Farsightedness
or
hypermetropia
is a refractive error of the eye (the degree of nearsightedness or farsightedness), in which the rays from the object in question converge not on the retina, but behind the retina.
Because of this, objects appear unclear and blurry. It was farsightedness that served as the impetus for the invention of glasses. For a long time, glasses were the only effective way to correct vision. But modern medicine has gone far ahead - today farsightedness is treated with a laser. At the Eye Clinic of Dr. Belikova, we use only advanced treatment methods that are safe for Patients.
Surgical treatment of farsightedness
The term “surgical treatment of farsightedness” means surgical intervention or laser correction of farsightedness. Surgical treatment of hyperopia, regardless of the technique used, is the fastest and most effective way to correct farsightedness. Surgical correction of farsightedness lasts for several minutes under local anesthesia, and the patient can be discharged home on the same day. Surgical treatment of farsightedness, regardless of the method, consists of enhancing the refractive ability of the farsighted eye. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications. Taking into account all the examination data, the doctor will suggest the most optimal operation for your eyes.
Laser correction. Let's talk about the benefits
This is an effective and safe method if a person has a disease of the first or second degree, the diopters do not exceed +5, and the patient’s age is not more than 45 years. Laser correction for farsightedness lasts no more than half an hour, and after one and a half to two hours a person begins to see.
At the moment, LASIK is considered the most common technique (it has existed for more than thirty years). However, it has its own nuances: the operation allows you to adjust your vision either on distant or close objects. That is, a person who decides to correct age-related farsightedness faces a dilemma: to resort to glasses only when working close up and to distinguish objects well at long distances, or vice versa.
Recently, another technique has appeared in ophthalmology, called Presby LASIK. Using the Teneo excimer laser and the Victus femtosecond laser, doctors regulate the functioning of each eye individually: one is given the opportunity to look into the distance without any interference, while the other is “left” myopic. Fortunately, it is small (up to –1 diopter). The peculiarity of this method is that not every patient can adapt to such laser vision correction for age-related farsightedness: some people experience headaches due to the difference in diopters, and also this operation is not durable, and sooner or later you will still have to use glasses.
Which method of laser correction of farsightedness to choose can only be decided by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics and nature of the disease.
And yet, laser vision correction has a number of unconditional advantages:
- efficiency of execution;
- no rehabilitation period;
- no stitches required;
- is done as a preventive measure for eye cataracts.
Causes of age-related farsightedness
The apple shell, in turn, is divided into outer, middle and inner (mesh), of which it is the mesh that is capable of perceiving light flux. However, an object can be displayed not on the segment of the retina itself allocated by Nature, but on the plane behind it. This phenomenon occurs with farsightedness, which accompanies almost every person who has crossed the 45th milestone in life. Such natural farsightedness, also called presbyopia, is characterized by the display of a nearby object on the retina in the form of an indistinct (blurry) image. The reason for the loss of visual acuity in this case is the thickening of the lens substance and laxity of the ciliary muscle that comes with age, as well as a weakening of the accommodative functions of the eyes.
The more significant the manifestations of such age-related changes, the more farsightedness makes itself felt, allowing a person to clearly see objects only at an increasingly distant distance. Correcting farsightedness with the help of glasses and contact lenses is, of course, very successful, but does not solve the problem at its roots. If the loss of visual acuity is significant, and the accommodation of the eye leaves much to be desired, then the patient, of course, needs treatment. Modern ophthalmology comprehensively answers the question of how to correct vision with farsightedness, offering more than twenty solutions for this.
The doctor will help you choose the method that is suitable for the patient, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s disease and the accompanying factors in his life. In case of any deviations, specialists combine various technologies to achieve the most successful solution to the problem. When choosing, you need to consider:
1. Features of the work, because for some specialties, for example flight, certain options for vision correction are prohibited.
2. The nature of physical activity. Sports and work activities that involve the possibility of head injury and blows to the face and eyes may also influence the choice of method.
3. The presence of certain diseases and conditions in the patient (diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, insufficient body immunity, etc.) can affect the outcome of the surgical intervention.
4. Existing eye diseases: glaucoma, inflammatory processes, herpes virus and previous surgical interventions on the organ may be a contraindication for some treatment options, even prohibited.
Symptoms of age-related farsightedness
Below we list the most common symptoms of age-related farsightedness, which are most often identified by experts. But let’s make a reservation that if you have identified them in yourself, then under no circumstances should you immediately self-medicate: buy drops, order glasses and contact lenses. First, make an appointment with an ophthalmologist: a competent specialist will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment depending on the age and degree of the disease.
Presbyopia is characterized by:
- blurred image;
- difficulty seeing pictures or letters or studying objects up close;
- difficulty understanding fonts when reading and writing;
- the need to move objects over a long distance:
- frequent headaches and eye fatigue.
Hyperopic laser keratomileusis
It has wide limits for the correction of hypermetropia and hypermetropic astigmatism, as well as a short rehabilitation period. The essence of the intervention is that the increase in corneal curvature necessary for the correction of hypermetropia is achieved through ablation (“cold” evaporation) with an excimer laser of the middle layers of the cornea on its periphery, as a result of which its refractive power changes, which makes it possible to obtain the refractive effect of the operation.
The main advantages of laser keratomileusis
- rapid restoration of visual functions (within 1 - 2 days after surgery),
- minimal restrictions in visual load after surgery,
- preservation of the anatomical structure of the cornea,
- absence of an open healing wound,
- minimal pain (2 - 3 hours after surgery),
- laser correction of farsightedness has stable results and a lasting refractive effect,
- treatment of farsightedness can be performed on both eyes at once, without applying bandages,
- absence of corneal opacification in the postoperative period,
- the ability to correct high degrees of farsightedness (including astigmatism).
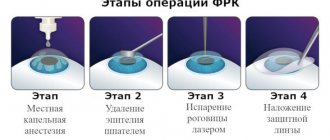
Progress of excimer laser keratectomy surgery
The operation is usually performed on both eyes at once. Before the operation, anesthetic drops are instilled. No general anesthesia is required. The patient is placed on the operating table, the skin around the eyes is treated with a special germ-cleaning solution and covered with a sterile delimiting bandage. Painkiller drops are instilled once again. Next, the following stages of the operation are carried out:
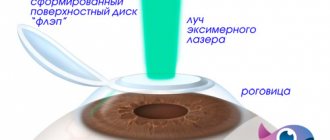
| To provide access to the middle layers of the cornea, using a special “microkeratome” device, a flap (“lid”) is cut out from the surface layers of the cornea and turned to the side. To achieve optimal results in forming corneal flaps of the required size, a computer method is used to calculate the operating parameters of the device. | |
| The laser then evaporates the middle layers of the cornea at its periphery, changing its curvature. | |
| At the end of the operation, the “lid” is placed in its original place. The flap is fixed without suturing, due to the adhesive properties of the cornea's own collagen. |
Install Flash Player to watch the movie.
Postoperative period
- It is better to spend the first day after surgery in our hospital under the supervision of experienced staff. It is not recommended to touch the operated eye or rub the eyelids to prevent displacement of the corneal flap. It is also not recommended to wash your face at this time. During these days, eye drops are instilled.
- The next day after examination by our specialist, eye drops (antibacterial and anti-inflammatory) are prescribed for a period of 2 - 3 weeks, and if there are no problems, the patient is sent home.
- In the first two weeks after surgery, it is not recommended to rub your eyes or put pressure on them; it is advisable for women not to use makeup on the eyelids and eyelashes, sprays or hairspray. It is not recommended to visit the sauna or swimming pool for 2 - 3 months.
- Visits to your doctor after surgery usually occur the next day, 2 weeks, one month, 3 months, and 6 months after surgery.
- Vision after surgery begins to recover within a few hours and reaches a sufficient level the next morning. In the next 2 to 4 weeks, vision reaches its maximum.
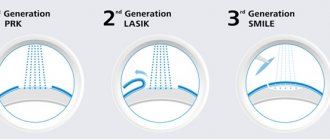
Methods
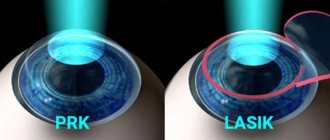
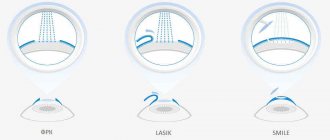
There are several methods of performing the operation. The most common are LASIK, PRK and LASEK.
LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis)
In Russia, this popular correction method is called “laser keratomileusis”. It is prescribed to improve visual functions in cases of myopia, astigmatism, and hypermetropia. The method is used for minor impairments of refractive functions and is not recommended for high degrees of farsightedness.
In terms of effectiveness, the method is similar to PRK, but the difference is that after the operation the pain syndrome is less pronounced, and visual functions are quickly restored.
The cost of the operation varies from 20,000 to 50,000 rubles. The price depends on the complexity of the specific case.
PRK (Photorefractive keratectomy)
This method allows you to correct the curvature of the cornea using a laser.
Although the corneal flap does not need to be cut, the process can be painful. After surgery, it is important to follow a special regime, since regeneration and recovery are slower than with other laser correction methods. The price for the procedure is from 15,000 rubles.
LASEK
During surgery, the cornea is softened with alcohol. After this, its curvature is corrected with a laser and the surface layer is replaced. Price – from 20,000 to 40,000 rubles depending on complexity.
In addition to these basic methods, there are advanced types of LASIK laser correction:
- Super LASIK. This method is called “personalized LASIK.” A thorough detailed examination is carried out before the operation. The excimer laser is adjusted more precisely, individually for each patient. This increases the efficiency of the procedure. Cost - from 30,000 rubles.
- Femto Super LASIK. The difference between this type is that the corneal flap is formed not with a microkeratome, but in a non-contact manner - using a femtosecond laser. This increases accuracy, which has a positive effect on the result of the operation. Price - from 50,000 rubles.
Features of laser correction
This therapy treats not only hypermetropia, but also myopia and astigmatism.
During the procedure, the laser affects the shape of the cornea, which ultimately gives it a naturally correct shape.
Laser therapy has its own characteristics
The characteristics of the effect of laser on the organ of vision are based on:
disease and its stages of development; presence of complications; individual physiological characteristics of the eyeball itself.
The rays do not cause any physiological changes and do not harm the organ of vision itself, since their effect is narrowly targeted and affects exclusively a certain zone of the refractive medium of the optical system.
This is how the treatment works
The shape of a natural lens tends to change, so refraction is restored and the image is focused in the right place. A person gains visual acuity at close distances.
With the help of laser correction therapy, you can get rid of hypermetropia up to +4.0 diopters in just one day.
The depth of exposure does not exceed 180 microns, which is why the method is considered the safest and most accurate.
The procedure itself takes no more than 20 minutes, most of which is setting up the laser.
Thanks to drip anesthesia, the patient does not experience any discomfort or other unpleasant sensations. There is only slight pressure on the eyeball.
Types of corrections
There are many developments now. But only a few of them are in active demand:
LASIK; SUPER LASIK; EPI-LASIK; LASEK; PRK; FEMTO-LASIK.
The specific type of correction is selected by an ophthalmic surgeon
The difference between them is:
accuracy of adjustment to individual patient parameters; method of shaping the corneal surface; level of impact.
The essence is always the same: to restore the patient’s vision.
Depending on the type of correction, the cost of the procedure also adds up. The price tends to vary, but it is also affected by the treatment center where the therapy will be performed.
Timely therapy increases the chances of a positive prognosis
In any case, before carrying out therapy in any clinic, an ophthalmologist will first be examined to determine the need for the procedure.
You can see how the operation is performed in this video:
If you need specialist advice, please contact:
Limitations after laser correction
The postoperative period is often accompanied by unpleasant sensations that go away on their own after some time. The most common effects: uncontrollable lacrimation, foreign body sensation, inflammation, photophobia.
The severity and duration of these effects are affected by the individual characteristics of the organism. Most often they go away within one month.
To reduce the risk of complications and speed up recovery, you must follow some rules:
- do not rinse, scratch, or touch your eyes for 3 days after the procedure;
- do not visit water parks, swimming pools, saunas, or swim in ponds;
- wear sunglasses outside;
- do not stay in the sun for too long;
- exclude any physical activity, avoid overexertion;
- do not use cosmetics;
- do not drink alcohol;
- no smoking;
- avoid smoky rooms;
- do not take any medications without consulting a doctor;
- do not overload your eyes, reduce the time you spend reading, watching TV and sitting at the computer;
- Pregnancy is not advisable for six months after surgery.
In addition, you must follow all the recommendations prescribed by your doctor, follow the instructions, and use medications prescribed by a specialist. This speeds up corneal recovery and prevents complications.
Removal of the clear lens of the eye with implantation of an artificial lens
Clear lens removal (CLR) differs from the vision correction methods described above in that the operation is performed not on the cornea, but on the lens. Instead of reshaping the cornea, the lens is removed and replaced with an artificial eye lens.
The operation is the same as cataract removal, only the clear lens is removed rather than the cloudy one. Like other refractive surgeries, clear lens removal is often performed on an outpatient basis through a small incision. The lens is removed using ultrasound (phacoemulsification). Instead, an intraocular lens (IOL) of the required optical power is implanted. There are no stitches. Vision is usually restored within 24 hours.
UPC is used to correct hypermetropia of any degree. The method is most suitable for patients over 40 years of age, because at this age the ability of accommodation begins to be impaired in most people.
How to cure high degree of farsightedness
In addition to laser correction, radical methods of treating hypermetropia include microsurgical operations. Sometimes the lens is replaced with a special intraocular lens.
Lenses are made from biomaterials, so they are not rejected by the eyes and become a natural part of them. There is no need to replace lenses during your lifetime. There are several types of lenses designed to correct various vision defects.
Replacing the lens is a way to correct farsightedness from 6 diopters. The operation is also prescribed if there are contraindications to laser correction.
The goal of farsightedness therapy is to achieve correct projection of the image onto the retina. With hypermetropia, when the optical system of the eye is distorted, the image falls into the area behind the retina. Laser correction quickly and safely restores vision in cases of mild to moderate farsightedness.
Poll Options are limited because JavaScript is disabled in your browser.
Other solutions for correcting farsightedness
If there are contraindications to standard laser correction, other effective methods can be used. They have their advantages, in some cases they are even preferable.
The first method is thermal keratoplasty. Exposing the corneal tissue to heat changes its shape and the corneal collagen fibers shrink. In medical practice, two options for carrying out the procedure are possible: non-contact, which is carried out using a laser, and conductive. Keratoplasty is often used to restore vision for presbyopia and astigmatism in patients over 40 years of age.
Another treatment method suitable for high degrees of farsightedness and cataracts is the introduction of intraocular lenses. During this operation, the human lens is replaced with an artificial one. This method is effective and often used, but there is a significant drawback, since the eye loses the ability to accommodate. Another possible side effect is the risk of retinal detachment. The introduction of intraocular lenses is more suitable for elderly patients and patients with reduced accommodative function.
Phakic lens implantation
Phakic lens implantation (IOL) involves placing an additional diverging (“positive”) lens directly onto the lens, which focuses light rays entering the eye onto the retina. Usually, phakic lens implantation is carried out at a young age and with large degrees of hypermetropia, which cannot be corrected by excimer laser vision correction. The IOL is implanted into the eye cavity through a puncture, without suturing. The biocompatibility of the lens material minimizes the risk of complications. The operation and postoperative period are painless, vision improves within a few hours after the intervention. The advantages of this operation include, among other things, the possibility of removing the lens, that is, returning the eye to the preoperative state.
If there is opacification in the lens due to hypermetropia, the lens is replaced for refractive purposes. This operation is similar to that performed for cataracts. Currently, when carrying out such an intervention, the method of phacoemulsification, or crushing the lens using ultrasound, is used. The natural lens is removed through a 2-3 mm puncture, and a soft artificial lens is implanted in its place, designed in such a way that the patient no longer needs distance correction. And recently, a number of large manufacturers have developed and are introducing multifocal artificial lenses, which allow one to see well not only near or far, but to combine sufficiently high vision for both near and far. This happens due to the fact that each such IOL has several focal lengths. True, quite often the patient needs to get used to such a correction.
The choice of tactics for surgical treatment of farsightedness is strictly individual and is determined based on the results of a complete ophthalmological examination. Since refractive surgery is the method of choice, the decision to undergo correction is made by you. We will help you find your way - recommendations depend on your age, general health, existing or pre-existing eye problems, your glasses or contact lenses, lifestyle, profession, work goals and the results you expect from the operation.
Farsightedness
The program “Live Healthy”, topic of the issue: farsightedness. Professor M.E. Konovalov tells.
For a story about farsightedness, risks to vision and methods of correction, see the 28th minute of the video (release dated September 28, 2010).
Laser correction of farsightedness - “Lasik”
Farsightedness or hypermetropia is a special optical defect in which a person cannot clearly see objects located both at a distant distance and close to it. This occurs because the optical focus of the eye system is located behind the retina, due to the mismatch between the refractive power of the eye and its length.
In order to correct an existing defect, you need to shift the focus to the retina. For this, various methods are used to treat farsightedness , including laser correction of farsightedness .
How to treat farsightedness. Methods for correcting farsightedness
The most popular methods for correcting farsightedness include:
- — excimer laser operations on the cornea: laser keratomileusis (LASIK, LASIK, REIC);
- - intraocular surgeries, which include IOL implantation and lens replacement.
It should be noted that the operation, which is laser keratomileusis, has correction limits of up to +4-5 spherical diopters and up to +4 diopters of hypermetropic astigmatism, and it also has a fairly short rehabilitation period. The essence of this method is that the increase in corneal curvature required for correction is achieved through “cold” evaporation of the middle layers of the cornea at the periphery with an excimer laser.
To allow access to the middle layers of the cornea, a small flap is cut out from the surface layer, which is turned to the side while the laser is operating, and after the operation is placed in its original place. Thus, farsightedness surgery occurs in a gentle manner.
Benefits of laser keratomileusis
The main advantages of laser keratomileusis include:
- — minimal pain after surgery;
- — rapid restoration of visual function;
- — the possibility of performing surgery on both eyes at once;
- — visual load after surgery has minimal limitation;
- — the anatomical structure of the cornea is completely preserved.
How to treat farsightedness if there are contraindications to laser keratomileusis? In this case, the patient is given the opportunity to undergo intraocular operations to replace the lens or implantation of a phakic IOL. This procedure involves placing a “contact lens inside the eye,” meaning an additional lens is placed on the lens to focus light rays onto the retina.
This type of operation is recommended for patients with farsightedness of more than 4-5 diopters. In this case, the IOL is implanted into the eye cavity through a puncture; there are no sutures. The lenses are made of biocompatible material, which avoids complications in the postoperative period. The operation for farsightedness is painless, vision improves immediately after a few hours after it is performed.
In patients with clouding of the lens or age-related changes in the lens, it is replaced for refractive purposes. This procedure is identical to that performed for cataract removal. Currently, this intervention is used to crush the lens using ultrasound. After this, the lens is removed through a tiny puncture and a new artificial one is inserted in its place.
In recent years, after removal of the lens, multifocal intraocular lenses have been used, which make it possible to see normally near and far without glasses. If astigmatism is present, the lens can be replaced with a toric intraocular lens, which allows you to completely correct both astigmatism and farsightedness. Tags: age-related farsightedness, farsightedness in children, glasses for farsightedness, lenses for farsightedness, how to treat farsightedness
Causes of presbyopia
Thanks to the ability of the lens to change the focal length (accommodation), a person is able to distinguish objects at different distances - both near and far. With age, the lens becomes more dense and gradually loses its elasticity, due to which its ability to increase its curvature when viewing objects close to the eye decreases, and the eye’s ability to accommodate is lost .
In addition, as a result of aging, the muscles that hold the lens weaken . This means that when the occipital lobes of the brain responsible for vision send a signal to the eye muscles, they are no longer able to sufficiently change the shape of the lens to focus the image of nearby objects on the retina. As a result, a person sees objects blurry and indistinct.
Prevention and treatment of complications of farsightedness
If you have developed complications of farsightedness such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision or strabismus, you need comprehensive treatment to improve visual acuity. Treatment includes various types of stimulation: laser, magnetic, classes on computers equipped with unique programs, as well as a number of other latest devices. If indicated, no earlier than 1 month after excimer laser surgery, you may be recommended to undergo surgical correction of strabismus.
You can find out more about lens replacement in the treatment of astigmatism here
Treatment of farsightedness in children
For young children, the natural age norm is mild farsightedness, which goes away over time.
Farsightedness above the age norm in childhood is a serious problem that requires adequate correction, since the child may develop serious visual impairments such as amblyopia (“lazy” eye), strabismus, etc. Treatment of farsightedness and concomitant amblyopia in children is carried out with the help of glasses corrections and courses of hardware treatment with mandatory game elements. These techniques are not difficult for children and are well tolerated by them. With proper treatment of a child using modern hardware treatment technologies in our Center, in many cases it is possible to save him from constant spectacle correction and cure amblyopia.
Treatment courses consist of several methods: photomagnetic stimulation, macular stimulation, accommodation development, a set of exercises on a computer and many other methods.
Features of laser vision correction
Farsightedness is a refractive error where the image is focused outside the retina. A similar defect occurs in people with short eyeballs and visual axes. With farsightedness, a person is able to clearly see objects in the distance, but has trouble making out small details up close.
Correcting farsightedness using a laser is considered the most effective treatment method. If just a few years ago the operation was a cause for concern, today the technology has been perfected and tested by thousands of patients.
This method can quickly correct hypermetropia up to 5 diopters in patients 18-50 years old. The operation also allows you to get rid of farsightedness, complicated by astigmatism within ±3 diopters.
For which diseases laser correction cannot be performed:
- glaucoma;
- cataract;
- keratoconus;
- lens spasm;
- inflammatory processes in the eyes;
- progressive visual impairment;
- diabetes;
- having only one eye;
- arthritis;
- retinal disinsertion;
- vascular pathologies;
- weakened immunity.
There are LASIK and PRK methods. The first is the most accurate and safe, and the second is an alternative if there are contraindications to LASIK surgery. The Super-LASIK technique is considered the most progressive and effective.
Results of laser correction of presbyopia
Laser correction has such advantages as relative safety, minimum complications, absence of scars, stable refraction, painlessness, and prompt restoration of vision. The only drawback is that the correction of hypermetropia is no more than 6 D. Higher degrees are corrected using FCL implantation.
After the intervention, the first hours may include discomfort, lacrimation, burning, and photophobia. This goes away in about six hours. The first day you should not touch the operated eye. You need to take antibiotics for a week and artificial tears for a month. You can't drink alcohol. For the first two weeks, it is not advisable to communicate with people who have colds, get hypothermic, use cosmetics, or visit saunas, steam baths, or swimming pools.
For the first two weeks, you should not rub or press on your eyes; you need to wash your face carefully. It is recommended to limit physical activity to persons who have undergone laser photocoagulation of the retina. The period of restriction is determined by a specialist. Visual acuity is restored after two weeks.
In case of redness of the eyes, discomfort or decreased vision, you should immediately contact the clinic where the operation was performed.
Indications
Laser correction for farsightedness is permitted if visual acuity is impaired by no more than 6.0 diopters. In the case of this pathology, the light beam is focused behind the retina and patients have difficulty seeing nearby objects. But there is presbyopia - a special type of hypermetropia. It is characterized by the same manifestations, but the etiology of its occurrence is different. In the case of presbyopia, the lens of the eye is damaged due to age-related changes. This is typical for people over 50 years old.
It is important to be able to distinguish age-related farsightedness from true hyperopia, since treatment tactics are different.