temperature of 190 degrees, after which its structure is destroyed and cell growth stops. During the rehabilitation period, you must strictly follow the care recommendations: protect your eyes from the bright sun, do not visit the solarium, and do not use facial cosmetics.
Surgical excision
This method is used in cases where it is necessary to remove xanthomas - large fused formations. The surface of the plaque and the area around it are carefully treated with an antiseptic, then separated using scissors or tweezers. The edges of the wound are treated with ferric chloride, then with potassium permanganate or brilliant green. The main disadvantage of this method is the high probability of relapse.
Surgical excision may be prescribed if the patient has contraindications to other techniques.
In general, this method is rarely used these days, trying to carry out treatment before the plaques grow to large sizes.
Treatment
Treatment should begin only after an accurate diagnosis has been established. If the doctor determines that the yellow areas of the skin are caused by problems with the liver or gall bladder, then diseases of these organs need to be treated.
Blood diseases are treated by hematologists in specialized hospitals. Typically, such treatment continues for a long time.
If xanthelasma is diagnosed, then yellow spots around the eyes on the eyelids can be treated by a dermatologist, therapist or cosmetologist.
Xanthelasma does not respond well to conservative treatment. As a rule, it is not possible to reduce the area of the tumor.
If there is a pronounced cosmetic defect, you can use surgical removal of the formation. Removal of small xanthelasmas can be carried out in a beauty salon. But if a large area of skin is affected, or the patient has other health problems, then it is better to remove the tumors in the surgical department.
There are several ways to remove xanthelasma:
- Surgical excision of the formation.
- Laser removal.
- Cryodestruction. Exposure to liquid nitrogen.
- Radio wave exposure.
For small plaques, the diathermocoagulation method is suitable. Large formations are removed using a scalpel and tweezers. The edges of the wound are aligned and secured with surgical glue. In this case, the wound heals quickly. And the scars after such an intervention are almost invisible.
How to prevent xanthelasma from appearing
A study of the contents of the plaques showed that they contained phospholipids and cholesterol. The same compounds are found in increased quantities in the blood of patients with xanthelasma of the eyelids. To prevent the formation of new lesions, even after surgery, you need to follow a diet low in fat and carbohydrates, avoid high-calorie foods, and monitor blood cholesterol levels. This is especially important in the presence of diseases that are risk factors for the formation of xanthelasmas (we listed them above). Lipotropic drugs may be prescribed as prescribed by a doctor based on a complete clinical examination. The schedule for their intake is also determined by the doctor.
Remember that your health depends on paying close attention to your body.
Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma has no specific treatment. If xanthelasma or xanthomatosis occurs against the background of a disease that may cause a disorder of fat metabolism, treatment of this disease is necessary. According to indications, insulin and thyroidin may be prescribed.
Patients with identified blood lipid disorders or increased cholesterol should adhere to a diet low in animal fats. To do this, animal fats are replaced with vegetable fats, for example, sunflower and olive oil. Such patients with xanthelasma are prescribed lipotropic drugs and drugs that reduce blood cholesterol. These include: cetamifene, pyricarbate, esters of unsaturated fatty acids, lipoic acid, thioctic acid, diosponin, clofibrate.
Among herbal preparations, the following have a lipotropic effect: birch buds, dandelion root, rose hips, corn silk, plantain juice, immortelle flowers. It should be remembered that these drugs have a choleretic effect and their use is contraindicated in case of violations of bile drainage along the biliary tract. In the treatment of xanthelasma, nicotinic and ascorbic acids, cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine, calcium pangamate, and choline chloride are used.
Surgical treatment of xanthelasma is indicated for cosmetic reasons. It is carried out by excision of xanthelasma, laser removal, electrocoagulation, cryotherapy or radio wave destruction. Removal in most cases is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis.
Small xanthelasmas are usually removed using diathermocoagulation. Larger plaques are separated with scissors and tweezers. The edges of the wound are brought together and lubricated with iron sesquichloride, which forms a strong scab and allows the wound to heal by primary intention within 1-1.5 weeks. After separating xanthelasmas with a wide base, the edges of the wound are cauterized by diothermocoagulation. When xanthelasmas are combined with an overhanging skin fold on the eyelid, they are surgically excised together with excess skin of the upper eyelid.
To prevent redivision of xanthelasma after surgery, the patient is recommended to follow a dairy-vegetable diet with the exclusion of animal fats and limitation of carbohydrates. The daily intake of butter should not exceed 25g, sunflower oil - 75g.