Causes
The most common causes of the development of pathology are the following diseases and conditions:
- herpes;
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- chlamydial infection;
- mechanical injuries;
- exposure to chemicals;
- exposure to high temperatures.
If the nature of the disease is infectious, pathogenic microorganisms spread through neighboring organs or through the blood. The most dangerous infection is the intrauterine type. During embryogenesis, this leads to impaired growth and formation of the fetus. A baby can also become infected when passing through the birth canal during birth. The child’s immunity is not sufficiently developed, so it cannot resist pathogenic microorganisms; in this case, clinical symptoms develop most clearly.
If a person's immune system functions normally, herpes in most cases will not be able to cause the formation of leukoma. In immunodeficiencies, the herpes virus spreads to many mucous membranes, forming a replacement with connective tissue.
Damage to the cornea from mechanical injuries, chemicals and household substances contributes to the formation of a wound. In case of complications, the tissue heals poorly, forming scars.
Causes
Leukoma of the eye can be congenital or acquired. The exact causes of the disease can only be determined with the help of an ophthalmologist and an examination. It is important to exclude the effect of unfavorable factors in order to begin treatment and prevent further tissue destruction.
The main predisposing factors for the development of acquired corneal leukoma are:
- chemical and thermal burns of the eyes;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of viral and bacterial nature;
- penetrating wounds of the cornea,
- ulcerative defects;
- pterygiums.
Any surgical intervention can lead to the formation of ocular leukoma. Postoperative corneal scar is a predisposing factor. Traumatic exposure triggers an inflammatory process, which is accompanied by swelling of the stroma and increased synthesis of special enzyme substances by keratocytes. This dilates the limbal vessels and enhances cellular infiltration. As a result, the injured tissue is replaced by connective cells and the process of neovascularization occurs.
It is quite difficult to say exactly what operations leave scars on the cornea. Any surgical intervention is potentially dangerous. But much depends on the body’s reaction, the person’s age and the presence of other ophthalmological pathologies.
Congenital corneal cataract occurs against the background of intrauterine infection of the fetus, when there is a failure in the synthesis of collagen fibers.
The disease is accompanied by other developmental defects. The most dangerous diseases for the developing fetus are chlamydia, gonorrhea, tuberculosis and syphilis. Important! Experts believe that one of the causes of corneal clouding is a lack of oxygen in the eye tissue, which occurs when wearing contact lenses for a long time. During the period of rest from them, it is better to use glasses. Contact lenses can be day or night, but in any case they are not used for more than 10-14 hours at a time.
Risk group
The risk group includes the following categories of patients:
- working in enterprises with harmful chemicals or with devices that can cause mechanical damage (welding machine);
- newborns whose mothers have herpes infection or other serious bacterial diseases;
- patients who have experienced mechanical eye damage;
- persons with immunodeficiency.
These categories of patients should be periodically examined by doctors of various specialties.
Belmo
Description
Eyesore Why do eyesores appear?
Is it possible to get rid of it? D.POMOSHNIKOVA, Penza.
Belmo
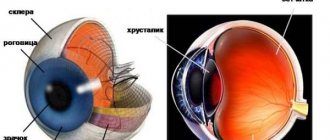
is a clouding of the cornea caused by cicatricial changes.
Its formation is caused by trachoma, keratitis, eye injuries (wounds, chemical and thermal burns), and surgical interventions on the eye. There are also congenital opacities of the cornea caused by an intrauterine inflammatory process. The cataract may occupy part or all of the cornea.
Its effect on vision depends on the location, size and intensity of the cataract. When located on the periphery, it affects visual acuity less than when localized in the center of the cornea against the pupil. The surface of the cataract is thinned tissue of the cornea, which, under the influence of intraocular pressure, swells and forms a staphyloma - an ectatic cataract. With a perforated ulcer or penetrating wound of the cornea as a result of scarring, the cornea becomes fused with the iris, which leads to deformation of the pupil and the development of secondary glaucoma. Sometimes (for example, in the presence of a fistula in the cornea, increased development of connective tissue), a flattening of the thinned cornea occurs, and its tissue in the area of the cataract may undergo secondary degeneration. In severe cases, the process ends with atrophy of the eyeball.
If minor opacities of the cornea do not require treatment, then the treatment of the corneal spot and the cataract itself is only surgical. In this case, keratoplasty is used, which in a significant number of cases makes it possible to restore vision even with dense, extensive opacities. For a cataract that occurs after a severe burn, as well as after repeated, ineffective keratoplasty, doctors resort to keratoprosthetics.
Drug treatment is carried out only for residual inflammatory processes in the cornea. The choice of medications depends on the cause of the disease. For example, a doctor can prescribe anti-tuberculosis and antiviral drugs, which in some cases leads to some clearing of the cataract.
Prevention of the appearance of cataracts is aimed at preventing eye injuries and timely treatment of diseases leading to their formation.
Clover treats the cornea.
Is it possible to get rid of a cataract using traditional medicine?
N. KOSTROVA, Ulyanovsk region.
Belmo
- This is a persistent clouding of the cornea of the eye, which is scar tissue.
A cataract often develops as a result of various inflammatory eye diseases or corneal trauma; less commonly, congenital opacification occurs. Depending on its location, the thorn can dramatically reduce vision or have no effect on it.
The thorn can resolve with the use of some medicinal plants, if it is not pronounced. In difficult cases it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. There are many traditional ways to treat cataracts. Here are a few of them.
- In fresh rye bread, cut a hole on top the size of a glass and place the glass in it upside down very tightly. Drops form on the glass, which need to be collected and instilled into the affected eye, 3 drops 2-3 times a day.
- To treat cataracts, especially for overweight people, in the old days it was recommended to make long-term poultices with hot water and bathe in a hot bath.
- The milky juice of dandelion removes thorns. Place 1 drop into the eye 1-2 times a day.
- After an eye injury, to prevent the appearance of a cataract and in case of danger of its formation, you need to instill 3 drops of onion juice mixed with honey into the affected eye 2-3 times a day: dilute the juice of a medium onion in a glass of boiled water, add 1 dessert spoon of honey and that’s it Stir thoroughly, then strain through cotton wool.
- Lubricate the affected eye with honey mixed with mashed poppy seeds.
- Burn a sprig of rosemary, mix the ashes thoroughly with 1 tbsp. spoon of honey. Apply to eyes at night for eyesores.
- Squeeze the juice from the flowering heads of red clover, mix by volume with natural bee honey 2:1. Lubricate the eyelids with the mixture 2-3 times a day, drop 3-5 drops into the eyes to get rid of cataracts. Clover clears ulcerative skin lesions.
- Mix the juice of the celandine herb 1:1 by volume with honey, cook over low heat until the foam stops and the mixture thickens to the consistency of honey. Lubricate your eyelids with cataracts and trachoma.
A drop will remove the veil
I have suffered from eye diseases all my life, so I have collected quite a lot of useful recipes that are so rich in traditional medicine. I want to share some of them with the readers of the magazine.
The thorn can be removed without surgery if you instill one drop of fresh fir resin daily into the eye at night. A burning sensation will be felt in the eye, but even an old cataract will resolve. Barley is treated with a decoction or infusion of yarrow herb.
To treat conjunctivitis, you need to take 2 chicken egg whites and a third of a glass of boiled water. Mix, let stand for 40 minutes in a warm place and apply this mixture to the sore spot 10-15 minutes before bedtime.
Fresh cucumber lotions help with all eye diseases. Pour 0.5 cups of finely chopped cucumber peel into 0.5 cups of boiling water, add 0.5 teaspoons of soda.
N. SLITKOVA, Khabarovsk region.
Classification
Diseases are classified depending on their location on the cornea:
- periphery - the pathological focus is located on the sides of the iris, so vision deterioration is impossible;
- total lesion - spread of leukoma to the entire area of the cornea, which sharply reduces visual acuity up to complete blindness; the patient can only distinguish between bright and dark light;
- central, which also reduces visual acuity, but is located only in the area of the iris and pupil.
There is a classification according to the form of pathological formation:
- spot;
- circle with uneven edges;
- thorn.
The formation is dangerous because it can cause fluid to leak from the internal structure of the eyeball outward. A scar will gradually form.
Forms of the disease
Congenital and acquired forms of cataract are determined. Leukomas caused by pathology of intrauterine development are classified as congenital forms of the disease. Despite the placental barrier, pathogens of some infectious diseases sometimes manage to overcome it and, as a result, damage to the cornea can occur. The remaining types of the disease belong to acquired forms of catarrh, i.e. The development of the disease occurs due to external factors.
The location of the cataract and the area of its distribution affect the patient’s quality of vision.
The most severe consequences occur when the cataract is located in the center of the cornea - opposite the eye pupil.
The formation of leukoma in the peripheral area of the eye has little effect on visual acuity, but can cause the development of astigmatism.
In addition, two types of leukoma are identified - fused and ectatic. The first includes leukomas fused to the iris as a result of a corneal wound or perforated ulcer. A cataract with stretching and thinning of the cornea, with bulging forward, is called ectatic.
Symptoms
When the disease appears, the patient experiences the following clinical symptoms:
- inflammation of the cornea with the formation of severe pain, which gradually disappears;
- the formation of a neoplasm with a cloudy consistency, different size and location;
- if the lesion is deep, it becomes permeated with vessels;
- if the damage is mechanical, the formation is cloudy;
- if it is infectious in nature, the formation will have a darker shade, a high tubercle;
- sensation of a foreign object under the eyelids;
- decreased visual acuity with concentration of scar in the pupil area;
- increased intraocular pressure, which can lead to glaucoma;
- adhesive process with the internal structures of the eyes;
- disruption of nutrition of the superficial structures of the eyes through blood vessels, which leads to gradual tissue death.
When the tissue is replaced with scar tissue, the patient's pain goes away. A person constantly feels discomfort in the eye area if the scar is large.
What it is?
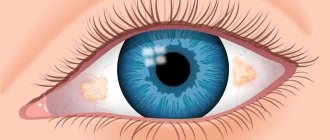
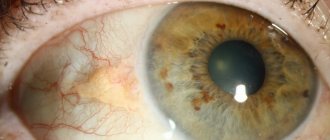
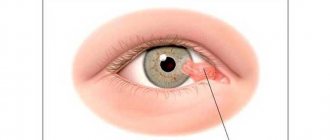
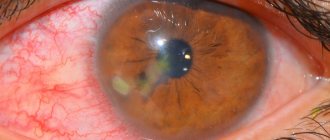
In essence, a corneal cataract is a clouding of the cornea, a scar on the cornea.
At the beginning it has a porcelain-white color and the shape of a spot or cloud. Over time, fat accumulates in this area, giving the cataract a yellowish tint, and a vascular network is formed. A larger cloudiness is called a thorn.
An eyesore on a person: photo
- Leukoma can be acquired or congenital . Acquired thorns are much more common. Congenital leukoma forms in the fetus during intrauterine development.
There are also total, central and peripheral leukoma.
- In the first case, the clouding is spread throughout the cornea. The patient distinguishes light, but does not perceive anything other than it.
- With central leukoma, the pupil is partially or completely blocked. In this case, visual acuity is noticeably reduced, and the field of vision is significantly narrowed.
- In peripheral leukoma, the spot is located away from the icon. The field and visual acuity remain unchanged.
There are several signs of leukoma:
- Decreased vision.
- Fear of light.
- Tearing.
- Sensation of a foreign body or sand.
- Photophobia.
- Soreness.
- Redness of the eyes.
- Changed color of the cornea.
- Haze before my eyes.
These symptoms do not necessarily appear, and in addition, they may indicate some other disease. In any case, if there are alarming signs, you should check with a specialist.
Video:
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the patient’s condition consists of several stages:
- Anamnesis collection. This is data obtained from the words of the patient or his close relatives. Based on these, the doctor can suggest the cause of the scar.
- General examination of the patient. The doctor determines the structure of the scar, its transparency, and thickness.
- Examination of the fundus to prevent the development of complications in the internal structure of the eyes. To do this, a solution is instilled into the patient's eyes, which temporarily disrupts the accommodation of the eyes. The doctor examines the condition of the lens, eye chambers, retina, and vitreous body.
- If the ophthalmologist suspects the presence of additional damage to the eyeball or brain, a CT or MRI is performed. This requires additional clinical symptoms indicating a complication.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. Only after this does treatment occur.
Symptoms and diagnosis
- A spot of various shapes, pale yellow (fat deposits) or white, appears on the cornea;
- Decreased visual ability;
- A veil forms before the eyes, images and shapes of objects are distorted.
To diagnose this disease, doctors use an ophthalmic lamp. In some cases, there are small opacities, as a result of which they are difficult to notice with the naked eye in the mirror, however, if the leukoma is located in the visual area, then it provokes discomfort. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, the clouding may increase in size.
Treatment
There are surgical, traditional and medicinal methods of treatment. Doctors advise using it in combination to reduce the risk of developing complications from the disease.
Scar absorbents
For this, Lidaza and potassium iodide are prescribed. The drugs eliminate the accumulation of tissue that has formed the scar. It is recommended to use them in the form of drops. When applied topically, their effectiveness increases.
Drugs that promote tissue regeneration
Korneregel, Balarpan, Actovegin are prescribed. These drugs help increase metabolism in the damaged area. Thanks to this, new cells are formed faster. The nutrition of the cornea through the blood improves.
Surgical techniques
To carry out the surgical technique, two types of operations are performed:
- excision of the scar under a microscope, which allows you to better see the damaged area and reduce the risk of removing excess tissue;
- corneal transplant from a recipient.
Treatment of corneal thorn
In cases of exposed nerve endings, severe hyperemia, lacrimation, and painful sensitivity to bright light, special contact lenses-protectors are sometimes prescribed. It should, however, be understood that this is not a treatment and serves only as a palliative method to alleviate symptoms.
Moreover, the countless “folk remedies” that quasi-medical websites vying with desperate patients cannot be considered a treatment: these “recipes” include honey (which for many people is a powerful allergen), aloe, and eyebright in various forms, and mother’s breast milk, and the bile of freshly caught pike, and many other substances, sometimes completely unexpected in this context.
As medicinal support, additional or symptomatic treatment, the ophthalmologist may prescribe an anti-inflammatory regimen, absorbable drugs; the use of physiotherapeutic procedures (for example, electrophoresis with hormone-containing agents) and the prescription of keratoprotectors (Balarpan, Korneregel, etc.) are reported.
However, conservative therapy in this case is just a palliative and does not radically solve the problem. The only effective method of eliminating a cataract has been and remains surgical treatment.
Our ophthalmology center successfully performs surgical treatment of all types of corneal opacities. Using various types of keratoplasty, our ophthalmic surgeons restore vision and remove cosmetic defects. You can find out prices for treatment and make an appointment by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Prevention
It is recommended to apply the following rules to prevent the formation of leukoma:
- timely consultation with a doctor if you receive an injury to the eyeball;
- preventive examination by an ophthalmologist at least once a year, especially for those categories of patients who have eye diseases;
- treatment of systemic diseases, infections that can cause complications on the visual organs.
Leukoma is a condition that can lead to complete blindness. When it forms, it is recommended to carry out urgent treatment so as not to cause complications.
Correct medical diagnosis
If characteristic symptoms of the disease occur, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will conduct a survey (collecting anamnesis) of the patient to determine the provoking diseases.
A visual examination will help detect the roughness of the surface of the eye, which rises above the membrane (an uneven white tubercle). He will determine the cause of the formation of the cataract and prescribe effective treatment.
Comprehensive diagnosis of leukoma consists of several methods:
- Biomicroscopy. Carrying out a slit lamp examination helps to identify the focus of leukoma, its structure, size, and depth.
- Ophthalmoscopy. Helps determine the degree of development of the disease, the level of scar transparency, and fundus reflexes.
- Keratotopography. Allows you to determine the condition of the cornea, its structure, the presence of defects, damage and their nature.
- Visometry. It is carried out to determine the quality of vision.
- Tonometry. It is carried out using a special non-contact device that helps determine the level of pressure inside the eyeball.
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision. It is prescribed to determine the presence of foreign objects in the eye: wood chips, plastic.
Based on the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed. If necessary, an examination is carried out by an endocrinologist, cardiologist, infectious disease specialist, or surgeon.
Diagnosis of leukoma
Diagnosing a cataract is not particularly difficult. First, the doctor determines what disease could provoke its appearance. After this, an eye examination is performed. Often, upon external examination, a whitish lesion is clearly visible. Sometimes it protrudes (with a thin cornea), sometimes it has an uneven or rough surface. Using ophthalmoscopy, the doctor determines the reflex of the fundus of the eye and the transparency of the cataract. Another method for diagnosing this disease is biomicroscopy. It makes it possible not only to examine the focus of opacification in detail, but also to determine its depth in the thickness of the cornea. This is a very important method, especially in the diagnosis of very small lesions.