The immune system of children develops over the years, initially functions weakly, and has antibodies against a small number of pathogens. The child's body is most susceptible to diseases, since at this age the immune system has not yet formed.
Once in the child's body, the virus travels through the blood. It can spread to one or both eyes, causing viral conjunctivitis. This condition must be treated with medications to improve the child’s well-being without allowing complications to develop.
Causes
Most often, viral conjunctivitis is caused by a pathogen that leads to colds. This could be adenovirus, influenza, parainfluenza, and various other infections. Often the viral form manifests itself against the background of reduced immunity, which is formed as a result of a lack of vitamins in the autumn-winter period.
Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Factors that predispose to the appearance of viral conjunctivitis:
- reduced natural defenses of the body;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic pathologies;
- lack of physical activity;
- unbalanced diet.
Viruses are constantly concentrated around the child. They can cause symptoms in any eye injury. This could be bacterial conjunctivitis, foreign body getting into the eyes, or seasonal allergies.
The essence of pathology
The viral form of conjunctivitis is most often diagnosed in children. Its development is caused by different types of infection - herpes, adenovirus, enterovirus. Other infections may also be provoking factors.
However, most often such an anomaly occurs against the background of colds. The classic variant is infectious pharyngitis, which is characterized by an increase in body temperature.
If a child has damage exclusively to the eyes, this disease is isolated. In most cases, its development is provoked by a herpes infection.
Symptoms
The disease produces characteristic clinical symptoms:
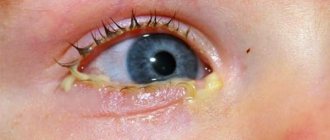
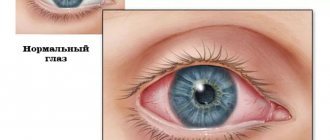
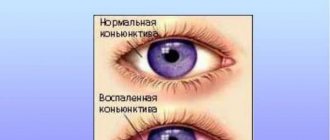
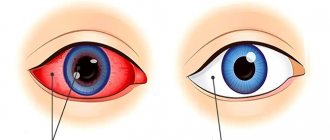
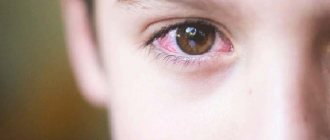
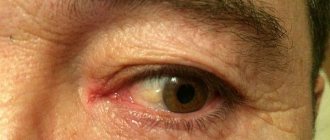
- severe redness of the conjunctiva, minor hemorrhages may form inside the cornea, which subsequently resolve on their own;
- swelling of the eyelids, which, if left untreated, becomes severe; the eyeball may be completely invisible;
- discomfort in the eyes: pain, itching, burning, sensation of a foreign body under the eyelids that is not actually there;
- increased lacrimation at the initial stage, which can often be replaced by severe dryness of the cornea, on which microtraumas and cracks form due to this;
- a common complication is elevated body temperature;
- malaise, manifested by weakness, drowsiness, constant fatigue;
- intoxication of the body with waste products of viruses - body pain, aching joints.
Gradually, the manifestation of clinical symptoms intensifies, leading to a deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
The herpetic form of the pathology develops with accompanying symptoms:
- unexpressed symptomatic picture;
- a rash appears on the inner area of the eyelid;
- there is a feeling of itching;
- follicles and ulcers form;
- scanty discharge from the organs of vision.
Conjunctivitis against the background of adenovirus infection develops with clinical manifestations:
- simultaneous damage to the nasopharynx and visual mucous membranes;
- the pathology begins in one eye and gradually affects the second;
- the disease is accompanied by high fever;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- a film forms on the surface of the eyeball;
- when the film is removed, bleeding spots appear;
- due to the healing of torn areas, scars appear;
- disturbances in the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The epidemiological type of conjunctivitis is characterized by symptoms:
- headache;
- the appearance of purulent contents in the visual apparatus;
- general weakness due to intoxication;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the area under the jaw;
- intense hyperemia of the visual apparatus;
- conjunctival infiltration;
- after a week's interval there is a significant improvement, which doubles before recovery.
Photo
Classification of types of disease
Infectious conjunctivitis in children is divided into bacterial, fungal and viral types. Viral conjunctivitis, in turn, has subtypes in accordance with its causative agent. The most common forms:
- Epidemic hemorrhagic. Caused by enteroviruses (these are pathogens of intestinal disorders). A distinctive feature is hemorrhages around the iris of the eye, which is why this conjunctivitis is called hemorrhagic. It received the name “epidemic” due to its high contagiousness (infectiousness). The virus is easily transmitted from person to person, causing epidemic outbreaks, especially in children's groups - schools, kindergartens. Often only one eye is affected.
- Herpetic viral conjunctivitis. Caused by the herpes virus, it is found everywhere. Its distinctive diagnostic feature is characteristic herpetic rashes. They are usually localized on the surface of the eyelids and on the wings of the nose. Follicles and ulcers appear in more severe cases.
- Adenoviral conjunctivitis is more common in children than in adults. Outbreaks of adenovirus infection are common in kindergartens and, to a lesser extent, schools. Adenovirus causes not only local damage to the eyes, but generally proceeds like an acute respiratory viral infection: with increased body temperature, runny nose, sneezing, and sore throat.
There are three forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- catarrhal: passes quickly, the course is mild;
- follicular form: characterized by the formation of follicles, a more severe course;
- membranous form: characterized by the formation of grayish films on the surface of the eye.
Contagious or not
A patient whose blood has been infected with a viral agent is considered infectious throughout the course of the disease. This effect extends to the incubation period, since the virus is also located in the respiratory tract. The distribution routes are:
- airborne droplets from breathing, sneezing and talking;
- personal hygiene items, for example, toothbrush, towel;
- various household items;
- skin-to-skin contact;
- interaction with the blood in which the pathogen is concentrated.
Therefore, from the moment the disease is detected, it is recommended not to contact the patient so as not to spread the infection.
Treatment
To achieve a quick recovery, it is recommended to carry out complex therapy aimed not only at eliminating pathogens and relieving unpleasant symptoms, but also at normalizing immunity. It is necessary to use drug therapy as the main method of treatment.
You can use traditional methods of treatment, but as an additional remedy.
Eye drops
It is necessary to use antiviral eye drops, since the drug will be concentrated in the lesion. This will help achieve maximum effect:
- Aktipol. Antiviral agent for topical use. It must be used 3-5 times a day. It is possible to increase the dosage as prescribed by the doctor if the patient experiences severe swelling and redness. Once all symptoms have resolved, the medication must be continued to prevent recurrence of the condition. Even in the absence of signs, the virus can be concentrated in tissues.
- Sodium sulfacyl . It is acceptable to prescribe the drug to infants, but they are prescribed a 10% solution. Instillation is carried out up to 6 times a day, which depends on the etiology and stage of the disease. Side effects may include increased lacrimation and a slight itching sensation.
- Poludan . Drops stimulate the immune response to damage by viral microflora. The main component is interferon. Possible use for newborns. The drug has antiseptic properties. The maximum dosage per day is 4 instillations. If side symptoms occur, discontinuation of the drug is necessary.
- Oftan-Idu . The medicine destroys the DNA of the herpes virus. It has a whole range of side effects. Prescription for children under 2 years of age is prohibited.
- Oftan. This is a medicine that can be used from 2 years. It is recommended to start using the drug in the first hours or days of illness, 1 drop every hour. It is necessary to instill the remedy at night in order to soften the clinical symptoms of the disease, as well as reduce the time for symptoms to appear. Intensive treatment must be continued until the symptoms are eliminated, then the use of the medication can be reduced.
- Oftalmoferon. An antiviral drug that not only eliminates the action of the pathogen, but also relieves pain, itching, and burning. It can be used up to 8 times a day, 2 drops in each eye. Therapy is carried out until symptoms disappear completely and then for 3-5 days.
- Visine. This medicine belongs to the vasoconstrictor category, so it can be used for no more than 4 days. After this time, addiction develops. The drug effectively eliminates swelling, redness, and inflammation.
- Interferon. These are medicinal drops that contain interferon similar to human interferon. It is used to improve the functioning of the immune system in the affected area. Thanks to it, an immune reaction is formed more quickly, which is aimed at suppressing and destroying the viral agent.
The peculiarity of antiviral medicinal drops is the lack of addiction and resistance in pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, they can be used for several months in a row until the disease is completely eliminated.
Ointments
If you put the ointment in your eyes, the effect will happen faster. But they cannot be used for all ages:
- Florenal. This is a medicine that eliminates the herpes virus. It must be placed under the lower eyelid in a long course 3 times a day. It is recommended to do this before going to bed so that excess medicinal substance is not eliminated from the eyes.
- Tebrofen ointment. This is a drug that is active against many viral agents. Has a minimum of side effects. It can be used for up to 4 days. Before going to bed, you can put it under the lower eyelid, and during the day - smear it on the inner corner of the eye.
- Bonafton. This is a drug that fights viruses. Its advantage is the absence of side effects in the form of dryness and itching on the skin. It must be used for at least 1 month.
- Zovirax . The active component of the drug is acyclovir. Apply until symptoms disappear. The first therapeutic effect is visible after three days of application.
- Virolex . The medicine actively eliminates viral microflora. The use of the drug may be accompanied by side effects, which are expressed through burning or irritation.
Before using the ointment, it is recommended to read the instructions for use, identifying at what age the product can be used.
Viral uveitis
Inflammation of the vascular tissue in the eye often occurs; it can occur in different parts of the eye, and the common name for the disease is viral uveitis. In terms of the number of visits to an ophthalmologist, uveitis accounts for about 30% of all visits. Serious consequences associated with partial loss of vision and further blindness occur in 15%. Such a high risk of bad consequences is associated with late seeking help from a doctor. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should contact an ophthalmologist for help.
The disease can occur for various reasons: physical impact (injury), viral diseases, or other diseases. Scientists have not studied the exact nature of its appearance. The most common development of uveitis is due to the herpes virus, as well as herpes zoster or cytomegalovirus. Symptoms of uveitis viral eye infection cause:
- discomfort in the eyes;
- redness of the surface;
- blurred vision, spots;
- fear of bright light;
- copious discharge of clear fluid from the eyes.
Due to slow blood circulation in the vessels of the eye, microorganisms accumulate. When a person’s immunity weakens, they begin to lead an active lifestyle, which results in illness.
Complications
In the absence of therapy or its incorrect implementation, the following complications of the disease may occur:
- development of secondary bacterial conjunctivitis, which leads to suppuration of the eyes and gluing of eyelashes;
- spread of a viral agent from the eyes throughout the body, leading to systemic disease;
- development of bacterial infection in neighboring organs and tissues, for example, sore throat, sinusitis, tracheitis;
- a decrease in visual acuity for a time, as an acute inflammatory state of the outer parts of the eyeball develops.
To avoid complications and restore the patient’s normal state of health, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist. He will prescribe the right treatment, which must be followed in a strict dosage of drugs.
Diagnostics
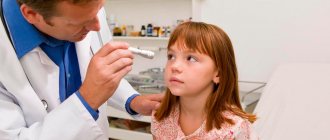
To identify the viral form of the disease, you should undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist. He must assess the condition of the mucous membranes and analyze the baby’s complaints. In addition, the presence of additional ailments should be determined.
If chronic anomalies are detected, consultation with specialists will be required.
To establish the type of pathogen and choose the right medications, you need to take a scraping of the material for research. Based on the examination data, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and select therapy.
Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis. A repeat visit to the ophthalmologist is carried out 7-10 days after treatment.
Komarovsky about viral conjunctivitis in children
Pediatrician Komarovsky adheres to several rules when treating viral conjunctivitis:
- the use of traditional medicine to treat diseases in children is prohibited;
- urgently visit an ophthalmologist at the first manifestations of pathology;
- it is recommended to eliminate the factors provoking the disease;
- it is necessary to balance the patient’s diet to increase the body’s immune strength;
- taking antibiotics will only intensify the manifestations of a viral disease and weaken the local protective reaction;
- during the active phase of the disease, it is necessary to rinse the organs of vision with sodium chloride;
- Before instilling the medicine, you must take care to clean your hands;
- for a quick recovery, you must strictly follow the course prescribed by your doctor;
- Before instillation, the medicine must be warmed in the hand for about 2 minutes;
- It is prohibited for the drug packaging to come into contact with the patient’s mucous membranes;
- Before instillation, it is recommended to wipe the eye with a clean cotton pad to remove secretions.
Following the recommendations will speed up the baby's recovery.
Does conjunctivitis affect vision?
In 90% of cases, conjunctivitis does not pose any particular danger to the child.
It often even goes away on its own, without drug intervention, only thanks to the active fight of the immune system.
No one dares to say that inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye cannot affect visual acuity.
There are such severe forms of this disease that can cause irreversible consequences. Therefore, for any dysfunction that lasts more than two days, you should definitely consult a specialist.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, it is recommended to adhere to the following preventive rules:
- timely treatment of systemic diseases;
- lack of contact with infected people;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during an epidemic of infections or viral diseases, especially in the autumn-winter period;
- proper nutrition containing large quantities of vitamins, trace elements and minerals to support immune function;
- availability of vaccinations against viral diseases;
- compliance with all hygiene rules, for example, frequent hand washing, hygiene procedures in the mornings and evenings;
- wearing contact lenses strictly according to the rules to prevent deterioration of the eye microflora;
- periodic visits to an ophthalmologist to promptly check your vision organs and carry out the necessary treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis can be dangerous for a child. If left untreated for a long time, the eyeballs may become inflamed and the eyelids may swell. It is recommended to use antiviral medications, which will prevent many complications for the patient in time.