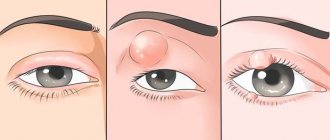
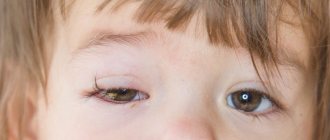
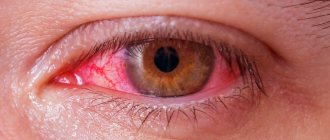
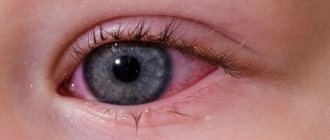
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the superficial structures of the eyes, which is formed as a result of exposure to an infectious agent, virus, allergen, fungi, or mechanical damage.
Depending on the underlying cause, different clinical symptoms are possible.
Some forms of the disease are quickly transmitted to others, while others do not have this ability. Therefore, not every type of conjunctivitis allows you to visit the street or public places.
Symptoms of the disease
During conjunctivitis, certain clinical symptoms appear. It may vary slightly depending on the form of the disease. The most common symptoms that appear are:
- redness of the eyes, which can be minor or extensive, hemorrhages into the internal structure of the cornea are possible;
- increased production of tear fluid, which, if left untreated, gives way to dry mucous membrane, leading to microtraumas and cracks in the cornea;
- when exposed to bright light, the patient’s eyes begin to hurt severely, spasms of the eyelids form, due to which they cannot be opened;
- in the bacterial form, purulent exudate is released containing pathogenic microorganisms and their metabolic products;
- in other forms of conjunctivitis there is no purulent exudate;
- pain, itching, burning, sensation of a foreign object under the eyelids;
- with the fungal form, nodules, grains, and films are formed on the surface of the eyes.
The symptoms of the disease differ depending on the cause that caused the inflammation. To accurately diagnose the disease, laboratory research methods should be carried out (bacteriological culture, PCR analysis, microscopy).
The occurrence of conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis occurs through contact with a sick person. Bacteria affecting the conjunctiva begin to actively spread, thereby causing inflammation.
Bacteria that most often affect the mucous membrane: staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Bacterial inflammation is extremely contagious; a sick person must be isolated from other people. The disease can be transmitted by airborne droplets, through common household items and by contact.
Bacterial conjunctivitis often develops together with diseases of the nasopharynx and otitis media. This type of conjunctivitis can occur together with other eye diseases.
All forms of conjunctivitis can be divided into two groups:
- exogenous;
- endogenous.
The classification of conjunctivitis is based on the cause of eye damage.
The development of conjunctivitis may be associated with chronic diseases - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, helminthic infestation, etc.
A significant role in the occurrence of the disease is played by the reactivity of the body, which determines the nature of the course and features of the clinical manifestation of conjunctivitis.
According to the characteristics of its course, the disease is divided into conjunctivitis:
- chronic;
- subacute;
- spicy.
The acute form begins quickly and passes quickly. There are usually no warning signs of the disease. Conjunctivitis occurs with pain in one eye, and later the second can become infected. Sometimes patients experience an enlargement of the eyeball. Patients complain that the eye protrudes and puts intense pressure on the walls of the eye opening.
Purulent discharge is abundant, external signs appear quite clearly. In addition to eye symptoms, a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition is observed. He feels weak and unwell, and his temperature rises. The duration of the disease is about 2-3 weeks.
Red eyes are a sign of conjunctivitis
Additional signs of the acute form include headache, general weakness and elevated body temperature. Treatment lasts from 7 to 21 days.
A subtype of acute conjunctivitis is a subacute type of the disease. Unlike the previous one, it is characterized by less pronounced symptoms and proceeds a little easier, but with the same symptoms, only in a less obvious form. At the same time, this type of pathology, such as chronic conjunctivitis, is characterized by a slow, gradual course. However, compared to acute, it lasts much longer. Clinically, the disease looks like this: the conjunctiva loses its smooth shape and becomes looser, there is a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, it is uncomfortable to move the eyes and blink, they quickly get tired.
Types of conjunctivitis
Chronic conjunctivitis , unlike the acute form, develops slowly and affects both eyes at once. In this case, the symptoms of the disease are not expressed. Patients constantly feel that there is a foreign body in the eye. It is very difficult to cure the chronic form of the disease, and failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions threatens the disease spreading to the cornea and the subsequent development of keratitis.
Types of eye disease according to external signs:
- catarrhal;
- purulent;
- fibrinous;
- follicular.
There is a classification based on the nature of the disease. Conjunctivitis can:
- have a bacterial nature;
- occur due to chlamydial eye damage;
- be obtained due to viral exposure;
- appear due to fungal infection;
- develop against the background of allergies;
- become a consequence of injuries or mechanical effects on the mucous membrane.
When should you not go outside with conjunctivitis?
There are certain health conditions of the patient in which they should not go outside during illness:
- Increased body temperature. It often manifests itself in viral and bacterial forms of the disease. It can increase to low-grade (37-37.5) and high (more than 38 degrees) values. Refusal to go outside is associated with the fact that a person’s well-being will worsen. You may feel dizzy and your body temperature may rise.
- Severe clinical symptoms. If a person experiences extensive redness and severe purulent discharge from the eyes, these indicators will intensify when outdoors. This is affected by strong winds, high or low temperatures, and precipitation.
- High degree of infection with bacterial and viral forms. If a person with the disease goes outside where many other people are present, the risk of them contracting and spreading the infection increases. Therefore, such people should sit out the period when they are contagious at home.
- High risk of complications. If the patient has purulent conjunctivitis, the infection can spread to the internal structure of the eyes, causing cataracts and glaucoma. The bacteria can spread to the optic nerve and brain, causing encephalitis. Such forms of complications are rare, but when exposed to negative environmental factors on the street, the risk of their occurrence increases.
- Symptoms of illness. Often, when conjunctivitis develops, the patient experiences weakness, fatigue, and drowsiness. If he goes for a walk, this feeling will intensify, which will lead to a deterioration in his health. Therefore, during an exacerbation, it is recommended to stay at home and receive treatment.
With each form of conjunctivitis, going outside for a short period of time is possible. Fresh air has a good effect on a person's well-being. If there are risks, it is recommended to postpone the walk for several days.
If a person has conjunctivitis without the proliferation of bacterial microflora, suppuration may form if he goes outside and is exposed to a negative environmental factor. At the time of illness, the patient's immunity is reduced. If exposed to low temperatures or strong winds, the disease may be complicated by a bacterial infection.
Conjunctivitis in a kindergarten group - what to do?
If there is an outbreak of conjunctivitis, kindergarten staff must take additional measures to prevent the spread of the disease. To do this, it is necessary to disinfect all surfaces, replace linen in children's bedrooms, and distribute new towels for faces and hands. Children with viral or bacterial conjunctivitis should stay at home; healthy children can visit the garden. Which children are prone to conjunctivitis? What factors negatively affect the body’s ability to resist viral and bacterial infections:
- frequent colds, chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract and nasopharynx (sinusitis, pharyngitis, etc.);
- ophthalmological problems;
- vitamin deficiency, reduced immunity;
- hypothermia, overheating.
If your child is prone to frequent colds and it is possible not to take him to the kindergarten for several days, it is better to do this as an effective preventive measure. Remember that the symptoms of conjunctivitis are unpleasant and painful, and the course of the disease is debilitating, especially for children. In cases where it is not possible to stay at home with the child, and there is conjunctivitis in the group, you can take the child to kindergarten, but try to protect him from infection. To do this, you need to teach your child not to use other people’s handkerchiefs and towels, and to wash their hands thoroughly with soap. Such measures will help reduce the likelihood of inflammation. What to do if it was not possible to avoid infection?
What to do before your walk
If a person has conjunctivitis, before going outside it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- determine weather conditions, whether there is precipitation or strong wind, during which the clinical symptoms of the disease worsen;
- use medications prescribed by a doctor (antibiotics, antivirals, fungicides, antihistamines);
- perform superficial eye hygiene using antiseptic solutions or running clean water;
- if pus is released abundantly in the eyes, you should wash it off with clean water or Furacilin, and drip an antibiotic;
- take sunglasses with you that will protect not only from the bright sun, but also from strong winds;
- Take with you wet wipes that can be used to clean your eyes if pus is discharged.
The patient should remember that when sick, walks should be shorter. It is recommended to avoid public places with large crowds of people to avoid spreading the infection among them. If weather conditions change sharply, your health will worsen and copious amounts of pus will be released. He should return home so as not to worsen his body's condition.
conclusions
With conjunctivitis, walking in the fresh air is not prohibited. This is due to the fact that clean air has a positive effect on the human body; oxygen actively enters organs and tissues, which increases metabolism and regeneration of damaged cells. The eyes also need oxygen to improve the quality of metabolism.
There are some restrictions on the disease that the patient should take into account so as not to cause complications. If a person’s health is poor, there are signs of malaise, you should postpone the walk for several days in order to go outside with full strength.
It is recommended to walk 1-2 times a day during illness for no more than 30 minutes. This will give a person the opportunity to breathe fresh air and go to the places he needs without causing a sharp deterioration in his health. At the same time, close contact with other people should be avoided; even a handshake can lead to infection, since bacteria and viruses spread to the skin.
If your health worsens, consult a doctor immediately. He will conduct additional examination methods and adjust treatment so that the person recovers faster.
Treatment at home
Conjunctivitis is usually treated at home, i.e. outpatient. Hospitalization is extremely rare, in advanced cases and with a high risk of complications.
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Note! All procedures must be performed only with clean hands. That is, they must first be washed with soap. Dry the child's face only with a sterile towel. It should be washed daily and ironed on both sides.
Eye wash
Doctors prescribe products for washing that are safe for the child. For example:
- Furacilin;
- Miramistin;
- Albucid;
- boric acid;
- a very weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- various herbal remedies (for example, a decoction of chamomile, sage, calendula, etc.);
- black or green tea (light strength):
- aloe juice
When washing, the following rules must be observed:
- wash your hands with antibacterial soap and cut your nails;
- use liquid at room temperature;
- The procedure should be performed on both eyes, even if only one is affected;
- remove excess solution with cotton wool;
- use an individual cotton pad for each eye;
- wipe from the inner corner to the outer, pausing a little and pressing at the starting and ending points;
- The procedure should be carried out every 3 hours, except when the child is sleeping
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Note! Rinsing is prescribed for any form of conjunctivitis, except the allergic type. During the procedure, discharge and dried crusts are removed.
Drops
Depending on the form of the disease, the following groups of eye drops can be used:
- antibiotics (Tobrex, Levomycetin, Floxal);
- antiviral (Poludan, Oftalmoferon);
- antimicrobial (Albucid, sodium sulfacyl).
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Important! These medications are potent and have contraindications. Therefore, they can only be used after consulting a doctor. If it is not possible to visit him, you can call an ambulance and ask for instructions on what to do.
How to bury correctly
The drops must be at room temperature, so they must be taken out of the refrigerator in advance. It is also important to know that most drugs in this form have an expiration date of only a month after opening the bottle.
Before using the medication, you should wash your hands thoroughly. Take the required amount of solution into a pipette (1-2 drops each). Pull back the lower eyelid with the fingers of your free hand and apply the solution into the conjunctival sac.
Rice. 2. Instructions for use of eye drops.
Ointments
They are also divided into groups depending on what caused the disease:
- antibacterial (tetracycline, erythromycin);
- antiviral (tebrofenova, Zovirax).
Just like drops, they are potent medications that have contraindications. Therefore, they can be used as prescribed by a doctor. Ointments are placed under the lower eyelid 3-5 times a day. If the child is an adult, he should be asked to blink after the procedure. Newborns need to lightly press the eyelid for a few seconds.
Rice. 3. Laying the ointment can be done not only with your fingers, but also with a sterile glass spatula, as shown in the figure above. The amount of medicine should be the one prescribed by the pediatrician. There is no need to apply any more, because... This will not give the best result, it can only do harm.
Traditional methods of treatment
At the very beginning of the disease, when the inflammatory process has provoked a few more symptoms, folk remedies show their effectiveness. They are harmless, the only contraindication is an allergic reaction to the constituent components.
To find out whether children have it or not, you need to apply a small amount of the product to the inner area of the elbow or wrist. Wait a quarter of an hour. If there is no hyperemia, rashes, burning sensation or itching, the composition can be used.