Conjunctivitis occurs quite often in children.
This is due to the negative impact of the external environment, poor hygiene, and insufficient development of the immune system.
Many parents don't know whether to treat the condition at home or see a doctor. In both cases, drug treatment is required, which can be supplemented with folk remedies. If a child develops complications, it is recommended to immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
Causes of conjunctivitis in children
In children, conjunctivitis can develop due to the following reasons:
- an increase in the number of opportunistic microflora in the eyes, which leads to inflammation of the conjunctiva and suppuration;
- penetration of a new pathogen into the eyes, which forms a bacterial form of conjunctivitis, this can be chlamydia, pneumococcus, gonococcus;
- exposure to viruses that can spread only in the eyes or affect the entire body;
- the appearance of allergic reactions to flowering plants, animal hair, bird feathers, house dust, household products, various chemicals;
- mechanical damage to the conjunctiva due to the penetration of a foreign body, which, if left untreated, can cause a bacterial infection;
- elimination of fungus on the mucous membrane of the eyes with improper antibiotic therapy, as well as in children with immunodeficiency.
Each cause has its own clinical symptoms, by which the doctor can guess the nature of the disease.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
In order to protect the child from the occurrence of conjunctivitis and then not undergo long-term treatment, special attention should be paid to preventive actions. After all, in fact, conjunctivitis is an infectious disease, in most cases, and it is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. As for precautions, they are as follows:
- Follow the rules of eye hygiene;
- Hands should always be clean;
- Do not rub or scratch your eyes to prevent the infection from being transmitted from one eye to the other;
- The child must have his own towels;
- If quarantine is declared in kindergartens and schools, it is not recommended to have contact with children for a certain period of time.
Important! If a child has suffered an eye injury or a speck, sand, midge, etc. has gotten into the eye, this can lead to the child developing bacterial conjunctivitis, do not ignore visiting and consulting an ophthalmologist.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor. Be healthy!
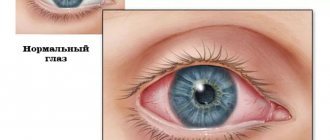
Manifestation of conjunctivitis in children
The disease in children is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
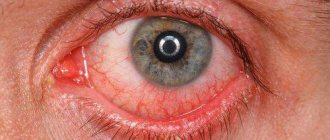
- severe redness of the eye; small hemorrhages may form in the cornea, which subsequently resolve on their own;
- increased production of tear fluid; if left untreated, the child develops dry eyes, which leads to damage to the cornea;
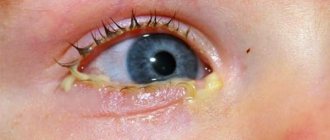
- if the condition is caused by a bacterial form, suppuration forms in the corners of the eyes, which spreads throughout the mucous membrane, sticking the eyelashes together in the morning;
- if the disease is caused by a fungal form, there will be a serous film on the mucous membrane of the eyes, which interferes with the normal function of vision;
- a feeling of discomfort appears in the eye area: itching, burning, pain;
- Photophobia is formed, that is, when exposed to natural or artificial light, a strong spasm of the eyelids appears, the child cannot open his eyes.
When these clinical symptoms appear, it is recommended to begin treatment immediately.
Description of the disease
The mucous membrane of the eyeball is called the conjunctiva. Like any tissue of the human body, the conjunctiva can become inflamed under certain circumstances. Children under four years of age are especially susceptible to this. Statistics on the incidence of conjunctivitis show 30% of all ophthalmological problems. In the future, children are susceptible to another form of ophthalmic pathology - problems with refraction.
Why are young children most susceptible to this inflammation? Because their immune status is not formed, and any infection can attack a weak body. There are two types of conjunctivitis:
- infectious;
- allergic.
Infectious conjunctivitis is caused by two types of microorganisms:
- viruses;
- bacteria.
It is necessary to identify the cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane, and then take measures to eliminate it. It is useless to treat the allergic type of disease with antibacterial or antiviral drugs: it is important to identify the aggressor allergen and eliminate it. After this, the mucous tissue returns to normal and the symptoms disappear.
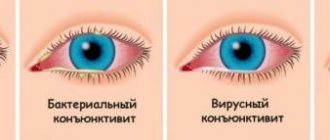
Bacterial conjunctivitis in children
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by the following types of microorganisms:
- coccal nature;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- Koch-Wicks pathogens.
Newborn babies become infected when they pass through the birth canal of a mother infected with chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Note! Inflammation of the conjunctiva can appear after mechanical trauma to the eyeball.
However, a bacterial infection does not necessarily have to enter the child’s body from the outside: when the immune defense is reduced, the source of infection is the child’s own bacterial pathogenic microflora. The eyes of young children can become inflamed from hypothermia or due to an existing purulent process:
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis;
- others.
Viral
This type of conjunctivitis accompanies influenza, measles, enterovirus/adenovirus infection, and herpetic infection. The child has a sore throat, snot, and a cough.
Children's conjunctivitis can also be of a mixed nature: viral and bacterial at the same time.
The child's eyes itch very much, tears flow profusely, the eyelids swell, and the whites of the eyes become very red. If redness of the eyes accompanies pharyngitis, then the nature of the disease is adenovirus.
Allergic
This type of conjunctivitis is provoked by an aggressor allergen. Inflammation of the eyes due to allergies is also combined with other symptoms and manifestations inherent in this pathology:
- rhinitis;
- skin rashes;
- bronchial asthma;
- hay fever
An allergen can be anything: dust, wool, food dyes and flavors, food, pollen, fungal spores, etc. Allergies can also be triggered by stress.
Allergic conjunctivitis can take a chronic form against the background of severely reduced immunity. The irritant can be smoky air or air conditioning, as well as household chemicals.
Is it possible to treat conjunctivitis yourself at home?
If parents are sure of a certain form of conjunctivitis, therapy can be carried out at home. Often the disease in children is chronic or recurs when exposed to negative environmental factors.
In this case, parents already know exactly what medications to use so that the condition goes away quickly and no complications arise. If therapy does not help, or the child develops severe swelling of the eyelids, due to which the eyes cannot be seen, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Perhaps the parents made a mistake with the diagnosed form of the disease; another treatment is needed.
Bottom line
Children's conjunctivitis is a common infectious disease transmitted from sick to healthy. Inflammation of the eye membranes is most often caused by viruses/bacteria, but recently the allergic form of the pathology has become widespread. Conjunctivitis in children is treated with various medications, so if an inflammatory process occurs, the child should be immediately shown to a pediatrician. It is impossible to rinse and clean the eyes before consulting a specialist, since in case of allergic conjunctivitis, rinsing will only aggravate the child’s condition. You can drop Albucid into your eyes, but other drops cannot be used.
After the child recovers, it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect the room, things and toys, because the infection can be transmitted through objects. Disinfection can be carried out using a blue lamp or other available methods. To prevent the child from getting sick again, it is necessary to take measures to strengthen the immune status. Consult your pediatrician about the use of vitamin complexes and restorative procedures. Monitor your baby's daily routine and don't let him get overtired.
Sources used:
- How to remove glasses forever / Ruschel Blavo. - M.: Ripol Classic, 2011.
- Taking care of your eyes. Vision problems from dry eye syndrome to macular degeneration. - M.: Art-Rodnik, 2011.
- Eye diseases. Atlas. Guide to practical training / E.I. Kovalevsky. - M.: Medicine, 1985.
- University of Nebraska Medical Center
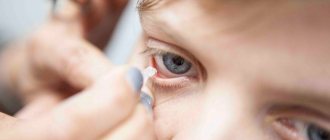
Washing a child's eyes
Most often, saline solution or Furacilin are used as a rinsing agent. The first product rinses and removes particles of pus. Furacilin has an antiseptic effect, therefore it suppresses the growth of pathogenic microflora.
If parents are sure that the child does not have an allergic reaction, they can use traditional recipes for rinsing. For these purposes, a decoction of chamomile, calendula, coltsfoot, and string is suitable. These products are often used for bathing children.
To wash your child's eyes, moisten a cotton pad with liquid. Then rub from the outer to the inner corner of the eyes. In this process, any pus or other discharge must be eliminated.
Drops
Medicinal drops are most often used to treat conjunctivitis. They can be for different purposes. The drugs act locally, so there are no systemic side effects.
Antibiotics
Vigamox, Tobrex, Levomycetin, Tsiprolet are suitable for these purposes. They must be used for no more than 7 days, after which time the bacteria develop resistance to the active substance. It is recommended to use the products only in the dosage prescribed by the doctor or prescribed in the instructions.
Antiviral drugs
Local antiviral agents are used in the form of drops, for example, Poludan, Oftalmoferon. They effectively destroy viral pathogens without causing systemic effects.
Immunomodulators
Interferon is most suitable for children. This remedy is similar to natural human interferon. It increases the number of immune cells in the lesion, so the destruction of the pathogen occurs faster.
Antifungal drugs
It is recommended to use Nystatin, Natamycin. This product destroys mycelium and spores of fungi, preventing their reappearance after discontinuation of the drug. The medicine is used in strict dosage so as not to cause adverse reactions in the child.
Vasoconstrictor drugs
The most suitable drug is Visin. It can be used for no more than 4 days, after which time it becomes addictive. The drug eliminates swelling, redness, and inflammation of the eyes.
Antihistamines
Doctors often prescribe Allergodil, Poludan, which eliminate the activation of immunity in the affected area. This reduces inflammation, redness, swelling, and even pain.
Ointments
Ointments must be used to eliminate viral or bacterial pathogens. They are used mainly before bedtime, since at this time a person does not feel a foreign element on the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Antibacterial ointments
Tetracycline and Erythromycin ointment are most often used for children. They are applied to the inner corner of the eyes or placed under the eyelid. In both cases, an antibacterial effect is achieved, which helps get rid of the pathogen faster.
Antiviral ointments
It is recommended to use Florenal, Bonafton. They effectively fight the viral pathogen when applied topically. Additionally, they eliminate dry mucous membranes and itching. They must be used over a long course of treatment so that the virus does not become active again.
Folk recipes
Most often, folk methods for making decoctions are used for conjunctivitis.
Most Popular:
- Oak bark. It is brewed, then cooled. Apply lotions to the eyes for 5-10 minutes. When applying the product, itching and burning, which often occur with conjunctivitis, are eliminated.
- Chamomile. This plant has a disinfecting effect, soothes, and relieves inflammation. It is often used for viral, bacterial, and fungal diseases.
- A series. It is a natural antiseptic. At the same time, it increases dryness, so if a child experiences this symptom, the series is not applicable for daily use.
- Calendula. The plant has an antiseptic effect that eliminates burning, redness, and swelling of tissues.
- Aloe. It is recommended to use fresh juice from the plant, which is squeezed directly into the child's eyes. It increases metabolism, thereby increasing the regeneration of damaged tissues. Inflammation, swelling, redness, itching and other manifestations of the disease are eliminated.
- Potato. This is the most effective remedy for eliminating eye puffiness. To do this, they usually grate the plant, after which they make an eye mask for no more than 5 minutes.
- Tea. This is an effective remedy for eliminating inflammation and destroying bacterial microflora. You can apply tea bags or cotton pads soaked in liquid to your eyes.
- Propolis. This is a substance obtained from bee honeycombs. It can be rubbed into the inner corner of the eyes and a solution can be made from it. It has an antibacterial effect, relieves inflammation, swelling, and redness. It also destroys pathogenic pathogens that cause the disease.
- Kalanchoe. The herbal remedy effectively eliminates discharge from the eyes and helps suppress the immune system during allergic skin reactions. You can use juice from a fresh plant, which is instilled directly into the eye. You can also soak a cotton pad in liquids, which are used for wiping to eliminate pus and other secretions.
With conjunctivitis of various forms, it is necessary to take into account the age of the child. When purchasing a drug, you should read the instructions for use, indicating at what age the drug can be used. If the child's condition worsens significantly, even after using medications, it is recommended to immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
Symptoms
How does conjunctivitis manifest in children? Even before the onset of characteristic signs of inflammation of the eye membrane, the child begins to behave restlessly and constantly tries to rub his eyes with his fists. Afterwards symptoms appear:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- severe lacrimation;
- heat.
The baby is irritated by daylight or lamps, his eyes hurt badly, and he has no appetite. The child does not want to play with his favorite toys, is capricious and gets tired quickly.
If inflammation of the conjunctival membrane occurs in isolation, the temperature may rise by a couple of degrees. If eye inflammation is accompanied by a general infection in the body, the temperature can rise to a critical level.
Signs of bacterial infection
When attacking a bacterial nature, characteristic signs stand out:
- severe suppuration;
- eyelashes stuck together from pus;
- moderate swelling of the eyelids.
The child is prescribed antibacterial drugs, restorative vitamin complexes and eye rinsing with special solutions. When the disease takes an aggressive form due to bacterial damage to the entire body, the child is prescribed systemic drugs. Sometimes it can be very difficult to defeat a bacterial infection due to the high resistance of microorganisms to many types of antibiotics. Healing is achieved by the correct selection of medications and the mother’s responsible attitude to the pediatrician’s recommendations.
Why is conjunctivitis dangerous in children? The risk of complications due to improper treatment or the body affected by a bacterial/viral infection is high.
Complications after bacterial conjunctivitis:
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- keratitis.
If the child’s immunity is severely weakened, anemia or signs of hypovitaminosis are observed, complications can take a more serious form.
Gonococcal infection in newborns can result in blindness or the formation of a cataract. It usually appears on the third day after birth and is accompanied by copious discharge of green pus. Chlamydial infection in newborns appears a week after birth. For her, copious discharge of purulent exudate is also indicative.
Signs of a viral infection
The activity of viruses in the body is not manifested by purulent discharge, characteristic of bacterial activity. Viral conjunctivitis always forms against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, or hypothermia. They are accompanied by sore throat, rhinitis, general malaise and hyperthermia.
Note! A viral infection is sometimes accompanied by a bacterial one. Sign: green purulent exudate is released from the palpebral fissure.
Viral conjunctivitis is characterized by copious discharge that resembles constantly flowing tears. They have a liquid consistency and are transparent. Herpetic infection is accompanied by the formation of small blisters with clear liquid located on the eyelids and conjunctival mucosa. If the disease accompanies measles, then the rash on the eyelids resembles the rash inherent to it.
Signs of allergic conjunctivitis
This form of inflammation is characterized by severe itching in the eyes, which does not accompany a viral/bacterial infection. Inflammation of the eye membrane is indicative of symptoms characteristic of all types of allergies: itchy skin, excessive lacrimation, rhinitis without fever and sore throat, intolerance to bright lighting. As you move away from the aggressor allergen, symptoms may disappear; upon contact with the irritant, they may reappear.