Varieties
Depending on the origin, experts divide strabismus into friendly and paralytic. Let's talk about them in more detail.
Friendly
This form is characterized by a violation of the coordinated work of the oculomotor muscles, in which not only eye fixation is impaired, but also binocular vision. When distinguishing objects, there is no diplopia - double vision.
Most often, concomitant strabismus occurs in young children. The following reasons can lead to the development of a pathological process:
- farsightedness;
- myopia;
- significant difference in diopters of the right and left eyes;
- pathological processes in the cerebral cortex;
- eye injuries;
- diseases of the optic nerve and retina;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- paresis and paralysis of the oculomotor muscles;
- infectious processes;
- psycho-emotional disorders.
Concomitant strabismus can be convergent or divergent.
Pathology can be congenital or acquired. The first type is associated with the anatomical structure of the eye and diseases of the central nervous system. Congenital pathology is often provoked by myopia and farsightedness.
The acquired form is associated with a decrease in the visual functions of one of the organs of the visual apparatus. In turn, the acquired type can be convergent or divergent.
Convergent type
The cause of this condition may be overwork or overexcitement. In a calm, relaxed state, there is no disturbance. In this case, vision correction should be carried out before three years, otherwise the pathology will become permanent.
The sore eye with convergent strabismus is always directed towards the nose. If you need to focus your gaze on some object, then only one eye can do this.
Important! In some cases, both eyes may become squinting in turn. Convergent strabismus is associated with the following complications:
Convergent strabismus is associated with the following complications:
- distortion of the overall picture;
- the brain turns off the amblyopic eye, otherwise double objects will occur;
- the retina of the squinting eye stops sending impulses;
- the functioning of the affected organ simply stops over time.
The convergent type is not characterized by progression. Sometimes it is even possible for the disease to disappear without the use of any methods. Still, you shouldn’t get your hopes up with thoughts of a cure. It is unknown how the pathology will behave with age, so contact a specialist for advice.
Divergent type
Compared to the above form, it is quite rare. Complications of the divergent type appear less frequently. Weakening of the internal muscles of the visual apparatus is a common reason that the eyes diverge.
A feature of the divergent form is the absence of discrepancies when concentrating on objects that are close. Basically, the disease occurs against the background of severe myopia - myopia. The visual axis of a squinting eye can deviate upward or downward.
Treatment of concomitant strabismus includes the use of the following techniques:
- optical correction, including the prescription of contact lenses or glasses;
- hardware procedures to improve the quality of vision;
- orthoptic and diplotic treatment to improve binocular vision. A special “Synoptophore” apparatus is used, as well as interactive gaming programs. Diploptics involves reading through a grid.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in extreme cases when other methods are ineffective
Paralytic
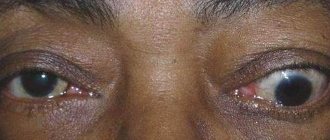
The pathology is based on the deviation of the eye away from the central axis. Most often it occurs against the background of paresis or paralysis of the extraocular muscles. This can happen due to injuries, infectious and inflammatory processes, tumors, intoxication and more.
The patient develops the habit of turning towards the paralyzed muscle. Due to impaired binocular vision, objects become blurred. Most often, the eyeball does not move at all. Patients complain of sore eyes, headaches, tinnitus and dizziness. A split picture occurs when viewing the same object with both eyes. The patient tries to compensate for diplopia by tilting the head.
How is strabismus treated?
Treatment of strabismus is always individual and depends on the type of pathology, its cause, and the angle of deviation of the eye. Doctors can correct strabismus using Evaluation and management of strabismus in children:
- Conventional and prismatic lenses. Regular glasses are prescribed to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness and astigmatism, which are the causes of strabismus. And to eliminate double vision, prismatic lenses are made. They refract the path of rays and shift the image to the side.
- Exercises for the eye muscles. In some forms of strabismus, such as exotropia, they help align the visual axes.
- Medicines Eye drops can be prescribed for strabismus with amblyopia: they will “fog” the strong visual organ so that the weak one works harder. Botox injections sometimes weaken the overactive eye muscle, which pulls the blanket over itself in controlling focusing.
- Bandages. Its task is to cover the strong eye in case of strabismus with amblyopia, in order to allow the weak one to express itself.
- Surgery operations on the eye muscles. The goal is to change the length and position of the muscles to align the organs of vision along the same axis. This method is resorted to if all else fails.
At any age, treatment can improve quality of life. After all, as surveys have shown, The psychosocial effects of adult strabismus: a review, many people with strabismus experience problems with self-esteem, establishing social connections, and work. In a small study, children with strabismus reported increased anxiety, depression, and other symptoms of emotional distress, which decreased after treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the patient’s condition consists of several studies:
- Anamnesis collection. This is data obtained from the words of the patient or his close relatives. Based on them, the doctor may prescribe additional research methods.
- General examination of the patient. The doctor looks at the surface structures of the eyes and eyelids and assesses his condition. If a person's eye optical powers vary excessively, this can cause strabismus, which is immediately determined by a doctor.
- Fundus examination. A solution is dripped onto a person’s mucous membrane, disrupting the process of pupil accommodation for a short period of time. The doctor assesses the condition of the lens, chambers of the eye, retina, and microcirculation vessels.
- Assessing vision using tables. They are used by doctors in three forms: with letters, with pictures, with symbols. Their use depends on the age and mental state of the patient. The doctor sequentially points to a separate symbol, the patient names it. The ophthalmologist looks at how many lines in the table the person saw.
- Assessment of visual acuity using a refractometer. Only when using this device can a doctor diagnose the degree of visual acuity in each eye separately.
Therapeutic treatment
If the eyes are directed in different directions, this does not mean that surgery is immediately required. First, therapeutic methods are used. If strabismus occurs against the background of a specific disease, then treatment is primarily aimed at it. If therapy is not started on time, a person may lose vision altogether.
View gallery
In any case, eye correction is carried out first. Previously, only glasses or special prismatic lenses were available. In modern times, soft contact lenses are also used for correction. Laser therapy is very popular. It is not only painless, but also very effective. For vision correction, diploptic, hardware and orthoptic treatment is used.
If amblyopia develops, penalization (temporary closure of the healthy eye) is prescribed. The corresponding eye socket or spectacle lens is sealed. This is done to increase the load on the muscles of the squinting eye.
Amblyopia is carried out over a long period of time. During treatment, the patient must be under constant medical supervision. As the load on the affected eye increases, vision begins to gradually recover and strabismus disappears.
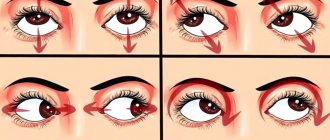
For its treatment, special exercises are prescribed. The technique of Dr. Bates, an American ophthalmologist, is very effective. His exercises can help even in cases where there seems to be only one option left - surgery.
There are various exercises by other professors (Roy, Zhdanov, Shichko, etc.) that help restore normal vision. Many techniques are very effective at the first signs of strabismus. An advanced disease takes much longer and is more difficult to treat.
View gallery
Symptoms and signs
The first warning signs of an ocular stroke are:
- temporary and/or progressive vision loss;
- gradual loss of peripheral vision;
- the appearance of white spots, glare, and other interference that blocks vision (“curtain effect”);
- sudden loss of areas of the visual field;
- color vision disorder.
Symptoms of eye stroke due to occlusion (blockage) of the central retinal artery
:
–
complete or partial loss of peripheral vision, which gradually develops into partial or complete loss of central vision (with retinal detachment);
– the appearance of blind spots, distorted outlines or distorted perception of the picture.
In most cases, the disease is not accompanied by pain and patients do not pay attention to the manifestations of the disease, but prolonged occlusion of the central artery causes irreversible changes in the retina, up to complete blindness.
Occlusion and separation of the central retinal vein
This disease occurs when the venous outflow from the vessels of the retina is disrupted - blockage of the central retinal vein. Most often, this pathology develops in cases of blood clotting disorders, in patients with diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis or other vascular changes.
The following are noted:
– deterioration of vision, initially peripheral with gradual loss of central vision;
– blurred images of objects;
– the appearance of floating reflections, clouding;
– loss of visual fields.
Most often, unilateral damage to the organ of vision is observed.
Signs of the disease appear in proportion to the degree of obstruction, they appear unexpectedly and gradually progress - from several hours to several days.
Centralized arterial occlusion occurs suddenly and is characterized by
unilateral loss of all visual functions (complete loss of vision).
For optic nerve strokes
which develop during the formation of a cerebral infarction or intracerebral hemorrhage in the area of the center of gaze in the precentral gyrus, the location of the oculomotor centers, optic chiasms, and optic lobes of the brain depends on:
- on the size and anatomical location of the stroke focus (cerebral hemispheres, brainstem, cerebellum, parieto-occipital lobe);
- degree of damage to the vascular system;
- type of stroke (hemorrhagic or cerebral infarction);
- side of the lesion.
Symptoms may occur:
– sudden blindness or a sharp decrease in vision in one eye with disturbances in movement (hemiparesis) and sensitivity in the arm and leg on the opposite side (cross syndrome);
– loss of visual fields (hemianopsia), often with preservation of color perception and visual acuity;
– acute pain, constriction of the pupil, limited eye mobility (ophthalmoplegia), nystagmus (swinging movements of the eyes), double vision, blindness in half of the eye on the side opposite to the lesion;
– various oculomotor disorders, strabismus.
The formation of visual images occurs in the visual lobes of the brain, so when they are damaged, loss of the corresponding parts of the visual fields develops.
The main harbinger of a stroke is the symptom of atrial scotoma (darkness) in the form of visual disturbances: periodic flickering of light - fog, glare, flickering, covering surrounding objects and rapidly increasing. They are often accompanied by impaired skin sensitivity and paresthesia in various parts of the body. The duration of the attack can last from several minutes to several hours, then vision is completely restored. This symptom often manifests itself against the background of hypertension, atherosclerosis, severe headache and nausea.
Kinds
There are several types of strabismus, which are distinguished by certain characteristics. The most common ones are:
- Time of occurrence. Early childhood (congenital), older age (acquired).
- Stability of manifestation. Observed constantly (constant), occurs only in some cases, for example, when looking upward (periodic).
- Eye involvement. It can be monolateral (only one eye is squinted) or alternating (both eyes are squinted).
- Deviation type. The eye(s) deviate towards the bridge of the nose - converging, towards the temple - diverging, downwards or upwards - vertical, in different directions - mixed.
When making a diagnosis, divisions based on all characteristics may appear. However, a more complete decoding requires types of strabismus, distinguished by type of deviation.
Convergent
The most common form of strabismus is observed in almost 80% of cases. Formed at the stage of the appearance of binocular vision (2-4 months of life).
In this case, bifurcation is not observed, but the eye deviating from the axis sees much worse, which is why a full binocular image is not formed (a picture that appears when data coming from both eyes merges and reflects the surrounding reality as fully as possible).
Most often, convergent strabismus can be diagnosed at the age of 3-4 years. In some cases, pathology occurs in babies in the first year of life (up to 12 months). The latter is associated with congenital abnormalities of the eye organs and impaired functioning of the brain.
Divergent
In most cases, divergent strabismus is congenital and associated with intrauterine pathologies. In this case, one eye squints towards the nose, and the second can be absolutely normal (moves freely in all directions) or static (the eye cannot look to the sides/up/down due to paralytic muscle damage).
In the first case, duality is not observed, but binocular vision is not formed (the squinting eye sees much worse).
In the second, these symptoms are supplemented by duality of the image, the inability to focus the gaze on an object and, consequently, obtain a clear picture, dizziness, etc. It appears in early childhood.
Vertical
It can be congenital or acquired and is caused by cuts (paralysis) of the muscles. In principle, the mechanisms of formation of this type of pathology are similar to those observed during the formation of convergent and divergent strabismus.
But correction of this form of the disease is complicated and requires mandatory surgical intervention.
Mixed
It is characterized by a combination of two other types of strabismus listed above. As a rule, horizontal deviation (convergent/divergent) is accompanied by vertical one.
This type of disease is the most difficult to correct and requires a complex of techniques for its treatment.
Imaginary strabismus
This is a visual effect that occurs due to various reasons. The most common ones are:
- Large angle between the visual and optical axes. Usually it is 3-4 degrees, but in some people the value can reach 10 degrees. This is not a pathology and does not require correction, however, due to the displacement of the center of the cornea, the appearance of strabismus is created.
- Asymmetry of the orbits and face. It is also a normal variant and does not require treatment. The main difference between false and true strabismus is the preservation of binocular vision. The perception of the environment and the emerging picture remain as complete as possible and are not subject to distortion.
Anomalies in the shape of the eyes
The shape of a person's eye can be determined by mentally drawing a line from the outer corner of the eye to the inner corner. People of Asian descent have eyes that are different and easily distinguishable from others. Their main difference is the presence of a vertical fold near the inner corner of the eye - epicanthus , which is a continuation of the upper eyelid.
For people of Asian descent, slanted eyes and epicanthus are absolutely normal, while in people of other races, the presence of such a fold may indicate a defect in the development of the eye or some kind of disorder at the genetic level.
In some people, slanted eyes may be a sign of certain pathologies.
One of the diseases in which people develop a mongoloid fold is Down syndrome . Such people often have slanted eyes.
Diagnosis of Down syndrome
Why do eye development abnormalities occur?
An abnormal tilt of the eye angle cannot be the cause of any congenital pathology of the organ of vision, but there are a number of diseases that cause the development of an abnormal tilt of the eyes:
- Down syndrome;
- disorders at the genetic level;
- the development of various structural anomalies when the mother drinks alcohol during pregnancy (fetal alcohol syndrome).
Fetal alcohol syndrome
If a child has an abnormal eye shape that is not typical for its origin, it is necessary to immediately show it to a specialist, especially if this is accompanied by other facial defects. Reasons to see a doctor:
- the child has abnormalities in the facial structure;
- the newborn does not move his gaze, looks ahead;
- the baby does not close his eyelids completely or does not close them at all;
- the presence of any abnormalities in the organ of vision. This could be discharge from the eyes, any protruding parts, or the presence of an unusual color of the iris.
Diagnosis and treatment
If you suspect the presence of abnormalities in the development of the eyes, which may be a symptom of any serious disease, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the patient. First, the specialist needs to collect an anamnesis of the child’s life and illness - to do this, he needs to ask a few questions to the patient’s parents.
A newborn baby who has eye development abnormalities will usually have a number of other symptoms. These symptoms should be identified by asking parents about their family, chronic and genetic diseases, as well as by examining the child himself or receiving test results.
Developmental anomalies of hereditary origin
First, it is necessary to conduct research at the chromosomal level to identify possible genetic defects and diseases. After this, it is necessary to take tests for enzymes, as well as conduct the necessary metabolic studies.
Therapy
Based on the diagnosis given to the child, the doctor is obliged to prescribe comprehensive treatment. Surgery is sometimes used to correct abnormally tilted eyes. Moreover, the operation is not only an aesthetic improvement of the face, but also the prevention of various eye diseases that in the future may be caused by such a structure of the incision.
This type of eye shape can be corrected through surgery.
To aesthetically change the patient's face, they resort to not only surgical intervention. Often, the patient undergoes injections of hyaluronic acid, which are most often placed in the upper eyelid area to achieve the effect of proportional eyes.
The same procedures are very often performed on older patients. This is done due to the fact that with age, the skin of the lower and upper eyelids becomes very thin, since in these places it already has a very thin and delicate structure, and also does not have a fat layer underneath.
Note! Hyaluronic acid is also often injected into the area near the outer corner of the eye. Most often, this procedure is also performed at an older age, since due to the thinning of the upper and lower eyelids, the corner of the eye drops down, making a person’s look tired. Injections will help restore the shape of the eyes to their previous appearance, as well as generally make the face look younger.
Introduction of hyaluronic acid
Injections are also given in the temple or eyebrow area. This procedure will help make a person’s gaze more open.
Hyaluronic acid injections are sometimes placed in the outer corner of the eyebrow. This procedure will help keep the eyebrow from falling down due to age-related thinning of the skin and weakening of the facial muscles.
It is worth noting that, of course, slanted eyes are often a decoration, and not a symptom of any pathology. Therefore, there is no need to sound the alarm!
Hyaluronic acid
Causes
They lie in the internal processes of the body. This condition sometimes returns to normal after some time.
Perhaps they are associated with diseases, and such an increase is just a symptom. To understand, you should indicate the main reasons for this condition:
- Eye diseases of infectious nature. For example, inflammation of the lacrimal canal and conjunctivitis can lead to deep damage to the internal tissues of this organ. A manifestation of the infection will be swelling of one of the eyes.
- Facial nerve neuropathy. Such diseases often lead to seizures. Muscle contraction can be so pronounced that the face becomes asymmetrical. For example, the corner of the lip is lowered, the eye is enlarged. An increase or decrease occurs due to spasms of the facial muscles. In this case, neuropathy leads to fixation of their distorted position.
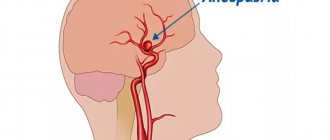
- Cerebrovascular accidents very rarely cause changes in the apparent size of the eye. They create a strong pressure inside the skull. High intraocular pressure may develop. Combined with blood stagnation, this leads to enlargement of the eye.
- Injuries to the head or eyes lead to changes in size. Thus, from a strong blow to the occipital region, the eye can move out of its orbit to some distance. He will remain in this position if he does not resort to the help of surgeons.
- A brain tumor affects intracranial pressure. Facial muscles are damaged. As a result, the eye can become larger or smaller. For example, it may turn out to be half-closed.
- Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve leads to convulsive muscle contraction. Its inflammation is associated with injuries and severe hypothermia. As a result, the face becomes distorted and asymmetrical. Consequently, the eye may become enlarged due to cramps that tighten the skin.
- Myasthenia gravis is also a nervous pathology that affects the facial muscles. As the disease progresses, ptosis of the eyelids occurs. One of them can be pulled downwards, which will create a feeling of enlargement of the eye.
- Ophthalmoplegia consists of complete immobility of muscles. In this case, the eye may be partially closed by the eyelid. This creates a visible sensation of the apple shrinking.
- Allergic reactions can lead to changes in size. As the reaction to the stimulus develops, the eye may be almost closed by the eyelid due to swelling.
The listed reasons are the main ones. But medicine knows the facts of congenital pathology, when the eyes have different sizes.
Causes
In children, convergent strabismus develops as a result of:
- Infections suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy.
- Hereditary factor.
- Presence of neurological diseases.
- Severe increase in body temperature.
- Diseases of the visual apparatus.
- Incorrect placement of toys above the crib.
- Abnormal development of the eye muscles.
- Intrauterine intoxication.
Convergent strabismus in the early stages of development of the baby’s visual system
Place the mobile above the crib correctly - otherwise the child runs the risk of developing strabismus.
In adulthood, convergent strabismus may appear as a consequence of:
- Injury
- Toxic poisoning.
- Various vision defects (most often farsightedness or myopia).
- A noticeable difference in the strength of the eye muscles.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Stress.
- Mental illnesses.
Convergent strabismus in adults
Paralysis of the eye muscles also leads to the development of strabismus in adults.
How to develop astral vision and see with your eyes closed
The essence of this technique is to teach vision with closed eyes. In this case, no other sensations play a role. You will have to rely solely on what the third eye will send, so techniques for opening it will not be superfluous here.
Relax completely and close your eyes. Look carefully at what appears before your eyes. You can see images and pictures. Your goal is to get a better look at them. It's good if you can notice something familiar. Remember what you see, you may have to see it with normal vision in the future.
A similar technique also exists for obtaining an out-of-body experience, and it is quite possible while performing such a vision with closed eyes. It helps not only to learn to see with your eyes closed, but also to develop clairvoyant talent.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of strabismus in children:
- Remove from the crib all objects that may motivate the child to look at one point.
- Avoid excessive stress and stress.
- Hang toys in bed at arm's length.
- Do not make sudden movements near the baby.
- Watch your posture and ensure that your child watches TV only while sitting and with a straight back.
The diet should be balanced. Buy books with large print.
Adults need:
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly.
- Do not self-medicate various pathologies of the visual system.
- Control the time they spend in front of a PC or TV.
- Do eye exercises.
- Do not read in public transport or in poor lighting.
- Avoid injury and infection.
Maintain personal hygiene. The habit of rubbing your eyes with dirty hands is a sure way to infection, and therefore the possible development of strabismus.
It is believed that the eyes do not lie
No matter how much a person wants to hide his true intentions, one look into the eyes is enough to sense something is wrong or even guess everything at once. Thus, a man’s gaze into a woman’s eyes during silence is most often a sign of sympathy. On the other hand, understanding the “language of views” at an elementary level can already make life easier for anyone and in any field of activity. Incredibly, visual contact is as valuable a tool of non-verbal communication as body language and facial expressions.
The look may:
- Instilling trust is the secret weapon of businessmen, actors, diplomats, negotiators and politicians;
- To inspire desire - the image of a femme fatale always begins with a stunning look;
- To subordinate - the boss’s imperious gaze is stronger than any words, every subordinate knows about this;
- Provoke - a clash of views during a meeting often becomes the starting point for a quarrel: “What are you staring at?”
A long gaze at your interlocutor has a special power of influence; it is difficult not to notice and impossible to ignore. If a person looks at you intently and does not look away, he needs something, and he is not afraid to show it. But how to interpret gaze into the eyes is almost always an open question.
How to master basic acting and public speaking skills?
Answer 4 short questions and we will select the optimal curriculum