Laser vision correction is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting refractive errors. Experts include myopia (nearsightedness), hypermetropia (farsightedness) and astigmatism as refractive errors. Laser vision correction is a real chance to get rid of the need to use external optical correction - glasses and contact lenses, which are necessary for the above anomalies. The goal of all existing methods of laser vision correction is to ensure that light rays passing through the eye are able to focus on the surface of the retina, and not before it, as in myopia, and not behind it, as in hypermetropia. This is achieved by changing the shape of the cornea with a laser beam, thus correcting its refractive power (refraction).
The refractive power of the human cornea is, on average, ±43 diopters (D). This is almost 80% of the entire optical power of the eye, which is approximately 58-60D. That is, by surgically modeling the curvature of the cornea, ophthalmologists correct refractive errors.
From the history of laser correction
The idea of correcting refractive errors by changing the shape of the cornea, which became the basis for laser vision correction, belongs to the Japanese ophthalmologist Sato. He tried to implement it in 1939, performing a series of operations on the eyes with non-penetrating incisions along the edge of the cornea. In 1949, José Barracuer, a Colombian ophthalmic surgeon, proposed using a laser beam in this operation. Our famous compatriot, academician S. N. Fedorov, completely improved the technique in 1972. And a little later, in 1976, the first excimer lasers appeared, produced by the IBM Corporation.
The first laser vision correction operation was performed in 1985. It was carried out in Berlin, and since 1988, excimer laser vision correction has been widely practiced in the USA, European countries and Russia.
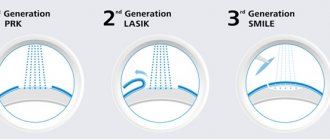
Today, laser vision correction operations are performed by ophthalmologists in 53 countries. Equipment for operations is constantly being improved, and methods of surgical intervention are changing. The following methods of laser vision correction are recognized as the most popular and effective: photorefractive keratectomy PRK (PRK), LASIK (LASIK), Femto LASIK (Femo LASIK) and SMILE.
How is LASIK laser surgery performed?
The specifics of the procedure largely explain the presence of all the listed contraindications. It is important to follow your doctor's instructions before and after laser vision correction. This will avoid complications.
Before LASIK is prescribed, the patient undergoes an examination. He is examined by an ophthalmologist using high-tech equipment. The ophthalmologist calculates all the parameters of the visual organs and determines whether correction can be carried out. You may also need to be tested for HIV and hepatitis.
14 days before vision correction, the patient stops using optics. Glasses and contact lenses slightly change the shape of the cornea, but it should take its natural shape. You should not wear makeup on the day of surgery. The doctor will definitely remind the patient about this. Particles of cosmetics can get into the operated area of the eye and cause infection or irritation. You should not drink alcohol before laser vision correction. It negatively affects the condition of blood vessels and the body as a whole.
LASIK/Femto LASIK
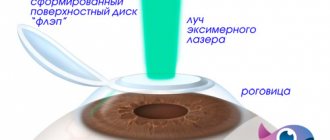
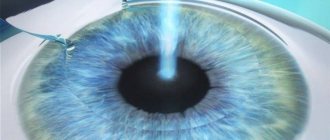
LASIK, or laser keratomileusis, is a more modern version of laser vision correction than PRK, which is performed in 2 stages. The first stage is the formation of a corneal flap (flap) from the epithelial layer, for which a special device is used - a microkeratome. The flap is then pulled back to make way for the laser beam.
At the second stage, direct remodeling of the corneal stroma is carried out using ablation (evaporation of tissue) using an excimer laser. After which the corneal flap is placed in its bed.
FemtoLASIK is a modification of the first stage of LASIK surgery. Namely, to form a flap at the first stage, a femtosecond laser is used here; at the second stage, ablation of the corneal stroma is performed with an excimer laser. LASIK and Femto LASIK are the most widely practiced methods of laser vision correction today.
Benefits of laser treatment
Laser treatment is a popular procedure around the world. Its undoubted advantages are:
— quick recovery after the procedure and its painlessness;
— guaranteed effectiveness of vision restoration;
— speed and absence of the need for hospitalization;
- long-lasting results;
— universality of the procedure (experts recommend it for any ophthalmological problem).
Thus, the modern method of laser vision restoration can rightfully be considered the best. Of course, the operation also has disadvantages, but against the background of its advantages, they become insignificant.
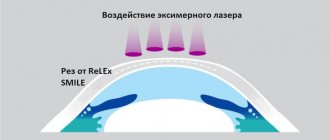
ReLEx SMILE
The ReLEx SMILE method or refractive lenticule removal through a small incision is a new generation of laser vision correction technologies. To implement it, innovative developments of femtosecond lasers are used, such as VisuMax from the company Carl Zeiss.
The active introduction of femtosecond technologies into refractive surgery has made it possible to develop completely new safe techniques for laser vision correction. Thus, in 2006, German scientists under the leadership of professors V. Secundo and M. Bloom presented the unique ReLEx technique. The first method they introduced was called ReLEx FLEx and consisted of removing the refractive error-correcting lenticule, an optical lens, through a corneal flap made with a femtosecond laser. The second, improved method is called ReLEx SMILE. Its purpose is to remove the formed optical lens through a small incision along the periphery of the cornea.
The main difference between SMILE and other laser correction options is the ability to correct refractive errors without forming a corneal flap and without the risk of displacing the surface epithelium of the cornea.
Thanks to the introduction of ReLEx SMILE, laser vision correction surgery has become a one-stage procedure, which has significantly reduced the number of potential complications. Now, using only a femtosecond laser (without an excimer laser, which is necessary with other methods), a precisely calculated optical lenticule (lens) is formed in the internal media of the cornea, a small corneal incision is made with the help of it, which does not interfere with vision in the future, and the lenticule is removed through it.
Restoring vision using LASIK technology
A correction method called LASIK (laser assisted keratomileusis) appeared in 1989 and is currently the most common method of vision restoration. Over the past ten years alone, about 15 million operations have been performed worldwide using this technology.
LASIK is a tandem of microsurgery and excimer laser treatment. During the operation, the ophthalmologist uses a microkeratome to create a flap of corneal tissue, then it is moved to the side, and the laser beam begins to act on the middle layers. The damaged areas evaporate and the desired shape of the cornea with the specified optical parameters is formed. Once completed, the flap is returned to its place. There is no need to apply stitches, since the incisions heal due to the cornea’s own collagen. Anti-inflammatory drops are placed in the eyes. Vision is restored approximately 2 hours after surgery. For the first few days, side effects in the form of slight blurriness will still be observed, but after three to five days, vision will finally return to normal.
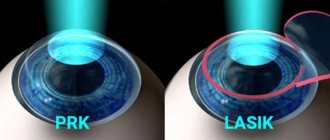
The difference between SMILE and PRK and LASIK
Operations using PRK and LASIK methods are performed with displacement of the surface epithelium of the cornea and modeling (ablation) of the required shape of the cornea in its deep layers using an excimer laser. However, when performing vision correction using the PRK method, patients experience significant pain during the first two days after the intervention, and the rehabilitation period until complete recovery and stabilization of vision lasts at least two months. Whereas when correction is performed using the SMILE technique, complete recovery and maximum visual acuity are possible already on the second day after surgery.
Contraindications to laser vision treatment
Despite the fact that today the procedure for laser vision restoration is affordable, not everyone can use it. The thing is that it has a number of contraindications that must be taken into account without fail. There are the following restrictions for this operation:
— the age of the patient (not younger than 18 years, cauterization of the immature retina of the eye with a laser in children is unacceptable);
— pregnancy and lactation;
- diabetes;
- diseases that reduce immunity;
- glaucoma, cataracts and optical neuropathy (treatment is allowed at certain stages of the disease).
In order to exclude possible complications, it is necessary to seek advice from a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination of the body. In the presence of diseases such as myopia, retinal rupture and lens clouding, coagulation is performed before laser treatment.
The difference between SMILE and LASIK and Femto LASIK
Carrying out two-stage LASIK and Femto LASIK procedures requires the formation of a certain flap on the surface of the cornea (flap) with further modeling of the corneal stroma with an excimer laser (ablation). When performing vision correction using the SMILE method, only the VisuMax femtosecond laser is used, in one step forming both an optical lenticule in the corneal stroma and a small incision along the periphery of the cornea to remove it. This ensures greater safety of surgical intervention and a reduction in rehabilitation time.
Comparison table of laser correction methods
| PRK | LASIK/Femto LASIK | ReLEx SMILE | |
| Ablation type | Subepithelial | Stromal | Lenticule extraction |
| Laser system | Excimer laser | Excimer laser/Excimer and femtosecond laser | Femtosecond laser VisuMax |
| Recovery period | 1-2 months | 5-7 days | 1-2 days |
| Negative consequences | Pain syndrome, possible complications | Possible complications | Complications are rare, there are no complications of Flap surgery |
Indications and contraindications
Vision correction using laser technology is carried out at the age of 18 to 45 years for farsightedness, astigmatism and myopia with a certain degree, which have been stable (not progressed) throughout the year.
Indications for laser correction
Table. Indications for laser vision correction.
| Visual impairment | Defect level |
| Farsightedness | up to 4.5 diopters (sometimes up to 6) |
| Myopia | up to 12 diopters |
| Astigmatism | up to 4 diopters (in some clinics up to 6) |
Myopia
Contraindications to surgical intervention include:
- serious impairment of visual function (more than 12 diopters) in any of the above diseases or progression of the pathological process over the past 12 months;
- having only one seeing eye;
- systemic, autoimmune and infectious diseases;
- ophthalmological pathologies that provoke changes in the cornea, retina, fundus (cataract, keratoconus, glaucoma, iridocyclitis, etc.);
- cornea too thin;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Laser correction is contraindicated during pregnancy
To determine the presence of contraindications, patients are required to undergo a complete diagnosis of the body before undergoing surgery.
For reference: it is possible to perform laser vision correction after 45 years of age, but in this case the risk of developing age-related farsightedness increases, which doctors always warn their patients about.
Features and advantages of the SMILE method
The SMILE laser vision correction technique differs significantly from all previously practiced ophthalmic technologies for the surgical correction of refractive errors. Among its obvious advantages are:
- No superficial corneal flap (flap ). This guarantees minimal risk or complete absence of serious complications of flap surgery - hays and keratoectasia.
- Ultra-small corneal incision (up to 4 mm). Despite the fact that Lasik and Femto-Lasik methods require a corneal incision, the size of which is up to 20 mm, which is almost 80% larger.
- Biomechanical stability of the cornea . Laser vision correction operations using the SMILE technique practically do not affect the upper layers of the cornea, leaving them absolutely biomechanically intact. In the case of the Lasik technique, on the contrary, due to ablation of the corneal stroma, its biomechanical strength is seriously reduced, which creates a risk of developing keratoectasia.
- Low risk of dry eye syndrome. A small incision along the periphery of the cornea during surgery using the SMILE technique, instead of forming a corneal flap, causes less trauma to the nerve endings present in the cornea. According to research, this is the main factor in the lower incidence of dry eye syndrome in patients undergoing vision correction with the SMILE technique.
- High precision of manipulations performed by the surgeon . Femtosecond laser technologies of the SMILE technique are provided by a unique laser from the company Carl Zeiss VisuMax, which is capable of sending laser radiation in very short compressed pulses, which makes it possible to achieve a high level of energy density and guarantees high precision of the surgeon’s manipulations.
Main indications for LASIK surgery
Laser vision correction using the LASIK method is prescribed for the following vision pathologies:
- astigmatism (from +/−1 to +/−4), in which a person sees the image blurred and therefore constantly squints his eyes;
- farsightedness/hyperopia (from +1 to +6 diopters), manifested in poor vision at close range;
- nearsightedness/myopia (from −1 to −13 diopters) is the most common refractive error in which a person has difficulty seeing into the distance.
People usually agree to laser correction due to intolerance to glasses and contact lenses, as well as lack of desire or ability to wear them. Thus, it is difficult to imagine a rescuer or, for example, an athlete wearing glasses. Laser correction is becoming an excellent opportunity for many people to do what they love, despite vision problems. LASIK surgery allows you to get rid of glasses and contacts forever or for many years.
Rehabilitation and recovery
After vision correction, follow certain rules that will help speed up recovery and prevent complications. Patient behavior after surgery:
- sleeping on your back will prevent swelling and eliminate bleeding;
- protect your eyes from sunlight;
- do not touch the operated organ with your hands, especially dirty ones (use clean napkins or a handkerchief to remove tears);
- do not read in the first two days after excimer laser manipulation and watch TV for a minimum time;
- do not use cosmetics and perfumes for the first 2 days;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- It is forbidden to visit the sauna, bathhouse, solarium and go to the sea during hours of strong solar activity;
- use drops prescribed by your doctor, according to the instructions provided by him.
If during the rehabilitation period there is pain, discomfort, vision is not restored, or a foreign body gets into the eye, contact an ophthalmologist for help, do not try to solve the problem by self-prescribing medications or trying to remove the foreign body.
Types of operation
There are two main methods of correction - PRK (photorefractive keratectomy) and LASIK (laser keratomyelosis). The first operation allows you to correct myopia up to 6 diopters, astigmatism up to 2.5-3 diopters. Both types of laser correction are carried out sequentially: first on one eye, then on the other. But this happens within the framework of one operation.
For laser correction of farsightedness and myopia complicated by astigmatism, Lasik is more often used. This is because PRK requires a long (up to 10 days) healing time. Each type of operation has its pros and cons, but still Lasik is a more promising direction, so this method is most often preferred.
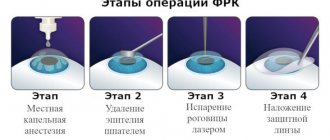
Photorefractive keratectomy
The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
The doctor treats the eyelid and eyelashes with an antiseptic. Sometimes an additional antibiotic is instilled to prevent infection. The eye is fixed using an eyelid speculum and washed with saline solution. At the first stage, the doctor removes the epithelium. He can do this surgically, mechanically and laser. After this, the process of evaporation of the cornea begins. It is carried out only with a laser.
The method is limited by the required residual thickness of the cornea. To perform its functions, it must be at least 200-300 microns (0.2-0.3 mm). To determine the optimal shape of the cornea and, accordingly, the degree of its evaporation, complex calculations are carried out using special computer programs. The shape of the eyeball, the ability of the lens to accommodate, and visual acuity are taken into account.
In some cases, it is possible to refuse excision of the epithelium. Then the operations are faster and with less risk of complications. In Russia, a domestically produced Profile-500 installation is used for this purpose.
Laser intrastromal keratomyelosis
Preparations are similar to those for PRK. The cornea is marked with safe ink. A metal ring is placed over the eye, which additionally secures it in one position.
The operation takes place under local anesthesia in three stages. At first, the surgeon creates a flap from the cornea. He detaches the superficial layer, leaving it attached to the underlying tissue, using a microkeratome instrument—specially modeled for eye microsurgery.
laser vision correction: progress of the operation
The doctor removes excess fluid with a sterile swab. At the second stage, he bends the flap and performs laser evaporation of the cornea. The entire process takes less than one minute. During this time, the flap is also covered with a sterile swab. At the third stage, the separated piece is placed in its place, according to the previously applied marks. After rinsing the eye with sterile water, the doctor smoothes the flap. No sutures are required; the cut-off piece is fixed on its own due to negative pressure inside the cornea.
The possibility of performing an operation is determined largely by the anatomical structure of the patient's eye. To implement this, it is necessary that the cornea of the eye is of sufficient size. The flap must have a thickness of at least 150 microns. The deep layers of the cornea remaining after evaporation are at least 250 microns.
Video: how laser vision correction is done
Risks and consequences of the operation
There are early and late postoperative complications. The first ones usually appear within a few days. These include:
- Non-healing corneal erosion. Its treatment is quite complex and requires consultation with specialized specialists. Common methods of therapy are the use of collagen coatings of the cornea, contact vision correction (use of soft lenses).
- Reduction in the thickness of the epithelial layer, its progressive destruction. It is accompanied by swelling and the development of erosions.
- Keratitis (inflammation of the eye). It can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. Keratitis manifests itself in redness of the eye, pain, and irritation.
- Opacities in the evaporation zones of the cornea. They can also occur later in the rehabilitation period. Their cause is excessive evaporation of corneal tissue. The complication, as a rule, responds well to treatment with the use of resorption therapy. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to repeated surgery.
The overall rate of long-term complications with Lasik is 1-5%, with PRK – 2-5%. In the later stages, the following negative consequences of laser correction may become apparent:
- Dry eye syndrome. With this pathology, a sufficient amount of tear fluid does not form. The patient feels irritation, pain, redness. Involuntary lacrimation often occurs. The syndrome is successfully treated with certain medications in the form of drops.
- Hypercorrection. This phenomenon occurs as a result of excessive ablation (evaporation) of the cornea. It leads to a change in the sign of ametropia, myopia is replaced by farsightedness and vice versa. We can talk about hypercorrection only after the end of the recovery period (3 months). Sometimes additional surgery may be required. It is only allowed if the cornea is thick enough.
- Irregular astigmatism. This is the name for the different refraction of light in one eye and along one meridian. In this case, glasses rarely correct astigmatism; the use of special contact lenses is necessary.
- Keratoconus. This is the process of degradation of the cornea, as a result of which it takes on a cone-shaped shape. As a result, vision begins to rapidly deteriorate. For treatment, both conservative and surgical therapy are used.