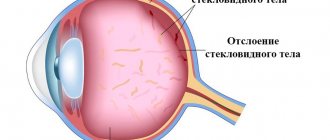
Ophthalmologists often encounter vitreous detachment when examining elderly patients. The pathology is not very severe or dangerous and can usually be successfully treated. The patient's vision can be preserved or restored. But if a person does not see a doctor and the vitreous detachment of the eye remains undetected, the risk of partial or even complete blindness increases significantly.
Note: Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) can develop at any age; athletes who often suffer head and visual injuries are at risk. In older people, pathology develops due to natural age-related changes in the body. According to WHO, more than 53% of people over 50 years of age suffer from partial detachment of the vitreous body from the retina, and about 65% are over 60 years of age. Moreover, in nearsighted people the pathological process begins about 10 years earlier than in farsighted people.
Causes
The destruction of the vitreous body is most often a consequence of natural aging of the body. This is due to the fact that the substance mostly consists of collagen, the production of which decreases with age. In addition, the disease can result from:
- high myopia;
- hormonal disorders and diseases;
- inflammation of the choroid and retina;
- various head injuries;
- physical and psychological exhaustion;
- excessive visual load;
- radiation, exposure to chemicals or toxins;
- previous eye surgeries;
- diseases of the vascular system.
Complications
According to doctors, the pathology is treatable, but only if it is diagnosed at the initial stage. In advanced situations, the risk of facing serious consequences increases several times.
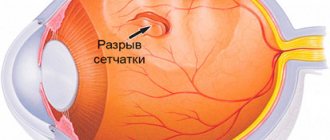
The most dangerous is partial detachment. In this case, the fibers are attached to the retina in some places, resulting in increased traction from the entire mass of the vitreous body. As a result, part of the retinal surface receives additional stress, which leads to its rupture. A similar complication is diagnosed in 8 - 15% of all cases. The anomaly is accompanied by the appearance of floating spots and decreased visual acuity.
A macular hole in the retina is almost always accompanied by vision problems. However, in most cases, patients do not even notice the deviation if the second eye sees well. Only an examination will help to identify the disease; the gap is repaired through surgery.
Pathology can cause blood to enter the vitreous body. This consequence of the disease will not lead to blindness, but requires immediate treatment.
Sometimes PVD is accompanied by dissection and detachment of the retina. This negatively affects the functioning of the visual system and can lead to blindness.
Risk group
The disease mainly occurs in people over 45 years of age, with women at this age suffering from this disease more often than men. Experts attribute this to hormonal changes during menopause.
In addition, the following are at risk of developing the disease:
- athletes (due to injury risk);
- welders, construction workers and factory workers;
- people who have had eye surgery;
- people with penetrating eye trauma.
Effective preventive measures
Vitreous detachment can lead to serious complications. Yes, the prognosis for treating the anomaly is favorable. It can be easily corrected, but only if identified at the initial stage. If retinal detachment is diagnosed and other severe consequences of the disease develop, then therapy may be powerless.
The essence of preventive measures is to reduce the risk of complications. Pathologies such as diabetes or thyroid problems must be properly treated in a timely manner. Also periodically give your eyes rest, this is especially important for people who spend a lot of time at the computer.
| If the work involves possible damage to the organ of vision, be sure to use safety glasses and other devices. |
Classification
Experts distinguish three main types of detachment, which differ from each other:
- Partial detachment. It is a consequence of thrombosis, penetrating injury, hemorrhage in the retina, its inflammation, as well as inflammation of the choroid. This type of detachment is uncommon, but can gradually become complete.
- An annular detachment is a separation of the vitreous from the optic disc.
- Complete detachment. The cause may be inflammation of the choroid and hemorrhage in the space between the vitreous body and the retina. The risk group for this type of detachment includes people under 35 years of age.
Mechanism of development of the disorder
In newborn children, the vitreous body has a very dense structure and is closely adjacent to the retina. With age, this organ begins to separate into two fractions - liquid (95% water) and fibrous, which is formed from protein particles united together. As the disease progresses, the proteins begin to change abnormally, which leads to the so-called exfoliation.
A defect in this structural component of the eye is a pathology that progresses over time, in which the tone of the hyaloid membrane weakens, which leads to serious complications such as loss of visual acuity and the development of myopia. Depending on the severity of the clinical case, damage to the macular area may occur, which always leads to irreversible ophthalmological damage.
According to statistics, the disease is diagnosed in most cases in people over 50 years of age, and vitreous detachment is much more common in women.
Posterior vitreous detachment
The disease manifests itself in different ways. Cloudiness may occur, which is clearly visible when looking at a plain light background. Most often, over time, the “front sights” fall below the optical axis and disappear. In addition, the patient may see flashes of light similar to lightning. They are especially visible if you close your eyes.
This phenomenon occurs due to the fact that the vitreous body begins to exert a pull on the retina where they are most strongly connected. As a result of the impact, they are perceived by photoreceptors as a bright flash of light.
What is the disease?
PVD is a fairly common disease that develops as a result of destructive processes affecting proteins located in the fibrous fraction of the vitreous body. Under the influence of negative factors, the process of separation of layers begins. Since the vitreous body is located as close as possible to the retina, even a slight violation of the integrity of its structure leads to vision problems.
| According to statistics, the disease most often affects women over fifty years of age. Men extremely rarely suffer from this pathology. |
Symptoms
In addition to harmless symptoms, there are also those that signal the danger of the exfoliation process:
- sudden deterioration of vision;
- the appearance of a curtain that blocks the field of view partially or completely;
- a sharp increase in various opacities;
- persistent flashes and floaters.
If you have these symptoms, it is important to quickly contact an ophthalmologist so that he can carry out diagnostic procedures to identify the cause of the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Diagnostics
The disease can be detected by studying anatomical transformations in the eyes and their consequences. To do this you can do:
- refractometry (determination of eye refraction);
- tonometry (measurement of eye pressure);
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye);
- ophthalmometry (measurement of the radius of curvature of the cornea);
- visual acuity test;
- biomicroscopy (study of optical media and eye tissues).
The anteroposterior axis of the eye is also checked. If its value exceeds 24 mm, then the risk of detachment is high. Ultrasound of the eyeball can reveal transformations in the structure, detect voids and compactions, as well as detachment and stretching of the retina.
Optical computed tomography will help to detail the clinical situation. Thanks to it, it is possible to more accurately examine the structure of the retina, measure the thickness of the posterior hyaloid and internal limiting membranes.
The main reasons for the development of pathology
Most often, the pathological process begins in the back of the eye, which is why the term “posterior vitreous detachment” often appears in medicine.
Why does such a disease begin? In fact, the reasons may be different. Vitreous detachment may be due to the following reasons.
- As already mentioned, age is a risk factor, because pathology most often develops in patients over 50 years of age. The fact is that as we age, various degenerative changes begin in the structures of the eye. In addition, the number of collagen fibers that support the dense structure of the vitreous body decreases.
- Patients suffering from frequent inflammatory diseases of the choroid and retina are also predisposed to a similar pathology. These diseases are accompanied by changes in normal pH. The acidic environment negatively affects the functioning of cellular structures and also contributes to a decrease in the level of adhesion between the posterior hyaloid membrane of the retina and the internal limiting membrane of the vitreous body.
- The list of risk factors also includes some systemic diseases, in particular, thyroid pathologies, diabetes mellitus and Marfan syndrome. The fact is that such disorders are accompanied by significant changes in hormonal levels. As a result of these processes, the normal synthesis of hyaluronic acid and glycosaminoglycans is disrupted, which primarily affects the structure of the vitreous body.
- Detachment can be the result of penetrating wounds in the eye area, as well as previous eye surgery.
Treatment
In most cases, no treatment is required. If the disease proceeds without complications, the exfoliated fibers fall below visibility, and the symptom in the form of “floaters” goes away on its own. But ophthalmologists can prescribe an additional course of strengthening medications:
- Wobenzym in tablets helps relieve inflammation, pain and swelling, and also strengthens the immune system and resolves blood clots;
- Taufon - drops that are used to stimulate metabolic processes in tissues and accelerate regeneration;
- Emoxipin is an antioxidant that strengthens blood vessels in the retina and mucous membrane of the eye and improves tissue nutrition;
- Potassium iodide is a 2% solution that has an antisclerotic effect and accelerates the resorption of hemophthalmos.
In addition, you need to protect your eyes from bright sunlight, refrain from visual stress and give your eyes a rest every 30 minutes spent at the computer or reading. During breaks, it is recommended to do eye exercises.
In case of a sharp drop in visual acuity and a high risk of complications, surgery is prescribed. There are two methods of surgical intervention, from which the specialist chooses the most suitable one, based on the specific case:
- Vitrectomy – removal of the vitreous body: complete or partial. Instead, the space is filled with a special saline solution. Possible side effects and risks: glaucoma, cataracts, extensive hemorrhage.
- Vitreolysis – YAG laser radiation. With its help, the vitreous body is processed to change its properties and restore transparency. Side effects and risks: damage to the structure of the eye, development of various types of hemorrhages.
These methods are complex and can lead to new vision problems, but there are cases in which surgical intervention is necessary.
How to treat
What to do if you are increasingly worried about the main symptom of retinal detachment - floating spots and cobwebs before the eyes? First, you need to contact an ophthalmologist or retinologist for examination. A retinologist deals with pathologies of the fundus of the eye; such a specialist may not be available in the district clinic, but finding one in private clinics or laser vision correction centers will not be difficult.
The question of whether treatment for vitreous detachment is necessary at all still remains open. The fact is that for PVD, treatment with conservative methods using medications or physiotherapy is completely ineffective. The only way to get rid of unpleasant symptoms is surgery. But many doctors do not consider floaters before the eyes, flashes and periodic deterioration of vision as a reason for performing surgery. And there are several good reasons for this.
Surgical removal of the vitreous and its subsequent replacement with an implant is currently the only available and effective method of eliminating the disease
Firstly, the floaters may disappear on their own. Or a person gets used to them and simply doesn’t notice anymore.
Secondly, if there is no or minor visual impairment, and the patient’s main problem is moral discomfort, it is not advisable to carry out serious measures with a number of side effects.
Thirdly, laser treatment for vitreous detachment is not indicated for everyone, and for some its cost is too high, since such an operation is performed only abroad.
However, if the patient is greatly disturbed by flashes, lightning, cobwebs and black dust constantly flashing before his eyes, the doctor will select the optimal treatment regimen taking into account the patient’s age and lifestyle. The following main points are taken into account:
Hemophthalmos and its treatment
- Treatment of chronic diseases associated with metabolic disorders. It is believed that the state of the vitreous body of the eye is a reflection of the state of the entire human body. For example, in diabetes mellitus, a large amount of glucose accumulates in the vitreous body, which causes clouding and, over time, detachment. With arterial hypertension, particles of excess cholesterol often float in the vitreous body, which penetrates into the structures of the eye along with blood or vessels covered with plaques.
- Rejection of bad habits. Since both smoking and alcohol consumption greatly affect the condition of blood vessels, at the first visual impairment it is better to give up both nicotine and alcohol. This will benefit the whole body, not just the eyes.
- Sports activities. When a person is actively involved in sports, his metabolic processes are more intense, the blood vessels receive enough oxygen and nutrients, and this significantly reduces the risk of developing vision pathologies. But sports should be reasonable and dosed, without overload - this can, on the contrary, become an impetus for the development of pathology and intensify its manifestations.
It is impossible to cure the pathology with folk remedies, but simple home recipes help strengthen the visual system and prevent other complications
You should not look for medications that help get rid of “floaters” in front of your eyes and eliminate vitreous detachment. They simply don't exist. Pharmacies and especially online stores often offer various homeopathic remedies and dietary supplements that supposedly restore blood circulation and metabolic processes in the tissues of the eye. But they are not registered as official medicinal products in Russia, which means that their effectiveness is not confirmed by full-fledged studies and remains at the risk of the buyer.
Surgical and laser treatment of PVD
The only effective method of restoring a clear visual image without removing and replacing the affected vitreous is laser correction using the vitreolysis method. A neodymium laser beam is used to carry out the procedure. The doctor, under high magnification, identifies foreign particles in the vitreous body, acts on them with a laser beam and breaks them into elements so tiny that they can no longer disrupt the quality of the visual image.
However, such an operation does not eliminate the causes of the pathology that caused “floaters” to appear in front of the eyes and the quality of vision to deteriorate - impaired blood microcirculation, deterioration of the condition of blood vessels and insufficient tissue nutrition. Every patient should understand this and still turn to disease prevention and a healthy lifestyle, and not look for a miraculous panacea. In addition, vitreolysis is not yet practiced in Russia; today such an operation is performed only in selected clinics in the USA and Great Britain.
Laser correction for vitreous detachment of various degrees has not become widespread due to the high risk of developing severe side effects. If the procedure is carried out carelessly, complications will exceed the therapeutic effect of vitreolysis. To perform this operation efficiently and accurately, high-tech equipment and great skill of the doctor are required, since you have to work with moving parts. Taking these nuances into account, the supposed benefits of the operation are not at all worth the actual risks - this method of treating PVD is not officially practiced in Russia.
Vitrectomy is a more common surgical operation, the essence of which is partial or complete removal of the vitreous. In Russia, it is performed in many ophthalmology clinics, the operation is considered serious, dangerous due to severe side effects and complications, vitrectomy also requires a high level of qualifications of the doctor.
Interventions on the visual organs are always accompanied by a high risk of developing serious complications, therefore the operation is performed only in exceptional cases
The method is extremely simple: first, the doctor conducts a full examination of the patient and determines how severely the vitreous body is affected. Then the affected areas or the entire vitreous body are removed and replaced with a saline solution. As a result, the flies disappear completely and forever, since the environment in which they were located is eliminated.
The effectiveness of vitrectomy is almost one hundred percent; patients who agreed to such an operation write about remarkable results. But since the main complications include hemorrhage in the cavity of the ocular structures, detachment of the retina, and the development of cataracts, it is performed only in exceptional cases, when there are other indications for removal of the vitreous body.
Prevention
Attention to existing eye ailments and their timely treatment will help prevent the disease. It is important to maintain normal hormonal levels in case of diabetes and thyroid pathologies. In addition, you need to take care of the safety of your eyes and protect them from injury. For example, when welding, wear special safety glasses.
To prevent various complications and visual impairment in the presence of vitreous detachment, you need to stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, and follow the prescribed diet.
Treatment Options
If there is no risk of retinal detachment and a significant decrease in visual acuity, the ophthalmologist will prescribe medication that will help improve the nutrition of the intraocular structures. Partial vitreous detachment does not require serious medical interventions: it is quite enough to see a doctor regularly and use preventive recommendations from a specialist. If the pathology is severe (wrinkling or complete posterior detachment), surgery to remove the contents of the posterior vitreous chamber (vitrectomy) may be required. An important factor determining the treatment tactics is the condition of the retina - if there is a high risk of detachment of the light-receiving layer, the ophthalmologist will suggest a laser therapy method.
Useful video
You can learn more about the disease and its causes from the following videos.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.