Reasons for the appearance of a seal on the eyelid
All ophthalmological diseases have different etiologies. But there are risk factors for many diseases. Therefore, you should pay attention to them.
Here are the common reasons for the appearance of a seal on the eyelid:
- decreased immunity;
- frequent viral and infectious diseases;
- hypothermia of the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis);
- frequent stress;
- intolerance to contact lenses;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules,
- excessive use of cosmetics (including low-quality ones);
- increased oily skin, excessive work of the sebaceous glands;
- general hormonal diseases of the body;
- previously suffered or untreated ophthalmological diseases;
- age factor (over 50 years).
Etiology of the appearance of a neoplasm
A ball that appears in the eye area may not cause discomfort or may be accompanied by pus and other problems. In this case, a comprehensive examination of the patient is indicated. A seal on the eyelid appears due to weakened immunity, severe hypothermia of the facial skin, vitamin deficiency, chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, stress, and improper use of contact lenses. These factors can provoke changes in the eyeball and tissues.
Ophthalmologists classify into a separate group diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of a growth on or under the eyelid:
- barley;
- chalazion;
- milium;
- xanthelasma.
A common etiology for the appearance of a lump is stye. In this case, the patient experiences pain and inflammation develops. It may hurt on the upper or lower eyelid, less often on both at the same time. More often this clinic is observed in children.
If a child has a ball on the upper eyelid, diagnostics reveals obstruction of the sebaceous glands. When they function correctly, a special secretion is produced that protects the eyelids from external factors. Barley ripens quickly and disappears on its own. Ophthalmologists distinguish 2 types of formation:
- external - inflammation of the sebaceous duct;
- internal - inflammation in the meibomian gland.
At the first stage, when a lump appears on the eye on the upper eyelid, the patient feels a tingling and burning sensation. A brighter negative clinic appears in the presence of internal barley. Lack of treatment leads to the formation of an abscess. The pathology goes away on its own, but ophthalmologists advise starting therapy at the initial stage to prevent complications.
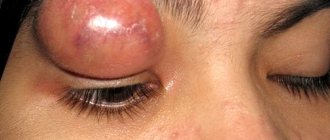
After the formation of barley, a hailstone may form, which clogs the sebaceous ducts and causes the affected area to swell. The secretion accumulated at the outlet forms a plug. If you feel the problem area, you can find a ball.
Chalazion or hailstones can become chronic if there is no timely treatment. The disease does not go away on its own. It is characterized by frequent relapses with suppuration and severe pain. A white growth can cause a cyst to appear.
Barley
Staphylococcus aureus under a microscope
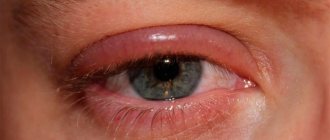
Barley is an infectious disease in which inflammation of the eyelash follicles or meibomian glands occurs. It first appears as a small lump, on which a head forms after a few days. The causative agent of this disease is usually Staphylococcus aureus, an opportunistic microorganism.
Barley has two types: internal and external. If the eyelash follicle becomes inflamed, an external stye is formed. In case of inflammation of the meibomian gland - internal barley. To find out whether stye is contagious and how it is transmitted, be sure to read the article on this topic, which you will find directly on our website.
Symptoms of stye
Typical symptoms of stye include:
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- redness;
- severe pain syndrome;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- temperature rise is possible.
The lump with barley is very painful and adheres to the skin. When barley ripens, a purulent head forms, after which the barley opens on its own.
The main thing you should not do is try to crush or pierce the stye, especially on your own.
Treatment of barley
Usually such a seal on the eye is treated with medication:
- Antibacterial eye drops are used. These include: albucid, levomecitin, tobrex. To learn more about drops against stye and how to use them correctly, be sure to read the article about drops against stye on our website.
- Use antimicrobial ointments. They are most often applied at night: tetracycline, erythromycin ointments. Find out a lot more about antibacterial ointments against stye here.
- Antiseptic solutions are used to wash the eyes: chlorgrexedine, miramistin.
Without treatment, barley ripens within 7-10 days, with treatment 3-4.
As a rule, barley affects one eye and the inflammation rarely spreads to the second, but for the purpose of prevention, antibacterial drops should be instilled into both eyes.
Be sure to read a separate section on how to treat stye, which you will find right here on the website. We also recommend reading the article about quick treatment of stye at home.
Chalazion
Chalazion is an inflammatory disease in which the ducts of the meibomian glands become blocked and secretions accumulate in the thickness of the eyelid. Sometimes a chalazion is called a hailstone. This disease looks very similar to barley, but in reality they are completely different. So, for example, with a chalazion, the compaction has nothing to do with the skin, but with barley, it’s the opposite. To easily distinguish a chalazion from a stye, be sure to read the article “Stye or chalazion,” which you will find on our website.
The main function of the meibomian glands is the production of a special fatty secretion, which is part of tears. This secretion performs a protective function; it lubricates the mucous membrane of the eye and protects it from drying out. When the meibomian gland ducts are blocked, secretions will continue to be released and accumulate in the gland. And thus, a compaction is formed, which increases over time.
Chalazion symptoms
What symptoms can tell you that you have a chalazion?
- externally, the chalazion looks like a pea;
- in the early stages, redness and slight swelling are possible;
- the chalazion is not fused to the skin, that is, the skin over the formation is mobile;
- there is no pain during palpation;
- Over time, a kind of capsule may form, the chalazion will increase in size, but redness will not be observed at this stage.
A chalazion can appear on both the upper and lower eyelids. There are no age restrictions for this disease. This seal occurs more often on the upper eyelid, as there are more glands there.
Chalazion treatment
This disease should be treated exclusively by a specialist.
The main thing is to go to the doctor in a timely manner and get the treatment regimen that will be effective specifically for your case. Under no circumstances should you try to squeeze out or puncture a chalazion yourself!
Conventionally, treatment methods for chalazion can be divided into the following groups:
- Local treatment - used in the early stages of the disease, when pus is just beginning to accumulate in the clogged ducts of the glands. At this time, a specialist, as a rule, can prescribe medications that resolve pus and relieve inflammation. For this purpose, antibacterial drops (levomecitin, ofloxacin) and ointments (tetracycline, erythromycin) are used. The ointments are applied in a thick layer to the tubercle (preferably at night).
- It is also possible to use compresses from the same ointments.
- It is possible to use antiseptic drugs (chlorhexedine, miramistin).
- One effective treatment method is physical therapy.
- If the chalazion is large enough, glucocorticoid therapy is possible; they are used to prevent the formation of a fibrous capsule.
Operation
Surgical removal of a chalazion is used if it is in an advanced stage or the use of conservative treatment has not produced a positive effect.
In this case, doctors resort to surgical intervention.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia.
The operation time usually does not exceed 20 minutes.
During the operation, the doctor makes a small incision in the area of the lump, then scrapes out the formation along with the fibrous capsule (if any). The possibility of relapse depends on how well the cavity is scraped out. After surgery, as a rule, a pressure bandage is put on the eyes and antiseptics are prescribed.
Laser removal
Today, laser chalazion removal is also carried out. The principle is similar to the classical operation, only the cavity is dissected with a laser.
This method has many advantages:
- fewer postoperative complications;
- No stitches are required after laser surgery;
- there is no need to apply a pressure bandage;
- After the operation, a crust forms, which disappears on its own after some time.
Under no circumstances should you peel off the crust yourself!
Treatment with traditional methods
It is worth noting that traditional methods of treatment are dangerous, as you can worsen your condition and allow complications to develop. First of all, you must be sure that the seal on the eyelid is a chalazion. To clarify the diagnosis, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The increase in the size of the pinguecula occurs slowly over years. It is safe for the organ of vision. As a rule, a person with a growth on the white of the eye does not have any complaints, except for the presence of a lump on the mucous membrane. Dry eye syndrome may develop. Sometimes the growth on the mucous membrane of the eye can become inflamed and swollen. This indicates the development of complications.
Diagnosis is not difficult. A doctor will be able to make a diagnosis during a routine examination. Examination of the fundus (biomicroscopy) allows the ophthalmologist to evaluate the features of the pinguecula and exclude concomitant pathology.
Prosyanka
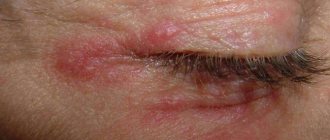
A millet is a small white internal blackhead that can form anywhere, including on the eyelid. These small lumps are also called milia. Millet is formed due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Symptoms of millet
So, what is characteristic of millet?
- the formation of small seals on the eyelid, usually no more than 2-3 mm;
- the appearance of compactions in groups;
- no pain;
- lack of redness and swelling;
However, there are cases when, when exposed to an infectious agent, the milia become inflamed. Mostly patients complain of externally unaesthetic manifestations.
Millet treatment
When millet appears, you should not try to squeeze out the blackheads yourself. You may get an infection or not get the lump out completely. To remove it, you need to contact a cosmetologist.
There are several ways to remove millet:
- manual method;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation.
A specialist will examine you and prescribe the appropriate method for removing the seal.
Prevention of the recurrence of millet is the normalization of nutrition and proper skin care.
Treatment
Treatment for a lump under the skin depends on what it is. Each disease has different treatment methods.
Medicines
Table. Treatment of diseases with drugs
| Name of the disease | Drugs |
| Barley | The disease is treated with conservative methods. Medicines are prescribed to speed up the ripening of the cone. The skin of the eyelids is lubricated with Tetracycline or Erythromycin ointments, and they are also placed inside. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, yellow mercury ointment and eye drops to relieve inflammation. |
| Cyst | After surgical removal, antibacterial drops and anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed. Additionally, the patient should rinse the eyes with a solution of furatsilin or medicinal herbs. |
| Papilloma | Antiviral medications are prescribed to prevent the growths from recurring on the eyelids or other parts of the body. |
| Herpes | Herpes infection is treated with systemic medications. Patients are prescribed antiviral tablets. Immunomodulatory drugs help restore the body's defenses; Viferon and Kipferon are prescribed - these are rectal suppositories. Medicines for removing seals are ointments and creams that are rubbed into the eyelids to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. |
| Prosyanka | It is recommended to exfoliate with urea or salicylic acid based cosmetics. After using medications, miliary cysts spontaneously come to the surface of the skin. |
| Pinguecula | Moisturizing drops - Visine, Oksial. The risk of developing an inflammatory process is reduced by Diclofenac, Nevanac, Tobradex. If an infection develops - Maxitrol |
Surgery
The cyst is removed by laser. Liquid suction from the capsule is not carried out, since after this method of treatment the disease recurs in 90% of cases.
For papilloma, cryodestruction is often used. Education is frozen. If necessary, the procedure is carried out several times. The laser method of removal and the chemical method based on keratolytic agents are popular.
Xanthelasma is surgically removed. You can also remove the tubercle using electrocoagulation or laser. The procedures are performed under local anesthesia. The highest risk of developing infection is when removing the formation using the traditional method - with a scalpel.
When millet appears, curettage, electrocoagulation, or removal of the tubercles with a laser are used.
Laser treatment is the most popular and painless, which is why it is prescribed most often and is recommended by ophthalmologists themselves. The fatty deposits are removed surgically. If the formation is small, you can try folk remedies or restore metabolism, but this does not guarantee removal of the growth. Types of operations:
- laser exposure;
- traditional way;
- chemical exposure.
Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma is an ophthalmic disease in which yellowish plaques appear that protrude above the surface of the skin. The lump may appear on the upper eyelid and under the eye. Xanthalasma is characterized by multiple occurrences. It does not cause pain; patients are embarrassed by the outwardly unaesthetic appearance of the disease.
Treatment of xanthelasma
As a rule, the cause of the appearance of these seals is a violation of the body's lipid metabolism. There is no treatment for xanthelasma; it is necessary to get rid of the underlying disease.
Prevention
The seal is a cosmetic defect; it is easier to prevent its occurrence than to treat it. Prevention measures:
- Wash your hands after visiting the toilet, going outside and before touching your face.
- If you get a speck of debris, wash your hands first and do not put your fingers in your eyes. Use cotton swabs.
- Do not use other people's cosmetics - mascara, eye shadow, eyeliner. This can cause infection in the eyes. After treatment, use hypoallergenic formulations until the immune system is restored.
- Eat properly. Eat enough fruits and vegetables. Provide the body with fiber.
- If barley appears frequently, take 2 vitamin courses per year and take dietary supplements prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
- Increase immunity through hardening and sports activities. A few hours in the gym or training at home will benefit the entire body. Hardening begins by rubbing with a wet towel, then dousing with water, gradually lowering the temperature.
- Treat ophthalmological diseases, especially infectious and viral ones, in a timely manner. Do not delay the course of the disease.
There should be no formations in the eyelid area; if any defects appear, consult a doctor. It is important to understand that these seals sometimes indicate internal problems, for example, metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases, lipid metabolism disorders.
Furuncle
A furuncle is a very dangerous disease in which necrotic inflammation of the eyelash follicle, sebaceous glands or connective tissue occurs. The disease is infectious in nature, the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus. As a rule, a boil forms on the upper eyelid near the eyebrows, but sometimes on the edge of the upper eyelid.
Symptoms of a boil
- the disease begins with the appearance of a painful lump;
- possible fever, headache, weakness;
- then redness and swelling of the eye rapidly develops.
- within a few days a yellowish dot forms - this means the boil has matured.
- opening occurs independently with the release of purulent masses.
- after the boil ruptures, a scar remains.
Treatment of a boil
For treatment, you must contact an ophthalmologist. Treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs for local and general use. It is strictly forbidden to open the boil yourself!
Papilloma
Papilloma is a wart-type growth that can form anywhere, including on the eyelids. Caused by the human papillomavirus. The disease is asymptomatic and does not bother the person in any way. Patients are embarrassed by the unattractive appearance of the formation.
Symptoms of papilloma
The disease begins with the appearance of a small compaction, which increases over time.
Papilloma is characterized by an elevation above the surface of the skin. To the touch they have a rough, uneven surface. Often papilloma occurs on the leg.
Treatment of papilloma
Before treating papilloma, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis; for this you should consult a specialist. Treatment of papilloma is carried out conservatively with the use of medications and surgery.
Today there are several methods of removal - electrocoagulation, laser method. These methods have been described above.
Possible complications and precautions
When a lump or lump appears on the eyelid, it is important to make a correct diagnosis. To do this, consult an ophthalmologist. Perhaps he will prescribe additional examination by other specialists, as well as laboratory and instrumental tests.
It is prohibited to begin treatment without a diagnosis established by a specialist!
It is strictly forbidden to try to pierce, squeeze out, or open the seal that has appeared on your own. This may threaten secondary infection of the formation.
Also, you will not be able to completely remove the pus on your own.
Education itself is dangerous. The larger the compaction, the more it puts pressure on the eyeball and thereby provokes a violation of the outflow of fluid and ocular blood flow. In this condition, astigmatism and decreased vision may develop.
One of the complications is suppuration. When an infection enters a pathological formation, an inflammatory reaction may begin. In this case, the patient will experience pain, severe swelling and redness of the surrounding tissues are possible. A cellulitis or abscess may form. In rare cases (with often recurrent chalazion), malignancy of the formation occurs.