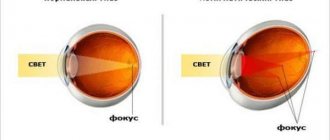
Myopia affects almost a third of the world's population. There are really a lot of people who have trouble seeing in the distance, and their number is growing. Sometimes vision begins to deteriorate in childhood, and sometimes in adults. Avoiding the appearance of myopia, stopping its progression and even improving vision - all this can be done if you seriously engage in eye exercises for myopia. By making such exercises a healthy habit, you can maintain excellent vision for many years.
What are the benefits of gymnastics for myopia?
The effectiveness of eye exercises largely depends on the degree of myopia and the presence of complications. With high myopia, especially complicated ones, it will not be possible to get rid of it with gymnastics alone. However, with a weak degree of myopia, especially with the so-called false myopia, which is caused by spasm of the eye muscles, gymnastics is very effective. Therefore, to the question whether myopia can be cured with exercises, we can confidently answer: yes, at least one type of it. Gymnastics relieves spasm of accommodation, improving visual acuity. In this article you will find the best eye exercises.
By doing the exercises, you will be able to:
- relax spasmodic eye muscles;
- increase blood flow in the organs of vision;
- activate metabolic processes;
- improve accommodation;
- make your eye muscles stronger.
Properly constructed gymnastics actively combats myopia.
Gymnastics to relax and train the eye muscles
Exercises for myopia, designed to eliminate visual fatigue, have an excellent effect, experiencing increased stress every day. This is the most suitable complex for schoolchildren, students, and office workers who spend many hours in front of computer, tablet, and phone screens. Exercises will help relax the visual organs, which is especially important for visual impairments such as myopia.
This is the gymnastics:
- We slowly draw figure eights with our eyes, trying to achieve maximum amplitude. Do 6 repetitions.
- Looking forward, place your arm straight with a raised finger in front of your eyes. Moving the limb to the right, move your gaze there without turning your head. Then repeat with the other hand. The head is fixed, only the eyes move. Do 6 repetitions.
- Place your finger 30 cm from your face, select a point far away at the same level. Look at your finger. Then begin to look at a distant point and back 12-15 times, fixing your gaze on both objects for 5 seconds. The head remains motionless.
- Standing and looking forward, slowly turn your head, shifting your gaze as you turn your head. Make 10-15 turns.
- Close your eyes tightly for 3 seconds, then open your eyes for 5 seconds. Do 15-18 repetitions. This exercise fully engages the muscles.
Training the muscles of the visual apparatus is one of the main areas of eye training for myopia.
Eye exercises for myopia
Regular exercise will strengthen the muscles of the eyeball. As a result, the visual organ becomes less tired and muscle endurance increases.
- Draw a figure eight in the air with your eyes. Movements should be smooth and slow. Repeat seven times;
- Raise your outstretched hand to eye level and look carefully at your index finger for a few seconds. Then slowly move your hand to the side, without taking your eyes off your finger. The head remains motionless. Duplicate the technique with the second hand. Perform seven repetitions;
- Gaze into the distance for a few seconds, then raise your hand so that your index finger is at a distance of thirty centimeters. Look at him, then look into the distance again. Perform ten repetitions;
- Raise your hand and place your finger at a distance of thirty centimeters from your face. Look at the finger for five seconds, close your left eye while continuing to look at the finger with your right eye. Then change them. Do twelve times;
- In front of the organ of vision, extend your hand with a pencil, move it in different directions, tracking its “journey” with your gaze. The head remains motionless;
- Stand up, place your feet shoulder-width apart, place your hands on your waist. Slowly turn the head to the right, then to the left. Move your gaze as you move. Perform twenty repetitions for each side;
- Open your eyes wide, squint, lower your eyelids. The technique trains visual acuity at different distances. Do it twenty times.
Return to contents
Gymnastics for blood circulation
Exercises against myopia can stimulate blood flow in the eyes. Blood flow is vital for the normal functioning of the complex human vision apparatus: the eyeballs must be fully saturated with oxygen.
Here is an effective set of eye exercises that improves blood flow:
- Move your gaze strictly horizontally in both directions.
- A similar movement, but vertically.
- The following movements are circular.
- Blink intensely, closing your eyes and opening your eyes.
- Squint your eyeballs, trying to see the tip of your nose.
- Place a mark on the window glass, find an object in the distance behind the glass and look at them alternately.
By increasing blood flow, you will improve the supply of oxygen to your visual organs and activate cell nutrition.
Chinese gymnastics
Among exercises for vision with myopia, one of the first places is occupied by Chinese eye gymnastics. Chinese medicine is known throughout the world as an ancient knowledge that considers the body as a complex complex, where everything is interconnected and each organ has its own biologically active points, and by acting on them, specific organs can be healed. There are also such points for myopic eyes.
Gymnastics includes four basic exercises:
- Impact on the Qing-ming point, which is located between the eyebrows: massage 35 circles with very light pressure.
- Stimulation of the Syb-ai point in the center of the cheek: also 35 movements in a circle with your fingers.
- Make 35 gentle pressures on the Tai-yang point between the end of the eyebrow and the outer corner of the eye.
- At the end of the gymnastics, you need to gently massage first the upper, then the lower eyelid.
You can find out where important points for influence are found from this video:
Such gymnastics does not include direct training of the eye muscles, but has a very beneficial effect on vision.
Avetisov method
Professor E. S. Avetisov has developed exercises to improve vision in myopia, which have a positive effect in children and adults. His technique offers several ways to train your eyesight for myopia at home. It perfectly relieves spasm of accommodation and relaxes the ciliary muscle.
This is the complex:
- Sitting position, straighten your back, do not tilt your head. Close your eyes tightly, then open them, blink every 5 seconds, repeat 6-8 times.
- Sitting in the same position, blink as quickly and intensely as possible for a couple of minutes.
- Standing, extend your right hand in front of you, stop your gaze on one of the fingers, then gradually bring it closer to your eyes, looking at the finger without looking up until the picture doubles. Do 6 to 8 repetitions.
- Without changing your position, while standing, place your finger in front of your eyes at a distance of 30 cm. Looking at the upper phalanx, cover your left eye with the palm of your second hand for 5 seconds, then open and focus on the finger with both eyes. Repeat with the left eye. Do 6-8 repetitions.
- Move the bent arm to the right and try to examine the finger, then repeat in the other direction. 10 repetitions of the exercise.
- A two-minute eye massage with your fingers in a sitting position, then a series of pressures on the eyeballs for 3 seconds 4 times.
Avetisov’s technique has established itself as a wonderful remedy for myopia.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Bates exercise system
This technique has not yet been recognized by science. A non-drug method of restoring vision was invented by William Horatio Bates. He concluded that a significant portion of refractive error develops as a result of abnormal muscle tension.
The exercises developed by Bates accustom the eyes to passive vision and relax them.
Palming:
- Take a comfortable sitting position. It will be more convenient if you sit at the table.
- Cross your fingers. Cover your eyes with your joined palms. Sunlight should not penetrate your fingers, and your palms should not pinch your nose.
- Calm your breathing and wait until the glare disappears. When maximum darkness comes, it means that the level of excitation of the nerve cells has decreased and the eyes have completely relaxed.
The second exercise is psychotechnics. A person is immersed in pleasant memories and relaxes as much as possible. Close your eyes and concentrate on something positive, try to reconstruct the event. This technique is recommended to be used with palming, but with open eyes. This can be achieved by regularly performing psychotechnics.
Bates recommends sunbathing. This system is called solarization. Close your eyelids and turn your face towards the sun. If discomfort occurs, you should blink frequently.
Complex by M. D. Corbett
Before performing the Corbett method, it is recommended to stretch your neck muscles. Complete the following exercises: Corbett is a student of Dr. Bates and has improved and developed her teacher's theory of improving visual perception without glasses or surgery. She also developed her own complex. To perform the exercises, the Sivtsev table is used. Algorithm of actions:
- Move 2 meters away from the table.
- Bring the drawn mini-table directly to your eyes.
- Read the first line from a small table, move it away, read it at arm's length.
- Look at the same line, but in a large table.
- Close your eyes and make a few turns to the sides.
- Repeat from point 1, but read the second line.
Thus you need to get to the last line. Slowly perform each step without losing your breath.
Gymnastics from R. S. Agarwal
Professor Agarwal systematized the Bates technique. Based on it, he developed his own complex. To perform this you will need an OM card.
Algorithm of actions:
- The card is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the face.
- Focus your gaze on the central part of the picture, mentally realizing that it has more contrast.
- Move your eyes around the circle, rotating your head. When moving, close and open your eyelids. Perform the exercise slowly, monitor your breathing.
- Move the card to a distance 2 times greater, but not more than 1.5 m. Perform several approaches.
Next, repeat the exercise only with half-closed eyes. Helps train the accommodative reflex and strengthen muscles.
A set of exercises from M. Windolf
Like previous professors, Windolf is a continuator of the Bates method. He pays more attention to improving accommodation. Windolf believed that the therapy was more effective in combination with relaxation of the tension of the eye muscles.
He proposed the following gymnastics complex:
- Place any object at a distance of 40 cm from the eyes. Blink, pause at times and close your eyelids completely.
- An object located at the same distance is mentally reduced in volume. When performing this exercise, squeeze the orbital muscles, which give the feeling of retracting the eyeball back.
The technique allows you to reduce the time of fatigue, relieve discomfort in the eye area and pain in the head.
Exercise system from Zhdanov
Gymnastics is prohibited during the rehabilitation period after eye surgery, if there is a threat of retinal detachment or ruptures. It is not recommended to use glasses when performing this task.
Exercises are performed at least 3 times a day for 10 minutes. This is more effective than a one-time lesson for half an hour.
Method according to Zhdanov:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Blink your eyes and sway slightly, moving from one leg to the other. Swaying, blinking your eyes. Make side turns. Do 10 repetitions, ending the exercise with blinking. Turn your head in different directions. Make sharp bends 2 in one direction. First right and left, then back and forth. After the exercise, blink again.
- Massage your hands until warm and do the following: press the inner corner and vibrate. Repeat the same with the outer corner of the eyes.
- Draw diagonals with your eyes, helping yourself with your hands. Draw a rectangle and other shapes. Shake your hands to relieve tension.
- Draw a dial with your eyes. Finish the exercise by blinking.
The gymnastics for the eyes ends with reading words. The first exercise is performed. At a distance of 1 meter, a sheet of words is attached, each line of which has smaller letters. You need to read the words while swaying.
Avetisov method
The professor’s technique gives positive results in children and adults. It relieves spasm of accommodation and relaxes the ciliary muscle.
Set of exercises:
- Take a comfortable sitting position. Keep your head straight. Close your eyes, open your eyes wide.
- Flash quickly, make intense movements.
- Extend your hand in front of you, fix your gaze on your finger. Gradually move your finger closer to your eyes until the image doubles.
- Perform a massage in a sitting position, then a series of 3-second pressure on the eyeballs.
Norbekov's technique
Dr. M. Norbekov developed a whole system for restoring vision, which he described in his book. He compiled a large set of exercises, which he uses as an eye exercise for myopia, which gives a noticeable effect of improving vision. Before gymnastics, straighten your shoulders, straighten your back and tune in to the positive.
This method of improving vision, including myopia, consists of eight exercises:
- Looking straight ahead, roll your eyeballs up as high as possible and mentally continue the upward movement, as if through your forehead. Don't throw your head back.
- The same principle as in the first exercise, but the movement goes down, and the gaze seems to be through the throat.
- We look to the left, mentally as if through the left ear. Then we move our eyes to the right and direct our gaze through the right ear.
- Exercise "Butterfly". You need to draw the outline of a butterfly with your gaze: with your head in a stationary position, your gaze moves from the lower left corner to the lower right, then to the upper left, then to the lower right, upper left and finally the upper right. Make sure that the muscles do not overstrain.
- “Eight”: with our gaze we draw the mathematical sign of infinity, that is, a figure eight lying on its side. At the end, blink to relieve excess tension after performing two difficult exercises in a row.
- Try to see the tip of your nose, then relax your eyes and try to see what is on either side of you, but looking straight ahead. Next, alternately look at the bridge of your nose - in front of you - at the side objects.
- Place both index fingers near the tip of the nose, looking at them with both eyes. Then begin to slowly move them apart in different directions, trying to see the finger of your left hand with one eye, and the right one with the other, using the lateral edges of your field of vision.
- The last exercise is to slowly move your gaze in the largest possible circle, like on a watch dial.
It is not difficult to perform such vision exercises at home, and the effect they give is colossal.
We invite you to watch the video in which you will find the necessary exercises using the Norbekov method. You can do them with us every day, for this you just need to start the video:
General strengthening exercises for myopia
To strengthen the muscles of the shoulder girdle, exercise with a ball is used:
- breast transmission;
- passing behind the head with arms raised and bent at the elbows;
- throwing a tennis ball at a wall;
- playing volleyball, badminton, basketball.
To strengthen your back muscles, you can perform the following set of exercises:
- Lying on your back, arms spread to the sides. The tennis ball is passed from one hand to the other at eye level, with each hand describing a semicircle.
- Perform a cross movement with your arms (arms crossed over your chest). The eyes follow first one hand, then the other. The head remains motionless.
- Lying on your back, swing your legs towards your opposite hand. Keep your eyes on the sock.
- Sitting with straight legs and supporting your hands behind you. Raise your legs off the floor and do cross swings. Look first at one foot, then at the other. Do not turn your head behind your eyes.
- The exercise is performed from the same position. Raise your right leg up, then to the left, then lower it. Repeat the movement with your left leg.
- From the same position, first raise one leg and make several circular movements with it. Then do the same with the other leg. Keep your eyes on your socks.
Read in a separate article: Simple exercises to restore vision in case of farsightedness
Exercise therapy is used to strengthen the neck muscles:
- Standing or sitting with a straight back, tilt your head to the right and left.
- Standing or sitting with a straight back. Tilt the head forward, then return to the starting position. Tilt of the head back (throwing back) is not recommended to avoid spasm of the vessels of the cervical spine and disruption of blood flow to the brain.
- Standing or sitting with a straight back. Lower your head onto your right shoulder, move forward and in a semicircle to your left shoulder. Then - forward and in a semicircle to the right shoulder.
- Standing or sitting with a straight back. Place the palm of your right hand extended upward and bent at the elbow joint on your left ear. Slowly pull your head towards your right shoulder with your hand until the left neck muscles tense. Repeat the same on the left side.
General strengthening exercises that affect the entire body:
- swimming in the crawl, butterfly, and backstroke styles;
- moderate intensity running;
- walking at a brisk pace;
- ice skating (including roller skating);
- skiing.
Gymnastics for myopia according to Zhdanov and Bates
The methods of Zhdanov and Bates include exercises for restoring vision in case of myopia, which have proven to be an excellent remedy for minor myopia. The essence of the exercises is to relax your vision as much as possible. The exercise should be done calmly. The less tension, the higher the chances of getting rid of myopia.
- Place a small picture in front of your face, examine it, then close your eyes and recreate the image from memory.
- Closing your eyes, imagine the bright colors of the spectrum in front of them.
- Imagine a flower in all its details, examine it, try to see it with your inner eye.
- With your eyes closed, mentally draw a letter or number, and then reduce its size to the tiniest.
Dr. Bates also developed a method - palming, which was later included in many sets of exercises by other authors.
Palming
- Rub your hands to warm them up. Close your fingers, place your palms on your face, closing your eyes.
- Feel the warmth that comes from your hands, concentrate on the sensation, and relax as much as possible.
- Spend as much time in this state as is comfortable for you.
This relaxing technique is a great preparation for other eye exercises.
For example, the complex of Dr. Zhdanov, described in this video:
Avetisov's set of exercises
Gymnastics, developed by a Russian ophthalmologist, is recommended for people who spend a lot of time on a PC or work with small parts (jewelers, watchmakers, etc.). Exercise normalizes blood circulation and strengthens muscles.
Exercises to restore vision in case of myopia:
- Sit down, straighten your back. Close your eyes for five seconds, then open your eyes wide for the same period of time. Repeat six times;
- Sit down and blink rapidly for a minute;
- Stand up with your feet shoulder-width apart. Look forward for three seconds, extend your arm and fix your gaze on your finger for five seconds. Repeat ten times;
- While standing, extend your arm in front of you and focus your gaze on your index finger. Gradually bring it closer to your eyes without looking away. It is important to achieve a split “picture”. Repeat eight times;
- Stand up and place your index finger at a distance of thirty centimeters from your face. Focus your gaze on it for five seconds, close first your left and then your right eye. At the end of the exercise, look at the finger with both eyes. Repeat eight times;
- Stand up and move your half-bent arm to the side, without turning your head, look at your index finger. Slowly move it from one edge to the other, following the movement with your eyes. Repeat twelve times;
- Sit down and try to relax as much as possible. Close your eyelids and gently massage your eyes with your fingertips for a minute;
- Sit down, close your eyes and lightly press three fingers on the upper eyelid, stay in this position for a couple of seconds. Repeat four times.
Corbett technique
Dr. M. Corbett's method is based on the classic letter chart for ophthalmic testing, so to perform her eye exercises for myopia you will need such a test chart. You can not only purchase it, but you can also make it yourself, and Corbett also recommends this. You need two tables: A3 format and a small, pocket-sized one.
Before class, you need to stretch your neck muscles and relax, prepare your eyes by palming. In a bright room, sit on a chair two meters from a large table. Take the small tablet in your hand. Read the first line, then read it at arm's length, and then look at the poster 2 meters away from you. Move from line to line until you reach the bottom one. Between lines, close your eyes and make a couple of circular movements with your head.
Such eye training gives a tangible effect of improving vision in myopia.
Agarwal technique
Gymnastics by R. S. Agarwal is also based on a vision testing table, which is called the Sivtsev table. This version of eye gymnastics for myopia helps reduce the level of myopia by activating neural connections created by visual images of letters in the human brain.
The exercise is as follows. It is necessary to look at one of the letters in the table for 5-12 seconds, then close your eyes and try to mentally recreate this letter in your mind’s eye, trying to visualize it as clearly as possible. The goal is to achieve a result in which the mental image is no less clear than the letter on the poster.
This mental exercise for the eyes helps to significantly improve the quality of vision and restore its sharpness in case of myopia.
Preparatory stage
Before starting the exercises, parents should carry out a set of preventive measures that are aimed at optimizing the work space. If the factors of external aggression are not eliminated, they will lead to a gradual deterioration of vision and then eye exercises for myopia for children will no longer help. During preparation, parents should:
- increase the child’s physical activity;
- optimize the workplace according to the child’s height to correct posture;
- ensure that the child reads books at a distance of 30 cm from his face;
- reduce the frequency of computer and phone use;
- Avoid watching TV in complete darkness.
Ischemia of the cervical spine can lead to severe stages of myopia. Beginning myopia can be accompanied by headaches, lethargy and decreased performance of the baby.
Eye exercises for myopia are prescribed only after visiting an ophthalmologist. At the appointment, the doctor puts drops into the child’s eyes to relax the eye muscles. This allows you to exclude or completely confirm the presence of a spasm of accommodation, in which the exercises will be most effective.