Causes
This disease occurs due to damage by such pathogenic microorganisms:
- chlamydia;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- Koch-Wicks bacteria;
- pneumococci.
It is worth considering that in a healthy person with high immunity, bacteria can remain in the body for a long time. At the same time, they do not negatively affect the visual organs. The development of the disease may be accompanied by the following factors:
- decreased immunity due to age-related changes;
- abnormal development of the eyelids;
- improper use of contact lenses (expired products, poor care of optics);
- lack of hygiene;
- injuries of various etiologies;
- dry eye syndrome.
Each person may have individual reasons for the development of bacterial damage.
Features of the disease in childhood
Bacterial conjunctivitis most often affects children.
The development of the disease is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms that, when they enter the conjunctival sac, provoke the development of inflammation. It is almost impossible to quickly cure bacterial conjunctivitis in children, since the disease is severe and requires long-term therapy. Infants often experience blenorrhea, a type of conjunctival lesion that is caused by gonococci and chlamydia that live in the birth canal of the mother through which the child passes. Its distinctive feature is that both eyes are affected at once, which significantly complicates the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis.
In children, the immune system is still weak, it is not able to block the bacteria that cause conjunctivitis of the eyes, so the disease is very severe and is accompanied by complications. If left untreated, bacterial conjunctivitis leads to perforation of the eye mucosa, ulcers on the cornea, and blindness.
Blennorrhea usually manifests itself immediately with the release of pus from the eyes and swelling of the eyelids. If a baby is infected with Staphylococcus aureus in the maternity hospital, then conjunctivitis is complicated by blepharitis and tends to become chronic.
Acute bacterial conjunctivitis depends on the season (it appears more often in autumn and winter). Most often it is diagnosed in children aged 2-7 years due to a weak immune system and in children's institutions it becomes an epidemic.
Parents should know whether bacterial conjunctivitis is contagious, because in young children the conjunctiva is still very tender and inflammation develops very quickly when it is exposed to pathogenic bacteria. Behavioral characteristics of children contribute to the spread of bacterial conjunctivitis. They often touch their eyes with their hands, not only their own, but also those of other children, use shared toys, and play in the sand. The disease is especially severe in premature babies, whose immunity is greatly reduced.
Read in a separate article: Why conjunctivitis in an adult does not go away for a long time: what to do?
Treatment is carried out with the same drugs as for adults, with the difference that the pediatrician prescribes a pediatric dose, and eye washes are more often used. Before treating bacterial conjunctivitis in children, it is worth knowing that some drops are not allowed to be used until a certain age. Thus, Ciprofloxacin is not prescribed to children under one year of age, and Levomecitin is not prescribed to children under 2 years of age.
Risk group
People with the following factors are at risk:
- autoimmune diseases;
- decreased protective functions of the body;
- chronic diseases of the eyes and eyelids (blepharitis, dry eye syndrome);
- injuries;
- infectious skin diseases;
- sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis;
- violation of sanitary standards in living and working premises.
The risk of encountering such a disease is always present. Often affects young children, especially under 1 year of age.
Complications and prognosis
If you do not start treating the disease in time under the supervision of a doctor, it risks becoming chronic, which is more difficult to cure. Complications of varying severity are also possible:
- dry eye syndrome;
- ulcerative keratitis (purulent ulcer) – ulceration of the surface of the cornea;
- formation of scars on the cornea of the eye;
- corneal clouding.
In some cases, advanced bacterial conjunctivitis leads to irreversible changes in the eye, leading to a serious decrease in vision. Therefore, it is necessary to treat the disease in a timely manner and under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
Self-medication leads to sad consequences: without the help of a specialist, it is very easy to confuse the forms of the disease and begin to be treated incorrectly.
Classification
Given the progression of inflammation, this disease can develop in different ways. This type of conjunctivitis has the following classification:
- Fulminant. Inflammation is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Severe swelling of the visual organs occurs, and purulent discharge appears. The danger is that there is a high risk of complications.
- Spicy. Symptoms develop slowly and appear unexpectedly. With timely treatment, successful results occur within 2 weeks.
- Chronic. In this form, the disease is accompanied by the constant presence of symptoms, but they are mildly expressed. Long-term treatment leads to an exacerbation of remission.
In a healthy person, tear fluid has a protective function against infectious and bacterial damage. It moisturizes the mucous membrane, and in the process of blinking it washes away pathogenic microorganisms. In newborn children, such functions are not fully developed. They often have staphylococcal conjunctivitis.
Rare forms of this disease:
- gonococcal - recently very rarely encountered in medical practice, the reason is associated with the presence of gonorrhea, which is sexually transmitted, accompanied by severe swelling and copious purulent discharge;
- pneumococcal - in most cases occurs in childhood, symptoms develop rapidly, have pronounced features, treatment is long-term, the method of cauterizing the conjunctiva with a silver solution is often used.
It is very important to determine the form of the disease, since treatment depends on it.
Conjunctivitis
Allergy
Herpes
Fungus
4567 06 November
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Conjunctivitis: causes, classification, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the outer mucous membrane of the eyeball and the inner surface of the eyelids of various nature.
Conjunctivitis is the third most common eye disease, and in children the infection is often bacterial in nature.
According to the definition used by Russian ophthalmologists, conjunctivitis is irritation of the conjunctiva of the eye in response to various factors, manifested by redness (hyperemia), swelling and itching of the eyelids, often complicated by visual impairment due to the spread of the pathological process to the cornea - the outer shell of the eye (with the development keratoconjunctivitis).
Causes of conjunctivitis
The causes of conjunctivitis include failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (infections enter the eye mucosa through dirty hands), decreased local and general immunity, the presence of allergic diseases, as well as the use of lenses, improper care of them and the use of damaged or expired lenses.
Classification of conjunctivitis
According to
the duration of the flow,
they are distinguished:
- Acute – symptoms of the disease last less than 4 weeks.
- Chronic – the disease lasts more than a month.
For the reason
that caused conjunctivitis:
- Viral (the main causes are adenovirus, human herpes virus, enterovirus, molluscum contagiosum virus, etc.).
- Bacterial. Typically, bacterial forms of conjunctivitis develop as a result of the addition of a secondary infection to an existing viral conjunctivitis. Children are diagnosed more often than adults. Bacteria that cause the development of this pathology include Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, gonococcus, and streptococcus.
- Allergic. Allergic conjunctivitis can be either an independent disease or observed together with other allergic manifestations (for example, hay fever). The following types of allergic conjunctivitis are distinguished: seasonal (for example, when weeds and trees bloom), year-round (if the allergen constantly circulates in the air - animal dander, dust mites), contact (for example, an allergic reaction to decorative cosmetics).
- Physical (due to physical or chemical exposure). When the mucous membrane of the eye is exposed to a chemical (low-quality cosmetics, household chemicals, etc.) or a physical agent (light of excessive intensity, radiation, mechanical impact on the mucous membrane of the eye), nonspecific inflammation develops.
- Autoimmune (urethro-oculosynovial syndrome, for example, with genitourinary or intestinal infections).
Symptoms of conjunctivitis
Regardless of the cause, conjunctivitis always begins acutely.
The occurrence of photophobia most often indicates involvement of the cornea in the process, which is fraught with a significant decrease in vision in the absence of proper treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis
- Herpetic conjunctivitis first affects one eye, then the infection can spread to the second. The development of the disease is sluggish, the symptoms are not clearly expressed. The appearance of swelling and redness of the eyelid is characteristic; there may be typical herpetic blisters with transparent contents; when a secondary infection occurs, a mucopurulent discharge appears.
- Adenoviral infection (pharyngoconjunctival fever) is an acute disease accompanied by a runny nose, fever, sore throat with possible enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. Eye damage is usually gradual - first one eye is affected, and after 72 hours - the second.
- With conjunctivitis caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus, mucus secretion from the eye and the formation of nodules with a concave center on the eyelids are disturbing.
- Viral conjunctivitis is also characterized by rapid spread in crowded groups (in kindergartens, schools).
Bacterial conjunctivitis
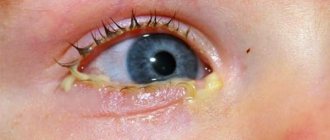
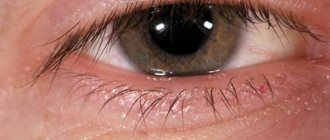
A distinctive symptom is the difficulty of opening the eyelids after sleep due to copious purulent discharge; in the early stages of the disease, the appearance of white threads when opening the eyes.
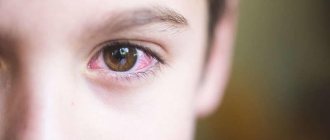
Bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized by sharp redness of the conjunctiva of the eye, a burning sensation in the eye, a feeling of a foreign body (sand), and the appearance of pathological discharge (pus).
In newborns, gonococcal conjunctivitis can develop due to infection during childbirth. Most often appears on the 2nd–5th day of life. A similar picture occurs when a child is infected with chlamydia.
Allergic conjunctivitis The development of symptoms of the disease occurs immediately after contact with the allergen or after a short time (up to 48 hours). There is profuse lacrimation. Over time, the secretion thickens, when a secondary infection occurs, it becomes cloudy and purulent. The patient complains of itching, burning in the eyes, redness of the eyelids (the lesion is often symmetrical (both eyes at once)). Soon these symptoms may be joined by a runny nose (this is due to swelling of the nasolacrimal duct), photophobia (if the cornea is involved in the process), and decreased visual acuity.
According to the course of the disease, acute allergic conjunctivitis is distinguished (if contact with the allergen is one-time or very rare, such a disease passes quickly, in mild cases it is enough to simply stop contact with the allergen) and chronic (in this case the contact is regular, the symptoms are wave-like and less pronounced - more often with allergies to house dust mites).
Physical conjunctivitis
Symptoms of this disease develop immediately after exposure to an irritating agent: burning, discomfort, itching, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, lacrimation, redness of the eyelids and eyeball.
Urethro-oculosynovial syndrome
Urethro-oculosynovial syndrome (previously called Reiter's syndrome) develops in response to the penetration of sexually transmitted infections (in particular, chlamydia) into the body, autoimmune inflammation, when the body's own cells of the synovial membrane of the joint, the mucous membrane of the eye and the urethra are perceived by the body as foreign. In addition to the eye symptoms of conjunctivitis, the patient is concerned about pain and swelling of large joints. Conjunctivitis is often purulent in nature. It is possible to develop iridocyclitis - inflammation of the middle (choroid) membrane of the eye, including the iris, which causes pain in the eyeball and its hyperemia (redness), clouding of the cornea, lacrimation and photophobia are characteristic.
Diagnosis of conjunctivitis
Diagnosis of the disease is based, first of all, on examining the affected eye and collecting anamnestic data to identify the factor that caused the development of conjunctivitis. An obligatory part of diagnostic measures is checking visual acuity. If necessary, scrapings of the conjunctival mucosa are taken (in particular, to identify the DNA of microorganisms), culture of pathological discharge from the eye, including an expanded spectrum of antibiotics and to identify molluscum contagiosum. Consultations with related specialists (for example, otolaryngologist, allergist, rheumatologist, etc.) are often required.
Symptoms
This disease is mainly accompanied by severe symptoms. A person observes such changes, especially after a night's sleep. The main symptoms include:
- profuse purulent yellow discharge, which is observed in large quantities in the morning (this leads to sticking of the eyelids and difficulty opening the eyes);
- sensation of foreign bodies in the eye;
- irritation, burning sensation that occurs against the background of dry mucous membranes;
- pain;
- swelling of the conjunctiva;
- increased lacrimation;
- sensitivity to light;
- Rarely, pinpoint bleeding may occur.
It is important to consider that in most cases the lesion begins in one eye, and after a few days it spreads to the second. It is very important to maintain good hygiene.
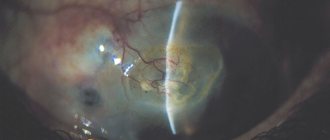
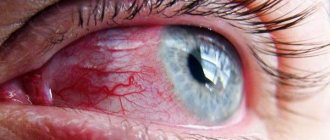
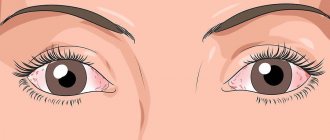
Photo
In the images you can see how this disease manifests itself:
Bacterial and viral conjunctivitis: what is the difference between the diseases?
Sometimes the bacterial form of the disease can be confused with a viral one, and then the treatment will be ineffective, which will lead to complications in the future. This happens because the symptoms of conjunctival lesions are very similar. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the exact root cause of the disease and only then begin treatment. To do this, you should visit an ophthalmologist and undergo all the necessary examinations.
Features
| Viral | Bacterial |
| Only one eye is affected | Initially, one eye is affected, then the infection spreads to the second |
| Among the first characteristic symptoms are redness of the eyeball and severe tearing. | Redness and tearing are practically not expressed. On the contrary, purulent discharge is clearly visible |
| Eyelashes stick together due to the secretion of mucus | Eyelashes stick together due to excessive discharge of pus |
| 80% of cases develop viral conjunctivitis, which, if not treated promptly, turns into a bacterial form | Infection occurs due to the contact of pathogenic bacteria on the membrane of the eye (chlamydia, staphylococcus) |
Diagnostics
Only an ophthalmologist can establish an accurate diagnosis after a full examination. Initially, a visual examination is carried out, and then biomicroscopy is prescribed. With the help of such an examination, you can determine any abnormalities in the eyes, detect foreign bodies, and carefully examine the condition of the cornea, conjunctiva, and iris.
Diagnostics helps to identify the disease at an early stage of development. Biomicroscopy is performed using a slit lamp. Inspection of the anterior portion is necessary to identify corneal defects. To determine the classification of conjunctivitis, a smear is taken for bacteriological examination. You can get the result within 7 days. This analysis allows you to identify a specific type of bacteria.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The signs of bacterial conjunctivitis are eloquent, so diagnosis usually does not present any difficulties for the doctor. With the bacterial form, the following complaints are noted:
- sensation of a foreign body, sand in the eyes;
- the eyes become very red, blood vessels appear on the cornea;
- swelling of the eyelids appears;
- pus is discharged profusely.
When diagnosing, it is important to distinguish the bacterial form from the viral one. They have certain differences: with the viral form, there is no copious discharge of pus (instead, mucus is released), severe lacrimation is observed, which is usually not present with the bacterial form.
The final diagnosis is made after laboratory diagnostics. Sowing a smear allows you to determine which pathogen caused the inflammation and prescribe a drug effective against bacteria.
Treatment
Treatment depends on many factors: stage, extent and form of the lesion. Basically, complex therapy is prescribed. The duration depends on the form and cause of the disease. Folk remedies are prescribed as adjuvant therapy in the absence of contraindications.
Ointments
After diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe the following ointments:
- Erythromycin;
- Gentamicin;
- Tetracycline.
They are put in overnight. Ointments have antibacterial, antimicrobial, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effects. Indispensable in the treatment of conjunctivitis.
Drops
Drops effectively help in the treatment of any type of this disease. Solutions for instillation have approximately the same mechanism of action. Such ophthalmic drops include:
- Ciprofloxacin. A drug from the group of broad-spectrum antibiotics. It has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms and prevents their development. It especially helps with damage from enterococci, staphylococci, and streptococci.
- Ofloxacin. An antibiotic from the same group as the previous medicine. Contraindicated in case of individual intolerance and hypersensitivity. It is forbidden to take during pregnancy and lactation.
- Framycetin. Antimicrobial, antibacterial medicine. Penetrates the membrane of microorganisms that caused the disease. The lesions are significantly reduced.
- Lomefloxacin. A potent drug that has a detrimental effect on almost all microbes. It has a pronounced bactericidal effect.
It is important to remember that medications can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Especially those that have a pronounced effect.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is possible only as an auxiliary therapy.
Using only such funds will not be effective. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor in combination with medications. It is important to consider that herbs can cause a strong allergic reaction, so they can be used in the absence of contraindications.
Safe and useful remedies will help you get rid of the disease faster. Effective methods include:
- Aloe. Dried leaves are poured with boiling water. When they cool down, use them as compresses. The liquid can also be used to rinse your eyes. If the patient does not have allergies, then juice from fresh leaves can be used. Dilute it with purified water in a 1:1 ratio. Can be instilled into the eyes or used for rinsing.
- Chamomile. The dried flowers of this plant are popular among the people. A decoction of them has a pronounced antibacterial and antiseptic effect. For bacterial conjunctivitis, it significantly helps reduce purulent discharge.
- Althea. The dried root is poured with cold water and left for 5-6 hours. After this time, it must be filtered. The eyes are washed with the prepared product 2-3 times a day.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited. This can cause the development of a chronic form and severe complications. It is impossible to cure this disease without the use of antibiotics.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in adults
At the first stage, it is necessary to exclude possible contacts with other people to prevent infection and re-infection. Bacteria are transmitted through personal hygiene items and touch. Do not touch purulent discharge - or at least wash your hands with soap and antiseptics after contact has occurred. The patient's home is regularly wet cleaned using bactericidal agents.
The general treatment regimen includes:
- Rinse with herbal solutions - tea, chamomile, St. John's wort. These infusions relieve general inflammation and reduce pain.
- Rinse with clean water before administering antibiotic therapy.
- Using antibiotic drops. A specific drug is prescribed after determining the causative agent of the disease, but most often Ciprolet, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Tobrex are used up to 8 times a day.
- At night, bactericidal ointments are used - tetracycline or erythromycin.
- To reduce pain, anti-inflammatory drugs are used - for example, Vitabact.
Most medications used against bacterial conjunctivitis in adults are quite toxic. Therefore, pregnant, breastfeeding and people with a tendency to allergies are selected therapy especially carefully.
Complications
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can quickly cure this disease without negative consequences. If you ignore the symptoms of its manifestation, then there is a risk of developing the following complications:
- keratitis – infectious lesion of the cornea;
- decreased visual acuity;
- ulcerative and erosive lesions;
- abscesses;
- corneal clouding;
- orbital cellulitis is a dangerous pathology that poses a threat to life, accompanied by severe inflammation of the tissues on the orbital septum.
The consequence can only be prevented with the help of correct and timely treatment. You should not self-medicate, especially with folk remedies. Bacterial damage can spread to other organs of vision.
Classification of the disease
There are several types of pathology:
- Catarrhal. Occurs due to a weakening of the body’s protective functions or as a result of an irritating effect on the mucous membrane over a long period of time;
- Pneumococcal. Develops when communicating with an infected person and using his personal belongings;
- Diphtheria. Manifests against the background of progressive diphtheria;
- Diplobacillary. Transmitted by airborne droplets. The disease develops rapidly and often develops into a chronic form;
- Blennoreynaya. It most often affects newborn babies who become infected while passing through the birth canal of a mother suffering from gonorrhea.
| Any type of pathology is dangerous to health, so if you suspect the development of a particular anomaly, immediately visit the clinic. |
Forecast
Timely therapy provides a favorable prognosis. Treatment generally lasts 2-3 weeks. It depends on the degree and form of the lesion. Comprehensive treatment helps prevent the development of a chronic form of the disease. In this case, medications can achieve a long period of remission.
Lack of therapy can have the most disappointing prognosis - loss of vision. Infection spreads to the cornea and deep tissues. Also, if treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease will quickly become chronic.
How is the treatment carried out?
If the disease is bacterial in nature, the mandatory use of antibiotics is indicated. Therefore, before starting therapy, it is necessary to find out the type of pathogen and only then select the necessary drug.
Treatment of conjunctivitis
Attention! The treatment of conjunctivitis should be approached with extreme caution; for example, after opening the package, drops can be used for 28 days.
Recommendations for carrying out procedures:
- Before using the drug (drops), rinse your eyes thoroughly with clean water.
- Next, you need to toilet the sore eye.
- Then using a gauze swab, which is moistened with an antiseptic. You can use furatsilin . In this way, the formed crusts from the secreted pus are removed.
- Please note that you must use separate swabs to treat each eye.
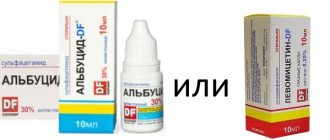
- Now you can start putting eye drops. Experts recommend using medications such as Tobrex, Levomycetin, Floxal. It is very important to adhere to the treatment regimen determined by the doctor (duration of treatment, number of drops).
- Before going to bed, it is necessary to perform additional manipulations - a small amount of ointment is placed under the eyelid. The drug must be antibacterial - among them, the most effective are Gentamicin, Polyphas, Tetracycline. Thus, a sufficient concentration of the drug is created throughout the night.
- To eliminate swelling and itching, antihistamines are used - Allergodil.
How to use eye drops correctly
Attention! It is forbidden to apply bandages to sore eyes, since such a closed environment promotes the proliferation of pathogenic agents.
What drops are recommended for therapy?
| Drug name | Image | Application and action |
| Tobrex | The main active ingredient in the drug is tobramycin. The drops have a wide range of bactericidal effects, so they do an excellent job against bacterial conjunctivitis if it is caused by streptococcus, staphylococcus or Klebsiella. The duration of use of the drug should not exceed one week, as side effects may occur: 1. Soreness in the eyeballs. 2. Swelling. 3. Redness of the membrane | |
| Dancil | The drops are based on the antibiotic ofloxacin. Drops are used if conjunctivitis was caused by chlamydial infection, Haemophilus influenzae, streptococci, enterobacteria. The maximum concentration of the active substance in the eye mucus can be achieved four hours after the instillation procedure. Side effects include possible dry eye, photophobia, blurred vision | |
| Levomycetin | A broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent that is based on blocking the synthesis of proteins of pathogenic microorganisms. After contact with the mucous membrane of the eye, it is quickly absorbed. An allergic reaction may occur. Long-term use of drops leads to disruption of hematopoietic function | |
| Phloxal | Basically, experts prefer this particular drug, since Floxal has an excellent effect on conjunctivitis caused by pale spirochete, streptococci and E. coli. The effect is achieved within ten minutes after instillation and lasts for six hours. Ophthalmologists recommend using it because there are virtually no side effects | |
| Oftaquix | The active ingredient is the antibiotic levofloxacin. If individual intolerance occurs, it can lead to contact eczema. Possible side effects include: 1. Itching. 2. Fear of light. 3. Burning sensation. 4. Prolonged tear production. 5. Decreased vision is extremely rare. The duration of use is determined by an ophthalmologist |
Advice! Additionally, for a quick recovery, you can use tetracycline and erythromycin ointment, which is placed under the eyelid every day before bed.
Video - Conjunctivitis treatment in children and adults
Prevention
With this disease, it is very important to strictly follow the rules of hygiene. The disease initially affects one eye, and after a few days the second. The reason lies in non-compliance with basic hygiene. Avoid getting any objects, particles, dust or sand into your eyes.
It is forbidden to rub your eyes, especially with dirty hands. If your work activity involves chemical, household, or construction products, you must use protective goggles and masks. When wearing contact lenses, you should take proper care of them. Use the correct solutions and remove them before going to bed. It is prohibited to use such optical products and medications after the expiration date.
How to distinguish viral conjunctivitis from bacterial?
| This is quite problematic since they have an almost identical clinical picture. To identify the type of inflammation, visit an ophthalmologist; after conducting tests and examinations, he will be able to give an accurate answer to this question. |
However, there are several signs by which you can distinguish the two anomalies at home:
- Viral conjunctivitis almost never spreads to the second eye, but bacterial conjunctivitis spreads very quickly;
- Inflammation caused by viruses is accompanied by increased lacrimation and severe redness of the eyes. The second anomaly has the same signs, but they are less pronounced;
- If after waking up you cannot open your eyelids because your eyelashes are stuck together, then you have conjunctivitis of bacterial origin. Since the viral form is not accompanied by the release of pus, it is characterized by an exudate of mucous consistency, which does not cause “sourness” of the eyes;
- According to statistics, 80% of all cases of conjunctivitis infection are of viral origin, but then gradually develop into a bacterial type.
What is acute conjunctivitis and why does it occur?
Usually the word “conjunctivitis” refers to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye.
In fact, this is a whole group of ophthalmological diseases in which an inflammatory process develops on the conjunctiva.
In this article
- What is acute conjunctivitis and why does it occur?
- General signs of acute conjunctivitis
- Acute bacterial conjunctivitis
- Treatment of acute viral conjunctivitis
- How to cure conjunctivitis caused by chlamydia?
- How can allergic conjunctivitis be cured?
- Why is acute conjunctivitis dangerous?
This pathology can take different forms. The nature of its development depends on the reasons that caused this inflammation, the age of the patient, the state of his immune system and other factors. The type and form of conjunctivitis, in turn, determine the treatment.
According to the intensity of its course, conjunctivitis can be acute, subacute and chronic. Based on the presence of certain symptoms, this disease is divided into purulent, catarrhal, membranous and follicular. According to the localization of the process, unilateral and bilateral inflammations are distinguished. In order to correctly prescribe medications, you need to determine the type of causative agent of the disease. On this basis, conjunctivitis is classified into several more types. He can be:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- chlamydial;
- fungal;
- allergic.
The classification can be continued. So, based on the type of bacteria, bacterial conjunctivitis is divided into streptococcal, pneumococcal, gonococcal, etc. Viral conjunctivitis can be adenoviral and herpetic. Allergic inflammation can be seasonal, drug-induced, etc. We are interested in the acute form of inflammation. It is usually taken for bacterial infections and allergies. A viral disease and an inflammatory process caused by chlamydia can be acute. Fungal infection in the eyes, or ophthalmomycosis, always develops in a subacute or chronic form. Let us list the symptoms of acute conjunctivitis.
What drops and antibiotics should I use?
Drops for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis (solutions for instillation) can be made based on different active components, but their mechanism of action is all similar.
Among the most common ophthalmic drops for bacterial conjunctivitis are:
- Ciprofloxacin. Broad-spectrum antibiotic from the category of fluoroquinolones. The drops actively affect pathogenic microflora, preventing their reproduction. Most gram-negative microorganisms and gram-positive pathogens such as enterococci, staphylococci and streptococci are most sensitive to this drug.
- Ofloxacin . Another fluoroquinolone antibiotic, which is highly effective , but is contraindicated in patients who may exhibit hypersensitivity to any components of the drops. Also, the product should not be used during pregnancy or nursing mothers.
- Lomefloxacin. A strong bactericidal agent based on fluoroquinolone, which actively fights most gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens of bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Framycetin. A bactericidal and antibacterial agent that penetrates the cell membranes of pathogenic microorganisms that cause the disease. As a result, the reproductive properties of microorganisms are disrupted, and the foci of their localization gradually decrease.
All products are used exclusively locally by instillation into the affected organs of vision .
Such drugs have low absorption: they are not absorbed into the systemic circulation, acting only on microorganisms that accumulate on the surface of the conjunctival membrane.
What it is?
Bacterial conjunctivitis is an inflammatory eye disease that is characterized by an infection of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva). The conjunctiva is a thin transparent tissue that lines the inner surface of the eyelid.
Bacterial conjunctivitis can take various forms:
- Lightning fast. It is characterized by bright, pronounced clinical symptoms that progress rapidly. The incubation period for fulminant bacterial conjunctivitis is usually 1-3 days. Since this disease has an increased risk of corneal damage, antibacterial therapy should be started as soon as possible.
- Spicy. Clinical symptoms in the acute form of the disease are less pronounced than in fulminant bacterial conjunctivitis. As a rule, the bulbar conjunctiva is very often affected and a large amount of purulent exudate is released. The disease caused by the pathogens Staphylococcus aureus and Moraxella catarrhalis can become chronic over time, and therefore requires mandatory treatment. Also, without treatment, if the conjunctiva is damaged by staphylococcal infection, chronic blepharitis may occur. The acute form of bacterial conjunctivitis is usually treated within 10-14 days.
- Chronic. In most cases, the causative agent of chronic bacterial conjunctivitis is Staphylococcus aureus. Very often this form of the disease is accompanied by blepharitis, which is very difficult to treat with antibiotics.
Chronic conjunctivitis: treatment with folk remedies
Antimicrobial drugs are effective against bacteria, their action is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. You can also fight symptoms such as swelling of the eyelids and inflammation of the conjunctiva with folk remedies. Use traditional recipes with extreme caution if you are prone to allergies, since an allergic reaction to any component of herbal preparations for the treatment of conjunctivitis is not uncommon. Allergies may also occur for the first time due to a weakened immune system. Try not to use bee products. Conjunctivitis cannot be cured with honey and propolis, but it is quite possible to experience the unpleasant consequences of an allergic reaction from these products.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes: treatment with folk remedies:
- Black and green teas for washing eyes (brew tea for no more than 5 minutes) are one of the most popular methods of folk treatment; You need to wash your eyes with warm liquid so that the pus that has dried after sleep can be easily separated.
- Decoctions of chamomile and calendula flowers (the liquid must be filtered several times through a folded piece of gauze) are often used in the treatment of chronic conjunctivitis with folk remedies; they can be used both to cleanse the eyes of pus, and you can make warm compresses with them - this will facilitate the outflow of pus.
- Dill, bay leaves, fennel seeds - these components of medicinal decoctions have antiseptic properties and help relieve inflammation and swelling of the eyelids due to conjunctivitis, therefore they are often included in folk treatment recipes.
- Brew crushed chamomile flowers in a glass of boiling water, cool, and then dip a cotton swab into the liquid and squeeze out a little - it is better to do such lotions in the evening, before going to bed; apply compresses to your eyes for 2-3 minutes, covering them with a towel; the procedure can be repeated 3-4 times.
- Blue cornflower flowers can also be used for lotions at home - to do this, pour boiling water over a tablespoon of crushed flowers (0.5 liters are needed) and boil for 2-3 minutes, and then infuse for an hour.
Eye conjunctivitis: treatment with folk remedies - effective or not? Lotions with herbal decoctions and warm compresses are an effective remedy that is often used in medical therapy. Lotions can relieve puffiness, and washing the eyes with herbal teas that have antiseptic properties will make it easier to cleanse the eyelids of purulent discharge and soothe the skin.
How can allergic conjunctivitis be cured?
Allergies in most cases are chronic, but they occur in acute form. This is the only one of all the pathologies listed earlier that is not transmitted from person to person. The cause of an allergic reaction is a malfunction of the immune system, which begins to perceive a substance that is safe for other people as an allergen. An allergy to plant pollen is often diagnosed. It manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- severe itching and burning;
- profuse lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- redness of the conjunctiva and eyelids.
Some patients experience the formation of a mucous film on the connective membrane. Most often, allergic conjunctivitis develops in both eyes. In this case, the first signs appear within a few hours after exposure to the allergen on the connective membrane. If you have an allergy, there is a high risk of bacterial infection, especially in children. They have less control over their actions, rubbing their eyes with their hands and introducing bacteria into them. Symptoms of allergic inflammation are accompanied by signs of bacterial acute conjunctivitis.
Depending on the age of the patient and the nature of the disease, the following types of drugs may be prescribed for allergies:
- Vasoconstrictors. With their help, swelling and hyperemia are relieved. In acute conjunctivitis, the eyes swell quite severely. Sometimes swelling leads to almost complete closure of the eyelids. Drops such as Visine, which are used in the first days of the disease, help to quickly relieve this symptom.
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. They are usually prescribed to children or adults for moderate inflammation. These drugs instantly eliminate all signs of conjunctivitis.
- Corticosteroids. These drugs are based on synthetic analogues of the adrenal glands, which suppress the inflammatory process. This group of drugs has many side effects, so they are used in extreme cases.
- Antihistamines. In allergy sufferers, histamine is released in the body in large quantities. He perceives certain substances as allergens. Antihistamines suppress histamine production and reduce inflammation.
- Moisturizing drops - “Systane”, “Vidisik”, “Artificial tear”. They are used not only for allergies, but also for other types of acute conjunctivitis. Such solutions do not contain preservatives. They instantly eliminate dryness, as a result of which lacrimation stops, itching, burning and other signs of conjunctivitis disappear.
The main thing in case of allergies is to exclude the patient’s contact with the allergen. Otherwise, the stopped symptoms will return after some time.
Recommendations of Dr. Komarovsky
To treat bacterial conjunctivitis, antibacterial agents are required. However, antibiotics have an unfavorable effect on the body, so only an ophthalmologist should select medications and prescribe dosage.
Self-medication may worsen the patient's condition. For example, in case of bacterial inflammation, it is forbidden to use warming lotions; they block the process of removing exudate.
You will learn useful information from Dr. Komarovsky about methods of treating conjunctivitis in children from the video.
Return to contents
Basic principles of treatment of conjunctivitis
Purulent conjunctivitis is contagious, transmitted by contact through common objects, as well as through napkins, handkerchiefs, towels, if they are used by both a sick and a healthy person at the same time. Therefore, the first task of the patient's environment is to maintain careful hand hygiene. It is necessary to provide the sick person with a sufficient number of napkins for lotions, removing purulent discharge, wash handkerchiefs regularly, and change pillowcases.
It is undesirable and even dangerous to completely cover your eyes with a cloth. Even if your eyes have become too sensitive to light, you should not cover them with a bandage, because bacteria will spread even faster under it. It is better to cover window openings with curtains during the day and dim the lighting in the evening. The treatment plan for conjunctivitis is prescribed only by a doctor, and it must be followed, strictly observing the intervals between the use of drops and ointments (so that the interaction of substances does not reduce the effectiveness of the drugs), and not violate the recommended dosages. What remedies are effective for conjunctivitis, how and with what to treat such a disease?
Eye conjunctivitis - treatment:
- The use of antibiotics is mandatory - conjunctivitis can be cured with eye drops with an antimicrobial effect: Tobrex, Ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin, etc.; antibiotic tablets are recommended in cases where laboratory tests have confirmed the presence of gonococcus or chlamydial infection.
- Antibacterial ointments will also help cure eye inflammation - they fight bacteria, have an anti-inflammatory effect, soften the skin of the eyelids, relieve irritation of the conjunctiva - Floxal ointment from Bausch + Lomb, an ointment based on tetracycline, is highly effective.
- Purulent discharge should be regularly removed from the eyelids before applying lotions, eye drops, etc., using warm solutions of antiseptics, for example, furatsilin - use different cotton swabs to clean each eye, remove the pus from the outer edge of the eyelid to the inner (this is where it accumulates the bulk of it).
- Use moisturizing eye drops and moisturize the room with special devices - these products will significantly ease the course of the disease, since the mucous membrane of the eye will not dry out and be subject to additional stress.
If your doctor has prescribed the use of both drops and ointment, use the ointment 20 minutes after instilling the eye drops. Do not apply eye drops after applying the ointment. If putting ointment behind the lower eyelid causes severe pain, you can use local anesthetics before the procedure, which will reduce sensitivity - such drugs will be prescribed by the attending physician. How can you cure a disease with folk remedies? You just need to combine the experience of folk and traditional medicine.