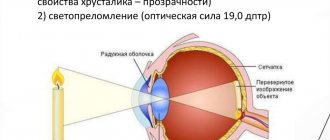
Causes of fibrosis of the posterior capsule of the lens
Many factors influence educational status:
- residual clouding after completion of the procedure;
- low degree of qualification of the doctor;
- poor quality intraocular lens model;
- ophthalmological or systemic diseases that cause deterioration in the quality of vision, reduced supply of blood with nutrients and oxygen to the eyeball.
Before treatment, the doctor identifies the cause of the development of secondary cataracts. If it is a systemic disease, laser discision alone will not help.
Causes
The leading factors in the manifestation of posterior capsular cataracts are:
- taking corticosteroid drugs for a long period of time;
- the presence of a pathology such as diabetes mellitus, which greatly increases the risk of bilateral damage to the organs of vision;
- diseases of the visual organs: uveitis, glaucoma, dystrophy develop into complicated cataracts;
- mechanical destruction of the lens - any injury to the organs of vision or head can provoke pathological changes in the lens; in this case, moisture gets inside and causes its swelling;
- carrying out surgical interventions in the field of ophthalmology, appears in the form of an exacerbation after surgery;
- aggravation after various diseases of the body;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- genetic predisposition;
- harmful working conditions, severe poisoning with thallium, mercury;
- radioactive, ionizing or ultraviolet radiation;
- psoriasis and skin cancer;
- bad habits - alcohol abuse, smoking.
Symptoms
The symptoms of primary and secondary cataracts are similar, as in both cases cloudiness occurs. This affects the following human functions:
- decreased visual acuity, which gradually progresses, leading to complete blindness without treatment;
- increased sensitivity to bright colors, glare in front of the eyes;
- frequent headaches that occur due to the fact that the patient overstrains the eye muscles;
- severe eye fatigue.
If a patient experiences these symptoms after phacoemulsification of a cataract, the doctor considers a diagnosis of a secondary disease. It can be confirmed based on instrumental examination methods.
Stages and forms of the disease
The following forms are typical for posterior capsular cataracts:
- initial form;
- immature cataract;
- mature form;
- overripe form.
In the initial form, obvious disturbances do not appear; blurred vision periodically occurs. A sick person complains of double vision, spots, and streaks before the eyes. Vacuoles filled with liquid begin to form under the capsule. These changes can be detected by biomicroscopic examination. The initial form lasts for a different period of time - from several months to a year or more.
Immature (swelling) cataracts are characterized by serious changes in the lens. A person's vision is significantly reduced. The lens itself becomes larger and occupies more volume of the eye. The pupil takes on a gray-white hue. This is accompanied by pain and increased intraocular pressure. The immature form of cataract quickly develops into a subsequent form.
In the mature form, all the unwanted symptoms of the disease appear. There is dehydration of the lens. It becomes smaller, thickens and frees the anterior chamber. A person has difficulty distinguishing colors and objects, but still sees light rays. A gray cloudiness appears in the pupil area. At this stage, surgery is performed to remove and replace the lens.
During the period of the overripe form, a person completely loses vision and becomes completely blind. The lens liquefies and becomes milky white. A small remnant of the nucleus remains, and the capsule is covered with cholesterol plaques.
Diagnosis of opacification of the posterior capsule of the lens
To diagnose the patient's condition, the doctor needs to examine the fundus of the eye using a slit lamp. Atropine or similar agents are first instilled into the eyes, which temporarily eliminate the accommodation of the pupil. That is, when illuminated by a slit lamp, it does not narrow.
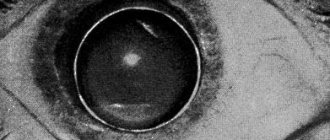
The doctor discovers clouding of the posterior wall of the lens capsule. This is a reason for laser correction.
Posterior capsular cataract in both eyes
The rapid manifestation of signs of posterior capsular cataract in both eyes contributes to the formation of specific suspicions regarding the cause of the ailment. In addition, determining the clinical picture of the disease is facilitated by identifying the dead zone, which occurs when lens disturbances characteristic of posterior capsular cataracts occur. The main factor in the impact of this type of cataract is a sharp deterioration in vision, both near and far.
Identifying such a diagnosis in our clinic becomes possible using methods such as:
- standard tests for visual acuity (they are subjective and therefore require additional research);
- determination of fields of view and its “dead” zones (if any);
- measuring pressure inside the eyes;
- ultrasonography;
- electrophysiological examination.
The last two points apply to the optic nerve and retina. If a cataract is still detected, the use of a slit lamp is added to the list of diagnostic methods. It is used to determine the maturity and location of cataracts.
Prevention
To prevent the development of fibrosis of the posterior capsule of the lens, the following rules should be followed:
- annual preventive examination by an ophthalmologist, especially for persons over 50 years of age;
- timely correction of primary cataracts before the disease reaches the stage of lens hardening;
- choosing a qualified doctor with extensive experience to remove primary cataracts;
- periodic examination by an ophthalmologist to determine the patient’s condition after the phacoemulsification procedure.
A small percentage of patients suffer from secondary cataracts. If a deviation is detected in time, it can be completely eliminated by resorting to laser treatment.
Signs and symptoms
It is very difficult to identify cataracts in their initial form on their own. Especially if the symptoms of the disease do not appear. The main indicators of the presence of this pathology are described below:
- vision deteriorates at close range - it gradually decreases at long distances;
- part of the field of view in the center of the image disappears;
- in the dark, flashes or glare may occur;
- the fear of light progresses - photosensitivity increases significantly, but pain is not observed;
- the image may double;
- color perception deteriorates;
- multiple changes of contact correction means, posterior capsular cataract is difficult to correct with glasses;
- perhaps the appearance of severe headaches, pain syndrome and inflammatory processes in the organs of vision.
Cataracts occur differently in all patients and have different rates of development. Over time, visual function may lose clarity and disappear completely. If the above symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor to make a diagnosis. You cannot self-medicate and ignore such symptoms.
Treatment
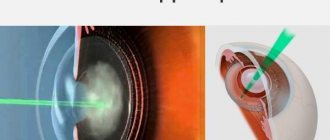
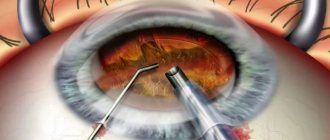
It is possible to get rid of posterior capsular cataract only through surgery. Surgery takes place in one of two ways:
- Intracapsular cataract extraction. This method of treatment is used in exceptional cases, since the eyeball is highly injured. The operation is performed using a special device – a cryoextractor. Using this device, the lens and capsule are frozen to a metal tip, then removed through a previously made incision.
- Extracapsular cataract extraction. The clouded lens is removed using a microcut and replaced with an intraocular lens. It is possible to remove only the damaged part. This maintains a barrier between the vitreous and the front of the eyeball. This method of treatment has a disadvantage - significant damage to the organ of vision is observed.
These methods of treating posterior capsular cataracts allow for partial or complete replacement of the lens. After the operation, a bandage is applied to the eyes of the operated person. It reduces the risk of complications or infection.
Healing after surgery occurs within 7-10 days. During this period, the patient is prescribed antiseptic drops and antibiotics. Compliance with all doctor’s recommendations promotes the fastest healing and restoration of visual function. Most often, vision returns by 90-100%.
Diagnostics
In publications and at scientific conferences, experts note the difficulties of early diagnosis of posterior capsular fibrosis. Occasionally, its presence can be detected already during surgery (in this case it can hardly be considered a postoperative complication), but much more often the opacification is detected some time after IOL implantation. At the same time, the patient’s complaints, as well as the data of an objective study, do not allow us to clearly determine whether this is a side effect of surgical intervention, or natural (but too intense) fibrosis as a consequence of amputation of an element provided by nature, or a pathological reaction to the presence of a biocompatible, but still a foreign body, or, finally, this is a purely optical aberration caused by defects or poorly selected parameters of the lens itself (especially if it is a complex multifocal model).
Leading experts in the field call this situation “puzzling”; according to them, you can “remove the lens and not solve the problem” (if the clouding was initially of an endogenous-organic nature) or, conversely, perform repeated corrective microsurgical intervention on the capsule - and as a result you will still “get a dissatisfied patient” if the source of the symptoms is in was actually an IOL.
Treatment of the disease
The drug may partially slow down the progression of the disease, but not stop it.
Posterior capsular cataracts can only be treated surgically. Vitamin drops (“Katachrome”) can slightly slow down the progression of the pathology, but surgical intervention is still recommended in the future. Replacing the lens apparatus with an intraocular lens is carried out under local anesthesia and does not require long-term rehabilitation.
Why do cataracts occur?
The causes of opacities on the posterior capsule include:
- Age over 40 years. Senile (senile) cataracts can occur according to this type.
- Rheumatological diseases: Still's disease;
- ankylosing spondylitis.
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- diabetes;