Miosis is a constriction of the pupil, which cannot always be attributed to any specific pathology. In some cases, it is a completely normal, natural physiological reaction, which occurs due to changes in lighting parameters, as well as during physical fatigue. But sometimes constriction of the pupil turns out to be a symptom of a developing pathology in the body.
What is miosis?
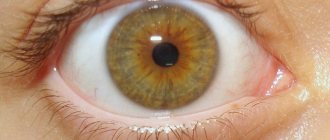
In the natural state, in the absence of any deviations, the pupil size is 2.5 mm. In some cases it may narrow. Don't be afraid of this condition. Most often, this is not evidence of a serious pathology, but a natural reaction to an instant change in the lighting in the room. This physiological change is necessary in order to minimize the negative effects of bright light on the retina.
There are also a number of situations in which constriction of the pupils is normal:
- in patients who constantly suffer from pathologies such as hypermetropia during sleep;
- newborn babies;
- old people;
- due to severe mental or physical stress;
- at the moment of contact of the visual axes of the right and left eyes, if the gaze is focused on any specific object.
The change in pupil size occurs due to the work of the dilator muscle, the ocular sphincter. The pupil can become either smaller or larger. Miosis is an abnormally stable constriction of the pupil of the eye without any reaction when switching to darker lighting. Normally, with such changes they always remain the same size. The moment you move away from the light, the pupils always become larger.
Reasons for the development of miosis
The following factors cause pupil constriction:
- A sharp jump in blood sugar.
- Contact of foreign substances with the cornea of the eyes, as well as violation of the integrity of its cover.
- Malignant and various benign neoplasms in the nervous system. Then miosis is accompanied by disturbances in the patient’s consciousness.
- The presence of damage to the fibers of the central nervous system (most often, constriction of the pupils of both eyes is observed).
- Horner's syndrome.
- Stroke.
- Various diseases of the central nervous system.
- Vasoconstriction.
Most often, the main cause of miosis is damage to the muscle that is responsible for dilating the pupil of the eye. Also, the cause of the development of pathology can be an abnormal condition in the muscles.
Symptom of pathology
Constriction of the pupils also accompanies a number of diseases and conditions for which medications are taken. Interestingly, the pupils return to normal size after the medication is cleared from the body.
- Miosis may be a side effect when treating eye diseases with the drug pilocarpine. The action of this medicine is aimed at reducing intraocular pressure, to which the pupil reacts. A decrease in the element can also be caused by drugs that contain morphine.
- Most often, miosis can be observed in people suffering from diabetes. In this situation, the constriction of the pupils is influenced by the course of the disease, as well as insulin medications.
- When a diagnosis is made, Horner's syndrome disrupts the functioning of nerve cells. In such a situation, constriction of the pupils occurs in the dark.
- The pupil can not only narrow, but also become oblong with meningitis.
- In Parkinson's disease, problems occur in the brain, which leads to narrowing of the pupils.
- During an epileptic seizure, the vowel element also narrows
- Miosis also accompanies high intracranial pressure, multiple sclerosis, and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- In some cases, the pupils become smaller due to various injuries, including the brain and spinal cord, wounds, as well as when foreign objects get into the cornea of the eye.
- Constriction of the pupils can also be observed with normal myopia, as well as farsightedness; this most often occurs when a person with poor vision tries to see objects far away from him without glasses, squinting.
People who are intensely involved in physical and mental labor often complain of miosis. To eliminate this phenomenon, it is important to constantly take at least five-minute breaks.
Forms of the disease
Based on the root cause of the deviation, the following types of pathological phenomena can be distinguished:
- Functional. It is a normal natural reaction in infants and elderly citizens, during physical and mental activity, with temporary exposure to bright light;
- Medication. Occurs due to the use of drugs that irritate the sphincter. This type of deviation is called reactive. Such drugs include: adrenergic blockers, anticholinergic stimulants with a nerve-paralytic effect, or agents containing bromine, morphine, and aniline dyes. Alcoholic drinks, coffee, nicotine and mushrooms also have a similar effect.
- Paralytic. It is a consequence of paralysis of the sympathetic trunk of the cervical spine.
- Spastic. The disease is caused by a disorder of the nervous system, followed by spasm of the sphincter of the pupil. A similar phenomenon is characteristic of diseases such as meningitis, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, and brain tumors.
- Syphilitic. Characterized by symptoms of neurosyphilis.
Types of miosis
In medicine, there is a conditional division of miosis into the following types:
- Functional, it is also natural. In this case, changes in pupil size will be normal.
- Drug-induced, also known as reactive miosis. It occurs as a reaction to a medicine injected into the eye. Miosis can also be caused by drug use.
- Irritable, also known as spastic. Occurs when, due to brain diseases, convulsive compression of the muscle valve of the eye occurs.
- Syphilitic. The cause of this miosis is a disease known to everyone as syphilis.
- Paralytic miosis, constriction of the pupils, is a consequence of pathologies in the cervical spine or in the carotid artery.
Classification of myomatous formations
The body of the uterus consists of a muscular layer and a mucous membrane that lines its inside.
Myomatous formations are localized in muscle connective tissue. The source of their growth growth is one defective cell, which undergoes certain changes and begins to divide at a faster rate than neighboring ones.
As a result, a myomatous node appears - a local accumulation of chaotically intertwined smooth muscle fibers. On average, its dimensions range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. However, sometimes very large tumors occur. Some reach a weight of several kilograms.
Myomatous cells practically do not degenerate into malignant ones. This happens in less than 1% of cases.
Attention! Even the rapid growth of fibroids is not a sign of its malignancy
Fibroids of the uterine body can be located in different layers. Based on these characteristics, nodes are divided into the following types:
- Submucosal or submucosal - grows into the uterine cavity. It can protrude inward completely, half or less.
- Intramural or intermuscular - located inside the wall of the organ.
- Subserous or subperitoneal - protrudes outside (into the peritoneum).
Among these types there is fibroid, which grows on a stalk.
How to diagnose?
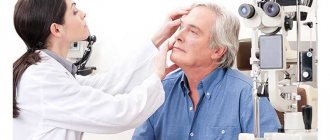
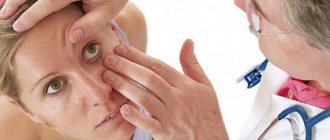
If there are no physiological reasons affecting the narrowing of the pupil, it is necessary to seek diagnostics. In this case, the doctor prescribes a number of examinations that help to most accurately determine the most accurate cause of the development of the pathology. These studies include:
- An analysis to determine the condition of the eyeball. A slit lamp is used.
- MRI of the organ of vision.
- Determination of the pupil's reaction to various changes in lighting.
- Ultrasound of the eyes.
- Perimetry - helps to examine visual fields.
When an ophthalmologist is unable to detect pathologies affecting the condition of the pupils, the patient is referred for further examination to a neurologist and other specialized specialists. The main thing is not to delay your visit to the doctor, so as not to worsen the condition. After all, miosis can be a symptom of a dangerous pathology.
Diagnostics
To properly treat miosis, you need to know exactly the causes of its occurrence. The correct diagnosis can be made by an experienced ophthalmologist. First he will conduct a visual examination. Look at the reaction of the pupil to light influence. Then he will start looking for the problem using a slit lamp. What kind of eye disease is cataract, read on our website.
The doctor may detect changes in the vascular system of the brain. Treatment can include vasoactive drugs and vitamins, carbohydrate metabolism measures.
Treatment
The treatment plan for miosis is determined as follows:
- If miosis is of physiological origin, then no special treatment will be required.
- With spastic as well as paralytic miosis, treatment will be required that affects the cause of the disease.
- When the cause of constriction of the pupils is poisoning, the following measures must be taken: rinse the stomach, give a blood transfusion (if necessary), put in an IV. When the patient's condition stabilizes, the pupils will stop constricting.
- When miosis is a consequence of taking medications, there is also no need to take any measures. The pupil will stop constricting when the medicine is completely eliminated from the body.
- If a foreign substance gets into the eye, it must be removed immediately. The constriction of the pupil will stop immediately after this.
- If the pupils are constricted due to injury, after first aid, symptomatic therapy is carried out. As soon as the body recovers, the pathology will disappear.
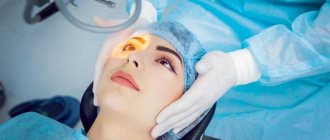
In some cases, surgical dilation of the pupils is used to eliminate the problem. The anterior chamber of the eye is opened and a special drug is injected into it.
What is the danger of adenomyosis (endometriosis)?
Endometriosis is considered benign hyperplasia (pathological growth of tissue), since endometrial cells that have migrated to other organs and tissues retain their genetic structure. However, such features as the ability to grow into other organs, the tendency to spread throughout the body and resistance to external influences make it similar to malignant tumors.
The word “benign” also speaks about the prognosis of the disease - it lasts for years and decades, as a rule, without leading to severe depletion of the body and death. However, as in the case of malignant hyperplasia (cancer, sarcoma, etc.), adenomyosis (endometriosis) is difficult to treat conservatively, and operations for this pathology are much more extensive than in the case of benign tumors, since it is difficult to determine the boundary between diseased and healthy tissue.
The most common complication of adenomyosis is due to the fact that endometrial cells functioning in accordance with the monthly cycle lead to heavy bleeding, which is fraught with the development of acute and/or chronic anemia. In some cases, patients have to be hospitalized and even undergo emergency surgery for life-threatening bleeding.
Adenomyosis is prone to spreading the process to other organs and tissues, leading to systemic lesions. With the extragenital location of endometrial cells, a number of complications are possible that require emergency medical intervention (intestinal obstruction in endometriosis of the gastrointestinal tract, hemothorax (filling of the pleural cavity with blood) in pulmonary endometriosis, etc.).
And finally, another danger of endometriosis in general, and adenomyosis in particular, is the threat of malignant genetic transformation of the migrated cells. Such a transformation is very real, since any hyperplasia has a more or less pronounced tendency to malignancy, and in a new place, endometrial cells are forced to exist in extremely unfavorable conditions.
About preventive measures
To prevent miosis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- It is important to exercise caution and attention to prevent injury hazards.
- Medicines must be taken with extreme caution.
- It is not allowed to take medications without a doctor's prescription.
- It is necessary to promptly seek advice from a neurologist, therapist, venereologist or ophthalmologist in order to prevent the development of serious pathologies.
- It is important to undergo medical examination every year.
- In work that involves strenuous activity, it is necessary to use protective equipment: glasses or a mask.
- When working with pesticides or paint, it is imperative to wear protective goggles and a mask.
- Systematically take a blood test for sugar. Avoid getting dust, shavings,
It is important to start treating miosis in a timely manner. If the size of your pupils suddenly changes, you should consult a doctor. It is important to constantly monitor your health. You should always protect your eyes from the sun's rays with dark glasses. You cannot self-medicate. Eye drops should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention
To avoid pupil constriction, you need to remember that:
- Medicines are taken strictly as prescribed by doctors.
- Neurological disorders cannot be triggered. These are one of the most insidious pathologies, the consequences of which negatively affect the patient’s body. Periodic visits to a neurologist's office will help avoid complications.
- As you age, you need to test your blood more often for glucose levels.
- The eyes are an organ that needs protection, so use different protective devices when working at a computer for long periods of time, in production, or when in the sun.
Forecast
Reactive and other types of miosis most often do not progress with treatment. It is also important to influence the causes of its occurrence. However, if miosis occurs against the background of neurological disorders, then the lack of timely treatment may cause the condition to worsen.
The development of miosis can also be prevented if you constantly donate blood for glucose. This is especially necessary for those who suffer from diseases of the endocrine system. If there are no serious contraindications, the doctor will pump up special rotors for treatment, which help improve the condition. A pathology such as miosis is easily treatable. Therefore, you should not delay visiting a doctor.
Miosis is a change in the size of the pupils. They can narrow as a result of the body’s standard reaction to any external stimuli. In some cases, various pathologies in the body lead to a narrowing of the elements. They require timely contact with a specialist who will select the right examination and treatment regimen. You should not try to solve the problem yourself and prescribe any medications to yourself, as this can lead to a worsening of the condition.
Sources used:
- British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (27 Feb 2006). "Relationship between sedation and pupillary function: comparison of diazepam and diphenhydramine." British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
- Farlex medical dictionary citing: Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition.
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Article about miosis on Wikipedia
Adenomyosis during pregnancy
Despite the fact that adenomyosis is one of the most common causes of infertility, after timely comprehensive treatment, pregnancy in women with this disease is possible. A frequent complication of pregnancy with adenomyosis is the threat of miscarriage, so such pregnant women are observed in a high-risk group. Careful observation and timely correction of emerging disorders in most cases help to avoid serious complications.
Paradoxically, in some cases, pregnancy can become a kind of “treatment method” for adenomyosis, since it is a “physiological menopause” (a known fact is that adenomyosis is a hormone-dependent condition and regresses with the onset of menopause). In such a situation, foci of adenomyosis become inactive and stop growing. It is a mistake to believe that the disease will disappear.
Any case of pregnancy complicated by adenomyosis requires an individual approach. An observation and treatment plan is drawn up for each such patient and takes into account a large number of factors, the form and degree of adenomyosis, the presence of complications and the combination of adenomyosis with other pathological processes in the uterus, for example, fibroids, being important. If before pregnancy adenomyosis did not cause any complaints in a woman and was asymptomatic, her pregnancy can proceed safely.
Sometimes pregnant women with adenomyosis worry about the impact of their disease on the condition of the fetus. Such fears are unfounded - adenomyosis does not threaten the normal intrauterine development of the fetus. Treatment of pregnant women with adenomyosis is aimed at eliminating the threat of miscarriage and premature termination of pregnancy. Sometimes hormonal agents and non-hormonal therapy are used for this purpose, similar to those for women with miscarriage and uterine fibroids.
Unfortunately, a doctor's ability to treat adenomyosis in a pregnant patient is limited. The chances of success increase if this pathology is detected before pregnancy, since the arsenal of therapeutic measures for adenomyosis in non-pregnant women is much larger. If a woman, knowing that she has adenomyosis, plans to become a mother, she needs to consult a doctor in advance for appropriate treatment.