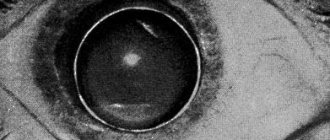
Intraoperative complications
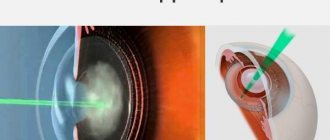
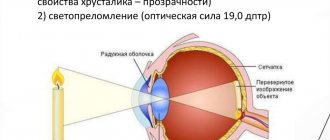
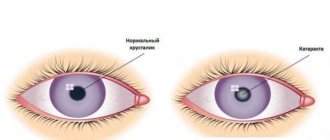
Eye cataracts are incurable with conservative methods: there are no means that can make the clouded lens transparent again. Phacoemulsification, an operation involving the replacement of a worn-out “biological lens” with an artificial one, can restore lost vision with a minimal percentage of complications. To crush the lens that has lost its quality, an ultra-thin needle is used - a phaco tip, which works under the influence of ultrasound. Microscopic punctures (1.8-2 mm) are made for the needle tip; they do not require subsequent sutures, because heal on their own. Through these holes, the crushed lens masses are removed, and an elastic lens is implanted in their place - an artificial lens substitute. The intraocular lens (IOL) expands inside the lens capsule and provides the patient with high-quality vision for the rest of his life. However, even during such a high-tech operation, there are complications:
- Rupture of the capsule wall and loss of parts of the crushed lens into the vitreous region. This pathology provokes glaucoma, damage to the retina. After 2-3 weeks, a secondary surgical intervention is performed to remove the clogged vitreous.
- Displacement of the implanted lens towards the retina. A malpositioned IOL causes swelling of the macula (the central part of the retina). In this case, a new operation is necessary to replace the artificial lens.
- Suprachoroidal hemorrhage is the accumulation of blood in the space between the choroid and the sclera. This complication is possible due to the patient’s advanced age, glaucoma and hypertension. Hemorrhage can lead to loss of the eye and is considered a rare but dangerous aspect of lens replacement surgery.
Intraoperative problems during phacoemulsification are not excluded, but occur rarely - in 0.5% of cases. Postoperative complications occur 2-3 times more often (1-1.5% of cases).
Other complications
Complications after lens replacement surgery include:
- Inflammatory processes that affect different ocular structures - uveitis (choroid), iritis (iris), conjunctivitis (mucous membrane). Any inflammation is considered normal and is considered as a protective reaction to surgery. To avoid an extensive inflammatory reaction, after phacoemulsification, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy or medications that block inflammation.
- Hemorrhage is associated with damage to small vessels and the entry of vascular contents into the anterior chamber of the eye. If the blood clot does not resolve on its own, the doctor may prescribe washing with special solutions.
- Corneal edema is often asymptomatic and mild. Puffiness can be relieved with the help of drops that normalize metabolic processes in the membranes.
To ensure that the postoperative period proceeds as easily as possible and is not accompanied by complications, the patient is strongly recommended to adhere to a number of preventive measures . It is prohibited to tilt your head, lift weights, drive vehicles, or visit the sauna and swimming pool. These restrictions are relevant only for the first weeks after installation of the implant.
When the artificial lens takes root, the patient will be able to lead a normal lifestyle and enjoy excellent vision.
Complications of the first postoperative weeks
For the first two weeks after surgery, it is necessary to protect the operated eye from bright light, infections and injuries, and use anti-inflammatory drops for tissue regeneration.
Despite preventive measures, complications are possible in the first and second weeks after cataract removal.
Pathologies amenable to conservative therapy
- Inflammatory processes. They are inevitable during operations - this is the body’s response to injury, therefore, upon completion of the surgical intervention, antibiotics and hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected under the conjunctiva, and the eye is irrigated with bactericidal drops for 2-3 weeks. With weakened immunity, symptoms of uveitis or iridocyclitis are added to the usual signs of inflammation (redness, itching).
- Uveitis is an inflammatory reaction of the choroid of the eye, manifested by pain, photosensitivity, spots or fog before the eyes.
- Iridocyclitis is an inflammation of the iris and ciliary zone, which is accompanied by severe pain and lacrimation.
Such complications require complex treatment with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory hormonal and non-steroidal drugs.
- Hemorrhage into the anterior chamber. Associated with minor damage to the iris during surgery. Minor bleeding inside the eye can be treated with additional irrigation and is not painful or interferes with vision.
- Corneal edema. If a mature cataract (with a hard structure) is removed, complications after cataract surgery on the cornea are caused by the increased effect of ultrasound during its crushing. Corneal swelling occurs, which goes away on its own. When air bubbles form inside the cornea, special ointments and solutions and therapeutic lenses are used. In severe cases, the cornea is replaced - keratoplasty.
- Postoperative astigmatism. Surgery changes the shape of the cornea, causing refractive error and blurred vision. It is corrected with glasses and lenses.
- Increased eye pressure. Postoperative (secondary) glaucoma can occur due to various circumstances:
- the remains of the gel-like suspension (viscoelastic) that were poorly washed off during surgery impede the circulation of fluid inside the eye;
- the implanted lens moves forward towards the iris and puts pressure on the pupil;
- inflammatory processes or hemorrhages inside the eye.
As a result, symptoms appear: redness, pain, pain in and around the eyes, tearing, retching and fog before the eyes. The pressure returns to normal after the use of special drops; sometimes a puncture is done to wash the clogged ducts of the eyeball.
Pathologies requiring surgical intervention
- IOL dislocation. During the operation, the cataract (clouded lens) is removed from the capsular bag, where an elastic artificial lens is placed. It straightens itself inside the capsule, and the desired position is fixed by the doctor. If not fixed correctly, the artificial lens can move back, forward, or to the side. In such cases, the patient experiences a double image of distant objects, the eyes quickly get tired, and the unpleasant symptoms do not disappear after rest. This complication is quite severe: surgery is necessary to correct the position of the lens. Otherwise, retinal detachment will occur or glaucoma will develop.
- Rhegmatogenous (related to rupture) retinal detachment. Serious pathology during lens replacement operations. The retinal layer, separating from the wall of the eyeball, ceases to receive nutrition and dies, which leads to complete loss of vision. Provoking factors are:
- intraoperative complications;
- contusions of the operated eye;
- high degree of myopia;
- diabetes mellitus, vascular diseases.
If symptoms of retinal detachment appear: light spots, floaters, a dark veil before the eyes, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. Treatment is carried out with laser coagulation, surgical filling, and vitrectomy.
- Endophthalmitis. Inflammation of the internal tissues of the eyeball (vitreous humor) is a rare but very dangerous complication of eye microsurgery. It is connected:
- with infection entering the eye during surgery;
- with weakened immunity;
- with concomitant eye diseases (conjunctivitis, blephatitis, etc.)
- with infection of the tear ducts.
Symptoms: sharp pain, significant blurred vision (only light and shade is visible), redness of the eyeball, swelling of the eyelids. Emergency treatment is required in an inpatient eye surgery department, otherwise eye loss and the development of meningitis will occur.
How to prepare the patient?
Research results confirm that proactive detection of dry eye disease and timely treatment can improve the condition of the tear film and ocular surface tissues before cataract surgery.
This is important both for accurate diagnosis before surgery and for better recovery in the postoperative period, and also, importantly, for the patient to be satisfied with the results of the operation2,3,4 .
When choosing treatment, it is important to pay attention to the type of dry eye syndrome and the severity of clinical symptoms.
Fig. 3 Corneal staining - according to ASCRS, the most critical clinical sign of dry eye syndrome
Unlike typical cases of dry eye syndrome, when preparing for surgery it is necessary to restore the condition of the ocular surface in a fairly short time. The American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ASCRS) Cornea Clinical Committee believes that the preoperative management of patients with dry eye syndrome requires more intensive treatment aimed at eliminating clinical signs, combining the use of tear substitutes and topical medications with medical procedures. According to the Committee, the most critical sign of dry eye in these cases is the presence of corneal staining8.
When choosing tear substitutes, it is important to pay attention to the moisturizing component and preservative in the composition. Toxic preservatives can have a negative effect on the epithelium of the ocular surface with frequent instillation.
Remote pathological changes
Undesirable consequences may appear 2-3 months after surgery. These include:
- Cystoid macular edema. Inflammation of the central part of the retina (macula) develops as a result of rupture of the lens capsule during surgery; infections in the vitreous body. Diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, and uveitis often provoke macular edema. The most important part of the retina is affected - the corpus luteum, where light rays are focused and nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain. Early diagnosis of retinal edema is difficult, the symptoms are not clearly expressed:
- blurred vision, especially in the morning;
- blurry wavy image of objects;
- pink tint of the image;
- light aversion.
An accurate diagnosis of macular edema is possible only with optical tomography and retinal angiography. The disease is treated with antibiotics in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. With successful therapy, after 2-3 months the swelling resolves and vision is restored.
- "Secondary cataract". Late postoperative complication occurs after 6-12 months. The artificial lens, which replaces the removed “biological lens,” works properly, so the name “cataract” in this case is inaccurate. The opacification does not occur on the IOL, but on the capsule in which it is located. On the surface of the shell, the cells of the natural lens continue to regenerate. Shifting into the optical zone, they accumulate there and prevent the passage of light rays. The symptoms of cataracts return: fog, blurred outlines, decreased color vision, spots before the eyes, etc. Pathology is treated in two ways:
- surgical capsulotomy - an operation to remove the clogged film of the capsular bag, during which a hole is made to allow light rays to access the retina;
- cleaning the back wall of the capsule using a laser.
The correct choice of IOL reduces the likelihood of developing complications: the lowest percentage of post-cataract development is achieved by implantation of acrylic lenses with square edges.
Does your eye hurt after cataract surgery?
Any manipulations on the organs of vision, even if they are carried out using modern techniques, are stressful for the eyes. Complications after phacoemulsification are noted in every fourth patient. So be prepared for them to appear. There is nothing wrong with this, but you will still have to take additional measures to eliminate these consequences.
As a rule, the eye does not hurt after cataract surgery. But sometimes inflammatory processes develop, which lead to pain and discomfort. Moreover, pain can appear not only in the eye itself, but also in the peri-ocular areas: superciliary arches, temples. The reason for this is:
- Infection of eye tissue due to improper selection of medications.
- Swelling or swelling of the retina.
- Bleeding.
- Inflammatory processes.
Often the sensation of pain is accompanied by a burning sensation, itching or increased tearing. This appears almost immediately after the operation is completed. For such complaints, the doctor prescribes therapy that is designed to eliminate the cause of these symptoms. If it does not go away, then the course of treatment is changed, selecting the most adequate method. In some cases, pain is a consequence of increased intraocular pressure. In this case, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist
Good afternoon. On December 15, 17, I had surgery on my right eye to replace the lens. There was cataract (immature). A month and a half has already passed. I followed all the doctors’ recommendations as expected for a month. A month later I visited an ophthalmologist, he said everything was fine. He canceled all the drops and allowed me to “live a normal life.” About a week ago, maybe a little more, the right eye again began to react to light, it stings, sometimes hurts, and waters. Sometimes the whole right side of my face ache. Not much, but not very pleasant. There are no visible changes in the eye. Doesn't blush, sometimes it seems like I see worse. I can't figure out what's wrong with the eye. I already regret having the surgery. By the way, the lens is American. The postoperative period was without complications. But what about the eye now? Why does it hurt, sting, or tear? Answer, please. Thanks Is this normal? Patient age: 1976 years
Consultations on this issue are carried out by practicing doctors. Medical education has been verified by the site administration. The service bears full moral and legal responsibility for the quality of consultations.
source
Eyes water after cataract surgery
My eyes are watering, what should I do?
In the morning, did you notice dry crusts in the corners of your eyes, and in the afternoon tears began to flow? If at the same time the white of the eyeball turns red and you feel itching, then most likely it is conjunctivitis. You shouldn't treat him with anything. Be sure to consult an ophthalmologist, as conjunctivitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or allergic in nature.
0 238
This material is about watery eyes, what to do and instructions for treating teary eyes
0 344
We continue to answer questions about watery eyes, what to do and what the article is about, instructions for treating teary eyes
0 27
0 68
Eye pain after cataract surgery
Good evening. On January 12, 2013, surgery was performed for immature cataracts in the right eye. After the operation the eye saw well. And from February 22, pain appeared in the eye area, and there was a feeling of a “veil” on the eye. It was impossible to touch the eyelashes if I touched the hellish pain of the eyeball, piercing the head and temple. I went to the ophthalmologist on February 25. I examined the eye. She said that everything was fine - the lens was in place. An injection of diprospan was given under the eye. The pain did not go away, I could no longer distinguish letters in newspaper text. Tell me, please, what can it be?
Hello! You need to check intraocular pressure and, if it increases, instill antihypertensive drops. An in-person examination by an ophthalmologist is required.
Tears flow spontaneously - what to do?
Based on materials from the newspaper “Vestnik ZOZH”
Why do my eyes water outside in windy and frosty weather?
A man contacted the newspaper’s editorial office with a complaint that he was in tears on the street during strong gusty winds and cold frosty weather, what to do and how serious it was.
Answered by a doctor - ophthalmologist of the highest category Minaeeva M.V.
The reason why tears flow from the eyes during wind and frost is that when leaving a warm room on the street, a reflex spasm of the nasolacrimal canal occurs, and, as a result, lacrimation begins. The best remedy for this phenomenon is to rinse your face with a contrast half an hour before going outside.
Be sure to finish rinsing with cold water. If this method does not help, you can take 1 tablet of no-shpa 20 minutes before going outside, which will help relieve this spasm 100%. course of treatment – 1 week.
If lacrimation from the eyes bothers a person constantly, and not just when going outside, then the cause of lacrimation is most likely a blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. In older people, the cause of blockage is often atherosclerosis. Minor blockage can be eliminated by rinsing the nasolacrimal canals with a solution of furatsilin under pressure. This procedure is painless and is performed in any clinic. (HLS 2012, No. 2 p. 13, 2012, No. 11, p. 10)
Herbal drops for watery eyes
If you have tears running outside in windy, cold weather, this folk remedy will help:
1 tbsp. l. Pour 1 glass of water over cumin seeds and bring to a boil. Add 1 tsp to the hot broth. plantain leaves and eyebright grass. Leave for 1 hour, strain, filter through cotton wool. Place a few drops in each eye 3-4 times a day. The infusion can be stored in the refrigerator for 3 days. (HLS 2013, No. 23, p. 33, 2013, No. 6, p. 40).
Apple cider vinegar for watery eyes
Increased tearing of the eyes may be a consequence of a lack of potassium in the body. Drink water with lemon juice for a month, then another month as needed. Another solution is also useful: 1 glass of water, 1 tsp. apple cider vinegar, 1 tsp. honey It is also useful to eat 1 glass of grated apples and millet porridge. (HLS 2005, No. 3, p. 26).
If your eyes are watery, add 1 tsp of water to a glass. apple cider vinegar and honey, drink 3 times a day before meals. (HLS 2010, No. 9, pp. 30-31).
Treating teary eyes with egg drops
Boil the egg hard, carefully cut it lengthwise along with the shell. Take out the yolk and pour granulated sugar in its place. Secure both halves with tape. Place the egg in a small glass so that it does not reach the bottom. Sugar will begin to drip and fill the glass. Place 1 drop of this liquid into the eyes in the morning and evening. (HLS 2004, No. 5, p. 24).
How to cure constant watery eyes with powdered sugar
Before going to bed, wash your eyes, go to bed and do the following procedure.
Pull back the upper eyelid and sprinkle a pinch of powdered sugar under it. Then lightly massage the eyelid. As soon as a tear appears, do the same procedure with the second eye.
Do not open your eyes and do not get wet, sleep like this until the morning. If your eyes have been watering for a short time, then three procedures are enough. In advanced cases, 7-10 procedures. (HLS 2006, No. 14, p. 34).
Strengthening the lacrimal muscle - massage
If your eyes are watery due to weakening of the lacrimal muscle, then a massage will help: with two fingers - index and middle, press where the outer corners of the eyes are. Then press a little closer to your temple. Do not move the skin, but press tightly and loosen, several times. (HLS 2007, No. 14, p. 31).
The cause of watery eyes may be clogged tear ducts, then massaging the bridge of the nose will help. The woman's eyes were constantly watering. She massaged the bridge of her nose on both sides with her little fingers 3-4 times a day for a very long time. It helped her. When she was given this prescription, they warned that the results could only be seen in a year. 5 years have passed, tears still do not flow spontaneously, but from time to time she still massages the bridge of her nose. (HLS 2009, No. 8, p. 32).
Tearing due to blepharitis
With blepharitis, increased tearing often occurs. The following folk remedy will help you cope with it: 1 tbsp. l. cumin, pour 1 glass of water, cook over low heat for 25 minutes. Add 1 tsp. cornflower flowers, 1 tsp. plantain and 1 tsp. eyebright herbs. Let the broth stand for 12 hours in a warm place. After this, cook it for another 10 minutes and strain. Place the decoction into the eyes, 1-3 drops 1-2 times a day. (HLS 2009, No. 8, p. 5).
If your eyes are watery, contrast baths will help.
The woman had increased watery eyes. As soon as I went outside, tears began to flow from my eyes, regardless of the air temperature. I had to carry a huge napkin with me and literally wash myself with my tears. Pharmaceutical drugs, even very expensive ones, helped only during their use. As soon as the tears stopped dripping, the tears started flowing again.
I accidentally found out that Vanga advised washing your eyes with this disease.
The woman took 2 bowls of water - warm and cold. First, I dipped my right eye in warm water for 10 seconds, and then the same eye in cold water. I did the same with the left eye. And the tearing stopped.
She has been doing this procedure every morning for several years now, and has increased the time to 30 seconds. Simple and hygienic. Result: no tears in any weather. One summer I was at the dacha and started washing. In September, tears appeared again, although not very abundantly. I had to urgently put aside my laziness and wash my eyes again. (HLS 2010, No. 3, p. 32).
Treatment of watery eyes after a stroke
A 76-year-old woman suffered a stroke in 2011. After this, the head remained tilted down, and tears constantly flowed from the eyes. She turned to “Herald of Healthy Lifestyle” with the question: “What to do if your eyes are watery”
The answer is an ophthalmologist of the first category of the Central Department of Eye Microsurgery. Varkentina I. V.
Watery eyes are a common complaint among older people. The cause of the reader’s lacrimation is most likely due to impaired innervation after a stroke. Unfortunately, in this case, treatment is only symptomatic: you need to use tear substitutes that will preserve the tear film: Systane, Oxyal, Ophtolic, natural tears.
If lacrimation is accompanied by inflammation, itching, purulent discharge, antiseptic drops are used for treatment: Vitabact, Okomistin.
To avoid addiction, medications are changed and breaks are taken between treatments.
If your eyes are watery, folk remedies will help.
Dill seed. Take 1 tbsp. l. dill seeds, pour 2 cups of boiling water, leave for 2 hours. Apply cotton swabs soaked in dill infusion to the eyes for 10-15 minutes once a day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Cornflower flowers. 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the flowers and leave for 1 hour. Apply cotton swabs soaked in the infusion for 10-15 minutes before going to bed. (HLS 2011, No. 18 p. 18, )
Dill seed for watery eyes
The woman brewed dill seeds at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. per glass of boiling water, cooled to room temperature and applied to the eyes for 15-20 minutes, covering the top with a towel. It took her 1 week to get rid of the disease. (HLS 2012, No. 14, p. 30).
Treatment of lacrimation with honey drops
What to do if tears flow outside in cold weather? Advised by the chief physician of the Research Institute of Eye Diseases, M. N. Lebedeva.
Prepare the drops: mix warm water and honey in a 2:1 ratio. Place 2 drops into your eyes before bed. This simple recipe should help. (HLS 2011, No. 12 p. 4)
Lotions from bird cherry flowers
1 tsp. flowers per 200 ml of boiling water. Fold the gauze in four, soak it in the warm infusion, and place it on your eyelids. As they cool, wet the tampons again in the warm solution. Lie like this for about 20 minutes. In case of exacerbation, do it 2-3 times a day, and for prevention – 1 time a day. The woman had tears constantly flowing from one eye from the cold and sun. These lotions helped her. (HLS 2012, No. 15 p. 31)
If your eyes are watery, herbs will help
All methods may have contraindications. Before using traditional recipes, be sure to consult your doctor!
More articles about this disease:
Sources: sovetclub.ru, doktor.ru, sredstva03.ru
Next:
- Visual acuity after cataract surgery
- Cataract surgery rehabilitation in Veliky Novgorod in Kolmovo
- loading…
No comments yet!
Share your opinion
How to properly paint your eyes with mascara and eyeliner
Golikova called criticism from Roshal
Visin eye drops during pregnancy
Popular articles
Cataract surgery Nizhny Novgorod hospital 35 (Read 132)
- Nivea eye makeup remover reviews (45 reads)
- Treatment of cataracts with honey and eggs (Read 44)
- Can cats take Visine (Read 31)
Latest Published
- The first eye clinic in Moscow
- Zhdanov, Vladimir Georgievich. Hard lenses. LJ OPHTHALMOLOGY.
- Visual tracts. Visual functions (II). Visual functions and age-related dynamics of their development.
- Living water for the eyes. Live x-ray. Life after laser correction.
loading…
Interesting:
Materials for making frames
A look at apartment renovation
Laser vision correction after 40 years. For astigmatism reviews
Patient's feelings after surgery
Many people are concerned about the question: after a cataract is removed: is pain in the eye normal or a sign of pathology? In the first days after manipulation, damaged tissues naturally send pain signals to the nervous system. During the operation, a microscopic puncture of the cornea is made, and an ultra-thin needle is inserted. Ultrasound is applied through it and the clouded lens is destroyed. The crushed particles are removed and an artificial lens is installed. If an advanced cataract is removed, the pain in the eye will be more noticeable—higher power ultrasound is used to crush dense formations. The body needs time to recover.
Prohibitions during the rehabilitation period
Following the patient's instructions, which can be found in the extract, will help reduce the risk of complications. The restrictions are significant, but reasonable.
- For the first 7 days, it is not recommended to go outside without a bandage.
- Do not use cosmetics for 10 days.
- Physical activity and lifting weights over 3 kg are prohibited for 8 weeks.
- Drinking alcohol and visiting saunas and baths are also not allowed.
- massage the eyeball until completely restored;
- be near a fire, oven, fire, fireplace;
- be exposed to cold temperatures (wind, frost);
- watch TV for a long time, read, work on the computer.
Why do negative consequences occur after lens replacement?
If the operation to replace the lens for cataracts is performed by an experienced ophthalmic surgeon, then it does not entail any special problems. For professionals who have performed more than one surgical intervention, removing the lens and placing an implant in its place - an intraocular lens - is a simple and quick operation. The recovery process is smooth for most patients. The likelihood of complications occurs infrequently. But still they cannot be excluded, although they are quite rare phenomena.
Each type of complication has specific causes. After surgery, swelling of the eye often occurs. Many patients encounter this problem during the postoperative period. It is usually associated with a weakened cornea. Another reason is the peculiarity of the body’s reaction to ultrasound. It is used in cases where the patient seeks medical help too late. If the cataract has been advanced, then ophthalmic surgeons need to use more powerful ultrasound waves. This often has an increased impact on the eyeball.
A possible cause of complications after lens replacement for cataracts can also be medical error. Such situations are not so common in medical practice, but they cannot be excluded. Problems may arise due to technical or tactical errors of the doctor who performed the operation. Medical errors usually occur accidentally. Therefore, it is difficult to predict their risk. Cataract surgery is the only possible method of treatment and ophthalmic surgeons have sufficient experience in performing it. But this does not negate the likelihood of complications arising due to the doctor’s fault.
Dry eyes during lens replacement: what to do?
Table of contents
What diseases require lens replacement?
How is lens replacement surgery performed? What is contraindicated after surgery? Possible consequences Causes of dry eye after lens replacement Diagnosis and treatment of dry eye syndrome after surgery Gilan solution to eliminate dry eyes When lens defects cannot be eliminated by therapeutic methods, a microsurgical operation (lensectomy) is performed to replace it with an artificial implant - an optical lens.
In our country, the most widespread technology is using ultrasound, which was first used in the clinic of Professor S.N. Fedorov. This operation has a number of advantages: painlessness, low degree of intervention, and speed of execution.
What diseases require lens replacement?
Refractive lens replacement is performed in the following clinical cases:
- with age-related farsightedness;
- for cataracts;
- for glaucoma in patients with farsightedness;
- with astigmatism associated with degenerative changes or lens defects;
- with myopia above -20D and farsightedness above +20D;
- in the absence of a lens.
The operation is performed not only on patients of active age, but also on elderly people; it is practiced to restore vision in patients with diabetes.
How is lens replacement surgery performed?
Preparing for surgery. It begins with a visit to an ophthalmologist, who evaluates the parameters of all eye structures necessary for the manufacture of an optical lens (depth of the chambers, size of the lens). The implant is manufactured taking into account the pathology identified in the patient.
During the consultation, the doctor gives recommendations on preparation:
- 7 days in advance - refusal to take hormonal drugs and medications that affect intraocular pressure and blood;
- on the day of surgery - do not eat or take medications (except sedatives).
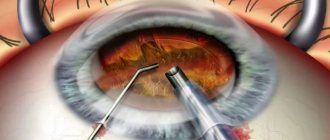
Progress of the operation. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. To reduce the risk of complications, only disposable instruments and materials are used.
Operation stages:
- treatment of the surgical field with an antiseptic solution;
- applying a sterile mask;
- installation of an eyelid speculum;
- local anesthesia;
- a corneal incision (instruments and a lens are inserted through it);
- crushing the lens with an ultrasonic phacoemulsifier and removing its particles out;
- filling the vacant space with viscoelastic (a special agent that maintains the volume of the anterior chamber of the eye);
- installation of the lens (thanks to the flexible structure, it straightens out on its own and takes its place);
- removal of viscoelastic;
- administration of an antiseptic drug and application of a bandage.
After the operation, which lasts no more than half an hour, the patient can go home.
Recovery period. The result of the intervention – improved vision – is felt on the day of surgery. After about a month, complete recovery occurs. During this period, it is necessary to instill an antibacterial agent recommended by a doctor into the eyes.
What is contraindicated after surgery?
During the first week after surgery you cannot:
- play sports, lean forward, work at the computer, use gadgets;
- wash your eyes and touch them with your hands;
- use decorative cosmetics;
- sleep on your stomach or side on the side of the operated eye.
Frequency of postoperative monitoring: the next day after surgery, on the 4th, and on the 8th day, 3-4 weeks after the end of the treatment course.
Possible consequences
Postoperative complications occur extremely rarely. Some patients experience secondary cataracts (clouding of the lens), surges in intraocular pressure, internal bleeding, and dry eyes.
Causes of dry eye after lens replacement
Surgery and the use of local ophthalmic drugs disrupt the stability of the tear film, which causes eye irritation, burning sensation and foreign body sensation. Such symptoms are usually felt by those patients who had problems with the formation of the tear film before surgery.
Diagnosis and treatment of dry eye syndrome after surgery
Signs of dry eye syndrome include increased sensitivity, redness of the eyes, pain when blinking, and a feeling of dryness. They can be established by visual examination and questioning of the patient. To clarify the diagnosis, traditional tests are used to determine the stability of the tear film.
Because topical medications dry out the surface of the eye, the only treatment for dry eye after lens surgery is artificial tears.
Gilan solution to eliminate dry eyes
Moisturizing ophthalmic solution "Gilan" is recommended for use after refractive lens replacement as a tear substitute. A drug based on hyaluronic acid quickly reduces the pain of symptoms, providing natural hydration to the eyes.
What are the intraoperative complications during lens replacement?
Lens replacement for cataracts is considered a well-established procedure. But even with this high-tech operation, complications are possible. One of them is the rupture of the wall of the capsule, inside of which the clouded lens of the eye was previously located, and the loss of its crushed particles into the area of the vitreous body. This complication often entails the development of glaucoma and retinal damage. Repeated surgery can help correct the situation. Typically, optometrists monitor the patient for 2-3 weeks. After this, the clogged vitreous is removed surgically.
Displacement of the intraocular lens towards the retina is another type of complications that are possible after replacing the lens for cataracts. This happens due to improper placement of the implant. This provokes swelling of the macula - the very center of the retina of the eye, in which light rays are focused. In this case, the only possible way to eliminate this problem is to perform a repeat operation and replace the “wrong” lens with a new one. A special type of complication is suprachoroidal hemorrhage. This is an accumulation of hemorrhagic contents in the space between the sclera - the white membrane of the eye - and the choroid. In most cases, hemorrhage due to cataracts occurs in patients of advanced age or concomitant diseases: glaucoma or hypertension. The danger of such a complication is that it can lead to a rapid decrease in vision and loss of the eye.
During the operation:
The surface of the eye is exposed to many aggressive factors: instillation of anesthetics and irrigation solutions, dry air and bright light, and possible mechanical stress. All of this can lead to damage to the corneal and conjunctival epithelium, decreased tear film breakup time, and decreased goblet cell density9. Therefore, in patients with dry eye syndrome, symptoms may increase in the postoperative period, causing anxiety and reducing patient satisfaction with the results of the operation2,4,5.
Vincent P. de Luise, MD, FACS, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York. Dry eye syndrome, left unaddressed before surgery, can progress in the postoperative period, causing the patient to feel that the operation was unsuccessful and the surgeon did something wrong.
Detection of dry eye syndrome is especially important when implanting premium IOLs (toric and multifocal). Patients expect excellent quality of vision with high-tech lenses, but problems with the ocular surface can spoil the result Caceres V. Primer for dry eye diagnosis and treatment before dry eye // EyeWorld (Asia-Pacific). –2017. –Vol. 13, No. 2. –P. 55–57.
Inflammatory processes as complications after lens replacement
They should be used for 2-3 weeks. The regularity of use is selected individually.
If the patient’s immunity was weakened even before the diagnosis of cataract, then the usual signs of inflammation may be accompanied by symptoms of uveitis or iridocyclitis. With uveitis, various parts of the choroid of the eye become inflamed:
This disease manifests itself as redness, pain in the visual organs, photosensitivity, blurred vision, and increased tearfulness. In some cases, floaters and floating spots may appear before the eyes. The basis of treatment for uveitis is the use of mydriatics, steroids, and immunosuppressive drugs.
Another ophthalmological disease that can be a consequence of the inflammatory process is iridocyclitis. This pathology affects the iris and ciliary body. The disease “makes itself felt” with swelling, redness, and pain. In particularly difficult cases and with advanced cataracts, the iris may change color, the pupil may narrow and become deformed.
Conservative treatment of iridocyclitis includes the following types of therapy:
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiviral.
Types of complications that can be treated conservatively
Hyphema is a negative consequence that can occur after cataract surgery. This is a hemorrhage into the anterior chamber of the eyeball, filled with intraocular fluid. That is, there is an accumulation of blood between the lens and the iris. Hyphema occurs due to the fact that during the operation the ophthalmic surgeon accidentally damaged the vessels of the ciliary body or the iris of the eye. This condition does not pose a serious danger to the patient, although it may persist for several months. Hyphema does not cause pain and does not impair vision. It is treated with additional rinses. Doctors most often prescribe hormonal drops, for example, Dexamethasone, and mydriatics, for example, Atropine.
Unsuccessful cataract surgery can cause increased intraocular pressure. This condition is often called "postoperative glaucoma."
Using eye drops
During the rehabilitation period, eye drops must be used after cataract surgery in order to speed up recovery. Medicines can have a complex effect and a specific focus. Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician; self-medication after cataract surgery is unacceptable and dangerous. The following types of eye drops are prescribed:
Ÿ Antibacterial.
Ÿ Anti-inflammatory.
Ÿ Painkillers.
Ÿ Regenerating.
When using eye drops during the postoperative period after cataract removal, special care should be taken to avoid introducing infection into the wound. The procedure is slightly different from the patient’s usual use of drops. I give the following advice to my patients:
Ÿ Ask another person, friend or relative for help.
Ÿ He should wash his hands and warm the bottle of medicine in his hand to body temperature.
Ÿ The patient needs to lie down and tilt his head back. The gaze should be directed upward.
Ÿ The assistant should pull back the lower eyelid and instill the drug between the eyelid and the eyeball.
Ÿ It is forbidden to touch the operated eye with a bottle, pipette, or hands.
Ÿ When prescribing several drugs, take breaks of 5 minutes between their uses.
The most common eye drops following cataract surgery are:
Ÿ Tobrex is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that can suppress the spread of many infections, including staphylococcus and streptococcus.
What complications after lens replacement require surgery?
Serious complications may occur after cataract removal. They require repeated surgery. If the intraocular lens, which is placed inside the capsular bag instead of the clouded lens, is not properly fixed, the IOL can independently move back, forward or to the side. In such situations, the patient complains of a double image of distant objects and rapid fatigue of the visual organs. This type of complication is considered quite severe. Its danger is that if no measures are taken, the patient may develop glaucoma or retinal detachment. Conservative treatment in this case will be useless. The situation can only be corrected by repeating the operation. During this procedure, the ophthalmic surgeon will adjust the position of the artificial lens.
One of the complications that arise after cataract removal is rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. This is a rather serious pathology that requires surgical intervention. Rhegmatogenous detachment occurs because the retinal layer, when separated from the wall of the eyeball, loses access to nutrients and begins to die. This condition is dangerous because it can lead to complete loss of vision. It can be identified by the patient’s complaints about the appearance of a veil before the eyes. Treatment is carried out by:
- laser coagulation - a medical procedure with which ophthalmic surgeons eliminate dystrophic and degenerative changes in the retina;
- vitrectomy - a surgical operation used for hemorrhages in the vitreous body, retinal detachment, injuries to the visual analyzer;
- extrascleral filling - a method of treating retinal pathologies by squeezing it with a special filling fixed on the outside of the sclera.
A rare, but very dangerous complication after removal of cataracts is endophthalmitis. This is a severe inflammatory process in which pus accumulates in the vitreous body. It occurs due to infection entering the eye during surgery, when the tear ducts become infected. Endophthalmitis often develops in people with weakened immune systems and in those who have suffered other ophthalmic pathologies, for example: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, etc. Symptoms of the disease:
- sharp pain in the eyes;
- swelling in the eyelid area;
- significant decrease in vision;
- redness of the sclera.
In case of endophthalmitis, emergency hospitalization in the ophthalmology department is necessary. If the necessary measures to treat the disease are not taken in a timely manner, this may lead to loss of the eye or the development of meningitis.
Recommendations from an ophthalmologist during the postoperative period of cataracts
Good day, dear friends! Surely you know that in order to restore vision during the postoperative period of cataracts, you must follow the recommendations of the attending eye doctor, which will speed up the rehabilitation process and prevent complications.
Thanks to modern technologies, the recovery period after eye surgery has been made less protracted and almost painless. Literally 3-4 weeks after surgery, most patients return to their previous lives, but for this it is necessary to follow certain rules, which will be discussed in this article.
Features of the rehabilitation period after cataract removal
The mistake of many people who have undergone eye surgery is to underestimate the importance of the rehabilitation period, which results in complications.
Can complications arise after a few months?
Some types of complications may “make themselves felt” several months after surgery. The main one is the development of secondary cataracts. This condition usually occurs after 6 months to a year. In this case, the cloudiness does not form on the lens. The capsule, inside of which the intraocular lens is located, suffers. Patients note symptoms typical of cataracts. The complication is characterized by:
- blurred image outlines;
- weakened color rendering of objects;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes.
Treatment of secondary cataracts is carried out using two methods. The first is surgical capsulotomy. This operation removes the clogged film of the capsular bag. The second method is to clean the back wall of the capsule using a laser. Another type of complication that can occur after replacing a lens that is clouded by a cataract is cystoid macular edema. The inflammatory process develops in the central part of the retina. It is caused by rupture of the lens capsule or infections in the vitreous. Cystoid macular edema involves damage to the corpus luteum, the most important part of the retina where light rays are focused. The danger of this condition is that early diagnosis is difficult. Symptoms are not clearly expressed. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by optical tomography of the eye and retinal angiography. Anti-inflammatory drugs play an important role in the treatment of the disease.
How to avoid complications after lens replacement?
In order to avoid complications after cataract removal, you should follow the recommendations of the ophthalmologist. This will speed up the rehabilitation process and avoid complications.
- You should not tilt your head sharply.
- It is better to sleep on the side where the healthy eye is located.
- Make sure that no water gets into the operated eye during hygiene procedures.
- Avoid visual stress. Read less, watch TV, work on the computer.
- Take vitamins, eat more fruits and vegetables.
- Give up bad habits, especially smoking.
- Do not lift anything weighing more than 10 kg.
- Refuse to drive.
If you follow the recommendations given by your doctor after replacing the lens, complications can be avoided.
source
Itchy eyes after cataract surgery
In the postoperative period after cataract removal, all measures must be taken to prevent complications and restore vision. The success of this process largely depends on how accurately the patient follows the ophthalmologist's recommendations.
Eye care after cataract surgery
Typically, after cataract surgery, the operated eye is covered with an onlay. It is not recommended to remove this protective bandage even while sleeping.
The doctor prescribes drops to prevent infectious complications and inflammatory processes. Most often, drops are prescribed in a decreasing pattern over the course of a month, and it is very important to strictly adhere to the instillation schedule.
The eye may itch after surgery, but under no circumstances should you rub it or touch it with your hands. Also, before your doctor’s permission, you should not apply cosmetics to your eyelids or dye your eyebrows and eyelashes.
As for control visits to the ophthalmologist, their number and frequency are determined individually.
Postoperative period: restrictions
You can lead your normal lifestyle, with the exception of driving, sex and intense sports, almost immediately after cataract surgery. But at the same time, during the month you should adhere to certain rules:
- do not lift anything heavier than seven kilograms
- do not go to the bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool
- When washing and showering, avoid getting water and detergents into the operated eye.
- do not carry out cosmetic procedures related to facial steaming
- do not perform “dirty work”, especially those involving dust
- When walking outside, you should wear sunglasses and avoid staying outside in windy weather.
- do not sleep on your side on the side where the operated eye is located
- Avoid tilting your head forward.
As for driving a car, sports and other active activities, this issue is resolved with a doctor depending on the general state of health and the dynamics of recovery processes.
Restoring vision after cataract surgery
After cataract surgery, vision returns immediately on the operating table, but full recovery takes about a month. During this time, both the eye itself and the visual analyzer in the brain adapt to the new artificial lens. It is important to help this process by engaging in a variety of activities, “loading” the vision with new impressions.
Do I need glasses after cataract surgery?
If you needed glasses before surgery, your previous prescription is unlikely to remain valid after surgery. An artificial lens (IOL) is usually selected to provide the best possible vision. Often after cataract surgery there is no need for glasses. If such a need persists, then the glass for the operated eye can be changed a month to a month and a half after cataract surgery.
*The result of the operation is individual and depends on the characteristics of the body and the patient’s health status
I am a pensioner and I was worried about cataracts. The operation took place 2 weeks ago, and I feel good now. The department's employees have golden hands.