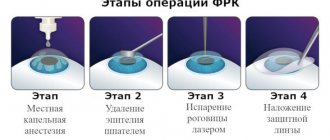
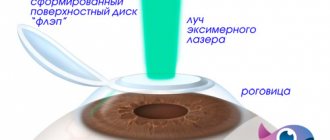
Normal odds
Visual acuity may be normal and decrease under the influence of certain factors.
The norm of vigilance at 100% is the ability to distinguish between two objects distant from each other. In simple terms, visual acuity is an indicator of vigilance that can be measured in numbers. In the Russian Federation, the norm is equal to one (1.0). You can determine how clearly a person sees using special tables. These tables are familiar not only to adults, but also to children. They undergo preventive examinations while still in preschool educational institutions. Tables may contain letters or symbols. Tables depicting symbols were developed specifically for children who cannot yet read and do not know letters. The norm is when a person sees the 10th line out of 12. At the same time, be at a distance of five meters from the table.
If the clarity of vision is impaired, this means that ophthalmic diseases are developing or are already present. The sooner a decrease in visual acuity is detected, the faster the situation can be corrected.
Interesting! You don't have to see an ophthalmologist to check for clarity. You can find the well-known constellation Ursa Major in the starry sky. Even in ancient times, traditional healers claimed that a person has excellent and acute vision if he is able to see the small Mizar star near the second star from the edge of the handle of the ladle.
Deviations from 1.0 are not always a pathology. For some people the ratio may be higher. In this case, visual acuity is called aquiline.
Interesting! The most acute vision in the animal world is that of the eagle. If we take a bird’s vigilance to be 100%, then a human’s vigilance is only 51%! At the same time, octopuses see clearly compared to eagles by only 32%, jumping spiders by 8%, cats by 7%, and goldfish by 5%.
Indicators above 1.0 are not a pathological deviation. The same cannot be said about numbers below 1.0. This indicates the presence of developing ophthalmological diseases. Indicators that are too low indicate diseases that are already present.
Corrected visual acuity (BCVA)
This is the line that the patient calls with the glasses that suit him
.
And to assess visual acuity, it is not the strength of the glass that is important, but what the eye can see as much as possible
- and this is not always line 10!
That is, if with your “minus 6.0 diopters” you are able to see the eleventh or even twelfth line - congratulations, you have 120% or 150% of vision. And vice versa, if the total is “minus 1.0”, and the tenth line is not visible, this means vision is less than 100%.
You will be surprised, but often people do not know that their eyes, in principle, cannot see 100%, never, with any glass. This is called "amblyopia", that is, a condition of "lazy eye"
.
This situation is faced by those who have different optics in both eyes, people with astigmatism, strabismus, high myopia, congenital cataracts, etc.
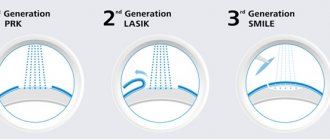
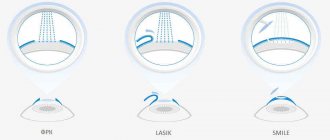
With amblyopia, visual acuity cannot be corrected to 100% by anything - neither glasses, nor lenses, nor laser correction! Although, it is an interesting fact that often after laser correction you can see more lines than with glasses and contact lenses - this is due to more correct focusing of light on the retina after correction. And for the nearsighted, the bonus is that the size of the image on the retina increases - visual acuity increases - sometimes up to 120 or even 150%.
So, if you are a user of glasses or lenses, then it doesn’t hurt to find out whether you are able to see 100% in principle?
I think it’s now clear that the question is: “Will you give me 100% or will there be minus one left?” corresponds to the question of round and green or flat and bitter.
What do indicators below 1.0 indicate?
If a visual acuity of less than 1.0 was recorded during an eye examination, this may indicate the presence of:
- Cataracts.
- Retinal detachment and rupture.
- Glaucoma.
- Neuritis, toxic neuropathy, optic nerve atrophy.
- Disorders of the functions of the corneal endothelium.
- Detachments of the choroid.
- Lens luxation.
- Corneal injuries.
- Lack of lens.
- Vitreous prolapse.
- Purulent endophthalmitis.
- Myopia.
- Hyperopia.
- Corneal burn.
- Astigmatism.
- Iridocyclitis.
- Chorioretinal inflammation.
- Neoplasms in the area of the craniopharyngeal duct.
- Acute increase in intraocular pressure.
- Scars of the cornea of the conjunctiva.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Keratitis.
- Chorioretinal scars.
- Tumors of the central nervous system.
- Foreign body on the cornea.
- Pituitary adenomas.
- Parasagittal meningioma.
- Late neurosyphilis.
- Lagophthalmos.
- Malignant or benign neoplasm of the eye.
- Scarring of the conjunctiva.
- Rossolimo-Melkersson syndrome.
You definitely won't believe that...
1. Many people are also surprised by the fact that there is no direct linear relationship between visual acuity and optics - that is, plus or minus.
For example, with “minus one” and “minus six” you can have the same visual acuity! That is, without correction in both cases, vision can be only 10% (the first line of the table), and with correction (each has its own) 100% - the tenth line.
Therefore, to the question “is it necessary to make a correction for myopia of minus 1.0 diopter”, the answer is “yes” if visual acuity without correction is low.
2. It seems incredible, but very often patients and their relatives have to explain that not all diseases can be treated with glasses
. For example, in the case of cataracts or glaucoma, I wrote about them here: and here:
We have to explain that glasses will not help, only surgery is needed.
We remember that our eye is like a camera, visual acuity is an indicator of the quality of the matrix. And optics with plus-minus-astigmatism are the characteristics of the lens.
Let's compare!
How to check eye clarity - basic rules
The procedure for determining how sharp a person’s vision is is carried out in an ophthalmologist’s office or in stores that sell glasses, contact lenses, and when selecting them.
But it’s better, of course, to choose a clinic.
Basic Rules:
- a person sits at a distance of five meters from the table;
- the location of the tables is strictly from the window on the opposite side;
- The 10th line of the table should be located strictly opposite the eyes;
- the table must be illuminated by special lamps (there are certain requirements for the supply of light);
- visual acuity should be measured for each eye separately (during examination, the second eye is covered with a special opaque instrument);
- It is unacceptable to close the other eye (this will not give an informative result!), both eyes must be open;
- You should not squint during the examination, this can also cause an unreliable result;
- a sign or letter in the table is recognized within 2-3 seconds, longer time indicates a deviation.
During verification, the norm is to make 2 errors in the 7th line.
Eye test procedure
Visual acuity is determined using the table
together and for each eye separately, without correction and with corrective glasses:
- in the right lighting,
- at the right distance
- with relaxed accommodation.
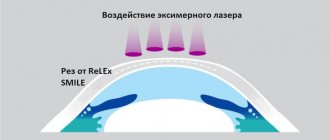
Sometimes a pinhole test is necessary - testing with a diaphragm (a shutter with a 3 mm hole) or a slit.
Diagram of the passage of light rays without a diaphragm and with a diaphragm
As can be seen from the figures, with the same degree of myopia, the diameter of the circle of light scattering on the retina when the rays pass through the diaphragm is smaller than without a diaphragm, and visual acuity is higher. For the same reason, people with poor eyesight squint to see better.
To clarify the optics, so-called force and axial tests with cross-cylinders are used in order to use them to obtain maximum visual acuity - to achieve the largest NUMBER of named lines. How this is done is written here.
Ten years ago, a patient entering an optical salon could immediately puzzle the employee rushing to him with the question: “Do you have a computer vision test?”, which, as a rule, meant the presence of an autorefractometer in the salon. An autorefractometer/keratometer is a piece of equipment that provides information about the patient's sphere, cylinder size, and astigmatism/corneal curvature axis.
Autorefractometer:
- DOES NOT TEST VISUAL ACUITY!
- gives an approximate
understanding
of the OPTICS
of the eye, - DOES NOT WORK
on the eyes
AFTER LASER VISION CORRECTION
using any of the methods, including ReLEX SMILE, it can “show the weather” and completely unreliable results.
The device looks like this:
Autorefractometer
This is that computer with infrared radiation that prints checks with minuses/pluses.
Here is an example of a keratorefractometer printout.
Such printouts look “reliable and convincing” and it seems that the device cannot make a mistake, unlike a person. But this is an illusion!
How to test your eyesight at home
Today, thanks to the World Wide Web, you can check clarity at home. There are online tests with detailed instructions on how to take them. But, of course, it is better to consult an ophthalmologist for more reliable results.
In addition to online tests, it is possible to print out the tables offered on the website. Arrange them according to the rules described above. The main thing is that table lighting, even in daylight, must be present.
To do this, you can take a regular fluorescent lamp and place it above the table. Or use two 40-watt lamps and place them on the sides of the table.
It is not necessary to print the table in a large format. It is enough to use white matte paper in landscape orientation in A4 format. Hang it on the wall so that the 10th line is approximately at eye level. If a person sees the entire 10th line, this indicates an indicator of 1.0. This is the norm. In all other cases, you should visit an ophthalmologist, and do not delay the examination.
No two eyes are the same - that's another fact!
Our two eyes are never the same, always, for everyone.
There is a dominant for distance and for near, and, like any paired organ, for example hands, they are not absolutely symmetrical. The quality of vision can and usually does vary. Take your photo and cut it in half, mirroring one half. It won’t be you in the resulting photo, because in nature there is no ideal symmetry, just as there is no ideal zero. Normal binocular disparity, that is, the difference between what the right and left eyes see, is more pronounced when perceiving close objects.
With the same shape of the eyeball and lens, and even the same refractive power of the visual system, the maximum visual acuity can be determined by the difference in the distance between the retinal receptors (rods and cones).
Before correction, this asymmetry is often not obvious, so after correction we strongly recommend looking with both eyes; the brain needs to adapt to new optical conditions.
SIMULATION (THE PATIENT IS LYING ABOUT WHAT HE DOESN’T SEE) AND AGGRAVATION (THE PATIENT IS LYING WHAT HE SEES)
– testing “with bias”
There are devices that objectively determine visual acuity - they are used in cases where examination using standard methods is impossible or the result is not trusted (for example, during an examination by a medical board). Not used in standard clinical practice.
The following objective methods exist:
1. Method of optokinetic nystagmus - special objects with a periodic structure are used. For example, a geometric lattice or a chessboard can be represented as such an object. Such an object in motion is presented to the patient being examined. The specialist monitors the patient's reaction to a moving object and determines changes in eye movement. As a rule, when recognizing the movement of an object, the patient's eyes involuntarily begin to move. The minimum size of the object is taken as the basis for determining the quality of visual acuity.
2. A detailed study of visual evoked potentials is a test of visual pathways all the way from the retina to the visual cortex, such as a “visual cardiogram”
3. The method of formed selective vision - this is not the first method with a periodic structure that is similar in principle.
Dangerous symptoms
Many people do not notice that visual acuity has begun to decline. Especially in the first stages of development of pathologies. There are some symptoms to be aware of.
If you have these signs, you should immediately visit an ophthalmologist:
- There is a black curtain before my eyes. Causes: progressive retinal detachment. A distinctive symptom is decreased visual acuity. This disease requires immediate hospitalization and radical treatment.
- Sharp pain in the eye, redness of the mucous membrane, fog before the eyes, attacks of nausea and vomiting, decreased visual acuity. Symptoms of angle-closure glaucoma. With a sharp increase in intraocular pressure, the optic nerve is damaged. The pathology requires urgent treatment. Otherwise, there is no way to do without surgery.
- An intense or gradual narrowing of visibility occurs (in medicine it is also called tubular vision). Causes: damage to the optic nerve. In this case, a sharp decrease in visual acuity occurs. Untimely treatment will lead to glaucoma and subsequently to removal of the eye.
- Deteriorated, blurry, distorted vision. There is a decrease in visual acuity. A straight line may appear curved. Causes: dystrophic lesion of the central region of the retina. The pathology is typical for older people. In this case, visual acuity will be below 1.0. If treatment is not provided up-to-date, this condition will lead to complete loss of vision without the possibility of recovery.
- Hazyness before the eyes, lack of brightness and contrast. These are signs of cataracts, in which clouding of the lens develops. Treatment is carried out surgically - a lens implant is implanted. If not treated in a timely manner, complete loss of vision occurs without the possibility of recovery.
- Appearance of dark spots, cloudiness, fog before the eyes. In diabetes mellitus, such signs indicate retinal damage. Complications include hemorrhage in the retina and vitreous body. This leads to loss of vision.
- Burning sensation, sensation of foreign bodies, lacrimation, dryness. This is a symptom of dry eye. At risk are people who spend most of their lives at computers and work with documentation. The condition can cause poor vision and many eye diseases.
Visual acuity is a characteristic that helps identify vision problems in the early stages. The examination must be completed at least twice a year.
Especially for those people who have a genetic predisposition (the person in the family had relatives suffering from ophthalmological diseases); if there were injuries to the upper cervical vertebrae (pinching of blood vessels occurs, which affects clarity); Diabetes mellitus and cervical osteochondrosis are present. A decrease in visual acuity occurs in old age and during difficult childbirth. Some sexually transmitted diseases also cause a decrease in clarity.
How accommodation affects visual acuity
Accommodation is a dynamic change in focal length from far to near due to tension - relaxation of intraocular muscles and a whole complex of changes in the structures of the eye.
In the context of this article, you need to understand that habitually excessive tension of accommodation (we call it PINA) or spasm of accommodation (as discussed earlier) can significantly reduce visual acuity and cause the appearance of “false” myopia, especially in childhood or during prolonged work at the computer. Laser vision correction does not cure this condition.
In such cases, instillations, sets of exercises, hardware treatment are prescribed, and the need for visual hygiene arises. In this case, thoughtless “additional correction” is not only unnecessary, but even dangerous!
Accommodation scheme
The main reasons for decreased visual acuity in adults and children
Pathologies of functional organs provoke various distortions that disrupt the normal perception of the picture. Placing the focus in front of the photosensitive layer of the retina (myopia) is accompanied by poor visibility of objects at a long distance. A similar situation occurs not only with increased length of the eyeball. A similar appearance can be provoked by the following reasons:
- spasmodic tension of muscle groups;
- a specific disease that reduces the thickness and changes the shape of the cornea;
- incorrect position of the lens after injury;
- sclerotic processes (in old age).
Shifting focus behind the retina impairs near vision. Farsightedness in children disappears naturally as the eyeball grows. But after 40-50 years, the elasticity of the lens decreases, and the functional state of the ciliary muscle deteriorates. Age-related changes contribute to the development of hypermetropia.
Certain distortions in the optical path divide the light flux into two beams (astigmatism). In this situation, a blurry image is formed!!! With amblyopia, one eye does not perform its functions normally. If timely treatment is not applied, complete loss of vision is possible.
A gradual or sudden decrease in vision is caused by various factors. Causes in adults are usually explained by aging and disease. In newborns - heredity, problems in the process of intrauterine formation. Reduced visual acuity in children occurs due to poor nutrition. Excessive physical activity and poor conditions for work and rest have an adverse effect.
What causes vision loss to 0.5?
There may be several reasons, some can be corrected and some cannot.
- Anatomical reasons . The cornea, vitreous body of the eyeball, or lens changes.
- Refractive errors . The distance between the lens and the posterior wall with the visual nerve endings does not correspond to the refractive index of the system.
Refractive errors cannot be treated; visual acuity can be improved by choosing the right glasses or contact lenses. Anatomical causes in some cases can be eliminated with medications; if the effect is negative, then they resort to surgical interventions, including replacing the lens.
Refractive errors
Refractive error has several types:
- distant objects are poorly distinguished (myopia);
- difficulty distinguishing close objects (hyperopia);
- objects are curved (astigmatism);
- difficulty perceiving objects at arm's length (presbyopia).
TRADITIONAL OPINION OF TEACHERS
Traditionally, little time has been devoted to eye examination in the curriculum. However, some findings obtained during physical examination can be extremely important, and practitioners should be aware of this. All methods of eye examination - from measuring visual acuity to ophthalmoscopy - provide chain information and can help in revealing important secrets not only of the eye, but also of the body as a whole.
| TYPE OF EYE EXAMINATIONS | TRADITIONAL OPINION | |
| Visual acuity | ↑ | By analogy with basic physiological indicators (heart rate, temperature, blood pressure), visual acuity is measured and recorded at the very beginning of the eye examination |
| Visual field examination | ↑ | This method allows you to identify (and differentiate) important neurological and ocular diseases |
| Pupil examination | ↑ | May provide invaluable clinical information |
| External examination of the eye | ↑ | Many outdoor examinations are performed using a flashlight pen. Pay attention to the orbits of the eyes, the position of the eyelids, the conjunctiva, the anterior chamber of the eye, the corneal reaction to light |
| Ophthalmoscopy | ↑ | The key to mastering this method is practice: the more often you perform ophthalmoscopy, the better results you will achieve |
| Redness of the eyes | ↑ | A common symptom that requires special attention |
Prevention and treatment of decreased visual acuity
To prevent problems, a set of preventive measures is used:
- strengthen and relax the eye muscles with the help of special gymnastics;
- regular walks in the fresh air strengthen the immune system;
- Wear safety glasses to prevent foreign objects from getting into your eyes;
- reduce the load with optimal light conditions and limited duration of work cycles;
- To treat myopia, specialized hardware is used for the functional state of the visual organs.
For dizziness, some people take a nitroglycerin tablet, which has a dilating effect on the coronary vessels. However, at the same time, the ducts supplying the brain narrow. As a result, the discomfort may intensify. This example demonstrates the need for a qualified choice of treatment even in relatively simple situations. You can use the “auxiliary” drugs presented below on your own.
Eye drops
Moisturizers are used to treat insufficient tear production. These Taufon eye drops can be purchased at pharmacies without a prescription. Eye drops are used during medical examinations, before installing contact lenses. As a rule, anti-allergenic substances are added to the composition.
If there are no contraindications, frequent application (more than 5 times a day) is acceptable.
Vitamins
If decreased visual acuity is detected in only one eye, you should schedule a visit to your doctor. However, to generally improve the supply of visual organs with useful substances, vitamin therapy is quite suitable. Such drugs are used as auxiliary drugs in the treatment of glaucoma. Vitamins are prescribed for prevention after the age of 40.
The following list shows some positive results from regular consumption of dosed amounts of vitamins:
- A – normalization of the functional state of the retina;
- C – activation of immunity;
- B2 – improvement of oxygen absorption by cells, protection from UV rays;
- B6 – calming effect on the nervous system.
Contacting an ophthalmologist
If a child’s vision sharply decreases, the causes of the problems will be identified by an experienced ophthalmologist during an urgent examination. The first examination is performed by Dmitry Dementyev immediately after birth. In preschool age, visits are scheduled every 6 months. Next, a minimum interval of 1 year is applied.
Our recommendations
Complaints of decreased vision in both eyes may indicate a stroke or exacerbation of a chronic disease. Timely diagnosis is recommended to solve problems without complications and significant harm to health. It is advisable to limit independent actions to preventive measures. Even vitamins are unsafe if taken in excess.
When choosing a device for physiotherapy, you must carefully study the principle of operation, technology, and operating features. Certain types of equipment should only be used by experienced personnel. Pharmaceutical drugs are used as prescribed by the attending physician.