Damage to the cornea of the eye is a serious condition that leads to complications. It can be caused by mechanical trauma, chemical or thermal burn, foreign body entry, exposure to radiation, or the consequence of an infectious process.
As a result, the cornea loses its properties. It does not fully protect against harmful factors; discomfort, disability and deterioration in the patient’s quality of life are possible.
It occurs in adults and children due to their active, busy lifestyle.
If you have any complaints, you should contact an ophthalmologist. Treatment is selected individually. Depends on the symptoms, the cause of the condition, the age of the patient and concomitant diseases.
Causes
Damage is caused by provoking factors:
- entry of a foreign body into the eye (sand, dust, particles of cosmetics, small fractions of debris, fragments, etc.), causing scratches, erosion, penetrating and non-penetrating wounds;
- drying out of the mucous membrane due to the harmful effects of computer radiation during prolonged use;
- congenital pathological conditions of the visual apparatus;
- vulnerability to radioactive and ultraviolet radiation;
- corneal burns when working with welding;
- consequence of infectious eye diseases.
Causes and types of corneal damage
There are many types of corneal injuries - domestic, industrial, criminal and others. Damage also varies in severity and can be external or penetrating. But with any injury, visual function deteriorates.
Scratches and erosion
A scratch on the cornea is not as dangerous as erosion. It has almost no effect on the visual functions of the eye, but causes unpleasant sensations that cannot be ignored.
Such damage occurs in 70% of all corneal injuries. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of a corneal scratch:
- mechanical damage - foreign bodies entering the eye (grains of sand, dust particles, splinters, metal shavings);
- long-term wearing of contact lenses;
- diseases of the organs of vision;
- trauma as a result of surgery.
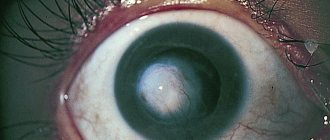
Corneal erosion refers to the appearance of an ulcer, which provokes infection into the eye. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor and begin treatment, since often the affected area can affect the deep layers of the eye. The condition of the visual organs deteriorates significantly.
Traumatic erosion occurs due to mechanical damage, as well as high temperatures or exposure to strong ultraviolet radiation.
Recurrent erosion is characterized by the constant return of the problem, even with adequate therapy. In this case, scars may appear on the cornea through which light does not pass. In severe cases, ulcers can reach the anterior chamber of the eye and become a source of primary infection.
Causes of infectious erosion:
- herpesvirus infection;
- fungal infection;
- bacterial conjunctivitis;
- chlamydia.
Causes of non-infectious erosion:
- improper wearing of lenses;
- contact with chemical reagents and foreign bodies in the eye;
- unsuccessful surgery;
- xerophthalmia;
- injuries;
- high temperatures and UV radiation.
Internal causes of erosion:
- atopic dermatitis;
- diabetes;
- rheumatism of the joints;
- demodicosis;
- neoplasms;
- diseases that interfere with the proper growth of eyelashes.
Penetrating and non-penetrating wounds
Penetrating wounds to the eyes damage the integrity of their membranes. The wounds may be punctures, lacerations or cuts. With a penetrating wound, ptosis, exophthalmos, and ophthalmoplegia occur. These complications indicate deep damage, even affecting the optic nerve.
If the penetrating wound occurs in the limbal region, vitreous prolapse may occur. When the lens or iris is damaged, the fibers of the lens swell and rapid clouding occurs.
Non-penetrating wounds do not violate the integrity of the cornea or sclera. Most often, they are possible when large grains of sand get into the eye. A foreign body can be easily removed by a specialist; you should not do this yourself - you can further damage the corneal layer.
Foreign body
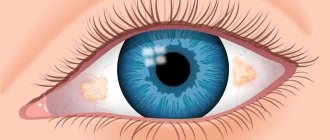
Foreign bodies of the cornea are divided into superficial and deep. They violate the integrity of the epithelial layer and create favorable conditions for the onset of an infectious and inflammatory process.
Metal particles penetrate deeply into the corneal layer, which quickly create an infiltrate, provoking infectious inflammation. Deeply located foreign bodies can become encysted and cause purulent inflammation.
Burns
Burns pose the greatest danger to the visual organs. Most often they lead to significant damage to eye tissue. Treatment is always difficult and does not in all cases lead to complete restoration of vision. According to statistics, 40% of patients with eye burns remain visually impaired.
75% of eye burns are caused by contact with acids. Such damage causes coagulative necrosis.
Important! Since the acid does not immediately penetrate into the thickness of the tissue, the consequences of the burn can only be determined after a couple of days.
22% of burns are caused by alkalis, which dissolve tissue protein. In this case, damage to the eye can occur in either 5 minutes or several days. The severity of such a burn can only be assessed after a few days.
Types of corneal injuries
The type of damage depends on the provoking factor:
- mechanical type - as a result of exposure to a foreign body, ingress of small objects (dust particles, carcass, fragments), improper use of contact lenses, unqualified selection of optics;
- chemical type - caused by burns of various substances (alkalis, household chemicals, acids);
- thermal type – for a burn caused by exposure to high temperatures on the organ of vision;
- ionizing or laser damage.
Why does it appear and what are the risk factors?
A child or an adult can accidentally scratch the cornea when rubbing the eye too hard. The stratum corneum is especially often injured when a foreign body penetrates. A scratch often occurs when sand, small gravel, dust, dirt or shavings get into your eyes when cutting metal. In the latter case, the eyeball takes longer to heal and is much more painful. A scratch on the eyelid often occurs in people who wear contact lenses for a long period of time. Careless surgical intervention can damage the conjunctiva, the area of the white and the pupil. At this time, the cornea is most vulnerable and scratch marks easily appear on it. The following factors are identified that influence the occurrence of a violation:
The membrane of the visual organ can be damaged due to wearing contact lenses.
- drying or thin layer of the cornea;
- use of contact lenses;
- work activity in which there is a high risk of eye damage;
- professional sports, during which the eyeball may be injured.
Symptoms
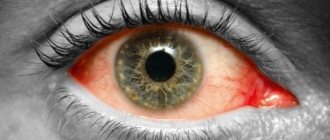
If the cornea is damaged, the patient complains of symptoms:
- feeling of “sand” in the eyes;
- feeling of being hit by a foreign body;
- discomfort, redness of the mucous membrane of the organ of vision;
- burning, acute pain syndrome;
- profuse lacrimation;
- possible headache;
- super-strong, unusual for a given person, eye sensitivity.
Visual disturbances of varying strength also occur. There is a blurred picture, blurring of the object, lack of a contour, and decreased visual acuity.
First aid
First aid must be fast, correct, urgent and qualified. It includes a consistent set of the following activities:
- if damage to the cornea is caused by the entry of a speck or foreign body, remove it with a tear using active blinking;
- rinse the eyelid with an antibacterial agent (aqueous solution of Furacilin, chamomile decoction);
- to further expel the foreign body, cover the lower eyelid with the upper eyelid pulled back and move the eyeballs left and right;
- apply anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drops or ointment with this effect (Tsiprolet, Tsipromed, Tetracycline, Tobrex, Levomycetin, etc.);
- Cover the injured eye with a sterile gauze pad and secure.
In case of severe pain, you can instill Novocaine solution or Inocaine eye drops once. Then immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
If an object with sharp edges or a large size gets into the eye and becomes entrenched in the organ of vision, it cannot be removed independently. Also, do not rub your eyelids, use non-sterile objects, or materials unsuitable for this (fluffy napkins, cotton pads).
First aid for eye injury
- When a foreign object gets into the eye, if possible, it should be removed and the eyes should be washed. It is important to remember that a foreign body located in the sclera of the eye or even deeper cannot be removed independently .
- A dry and cold object is applied to the site of the bruise - most often ice and food from the freezer, wrapped in plastic and a clean napkin.
In case of a thermal burn, you should use antibacterial ointment or drops, apply a napkin and a cold compress. Of course, the root cause of this burn needs to be eliminated.
- If an eye injury is accompanied by bleeding, then it is necessary to apply antibacterial drops and a sterile bandage. Only a specialist can provide further assistance.
- After an ultraviolet , the victim needs a darkened room. You need to put antibacterial ointment behind the eyelid, and then put dry cold on your eyes.
- If there is a penetrating injury to the eye, the victim should not be disturbed. It is important to keep him still and call 911 immediately.
First aid for eye injuries
In case of a chemical burn, rinse your eyes thoroughly with running water (at least 20 minutes). If the injury was caused by quicklime, then you first need to remove all its particles with a dry and clean napkin (cloth) and only then rinse with water.
- If your eyes are injured, you should never rub them, touch them with dirty hands, or put pressure on your eyelids. When applying a bandage, you must use gauze (cotton wool is prohibited!). Do not wash a penetrating wound.
Treatment
Therapy for eye damage is aimed at eliminating the provoking factor, relieving pain and signs of inflammation, healing and fusion of corneal tissue.
For pain relief for up to 2 days, Lidocaine drops, Novocaine solution, Inocaine are used. To relieve pain and inflammation, medications from the NSAID group are used in the form of eye drops (Indomethacin, Indocollir, Broxinac, Diklo-F, Diclofenac).
In case of severe pain, it is possible to take additional painkillers (Analgin, Nimesulide, Ketoprofen, Nurofen).
When a bacterial infection occurs, antibacterial ointments and drops are used (Tobrex, Sulfacyl sodium, Levomycetin, Floxal).
For the healing of corneal tissue, the medications of choice are Korneregel and Solcoseryl.
Before using all medications, the eyes must be rinsed with an aqueous solution of Furacilin or fresh chamomile infusion.
Prevention
People in construction professions are at risk of corneal damage. For prevention, you should use safety glasses, special suits, and protective equipment, especially when working with cement, welding, and bulk components.
Children are also at risk due to their busy, active lifestyle and inattention. If a foreign object or blow gets into their eye, they should immediately contact an ophthalmologist to rule out serious pathologies.
One of the reasons for damage to the cornea of the eye is exposure to ultraviolet rays. You can reduce the impact of the provoking factor by wearing sunglasses. Wear them year-round when there is bright sun.
When constantly working at a computer for a long time, it is important to take breaks periodically and use moisturizing drops to reduce the symptoms of “dry eye” and prevent damage.
Diagnostic procedures
Usually, using a slit lamp, the doctor is able to identify the cause of the patient’s discomfort.
If a child or adult scratches the cornea area, you should urgently consult an ophthalmologist. To better examine the damaged area, an anesthetic substance is injected into the conjunctival sac twice or three times with a short break. After 10 minutes, a diagnostic examination is performed using lateral illumination and a slit lamp. If in this way it was not possible to discern a scratch on the cornea, then a fluorescent substance is used, which is illuminated. The drug is also injected into the conjunctival sac. Thanks to this diagnostic technique, the damaged areas are tinted green and it is easier for the doctor to assess their area.
Useful video
A feeling of pain and “sand” in the eyes often indicates damage to the cornea. It can be caused by various injuries (bright light rays, foreign body entry, careless application of mascara). It is important to take the right actions when symptoms occur.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 10 ratings, average: 4.50 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.