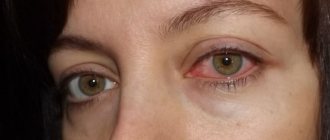
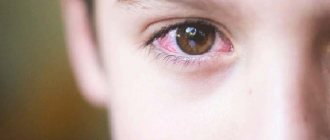
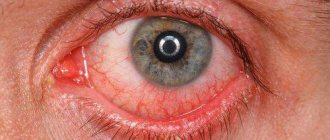
Bacterial conjunctivitis in children is a common disease that develops due to infection in the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva). Bacterial conjunctivitis is more common in children than in adults, and can be distinguished by copious purulent discharge. Is this dangerous and how to treat such a disease?
Causes
The main causes of the bacterial form of conjunctivitis are the following conditions and diseases:
- reproduction of pathogenic microflora in front of the eyes due to the influence of external negative factors (low temperature, swimming in a polluted body of water);
- violation of personal hygiene rules, for example, many children forget to wash themselves in the mornings and evenings, scratch their eyes with dirty hands, and rarely wash them;
- complications of a bacterial infection as a result of the appearance of another primary disease (allergy, virus);
- narrowing and blockage of the lacrimal duct, in which pathogenic microorganisms accumulate, causing suppuration;
- infection with a bacterial infection from other people; it may be a microbe that did not previously exist as part of the normal microflora (pneumococcus, chlamydia).
Despite the many types of causes, bacterial infections almost always resolve in the same way. But the doctor needs to identify the root cause to prevent the condition from reoccurring.
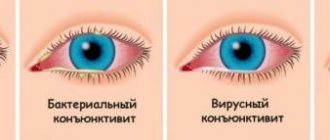
How to distinguish bacterial conjunctivitis from other forms
The main difference between bacterial conjunctivitis and other forms of the disease is the formation of suppuration. It cannot occur in other pathologies. The only exception is the formation of a bacterial complication. For example, a child could develop viral conjunctivitis, which, if left untreated, activates pathogenic microflora, causing secondary bacterial conjunctivitis with the formation of pus.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature, since the source of infection is localized only in the eyes. In the morning, the patient's eyelashes are stuck together and he cannot open one or both eyes. The patient's condition improves significantly with the first or second dose of an antibacterial agent in the form of drops or ointment.
Other forms of conjunctivitis require long-term treatment.
Symptoms
With the bacterial form of conjunctivitis, typical clinical symptoms develop:
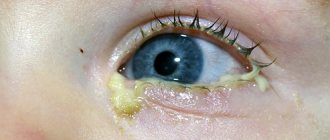
- the formation of pus from the inner corner of the eyes, which spreads over the eyelids and mucous membrane, sticking the eyelashes together in the morning, so the patient cannot open his eyes without first washing his face;
- severe swelling of the eyelids, when bacteria are widespread, the patient’s eyeball becomes invisible;
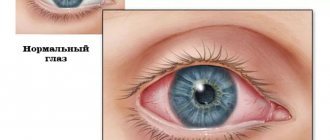
- redness of the conjunctiva, which becomes very inflamed and irritated, minor hemorrhages often form in the cornea, which gradually resolve on their own;
- photophobia, that is, under the influence of sunlight or artificial light, the patient cannot open his eyes, he experiences a spasm of the eyelids;
- Increased lacrimation occurs in the initial period of the disease, then it can be replaced by constant dryness of the mucous membrane, which leads to damage to the cornea, injuries and microcracks form on it.
Depending on the pathogen that caused the irritation, as well as on the duration of the disease, the pus may change its color. It can be whitish, yellow, green, and also brown. Despite the difference in color, all this is bacterial suppuration.
Factors that provoke the development of conjunctivitis
Two years is an important period in the life of a child who begins to actively explore the world around him. The baby likes to touch objects, so he wants to touch everything with his hands. When he is at home, in a familiar environment to which he has already adapted, his body steadfastly resists bacteria and viruses that are on various surfaces. If conditions change: interaction with another environment while visiting, in a kindergarten group, places with large crowds of people, the child’s body may not be able to cope with such a load. The immunity of a 2-year-old child, formed by this moment, is not strong enough to resist various viruses and bacteria, and is therefore vulnerable.
Conjunctivitis in a 2-year-old child - what can cause the disease:
- weakened immunity, frequent colds;
- lack of hand hygiene, sharing of toys and towels;
- chronic, systemic, ophthalmological diseases.
What are the causes of conjunctivitis? Against the background of colds and viral diseases, frequent use of antibiotics, protective functions weaken, which is why conjunctivitis develops. The mucous membrane of the eyes of a healthy 2-year-old child, even if an infection gets on its surface, neutralizes the threat, since with a normal volume of tear fluid, lysozyme, which is part of the tear, is active. This is a protein that has antibacterial and antiviral effects.
A child’s body with reduced protective functions will not be able to cope with a large number of viruses and bacteria that it has not previously encountered. This vulnerability will manifest itself in the form of frequent colds with conjunctivitis. How to treat conjunctivitis in a 2 year old child? First of all, you need to consult a specialist. The treatment of conjunctivitis is carried out by a pediatrician who, depending on the type of causative agent of the disease - viruses or bacteria - prescribes a treatment regimen. If complications of conjunctivitis appear at 2 years of age, the child will need to consult an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
To treat the disease, it is recommended to use complex treatment, which consists of medications and traditional methods. In this case, the patient’s condition will improve faster and the risk of relapse will be reduced.
Medicines
Drug treatment is the main point for eliminating a bacterial infection. For this purpose, antibacterial and antiseptic drugs are used, which are used only locally. Thus, patients will have less possibility of adverse reactions and deterioration in well-being.
Eye drops
This is the most important remedy for eliminating bacterial conjunctivitis. For these purposes, Levomycetin, Tobrex or Tobradex, Vigamox, Ceftriaxone are used. If the patient has never undergone bacterial treatment, any drug can help.
If a child has resistance to certain drugs, doctors recommend bacteriological culture. The study determines not only the exact type of pathogen, but also the antibiotic to which it is sensitive.
Antibiotic eye drops should be placed in the eyes only as directed. To do this, the pus is first removed with an antiseptic solution, only then the liquid is instilled onto the area of the conjunctival sac. In this case, the person must have clean hands, and the bottle should not touch the mucous membrane of the eyes.
This is necessary to prevent bacteria from penetrating inside the droplets.
In addition to antibacterial agents, the doctor may prescribe an antiseptic. Albucid is most often used for these purposes. Its disadvantage is a burning sensation in the eyes.
Ointments
During the daytime, doctors prescribe the use of drops. But at night, pathogens can accumulate inside the eyes to completely eliminate the effect of the drops. Therefore, it is recommended to use antibacterial ointments:
- Erythromycin;
- Tetracycline.
The drugs can be applied in two ways:
- superficial application to the corner of the eyelids;
- placing the product on the inside of the lower eyelid, which should be done only before bedtime, so that excess drug does not come out of the eye when it opens.
The pathogenic microflora must also be sensitive to the ointment for it to have an effect.
Cleaning and disinfection
If pus has accumulated in the patent's eyes, eye drops or ointments should not be used immediately. It is necessary to first clean the ocular surface so that the drug gets into the affected areas. For cleansing, use saline solution or Furacilin. The saline solution does not have any antiseptic properties, it only cleanses. Furacilin is an antiseptic that suppresses the growth of pathogenic microflora.
To get a greater effect from Furacilin, it is recommended to increase the concentration of the active substance. To do this, 1 tablet is diluted in 100 ml of water, and not in 200 ml, as usual.
To cleanse, apply the liquid to a cotton pad and wipe the eyes from the outer to the inner corner. After cleansing, all pus must be removed so that the following medications can be applied.
Antibiotics
Systemic drugs are used only in cases of complications. This may be the penetration of a bacterial infection into the sinuses or tonsils. The drug enters the bloodstream, affecting the entire body as a whole. Therefore, the risk of side effects from the drug increases. Amoxiclav, Suprax, Zinnat and other drugs are often used.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is used only in combination with medications. The following herbs are used for these purposes:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- Oak bark;
- coltsfoot.
All these plants have an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing effect. They relieve irritation and redness. The negative side of traditional medicine is the increased possibility of side effects in the form of allergic reactions. Therefore, it is recommended to use such decoctions and tinctures only as prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children aged 2 years
Children as young as 2 years old find it difficult to tolerate diseases such as conjunctivitis. The main difficulty is that therapeutic manipulations are painful and unpleasant, and therefore 2-year-old children begin to be afraid of them. Resistance during eye drops can lead to insufficient therapeutic effect, since the required amount of the active substance does not enter the body. Therefore, it is important for parents to establish trusting contact with the child, reassure him, and carry out treatment without using violent measures.
How is childhood conjunctivitis treated:
- allergic - such conjunctivitis in children aged 2 years is treated with the use of antihistamines, which quickly eliminate symptoms such as swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva;
- bacterial - treatment of conjunctivitis involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics that are active against staphylococcus, streptococcus, etc., usually a specialist prescribes eye drops “Sulfacil”, “Albucid”, “Tobrex”;
- viral - to relieve the symptoms of viral conjunctivitis in a two-year-old child, drugs such as Acyclovir, Zovirax, Floxal are used.
How to treat conjunctivitis in a child with ointments? In some cases, treatment with ointments may be indicated. You will need to place them behind the lower eyelid, squeezing out a thin strip of medicine 0.5 cm long from the tube. This manipulation can be problematic for children aged 2-3 years, because the ointment must be carefully placed behind the eyelid, and the child must be calm. Such ointments are really effective, you should not refuse them, as they are necessary to soften the skin of the eyelids and relieve swelling. Use the ointment no earlier than half an hour after using the drops so that each medicine has the desired therapeutic effect. To wash the eyes and remove purulent discharge, it is best to use warm solutions of furatsilin, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and dill seeds.
Complications and consequences
If medications are not prescribed on time, the following complications may occur for the human body:
- severe swelling of the eyelids, due to which the eyes are not visible;
- movement of the pathogen into neighboring tissues and organs with the development of a secondary bacterial infection (otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis);
- infection entering the eyeball, which causes clouding and decreased visual acuity;
- contact of a bacterial pathogen with the muscle tissue of the eyes, which can relax it and cause strabismus;
- movement of infection into the blood, which occurs extremely rarely, but can cause sepsis, which is dangerous to human life and health.
To completely eliminate the risk of complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis, but not to carry out self-treatment.
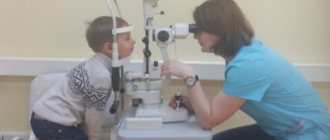
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out on the basis of clinical manifestations, medical history, external examination of the conjunctiva, and the nature of the discharge. Differentiation is carried out with keratitis, blepharitis, uveitis. In order to correctly prescribe treatment, it is necessary to determine the etiology of the disease and differentiate it from viral or allergic conjunctivitis.
For this purpose, bacteriological and cytological examination of the discharge . The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined. If you suspect conjunctivitis of a specific etiology, you may need to consult a venereologist.
What Doctor Komarovsky says
Dr. Komarovsky says that bacterial conjunctivitis must be treated with topical antibiotics. Self-therapy cannot be carried out. If the disease occurs in children, it is necessary to use only those medications prescribed by the doctor. It is also necessary to maintain normal conditions in the room where the child is constantly located.
The ambient temperature should be no higher than 20 degrees, the set humidity in the room should be approximately 70%. The doctor says that antibiotics should not be used orally unless complications arise. The bacterial form of conjunctivitis can be cured with drops and ointments.
Prevention
To prevent the disease, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- frequent hand washing and other hygiene rules;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during an epidemic of viruses or infections;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, as well as other forms of conjunctivitis, so as not to cause activation of pathogenic microflora in the eyes and other organs;
- use contact lenses only according to the rules, subject to hygiene conditions;
- a preventive visit to an ophthalmologist in order to promptly identify any deviations in the development and condition of the visual organs.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is not a dangerous disease that can be eliminated with timely treatment. But in the absence of drug therapy, the possibility of complications increases, which worsens the patient’s condition.
Kinds
The following types of bacterial conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- staphylococcal – caused by staphylococci. Often occurs in newborns after discharge from the hospital;
- pneumococcal – caused by pneumococci;
- diphtheria. Occurs in children suffering from diphtheria;
- blenorrheic. Infection occurs during childbirth due to the presence of STIs in the mother (a group of infectious diseases, the main route of transmission of which is unprotected sexual contact. A number of such infections pass from an infected mother to the baby during pregnancy, during childbirth and during blood transfusion).
- diplobacillary (angular). Caused by diplobacillus, which is transmitted by airborne droplets;
- catarrhal It can be specific (prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane of the eye) or nonspecific (due to weakened immunity and activation of pathogenic flora present in the body).