Functions of the lens of the eye
To understand what replacing the lens of the eye provides, it is important to understand the functions of this element:
- it is responsible for focusing when looking near or into the distance;
- transmits light to the retina, responsible for the ability to see at all;
- refracts the flow of light;
- acts as a partition between the parts of the eye.
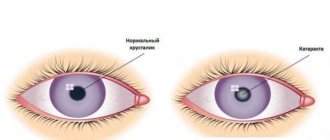
Lens opacities and other defects often lead to significant vision loss or blindness.
Indications for surgery
Indications for the installation of an artificial lens, or intraocular lens (IOL), are various diseases and disorders:
- cataract – clouding of part of the organ of vision due to aging or degenerative changes;
- age-related farsightedness – surgery is recommended for significant impairments;
- high myopia – in cases where the lens loses its ability to accommodate;
- lens astigmatism - the element does not focus light rays, as a result of which everything blurs before the eyes;
- the absence of a natural lens is a congenital defect or a consequence of surgery.
However, refractive lens replacement is not possible in all cases.
Contraindications to the procedure
The main contraindications to surgery can be temporary or permanent:
- inflammation of the organs of vision - first you need to cure it;
- the anterior chamber is too small;
- recent stroke or heart attack;
- destruction or detachment of the retina;
- reduced eyeball due to farsightedness;
- eye infections;
- decompensated glaucoma;
- pregnancy or breastfeeding period.
After treatment of conditions that can be eliminated temporarily or in the long term, re-appointment of cataract surgery with lens replacement or in case of other problems is considered.
Causes of hypermetropia
The key reasons for the development of farsightedness include damage to the refractive structures of the visual organs and the irregular shape of the eyeball. Depending on the nature of the pathology, the following types of hyperopia are distinguished:
- Physiological (in children) - all babies are born with farsightedness, as the visual system continues to develop. As the child grows and develops, the axis of the eyeball lengthens and the curvature of the lens and cornea increases. Thus, at the age of about 7 years, the degree of hypermetropia reaches only 1.5-2 diopters, and by the age of 14 it completely disappears. This process is natural and is not considered a pathology.
- Congenital - it can be detected no earlier than by the age of 7-8 years in a child, when the visual apparatus is already practically formed. The causes of this disease may be associated with developmental disorders of the eyeball, lens or cornea.
- Acquired - occurs after mechanical injuries to the visual apparatus, tumors of the orbit, unsuccessful surgery, or the development of cataracts (clouding of the natural lens).
- Age-related – associated with the aging of the lens structures and the loss of its basic functions; this pathology is called presbyopia.
Choosing an artificial lens
All prostheses are made from biologically compatible materials, and rejection by the body is almost impossible. There are several types of IOLs that are used most often.
Accommodating lenses
Under the action of the ciliary muscle, implants can move in the eye and change focus, imitating the work of the lens. They have one optical zone, so among the disadvantages there is insufficient quality of vision in twilight conditions. Reading glasses are often required after accommodating IOLs are placed.
Important! These are the cheapest lenses, often presented by domestic manufacturers for quota lens replacement.
Among the highest quality manufacturers, Alcon lenses (USA) stand out, the price of which starts from 19,000 rubles and reaches 48,000. IOLs are also produced by Rumex with a price of 9,000 (Britain), B&L (USA) with a price of 15,000 and Silco (USA) – 5,000 rubles.
Aspheric IOLs
Designed to correct spherical distortions that often occur after IOL implantation. Previously, spherical elements were used, but they led to severe distortion.
The most popular manufacturers and prices:
- ACRYSOF IQ NATURAL (USA, Alcon) – 22,000 rubles;
- CT ASPHINA 509M – (“Carl Zeiss”, Germany) – 25,000 rubles;
- HOYA ISERT 251 – (“Hoya”, Japan) – 32,000 rubles;
- TECNIS 1 ZCB00 – (“Abbot”, USA) – 25,000 rubles;
- ASPIRA -AAY - (Human Optics, Germany) - 24,000 rubles.
These lenses are often used in younger patients and for a wide range of conditions. But for complex forms of cataracts with additional pathologies, they are not always suitable.
Toric IOLs
Used for cataracts complicated by astigmatism. Prices and manufacturers:
- AcrySof Toric (Alcon, USA) – from 32,000 rubles;
- At Lisa Toric 909 M – (“Carl Zeiss”, Germany) – from 50,000 rubles;
- Rayner T-Flex (Britain) – from 15,000 rubles.
IOLs are distinguished by greater refractive power in some areas, due to which distance vision is corrected.
Multifocal IOLs
Used for lens correction in patients over 40 years of age. They perfectly imitate the work of the lens and can focus far and near. Prices and manufacturers:
- ACRYSOF RESTOR (“Alkon”, USA) – from 48,000 rubles;
- M-FLEX (Rainer, UK) – from 38,000 rubles;
- ATLIS ATRI 839 MP (“Carl Zeiss”, Germany) – from 66,500 rubles.
After implantation of these IOLs, 80% of patients no longer need glasses.
Phakic IOLs
Used for implantation without removing the lens for myopia or farsightedness. The procedure is relevant when laser vision correction is prohibited. The cost of phakic IOLs starts from 20,000 rubles.
What happens in the visual system with farsightedness?
Farsightedness or hyperopia is a pathology of visual ability, which is explained by a defect in the refractive system. As a result, the patient's images become blurry when viewing objects located at close range, since light rays are focused behind the retina and not on it, as under normal conditions. The closer an object is to a person, the worse he recognizes it.
In order to understand the causes and mechanisms of progression of hypermetropia, determine its nature and prescribe the optimal treatment method, it is necessary to know the structure of the visual system.
Ophthalmologists distinguish two sections - the retina and the refractive system. The first is the peripheral part of the visual analyzer and consists of a huge number of light-sensitive cells. Particles of light, called photons, when reflected from objects, penetrate into the retina, with their help in the cells responsible for photosensitivity, nerve impulses are generated. They are sent to a special part of the brain and transformed into pictures.
The refractive system has a number of components:
- The cornea has the shape of a hemisphere and has a regular refractive ability of up to 40 diopters.
- Lens - located behind the cornea, it is a biconvex natural lens, which is fixed by several muscle ligaments. When a person examines a variety of objects, the lens changes its shape, so its refractive power varies from 19 to 33 D with healthy vision.
- Aqueous fluid is found in special chambers in the eye in front and behind the lens. Its function is to nourish and transport beneficial substances to the tissues of the eye and the natural lens. In addition, it protects the visual system from various harmful bacteria and viruses due to the content of immunoglobulins.
- The vitreous is a jelly-like mass that fills the space between the lens and the retina. Its main task is to maintain the correct shape of the eyeball; its ability to refract light is not so insignificant.
It is important to understand that with healthy vision, all light rays, after passing through the refractive system, are focused on the retina, so a person can clearly see the object in question. If it is far away, the refractive power of the lens decreases and vice versa - when looking at a close object, this power increases. The mechanism described above is called accommodation.
Preparation and performance of the operation
For successful intervention, preparation for eye lens replacement surgery is required:
- 10 days before the procedure, avoid contact lenses and glasses;
- 5 days before the intervention stop drinking alcohol or smoking;
- one day before surgery, you need to take a shower and wash your hair;
- On the day of the scheduled intervention, you cannot use cosmetics, eat or drink.
Before the patient goes to the hospital, he takes blood tests, a coagulation test, an ECG, fluorography, and a urine test. You must first visit an ENT specialist, an allergist, a cardiologist and an endocrinologist, and also take a test for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis.
After completing the procedures, a conclusion on suitability for surgery is issued by a therapist or doctor in a private clinic.
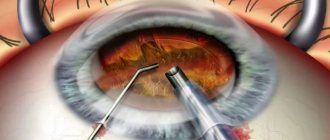
Progress of the operation: overview of the methods used
Several surgical techniques are used to replace the lens. Regardless of how the lens replacement surgery is performed, no stitches are required after the operation. The relevance of the methods for a particular patient is determined by the doctor:
- Extracapsular extraction . After removing the damaged element, only the posterior capsule remains.
- Intracapsular extraction . The lens is removed along with the capsule through an incision in the cornea.
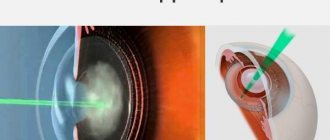
- Ultrasonic phacoemulsification . Using an ultrasound device, the transparent body is destroyed and removed through a tube, preserving the posterior chamber of the lens. An IOL is placed in place of the polished posterior machine. The preferred method, which began to be done more often than the previous two.
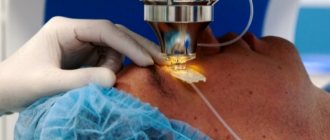
- Femtolaser phacoemulsification . The most modern and safe procedure that uses laser.
After the operation to replace the lens of the eye takes place, the patient is placed in the hospital for several hours. He is then discharged home.
How is an artificial lens implanted in CELT?
Surgical intervention requires a mandatory preparatory stage. It consists of conducting comprehensive diagnostic studies and consultations with specialists in other fields (if necessary).
In order to minimize the risk of infection, the patient is prescribed antibacterial drops three to five days before surgery.
At the CELT clinic, the operation is performed under local anesthesia (anesthetic eye drops). Its stages include the following:
- fixation of eyelids using expanders;
- incision of the eyeball (2‒2.5 mm) and insertion of a special needle;
- the use of ultrasound to whip up the cloudy contents of the eye lens and remove crushed particles of the lens by aspiration;
- placing the implant in the vacant space, straightening it and filling it with liquid;
- applying a sterile dressing.
If the patient has no violations, he is sent home. It is important to understand that after surgery, vision and spatial orientation may be impaired, so it is advisable to come to the operation with an accompanying person.
Rehabilitation after IOL implantation
If the replacement of the eye lens for cataracts or another disease is successful, the postoperative period will go smoothly. At this time, the patient must strictly follow the regimen and recommendations of doctors:
- in the first 2 weeks, wear a bandage (sometimes less);
- use antiseptic drops;
- rinse eyes with the prescribed solution;
- do not strain your eyes while driving, do not drink alcohol;
- do not go to the bathhouse or sauna, avoid sudden temperature changes;
- Avoid lifting weights greater than 3 kg;
- do not bend over for 3-5 days after surgery;
- try to sleep on the side opposite the operated eye (rest on your back in case of bilateral surgery);
- You should not do any physical exercise after replacing the lens;
- you should not drink carbonated drinks or eat too fatty foods;
- it is important to get plenty of rest and sleep for at least 8 hours;
- When taking a shower, your eyes should be protected from splashes of water;
- Do not rub or press on the operated eye;
- Do not wash your hair for 5-7 days after the intervention.
Throughout life, restrictions apply after replacing the lens on going to the bathhouse, as well as on eye strain. Some patients note that surgical intervention weakens local immunity for a long time, and conjunctivitis may develop. It is important to monitor the health and hygiene of the visual organs. Also, prevention after eye lens replacement includes proper nutrition.
Video about how the operation is performed:
Possible complications
The consequences of replacing the lens of the eye are directly related to the method of intervention. So, with a laser procedure the risks are minimal . But with other methods they can occur more often:
- inflammation of the eye - goes away on its own after 2 days;
- increased pressure in the eye - you need to use eye drops after replacing the lens, which are prescribed by the doctor;
- displacement of the prosthesis - corrected by a doctor;
- retinal detachment - occurs only after an accidental injury;
- hemorrhage in the anterior chamber - treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Late complications may also occur after cataract removal with lens replacement: macular edema, secondary cataract. In most cases, correction occurs conservatively, but sometimes additional surgical intervention is required.
How to get a quota
In 2012, the possibility of lens replacement under the compulsory medical insurance policy was introduced. However, to get a quota, you need to meet certain parameters and join the general queue. Persons of retirement age and disabled people are given priority places.
Here's how to get a quota for lens replacement for a pensioner, what conditions must be met:
- positive prognosis from the ophthalmologist;
- absence of eye diseases that may interfere with vision restoration;
- consent to the installation of Russian IOLs (foreign ones are paid for independently).
To receive a quota, a person needs to go to the clinic at his place of residence - first to a therapist, or immediately to an ophthalmologist.
Answers to popular questions
Before surgery, patients often ask certain questions that concern them most.
How long does the operation take?
The minimum duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, and the maximum can reach 2 hours, but this happens rarely. On average, the operation lasts 30-40 minutes.
How much does eye lens replacement surgery cost (average price in St. Petersburg and Moscow)?
The cost of the operation depends primarily on the implant used. In capital cities, minimum prices start from 35-40 thousand rubles and can reach 140 thousand.
When will vision be restored?
When vision returns after lens replacement is greatly influenced by the general health of the patient, his retina and the optic nerve. The rehabilitation period after surgery is at least 4 weeks, by the end of which vision should fully return.
After lens replacement, the eye sees cloudy - why and what to do?
Normally, after lens replacement, the eyes are very afraid of light. During the first week, decreased vision and a hazy effect persist. This is a natural state of the body, it does not require correction, but the doctor’s recommendations must be strictly followed.
To combat complications in which fog in the eyes persists for a long time after lens replacement, the following measures must be taken:
- clouding of the lens capsule, or secondary cataract - after the intervention, the patient in rare cases begins to see worse. Correction requires laser discision - a small operation that lasts 10-15 minutes and does not require long-term rehabilitation;
- increased intraocular pressure - along with the fact that the eye, after replacing the lens, does not see as it should, painful sensations arise. Correction requires drug therapy as prescribed by a doctor;
- infection - the bacterium enters at the time of surgery or during the rehabilitation period, various symptoms occur, including acute pain and discharge from the eyes. To prevent it, it is necessary to undergo a course of antibacterial therapy during the recovery period;
- Corneal edema is a complication that affects the ability to see normally, but lasts no longer than 1-2 days. No specific treatment is needed;
- retinal detachment – accompanied by pain and requires consultation with a doctor. Laser and cryotherapy are used for treatment; in severe cases, repeated surgery is required.
Other reasons why complications arise after cataract removal with lens replacement are extremely rare (less than 1%).
When does vision return after eye lens replacement?
During the first week, vision remains cloudy, but if you follow medical recommendations, complete recovery occurs after 2-3 weeks. The replaced lens is fully rehabilitated after 4 weeks of rehabilitation. Laser vision correction after lens replacement is required in very rare cases complicated by eye pathologies.
What are the reviews after the operation?
In general, reviews of lens replacement for high myopia, cataracts and other diseases are positive, and patients note the following:
- no serious consequences;
- quick opportunity to return home;
- simple rehabilitation with strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
However, patient reviews often describe minor disadvantages: a cloudy look on the first day after surgery, the high cost of the procedure for complex interventions, the presence of edema. Some people are very nervous before surgery.
In the video, a man shares his impressions after replacing the lens of his eye:
When can you watch TV?
You can watch TV after replacing the transparent lens within a few days - the exact period is determined by the doctor. Reading and working on a computer is allowed after 1-2 weeks.
Implantation of phakic lenses for farsightedness
This operation is somewhat different from the lens replacement procedure. When a phakic lens is implanted, the transparent body is not removed. An optical lens is installed in one of the chambers of the eye. This procedure is possible only with a mild form of farsightedness, as well as in cases where accommodative abilities have not been lost. Implantation is carried out through a micro-incision in the cornea. Soft hydrogel lenses are used. They roll up into a tube, and therefore are easier to install under the cornea than optical products made from hard materials.
There are several types of phakic lenses, the most popular of which are posterior chamber ones for the following reasons:
- do not come into contact with the iris and cornea and do not provoke atrophic processes;
- biocompatible with eye tissues;
- protect from ultraviolet radiation;
- provide rapid restoration of vision.
The choice of treatment method depends mainly on medical indications. Lens replacement surgery is not the most popular for farsightedness, but in some cases it is the most effective and even the only possible one. Before any procedure, the patient undergoes a thorough examination, the results of which determine which treatment method is suitable for the patient.
Should I have surgery: pros and cons
Replacing the lens for astigmatism, farsightedness, cataracts and complex combinations of eye diseases is one of the few ways for patients to painlessly get rid of poor vision and the prospect of complete blindness. The operation is successful in 98% of cases, and only in 15-20% of them are complications that can be easily corrected.
The operation is supported by positive reviews from patients and the relative ease of the procedure (in most cases it takes a little more than 20-30 minutes for the intervention). At the same time, the health risks are minimal, which is also associated with the absence of general anesthesia.
However, it cannot be done if at least one of the contraindications is present - this can significantly affect the result. If there is financial opportunity or a quota, then lens replacement is a recommended intervention for various diseases: glaucoma, cataracts, astigmatism.
Contraindications
The operation is not possible if the following conditions and diseases are present:
- acute infectious and viral processes throughout the body or separately in the eyes;
- hepatitis, HIV infection;
- acute inflammation of any parts of the visual organs and surrounding skin surfaces;
- immune diseases in which tissue healing takes a long time (autoimmune condition, diabetes mellitus);
- corneal clouding;
- glaucoma – increased intraocular pressure;
- thinning of the cornea.
If the procedure is performed in the presence of contraindications, the patient's condition may worsen.