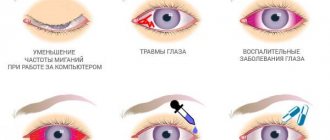
Cause
There are many varieties of viruses that multiply and mutate every year. They take on a new form, so immune cells cannot cope with them at the initial stages. There are the most common types of viruses that most often form conjunctivitis:
- Adenovirus. It penetrates from an infected person into the body of a new host through airborne droplets, household contact, and water. At the onset of the disease, the throat turns red. A person develops characteristic clinical symptoms of a viral disease. Body temperature rises. Complications to the eyes always form. But if it occurs, the patient develops redness of the conjunctiva without the formation of additional elements (films, pus, nodules).
- Herpes. The herpes virus circulates in the body of almost every person. It is concentrated in nervous tissue. If the patient is exposed to negative environmental factors, it becomes activated and multiplies. Characteristic clinical symptoms of viral conjunctivitis appear, which can be complicated by the formation of bubbles on the mucous membrane, inside of which there is a clear liquid filled with the pathogen.
- Influenza, parainfluenza. This is a fairly common disease, which is most often complicated. An increased body temperature develops, which reaches 40 degrees. If the disease is complicated by the spread of the virus to the eyes, this form is called influenza conjunctivitis. It is characterized by excessive swelling, the patient cannot open the eyelids.
For each form of the disease, there is a specific treatment, which differs from the other type of viral conjunctivitis. Therefore, the doctor is recommended to conduct diagnostic tests that will help make an accurate diagnosis.
Definition of disease
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, that is, the outer transparent mucous membrane (it covers the inner surface of the eyelids and the sclera). Viral conjunctivitis causes upper respiratory tract infections (adenoviral, herpes); they can also appear with a common cold. The disease spreads quickly.
Conjunctivitis is caused by different types of viruses. The disease is epidemiological in nature.
Risk group
The risk group includes the following categories of patients:
- persons with reduced immune function;
- patients suffering from congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- patients suffering from viral and infectious diseases;
- people visiting public reservoirs, especially those with stagnant water in the hot season;
- children and elderly people whose immune system function is underdeveloped.
These categories of patients are recommended to undergo an annual preventive examination with an ophthalmologist and other doctors, conduct diagnostic tests, and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Traditional methods of therapy
With the help of traditional methods, discomfort is greatly alleviated. But it does not replace basic medical treatment. Use traditional medicine only after consulting a doctor.
Lotions are considered the most effective.
Moisten a small piece of cotton cloth or gauze with freshly squeezed dill juice. Apply to the eyes for fifteen minutes.
Grind two teaspoons of rose hips, leave in a glass of boiling water, and strain.
Freshly squeezed potato juice is effective for lotions.
Two tablespoons of dried cornflower flowers, pour a liter of water, boil for ten minutes, leave for half an hour, strain, use for lotions.
Rinse your eyes well with infusion of sage, chamomile, calendula, celandine, and strong brewed black and green tea.
Remember, the disease can lead to complete loss of vision. Therefore, it is important to carry out preventive measures in a timely manner and, if a disorder occurs, to begin treatment in a timely manner.
Classification
The disease is divided depending on the pathogen that caused the inflammation:
- adenovirus;
- influenza, parainfluenza;
- herpes.
Depending on the form of symptoms, viral conjunctivitis is divided into:
- catarrhal form - the symptoms are not pronounced, there is slight inflammation and swelling;
- acute form - the symptoms are pronounced, the tissues become very inflamed, swell, the person has photophobia and increased lacrimation;
- chronic form - the virus is constantly in the human blood, periodically activated and causes inflammation.
The doctor needs to classify the disease in order to prescribe treatment. For each form and degree of the disease, a certain range of medications is prescribed.
Drops and ointments during therapy
In the treatment of viral conjunctivitis, various medications are used: special antiviral drops with interferon; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation; hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs; drops containing antibiotics; ointments.
Typically, medications are used as follows: wash the eye to remove purulent discharge with special antibacterial solutions; then use antiviral drops; After half an hour, antiviral ointment is applied.
Treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. The course of healing is three weeks. In severe cases, a month. The eyes should not be sealed, tied, or covered with compresses, as this will only create favorable conditions for inflammation.
A repeated consultation with an ophthalmologist is necessary if, despite strict adherence to all the specialist’s instructions, there is no improvement in the condition, new signs of the disease appear.
Eye hygiene is performed using a cotton swab, moving from the outer corner to the inner one. For the procedure, be sure to use a separate swab for each eye.
Remember that all types of viral conjunctivitis are contagious, transmitted by contact, and spread easily. Timely treatment will help avoid complications. Don't neglect your health.
Symptoms
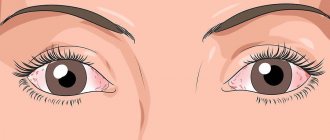
An inflammatory eye disease of a viral nature has characteristic clinical symptoms:
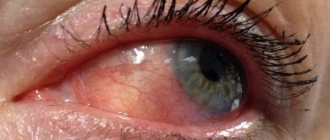
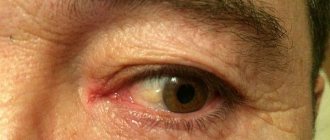
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- when complications occur, the disease spreads to the cornea and hemorrhage forms on it;
- swelling and inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- increased lacrimation, which, if untreated, is replaced by dryness, which leads to the formation of microtraumas and cracks in the cornea;
- absence of purulent discharge;
- increased sensitivity to the action of bright light, due to which a spasm of the eyelids is formed, the patient cannot open them;
- the possibility of a bacterial infection accompanied by the formation of purulent exudate.
The degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on the cause of conjunctivitis, the prevalence of the pathogen, the patient’s immune status, and the start of treatment. At first, the patient experiences slight redness and inflammation, which intensifies over time. If the disease is not treated promptly, the virus spreads to the cornea and internal tissues of the eyes.
Diagnostics
Different forms of conjunctivitis may be similar to each other. To identify the root cause of the disease, the doctor needs to prescribe several diagnostic tests for the patient:
- Collection of complaints. The patient tells the doctor about the symptoms that bother him. The doctor asks the person about the presence of previous diseases, contact with infected people, visits to public bodies of water, mechanical damage to the eyes, and allergic reactions in the medical history.
- Inspection of the affected surface. The doctor detects swelling and inflammation of the eye tissues, redness of the conjunctiva. There are no purulent formations.
- Determination of the patient's visual acuity. This is a standard diagnostic test when visiting an ophthalmologist. Often with viral diseases, visual acuity may decrease. To determine the degree, the patient looks at the diagnostic tables and tells the doctor the number of lines with letters that he can clearly see.
- Bacteriological culture. The technique is used as a differential analysis to exclude the infectious nature of the disease. A smear is taken from the inner corner of the patient's eyes and inoculated onto a nutrient medium. If the disease is caused by bacteria, microflora growth is detected. In this case, the laboratory assistant selects an antibiotic to which she is sensitive.
- PCR research. A swab is taken from the patient's eyes and sent to the laboratory. There it is examined using a semi-automatic analyzer, which determines the exact virus that caused the disease.
- Microscopy. The technique is used for differential analysis to exclude fungal and bacterial microflora. A smear is taken from the inner corner of the person's eyes and applied to a glass slide. It is studied under a microscope. The laboratory doctor counts the number of bacteria, fungi and spores that he sees in all fields of vision.
Based on diagnostic tests, the doctor makes a reliable diagnosis. Only after this do they begin treatment for the viral disease.
Treatment
Doctors use complex treatment to eliminate the viral agent. Additionally, medications are used to improve the patient’s well-being. Drugs are used that act systemically on the entire body, this reduces the risk of complications.
Antiviral therapy
Antiviral agents are used that act systemically on the entire body, for example, Acyclovir, Ingavirin, Arbidol. If a virus enters the human body, it always spreads through the blood to various organs and tissues. Therefore, it is necessary to eliminate the action of the pathogen throughout the system.
To quickly eliminate the effect of the virus on the eye area, drops of antiviral agents are used. For example, Oftalmoferon, Poludan. They can be used up to 10 times a day without becoming addictive.
Antibacterial therapy
It is used if the patient's condition is complicated by a bacterial infection. In this case, purulent discharge from the eyes necessarily appears. It is recommended to use local products in the form of drops:
- Tobrex or Tobradex;
- Vigamox;
- Levomycetin.
At night, ointments are used that prevent the growth of bacteria:
- Erythromycin ointment;
- Tetracycline ointment.
It is recommended to undergo bacteriological culture first. But more often, doctors do not resort to this method, but prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Immunostimulants
Local agents are used in the form of drops, which enhance the immune response in the affected area. For this purpose, drugs containing immunoglobulin are used, for example, Interferon. The drug is used 2-3 times a day, alternating with antiviral agents.
Vitamin therapy
Vitamin complexes containing substances beneficial for the eyes are used. The drug stimulates metabolism, which enhances the regeneration of damaged tissues, including the conjunctival sac. Vitamin therapy improves the function of the immune response.
Moisturizing drops
A complication of viral conjunctivitis is drying of the mucous membrane of the eyes. This injures the cornea, microtraumas and cracks appear on it. To prevent this condition, it is recommended to use moisturizing drops, for example, Defislez, Slezin. They can be used an unlimited number of times during the day if dry eyes occur.
Features of conjunctivitis of viral etiology
For people not related to the medical community, there is no division of conjunctivitis into types - viral, bacterial or allergic, which often leads to cases of self-medication that do not give a positive result.
Pharmacies offer a wide range of medications for eye pathologies, which cannot be considered a universal remedy for all symptoms of discomfort in this area.
Conjunctivitis is just a general term for diseases that actively involve the conjunctiva of the eye, but the symptoms and causes are not always the same.
- In the bacterial form, the cause of the pathology is considered to be the active work of bacteria entering the conjunctival zone through dirty hands, the wind, the use of foreign objects, cosmetics or glasses, lenses, and features of professional activity.
- The allergic form is the result of an immune reaction to an allergen, which can enter the body in different ways and cause specific symptoms in the visual organs.
- The viral form occurs as a result of damage to the human body by viral agents, the number of which, according to laboratory studies, is more than a hundred.
It is the viral form of conjunctivitis that is subject to detailed analysis in the article, so that people with eye discomfort develop a correct understanding of the problem and the desire to self-medicate without consulting an ophthalmologist disappears.
Some viruses, such as herpes, are dormant in the body and become active if the immune system is severely weakened and there are accompanying circumstances for the activation of pathogenic microflora.
But most of the viruses, which in medicine are classified as adenoviruses, enter the body from the outside and provoke pathological processes in the nasal and oral cavities.
Conjunctivitis in this case can be considered a secondary symptom, which occurs due to the rapid spread of the agent through the lymphatic and vascular system connecting the nasopharynx with the organs of vision and hearing.
Treatment methods for each form of conjunctivitis are different. This is due to various reasons leading to inflammation of the conjunctiva and associated discomfort.
Prevention
To prevent the development of viral conjunctivitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- an annual preventive examination by an ophthalmologist with laboratory tests and the start of timely therapy if abnormalities are detected;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, especially viral or infectious in nature;
- wearing contact lenses according to the rules, maintaining sterility;
- daily hygiene procedures for hands, face, eyes;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during periods of exacerbation of diseases;
- no visiting public bodies of water with standing water;
- When in contact with an infected person, you must wash your hands with bactericidal soap and take a shower at home.
Viral conjunctivitis is a disease that affects the conjunctiva of the eyes. With timely treatment, all symptoms are quickly eliminated, and the patient completely restores the function of the visual organs. To avoid complications, you should strictly adhere to your doctor's recommendations.