The visual organs of a small child are somewhat different from the organs and systems of an adult. All children are born with hyperopic astigmatism. Ophthalmologists believe that such a diagnosis in a child under 10 years of age is the norm. As the baby grows, his eyes improve, and farsighted astigmatism, as a rule, disappears. But this again is the norm. Unfortunately, there are exceptions when the disorder remains with the child. In this case, the disease “hypermetropic astigmatism” is diagnosed, which requires treatment and preventive measures.
Definition of disease
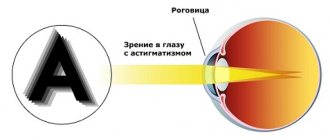
Hypermetropic astigmatism is a vision disorder characterized by changes in the shape of the lens or cornea.
In a healthy person, the lens has a smooth spherical surface. With farsighted astigmatism, a violation of the sphericity of the lens is observed, the shape of the eye itself is elongated vertically, which is why the focal point is located outside the macula - the center of the fundus. Astigmatism bifurcates this focal point, resulting in severe distortion of visual information. Children with this disease cannot focus their eyes on close objects, so they see the picture blurred and unclear.
Hypermetropic astigmatism is sometimes called hypertrophic astigmatism, since they are the same disease. It causes visual impairment and farsightedness in the child.
Childhood astigmatism: what is it and what is the cause of its occurrence?
Strictly speaking, astigmatism is not a disease, but a so-called refractive “error” of the eye. However, this does not mean that it is safe. Astigmatism is a curvature of the cornea or deformation of the lens. As a result of improper refraction of light, the focus of the object perceived by the eye appears not on the retina, but in front of it or behind it. With astigmatism, objects appear blurry or slightly deformed - for example, a child sees a dash or an oval instead of a dot. This disorder is treatable, and the sooner a diagnosis is made and treatment begins, the better.
It should be noted that most children are born with a small degree of astigmatism, which by the end of the first year decreases and becomes less than 1 diopter. This astigmatism is called physiological; it does not have a significant effect on vision and does not require treatment.
Astigmatism in children is most often hereditary. In this case, it manifests itself at an early age and an experienced ophthalmologist can detect it even in a one-year-old baby. Hereditary astigmatism is caused by abnormalities in the shape of the lens or cornea.
Acquired astigmatism may be a consequence of previous eye injuries, subluxation of the lens, or pathology of the dental system, causing deformation of the walls of the orbit.
Symptoms
The most important problem in diagnosing astigmatism in children is the fact that parents do not pay attention to the numerous warning signs of the disease and, sometimes, do not even suspect that their child has poor vision. Children themselves very rarely complain about their eyesight. Indirect signs help determine the presence of astigmatism. In the presence of pathology, children often suffer from headaches (especially in the forehead above the eyebrows) and dizziness, do not like to read and write, and even avoid looking at pictures in books. Most often, parents ignore this, considering the child lazy or capricious. Trying to look at something, a baby suffering from astigmatism squints his eyes and tilts his head at different angles.
The presence of these signs does not mean that the child necessarily has such a disease, but this can be considered a good reason to visit an ophthalmologist.
Types and degrees of astigmatism in children
Astigmatism in children is divided into several types, depending on the nature of its occurrence, changes in refraction, severity, location of focus and other factors.
- Corneal. This type of astigmatism is caused by defects in the cornea. The effect of corneal astigmatism on vision is stronger than that of the lens, since the cornea has a greater refractive power.
- Lens astigmatism is caused by a change in the shape of the lens.
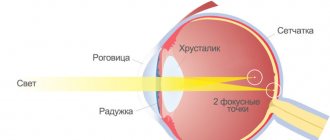
- Hypermetropic. It is characterized by a predominance of farsightedness, in which images of objects are focused behind the retina.
- Myopic astigmatism is usually accompanied by myopia.
- Simple. In this type, there is a disturbance in the functioning of only one eye (myopic or hypermetropic astigmatism).
- Difficult. Impaired functioning of both eyes (myopic or hypermetropic astigmatism in both eyes).
- Mixed. Various disorders in both eyes (myopic astigmatism in one and hypermetropic in the other).
According to statistics, with age, in 31.1% of cases the manifestation of disorders associated with astigmatism decreases, in 42.8% they remain stable, and in 26.1% they increase. A weak degree of astigmatism in children is less constant than a high degree.
- Weak – up to 3 diopters;
- Strong – more than 6 diopters;
- Average - from 3 to 6 diopters.
Diagnostics
A child suffering from congenital astigmatism (or acquired acquired astigmatism at a very early age), as a rule, does not complain about vision - for the reason that he has always seen this way and does not know that it is “wrong”. This fact complicates timely diagnosis. Therefore, parents need to be very careful. Astigmatism in children is usually detected during an appointment with an ophthalmologist. Therefore, it is recommended to show the child to the doctor from 2 months of age and, if the doctor diagnoses astigmatism, to visit this specialist every 6 months.
To diagnose astigmatism, an ophthalmologist can use a special device - an autorefractometer. Astigmatism is also diagnosed using a symbol plate and a cylindrical lens. Keratometry is also widely used - a method that allows one to determine the degree of curvature of the meridians of the outer surface of the cornea. In recent years, computer topography of the eye has often been used - a method that makes it possible to create a three-dimensional image of the cornea of the eye and most accurately assess not only the degree of its curvature, but also its shape and thickness.
Treatment of astigmatism
Astigmatism detected in time can be easily corrected. Doctors have several ways to correct the vision of a child suffering from astigmatism. Until the age of 18, only conservative methods are used, since the eye still continues to grow and develop, and after the age of 18, surgical or laser correction can be done.
How is astigmatism treated with glasses?
Special astigmatic glasses with cylinders that allow you to gradually correct astigmatism are the simplest and most common way to correct this pathology. In the first days of wearing glasses, the child may experience discomfort and headache, but these unpleasant phenomena disappear after a week. If your headaches persist, your glasses may have been chosen incorrectly and should be replaced. Treatment of astigmatism with glasses is a simple and cheap method, but not without its drawbacks - glasses limit lateral vision, do not allow the child to play sports, and many children flatly refuse to wear them.
Treatment with lenses
Orthokeratology is a method, the essence of which is the temporary wearing of hard contact lenses that correct the curvature of the cornea. The lenses are worn at night. Gradually, the cornea takes on the correct shape, and vision improves. However, this method is only suitable for correcting mild astigmatism up to 1.5 diopters.
Laser correction (surgical treatment of astigmatism)
Laser correction of astigmatism is a quick and painless procedure. It takes 15 minutes and is performed under local drip anesthesia. Sutures are not required, since the damaged epithelium recovers on its own in a short time; there is no rehabilitation period - immediately after the operation you can return to your normal lifestyle. Vision improves noticeably within 1-2 hours after the end of the operation, and is completely restored within a week. The most common technology today is called LASIK.
Prevention
The development of astigmatism can be “slowed down” (and in some cases, prevented) with the help of special preventive measures.
To prevent astigmatism, the lighting regime should be observed - any visual stress should take place in bright light, and point sources of lighting should not be neglected. Avoid using fluorescent lamps. Visual stress should not be excessive or too long; it should be alternated with physical activity. Every half hour you need to do eye exercises - blink frequently, alternately focus your gaze on close (30 cm from the eyes) and distant objects, close your eyes for 5 seconds and then keep your eyes open for the same amount of time, “draw” a figure eight with your eyes in the rhythm of your breathing. Each exercise must be repeated 7-10 times. A gentle and gentle massage of the eyelids using circular movements gives a good effect - it helps to normalize intraocular pressure.
Types and classifications
Doctors distinguish 2 types of this pathology:
- Simple hyperopic astigmatism: involves the image in one of the meridians of the eye being focused on the retina (which is normal), and in the other behind the retina (farsightedness).
- Complex hyperopic astigmatism: farsightedness of varying degrees is diagnosed in both meridians.
Both types of astigmatism are most often caused by the aspherical shape of the cornea; in rare cases, the cause lies in a change in the shape of the lens. Due to a disorder in the cornea, rays refracted in the optical system of the eye are not collected at one point. In addition, the anterior surface of the cornea is usually more curved and refracts rays more strongly. Mild corneal astigmatism (up to 0.5 diopters) is common, is considered an acceptable norm and does not lead to changes in visual acuity.
There is also a mixed type of astigmatism, which is manifested by the following disorder: myopia is noted on one of the meridians, and hypermetropia is noted on the second.
Hypermetropic astigmatism of the eyes in children comes in several degrees of severity:
- A mild degree causes virtually no symptoms.
- Moderate degree is characterized by the appearance of fog in the eyes and headache.
- In severe cases, the child may complain of a sharp decrease in vision, and from the outside, adults may notice the baby’s strabismus. The child suffers from pain and pain in the eyes, as well as tearing. Children with severe astigmatism become nervous and irritable, and their mood often changes.
Types of hyperopic astigmatism
In medicine, a classification of the disease is accepted according to the form of refractive error in two perpendicular meridians:
- Simple hypermetropic astigmatism (H) - the distortion passes along one meridian, and in the other the refraction is normal.
- Complex hypermetropic astigmatism of both eyes (CH) – the child’s refraction is distorted along two meridians. In this case, one may have farsightedness, and the other may have myopia or also farsightedness. The child sees a very distorted picture because there is a high degree of refractive power pathology. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24637486 Kulp MT, Ying GS, Huang J, Maguire M, Quinn G, Ciner EB, Cyert LA, Orel-Bixler DA, Moore BD; VIP Study Group Associations between hyperopia and other vision and refractive error characteristics // Optom Vis Sci. 2014 Apr;91(4):383-9. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000223
Causes
The main reason for the development of farsighted astigmatism is a hereditary factor. Doctors believe that predisposition to this disorder is inherited.
If there is already a person in the family with hypermetropic astigmatism, then the likelihood of developing the same disease in his descendants increases significantly.
Acquired astigmatism usually develops after eye injury or surgery. The reason is that a scar forms on the cornea of the eye, which leads to blurred vision and blurred vision of objects.
In pediatric practice, mild astigmatism is most often encountered. A similar disorder is detected in approximately 50% of schoolchildren.
Causes of amblyopia
This disease of the visual system is quite common, detected in 3% of children.
The first place among the causes of amblyopia is strabismus, as a result of which the coordinated work of the eye muscles is disrupted. Binocular vision is impossible if one eye is squinting. The child experiences a double image due to the focusing of rays from objects not on symmetrical areas of the retina.
The second most common cause of amblyopia is structural changes in the lens or cornea. When they become clouded, the brain believes that the signals from this eye have become worse and begins to ignore them, switching to working with the other eye. Sometimes situations arise that even when a cataract or defect in the cornea is eliminated, the brain “does not understand” that vision has been restored in a previously non-functional eye. He does not perceive signals coming from this eye.
Another cause of amblyopia is a disorder of the brain. The visual part of the brain on the side of the defective eye may undergo morphological changes due to reduced blood flow and impaired glucose metabolism.
The congenital cause of amblyopia can be eye pathologies - myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism. These ailments are often diagnosed in young children due to the incomplete formation of the visual system. The brain excludes from perception eyes with severe refractive error - farsightedness, myopia, astigmatism.
Amblyopia can also be caused by eye injury. Childhood contributes to the occurrence of injuries, as a result of which the child is forced to wear a bandage, which contributes to the development of amblyopia.
Symptoms
It is easier to recognize hyperopic astigmatism in a teenager than in children of primary school age. The baby does not yet understand that he has vision problems and, as a rule, does not make any complaints. In addition, not all parents can notice this disorder in a timely manner.
Parents with a predisposition to astigmatism should carefully monitor their child. Only in this case can they notice the following symptoms in children:
- Difficulty reading text;
- Inability to examine a nearby object;
- Lack of focus on an object;
- Dizziness.
Due to the discomfort, the baby may refuse to read or write and often complains of a headache. He tilts his head a little and squints his eye to look at the object that interests him. If parents notice one of these signs in their child, they should consult an ophthalmologist.
Possible complications
Childhood hypermetropic astigmatism can cause amblyopia and strabismus. Visualization of the image by parts of the retinas is disrupted as a result of blurriness in one of them, which leads to the formation of amblyopia, which is often a consequence of this eye disorder. This complication can occur when the difference in refractive power is more than ± 1.5 diopters in both eyes simultaneously.
Read the material on how to treat strabismus in children.
Complex farsighted astigmatism diagnosed in both eyes can be complicated by albinism.
If hypermetropic astigmatism detected in a child is not treated in a timely manner, then after the age of 10 he may develop convergent strabismus.
This pathology causes discomfort to the teenager and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect, due to which the teenager may develop complexes and psychological problems. That is why it is so important to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist and, when such a diagnosis is made, to promptly treat the pathology. The parents’ task is to follow absolutely all the doctor’s recommendations.
Convergent strabismus in a child is a complication due to hyperopic astigmatism
Treatment of amblyopia in children
Spontaneous self-healing of amblyopia is not typical, etc. “folk remedies” have not helped a single patient so far. In other words, in this case it is impossible to do without long-term adequate treatment, patient and targeted.
Considering the mutually potentiating relationship between amblyopia and strabismus, treatment is aimed at correcting and preventing both types of pathology: it is necessary to restore fusional functions (binocular vision), strengthen accommodation, achieve oculomotor coordination, and correct insufficient visual acuity in the amblyopic eye.
The therapeutic strategy, scheme and chronological treatment plan are always strictly individual. The main principle is to first eliminate the immediate causes of amblyopia. For example, with obscuration amblyopia, surgical intervention is necessary to eliminate the optical obstacle (cataract, ptosis, etc.), and the earlier the operation is performed, the lower the risk of complications and side effects, one of which may be severe irreversible amblyopia. The optimal and relatively safe period for ophthalmic surgery is up to 6 months of age. The exception is small cataracts that do not interfere with fundus ophthalmoscopy - in this case, intervention is carried out at the age of 5-6 years and older.
Dysbinocular amblyopia also often requires ophthalmic surgery to correct the position of the eyeballs.
For amblyopia of the refractive or anisometropic type, treatment is predominantly conservative, training-stimulating, and it begins with mandatory optical correction (glasses). Then, usually after three weeks, pleoptic treatment is added to restore coordinated functioning of both eyes. Today, both active and passive pleoptic therapy are practiced. By active we mean occlusion of the better seeing eye; passive includes various trainings, primarily computerized, to activate the amblyopic eye.
At the age of 1-4 years, the initial stage of pleoptic therapy is penalization - an artificial decrease in visual acuity in the more intact eye, which forcibly involves the amblyopic eye in visual processes. Like other components of pleoptic treatment, penalization is used in numerous modifications and options that are optimal for each individual case. Thus, sometimes near vision is artificially hindered for a healthy eye, and in other situations, distance vision is artificially impaired; vary the degree of optical correction for amblyopic and healthy eyes; in some cases mydriatics are used, etc.
The dynamics of the visual functions of each eye should be constantly monitored - first of all, to avoid possible negative consequences of treatment for a healthy eye. This is especially true for the method of direct constant occlusion, when the work of the better seeing eye is blocked throughout the day.
In addition, when choosing a treatment method, be it penalization or occlusion (which is prescribed from the age of four), the state of central fixation is always taken into account and monitored. In general, during the treatment period it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist at least 1-2 times a month.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the child’s psyche, at an early age relatively uncomfortable methods (associated with wearing glasses or occluders) are introduced into the treatment regimen gradually, starting with just a few minutes a day, and are also gradually discontinued when the desired result is achieved.
It should also be mentioned blinding light techniques (local or general), designed to stimulate the foveal region of the retina with an intense light flux from a conventional or laser source. Local illumination is used only when central fixation is preserved. In case of violations of this function, general illumination of the posterior retinal pole is sometimes indicated, or, starting from the age of two, the method of negative sequential image (a light flux of a special shape is formed, with a small opaque obstacle in the center, which allows illumination of the retina when the foveal zone is shaded).
Various hardware-training methods for the treatment of amblyopia and its complications are widely used and are often the main therapeutic agent.
Thus, macular testers restore the ability for stable fixation; Devices such as “amblyotrener” (with visual acuity of at least 0.2) and “amblyostimulator” (this pulse-action device can be used even at home), special software, and reflexology are effective.
As a rule, from the age of four and when a visual acuity of at least 0.4 has been achieved in each eye, they switch from pleoptic to orthoptic therapy. Its goal is to eliminate one of the leading symptoms of amblyopia - the inability of binocular vision. Here, too, the leading role is given to hardware methods of activation, training and consolidation. The standard device is a “synoptophore”; Various options and methods for its use involve broadcasting separate images to each eye - so that the eyes and brain learn to merge these one-sided monoscopic fragments into a holistic three-dimensional, stereoscopic image. The same problem is solved with the help of computerized hardware systems.
The consolidation of binocular skills is facilitated, in particular, by diploptic gymnastics - an artificially induced effect of double vision, which, with a certain volitional effort of a small patient, the central nervous system can and should overcome.
Despite the fact that some additional hardware methods and exercise systems are applicable at home (and are prescribed for parents to work independently with their child), the main therapeutic course is strongly recommended to be carried out in a specialized kindergarten for children with low vision. Such institutions are staffed with specially trained personnel and have all the necessary equipment. The daily routine and program of developmental activities are built taking into account a common problem for all. Finally, perhaps the most important argument in favor of such preschool institutions is the minimization of psychological discomfort and microsocial stigma: all pupils are in equal conditions and do not feel like an “ugly duckling” or a “bespectacled child”, which would not be excluded in an ordinary children's group.
By contacting our ophthalmology center, you can be sure of an individual approach to the diagnosis and treatment of amblyopia in your child. Attentive attitude, the latest equipment and experienced doctors are a guarantee of high treatment results.
Diagnostics
To determine an accurate diagnosis and assess the extent of damage to the visual organs, it is necessary to examine both eyes.
Clinical researches
The main diagnostic methods for hypermetropic astigmatism are:
- Visometry (determining visual acuity). During the examination, the child’s one eye is covered, and lenses of varying strengths are put on the other;
- Skiascopy;
- Biomicroscopy;
- Refractometry;
- Ophthalmoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the eyeball.
In difficult cases, the child is prescribed computer keratotopography.
Most often, ophthalmologists make the diagnosis of “hypermetropic astigmatism” in children in the second year of life.
Tests at home
You can recognize the disease in a child at home using schematic tests. It’s easy to make a drawing for the test yourself; you can also get ready-made samples on the Internet.
Siemens star
The Siemens Star test allows parents to monitor their child’s visual acuity and monitor its changes. To do this, you need to turn on full lighting and cover one of the baby’s eyes with your palm. Next, you need to ask the baby to look at the lines and determine whether they are all the same. A similar test is carried out with the other eye, then the results are compared.
Siemens Star test for determining astigmatism
Lines
Ask your child to determine if all the lines are the same. The technique test is similar to the Siemens Star test.
Dark lines
The task for the child is the same: determine whether all the lines are identical.
If the child presents different results after viewing pictures with both eyes, immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
In order for the treatment of simple and complex variants of hypermetropic astigmatism in children to be effective, it must be started as early as possible, taking a whole range of measures.
Optical correction
The doctor usually prescribes glasses for children under 7 years old, and lenses for older children. The lenses of the glasses are not simple, but spherocylindrical. Contact lenses are selected strictly individually for each patient. A line of toric contact lenses has been developed to correct astigmatism. The degree of damage and possible concomitant pathology are taken into account.
How to choose glasses for astigmatism, read here.
Glasses and lenses for astigmatism are exclusively vision correction. If you remove the optics from your eyes for a long time, your vision will begin to deteriorate again.
Surgical intervention
To permanently get rid of farsighted astigmatism, it is necessary to correct the shape of the cornea. Only microsurgery doctors can do this. At this stage, the most effective ways to influence the cornea are:
- Laser thermokeratoplasty;
- Laser keratomileusis.
Read more about laser keratomileusis here.
Laser thermokeratoplasty.
These procedures change the shape of the cornea, making it convex and flat in the central part. Visual acuity is restored.
As a rule, modern medicine uses surgical intervention for patients over 18 years of age. However, in severe cases of hypermetropic astigmatism, doctors also perform laser surgery on young patients.
Other treatments
Conservative treatments include:
- Eye muscle training;
- Proper nutrition;
- Swimming;
- Massage.
Eye exercises to improve vision are described at this link.
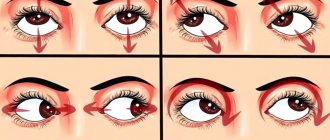
To treat astigmatism, ophthalmologists often prescribe special exercises for children. The complex may include the following exercises:
- The child needs to look into the distance, then fix his vision on some object located nearby, at a distance of 20-30 cm.
- Eight. The young patient needs to make a figure eight with the pupils of his open eyes.
- Alternately closing the organs of vision while fixating the open eye on a nearby object.
- Index finger exercise. The baby needs to look closely at the index finger, slowly bringing it closer to the nose.
- Massaging closed eyes with thumbs.
Gymnastics for the eyes
After performing gymnastics, you need to close your eyes and let them rest.
Gymnastics, taking various medications, wearing glasses, as well as surgical intervention are prescribed only by an ophthalmologist after a thorough diagnosis.
Prevention
Hypermetropic astigmatism in children is overwhelmingly a congenital defect. Prevention of this disease should be carried out from a very early age. As preventive measures, ophthalmologists recommend:
- A set of exercises for the eyes that strengthen the eye muscles (circular movements of the eyes, alternating glances up-down-right-left; slow blinking and strong squinting);
- Swimming and running;
- General physical exercises;
- Hardening procedures;
- Eyelid massage;
- Proper nutrition (the child’s diet must include fresh carrots and parsley, which have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the visual organs).