Symptoms
The symptoms that arise from an injury to the eyelid depend on the characteristics of its occurrence. If it is a bruise, the victim complains of severe pain and discomfort. Swelling develops, hematomas and bruises appear. When the top layer of the eyeball is damaged, bruises are visible on its surface.
In especially severe cases, such injuries affect the lens and cause retinal detachment.
When the eyelid is bruised, the reaction of the pupils to light often changes; they unnaturally increase in diameter. When exposed to light rays, the victim feels pain in the eyes, lacrimation is observed, and visual acuity decreases.
Very often, when the eyelid is injured, damage to the cornea occurs. In this case, the victim complains of the following symptoms:
- loss of clarity of vision;
- pain and discomfort when exposed to any light sources;
- “feeling of sand” in the eyes;
- swelling and redness of the eyelids.
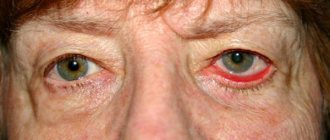
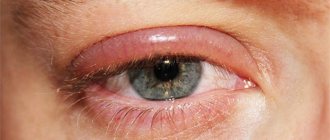
Conjunctivitis and swelling of the eyelids
With this disease, the connective membrane of the eye becomes inflamed. In this case, the swelling can spread to the eyelids, usually the upper ones. Depending on the causes of conjunctivitis, it is accompanied by various symptoms. These may include:
- swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva;
- hyperemia;
- itching and burning;
- Pain in the eyes;
- mucous or purulent discharge;
- formation of films or infiltrates.
With herpetic conjunctivitis, blisters are observed on the skin. Adenoviral inflammation manifests itself in elevated body temperature, cough, runny nose and general malaise.
Conjunctivitis occurs due to pathogenic microorganisms entering the conjunctiva. This can also happen as a result of an eye injury. People often bring germs into their eyes with their hands.
Species and types
Eyelid injuries are usually classified based on their causes. On this basis, several varieties are distinguished:
- Contusion. Diagnosed after a blow with a blunt object. It is always accompanied by bruising of soft tissues, which leads to the appearance of a bruise under the eye. In severe cases, the conjunctiva ruptures and damage to the lacrimal canals occurs.
- Erosion. Characterized by the appearance of scratches or abrasions. Such injuries are always accompanied by bleeding, pain, and swelling of the tissues. If there is no damage to the eyeball, there is no need to see a doctor. Often, only a light antiseptic treatment of the skin is sufficient.
- Wound (puncture, cut, laceration). It can be superficial and through. This variety is very dangerous and requires qualified medical intervention .
Classification by type of traumatic factor
Injury to the eyelid can occur not only when exposed to mechanical factors. Damage to the eye area can occur for other reasons, according to which classification is carried out.
- Thermal burns. Occur due to skin contact with hot liquids, hot objects, or open fire.
- Chemical burns. Occurs when aggressive chemicals - acids, alkalis - come into contact with the surface of the eyelid.
- Frostbite. Observed when the skin is exposed to extremely low temperatures.
- Burns from ultraviolet radiation. Most often occur during prolonged exposure to the sun or due to non-compliance with the rules for performing medical procedures where quartz lamps or other light sources are used.
Injuries to the eyelids and tear ducts
- Clinical picture
- Treatment
- Restoration of tear ducts
One of the most common eye injuries is damage to the eyelid, which protects the eyeball from any manifestations of the external environment and prevents the eye from drying out. Performing the same functions, the upper eyelid differs from the lower eyelid in the size of the tarsal plate, as well as in the fixation of the position provided by the levator muscle. The lower eyelid plate is much smaller and is held in place by retractors.
When the eyelids are damaged, the doctor’s primary task is not only to collect accurate information and analyze the condition of the eye organs, but also to assess the consequences of the injury.
Depending on the cause of the injury, its severity and possible consequences, eyelid injuries are divided into several types:
- Contusion is an injury resulting from a blow with a blunt object. The consequences are pain, swelling, hematoma, sometimes subcutaneous emphysema; with severe injuries of this kind, rupture of the conjunctiva often occurs, as well as damage to the eyeball itself. With blunt injuries, possible ruptures of the eyelids or tears, most often in the area of the inner canthus. Injury to the lacrimal ducts, their displacement and rupture of the lacrimal ducts may be inevitable. In the first minutes after receiving such a wound, it is recommended to apply cold to the affected area, and a painkiller may be administered in a medical facility.
- Erosion is damage to the tissue in the form of scratches or abrasions. It is accompanied by bleeding of the damaged area, pain and does not always require special medical care. It is enough to treat the wound with antibacterial agents and apply cold to it.
- Injuries . Among them there are chipped, torn and cut ones, depending on the nature of the injury and the conditions of its application. Wounds to the eyelids can be non-through and through, with a tear of the edge, partial or complete separation of the edge in the area of the outer or inner canthus. When the eyelid is torn off, the lacrimal canaliculi rupture in the area of the inner canthus. With penetrating wounds of the eyelids, the wound course can go deep into the orbit, where injury to its nerves and vessels is possible, especially in the area of the superior orbital fissure and optic foramen. Penetrating wounds of the upper eyelid are dangerous because the object that causes the wounds can penetrate through the upper wall of the orbit into the anterior or middle cranial fossa, where brain injury is possible, which can threaten the life of the victim. With penetrating wounds of the eyelids, a purulent infection can enter the orbit, leading to dangerously serious complications - phlegmon of the orbit, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus and purulent meningitis, which pose a threat to the vision and life of the patient. Also, if the upper eyelid is damaged, injuries to the levator muscle, the muscle responsible for its fixation, and internal and external commissures are possible.
Clinical picture
With blunt injuries to the eyelids, depending on the severity, they swell and bruises are visible under the skin. The palpebral fissure is narrowed. It is also necessary to feel the eyelids and edges of the orbit with your fingers. If there is a gentle crunch under the skin (crepitation), this indicates the presence of air under the skin, which can penetrate from the paranasal sinuses if the integrity of the inner, thinnest, wall of the orbit is violated. By palpation of the edges of the orbit, bone fractures can be detected.
With eyelid injuries, depending on their nature, the wound will be visible. If the wound of the eyelid is parallel to its edge, then it is always well adapted. When the wound is perpendicular to the edge of the eyelid, it always gapes. In cases of a through wound of the eyelid, it is necessary to inspect it to see if there is a foreign body in it and how deep it is. In such cases, it is also necessary to check the range of movements of the eyeball, the sensitivity of the cornea, conjunctiva and visual functions, pay attention to the width of the pupil, the position of the eyeball in the orbit.
With deep wounds of the orbit with damage to the nerves and vessels passing through the upper orbital fissure, the sensitivity of the skin and conjunctiva of the drooping upper eyelid and eyeball is impaired, there will also be external and internal ophthalmoplegia - there are no eye movements, the pupil is dilated and does not respond to light, exophthalmos may also be observed . When the edge of the eyelid is injured, the edges of the wound diverge and the eyelid becomes deformed. In cases of separation of the edge of the eyelid, deformation of the palpebral fissure is noted. With deep through wounds of the upper eyelid, it is necessary to pay attention to whether the victim has brain disorders and the presence of cranial fluid in the wound. The detail of the examination and the correctness of the diagnosis are extremely important in the provision of emergency care and further tactics of the doctor.
Treatment
For blunt injuries without breaking the integrity of the skin in fresh cases, cold is prescribed on the eyelids for 30 minutes. Ascorutin, etamsylate, and calcium dobesilate are given orally. Inject 10 ml of 10% calcium chloride solution daily for 5-10 infusions. After a few days, dry heat on the eyelids and resorption therapy are recommended.
In case of eyelid wounds, according to the general requirements of surgery, it is necessary to receive an antitetanus vaccination (antitetanus serum 3000 units according to the regimen and tetanus toxoid 1 ml). Eyelid wounds are subject to primary surgical treatment. When performing primary surgical treatment of eyelid wounds, one must always remember their functional and cosmetic role. Surgical treatment should be carried out in such a way that after it the function of the eyelids is not impaired and there is no cosmetic defect. For through wounds of the eyelids, sutures must be applied separately to the conjunctival-cartilaginous and musculocutaneous plates. In cases of rupture of the edge of the eyelid, the edges of the wound are brought together with a tightening suture along the intermarginal space, and then sutures are placed on the conjunctival-cartilaginous and musculocutaneous plates. When eyelids are torn off in the area of the palpebral fissure, a tightening suture must be applied, thereby forming a palpebral fissure, and then sutures are placed separately on the conjunctiva and the musculocutaneous plate.
Restoration of tear ducts
When the eyelids are damaged, the percentage of damage to the lacrimal canaliculi reaches 47.6%. In contrast to damage to the eyelid without traumatizing the lacrimal ducts, this pathology must involve suturing the lacrimal canaliculus and matching its torn edges, otherwise cicatricial adhesions of the soft tissues and the mucous membrane of the canaliculi will form, which leads to the development of persistent lacrimation, requiring repeated, and not always successful, surgical intervention.
Usually, to restore the patency of the lacrimal canaliculus, excision of the scar with temporary intubation of its lumen with a silicone tube, latex tourniquet or metal probe is sufficient. The technical difficulty increases the closer to the lacrimal sac the site of the canaliculus rupture is located. This leaves an imprint on the outcomes of operations, which in some cases turn out to be suboptimal, which leads to a lack of active patency of the tear.
Restoration of the lacrimal ducts is carried out according to a method that includes several stages.
- The first stage is probing the lacrimal ducts. Under local anesthesia with a 2% novocaine solution, the lacrimal ducts are probed through the superior lacrimal punctum with a Johnson needle and thread (4/0 nylon).
- The second stage is the preparation of a tubular steel probe. Considering the fact that the distance from the proximal part of the inferior lacrimal canaliculus to the bone wall of the fossa of the lacrimal sac is 3 mm, during proximal separation the implant should not exceed this value. A tube is made from an injection needle - a probe is 3 mm longer than the length of the damaged tubule. The free edge of the thread is passed through the probe and, changing direction, it is passed back.
- The third stage is suturing the tear of the lower eyelid from the inner corner. Under local anesthesia with a 2% novocaine solution, a “U-shaped” suture is placed on the damaged eyelid. The wound is sutured layer by layer in such a way that the damaged area of the lower lacrimal canaliculus is amenable to visual inspection.
- The fourth stage is installing the probe into the damaged canal. The lower lacrimal canaliculus is sutured with 2 interrupted 10/0 sutures. By pulling up the thread passed through the upper lacrimal canaliculus, the probe is passed into the lower lacrimal punctum. Immersion is carried out until the tube completely enters the lower lacrimal canaliculus to the level of the loop.
As a result of such manipulation, the damaged part of the lower lacrimal canaliculus is located on the probe like a “stocking”. The thread in the area of the superior lacrimal canaliculus is cut off in the area of the superior lacrimal opening.
The ends of the nylon thread inserted into the lacrimal canaliculi are overlapped and glued with an adhesive plaster to the skin of the cheek and forehead. The inserted thread into the lacrimal canaliculus is removed after 2-3 weeks. Silk, nylon, nylon, supramid thickness are used as suture material. After surgery, antibacterial drops are instilled into the conjunctival sac. Dressings are done daily. If necessary, general treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides is carried out. Eyelid wounds heal quickly due to their good blood supply, and stitches can be removed 5-6 days after they are applied.
Thus, when using this method of restoring the lacrimal ducts, the aesthetic effect of the position of the lower lacrimal opening and the patency of the lacrimal ducts is achieved. When scar tissue forms, the diameter of the stricture is limited by the diameter of the probe. When a nylon thread is used as an implant, the maturation of granulations is disrupted in the tubule wall, and excessive synthetic activity of fibroblasts leads to excessive formation of collagen fibers and their hyalinosis.
Consequences
With minor injuries to the surface of the eyelid, deep damage usually does not occur, which poses a potential danger to humans. But in many cases they are quite painful, accompanied by swelling and other cosmetic defects.
The bruise that appears at the site of the injury completely disappears only after two weeks.
In the absence of adequate treatment or with deeper injury, the following complications may develop:
- Infection of surrounding tissues. The penetration of a bacterial infection into the human body can lead to the development of serious diseases - purulent sinusitis, conjunctivitis.
- When muscle structures are involved in the pathological process, adhesions occur. This leads to the fact that a person cannot close his eyes normally. To correct such a defect, surgery is required.
- When infection enters the wound, there is a possibility of scarring. This is not only aesthetically unattractive, but can also disrupt the process of closing the eyes.
- If organ structures are damaged, complete or partial loss of vision is possible.
How can minor eyelid injuries be dangerous?
With minor erosions, bruises, and wounds, as a rule, damage occurs that does not affect other structures of the eye or parts of the face (superficial). They are quite painful and create significant discomfort, as a cosmetic defect occurs: swelling, redness, lacrimation. After 4–24 hours, a hematoma will form at the site of the blow or bruise, which will change color as it resolves: from purple and blue-black to pale green. It will take up to two weeks for the cosmetic defect to completely disappear.
In addition to these complications, such seemingly insignificant injuries as cuts and scratches can provoke more complex consequences:
- Infection of other structures, which leads to purulent sinusitis, conjunctivitis; in the most severe cases, pus can enter the brain. This will require complex and lengthy treatment.
- When muscle tissue is damaged, adhesions occur, which lead to incomplete closure of the eyelids (ptosis); only surgery can restore normal mobility.
- If an infection gets into the wound, a scar may appear in its place, which will disrupt the correct position of the eyelid, and it will turn outward. Treatment will take up to 1 month, and this defect can only be completely eliminated through surgery.
First aid
Only a specialist can provide qualified assistance for eye injuries. However, first aid can and should be provided immediately after the injury occurs. So, a number of actions should be taken:
If the eyelid is damaged, cold must be applied, but one should not forget about the rules of sanitation. The skin of the eyelids stretches well and this leads to faster formation of hematomas; cold will help stop the bleeding and thereby reduce the hematoma.
The injured eye should be covered with a sterile bandage and consulted with an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
If there is severe pain in the eye or headache, the victim is given painkillers and an ambulance is called.
It is not recommended to treat wounds yourself.
If an eyelid injury is detected in a child, it must be shown to an ophthalmologist. Only he can competently conduct an examination and prescribe competent treatment.
Symptom of glasses
Sometimes blue-black circles appear on the eyelids and around the eyes, very reminiscent of glasses applied to the eyes (reminiscent of glasses). This manifestation occurs as a result of a fracture of the base of the skull or facial bones, approximately every fifth person with this diagnosis.
Most often, the “glasses symptom” appears immediately after injury, but it can also occur a day after the incident.
This pathology requires immediate treatment at the hospital.
First aid
After receiving an injury, it is necessary to provide the victim with first aid:
- If there are open wounds, it is advisable to apply a sterile bandage to the problem area . In case of deep tissue injury, it is recommended to carry out the same manipulations with the healthy eye. This will prevent them from moving in sync.
- If you receive a contusion, apply a cold compress to the problem area. To do this, use ordinary water, ice, and metal objects.
- In case of deep injury to the eyelid, it is not recommended to independently engage in antiseptic treatment of the skin. To do this, it is best to consult a doctor who can correctly assess the extent of tissue damage.
- If a serious injury to the eyelid occurs involving the eyeball in the pathological process, measures are taken to stop the bleeding. You should not try to remove foreign objects yourself, as this can lead to even more serious consequences. It is best to cover the area of injury with a sterile cloth and seek medical attention.
- If you receive a chemical burn, you should rinse your eye thoroughly with running water to remove particles of aggressive substances. After this, a sterile bandage is applied to the problem area.
If a child has suffered an eyelid injury, it is recommended to contact a pediatric ophthalmologist as soon as possible and not take any action on your own.
How is traumatic eyelid edema treated?
The method of treatment depends on the type of injury. In case of a bruise, no measures usually need to be taken. But if you experience headaches or eye pain, you need to undergo an examination.
If the swelling is caused by a penetrating wound, you should determine whether there is a foreign object in the eyelid. It could also be the sting of some insect. The risk of an infectious disease increases. If there are bacteria, viruses or fungi in the wound, inflammation will begin. In this regard, in case of eyelid injuries, infection prevention is carried out. Antibacterial drops or ointments may be prescribed.
The duration of treatment for eyelid burns depends on the degree. For the first and second, ointments are used, including antibiotics. Third and fourth degree burns are treated surgically. Mild eyelid injuries are not complicated. Swelling and other symptoms disappear after 5-6 days. The second degree is treated for 7-8 days. Treatment for complex burns can take several weeks or even months. In this case we are talking about injury to the eyelids. If the eyeball is damaged, treatment may be longer and more difficult.
For some eye diseases, massage is used. It promotes the outflow of excess fluid, as well as improving blood circulation, which leads to a reduction in swelling. If you have an injury, you should not massage your eyelids. The wound may become infected. For the same reason, it is not recommended to make lotions or use other means of so-called traditional medicine.
Therapy
You can begin home treatment for such injuries (even minor scratches) only after consulting an ophthalmologist. It is necessary for a specialist to examine the victim and determine the extent of tissue damage. Very often, when the lower eyelid is injured, the tear ducts rupture, which does not appear outwardly. This requires mandatory medical intervention.
Typically, treatment of such injuries is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- If you receive a bruise on the first day, it is recommended to apply cold to the problem area . Only after this can you apply warm compresses, which will speed up healing by increasing blood flow.
- When diagnosing erosion, antiseptic treatment of damaged areas is recommended. If deep layers of tissue are injured, it is advisable to entrust this process to an ophthalmologist.
- Cut and lacerated wounds require suturing followed by antiseptic treatment of the damaged area.
- For serious injuries, the use of drugs such as calcium dobesilate, Ascorutin, Etamzilate is indicated. These medications reduce the risk of complications and speed up the onset of recovery.
- If the tear ducts are damaged, surgical intervention is performed to restore their patency.
- If the cornea of the eye is affected, the use of special drops that produce a restorative effect is indicated. The most popular drugs from this group are Korneregel, Vitasik, Solcoseryl, Hyphen.
- With the development of severe pain, drops are used - Lidocaine, Alcaine.
- In case of superficial injury to the eyelid, it is permissible to use folk remedies. You can use infusions of medicinal herbs - calendula, chamomile. Pour 235 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of plant material and wait until the liquid cools. After this, the infusion is filtered and applied as a compress.
Treatment of injuries localized on the surface of the eyelids requires a professional approach. Only by following all the doctor’s recommendations will it be possible to achieve a positive result and avoid the development of complications.
Dacryocystitis and eyelid edema
This pathology develops due to obstruction of the nasolacrimal ducts. They become clogged, which leads to disruption of the outflow of tear fluid. Any infection that gets into the lacrimal sac can cause severe inflammation. The swelling is localized in the corner of the eye and can cover the upper and lower eyelids. Also observed with dacryocystitis:
- severe lacrimation;
- Pain in the eyes;
- swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva;
- discharge of mucus or pus, especially when pressed;
- increased sensitivity of the eyes.
In most cases, unilateral dacryocystitis occurs. The disease cannot be called very dangerous, but it, like any inflammatory eye pathology, requires proper treatment. Due to its absence, swelling increases, which can cause complete closure of the palpebral fissure. When an abscess forms, the lacrimal sac is opened and the nasolacrimal duct is surgically restored.
First aid for injury
If your eyes are damaged, the following rules should be observed:
- You can't rub your eye.
- Do not touch the injured area with dirty hands.
- It is forbidden to press on the eyelids.
- It is not recommended to independently remove a foreign object that is in the sclera or even deeper.
- If the wound is penetrating, then it is forbidden to wash the eyes.
- In case of a chemical burn or eye damage, do not use soda for rinsing.
- Do not use anesthetic drops.
- A medical eye patch should not have a cotton base, but only a bandage.
If your eyes are damaged, you should not self-medicate, as this may result in partial or complete loss of vision. If the foreign body in the eye is on the surface and has not penetrated inside, then you can get it out yourself. To do this, the lower eyelid is pulled back and the object is taken out, and the eye apparatus is washed with clean water. After this procedure, drops with an anti-inflammatory effect are dripped into the eyes.
If there is a bruise, then apply dry cold. These are spherical metal objects, as well as cold and frozen foods that must first be wrapped in plastic.
First aid for chemical eye burns consists of removing the source that caused the injury. Drops for eye burns should contain both an antibiotic and an anti-inflammatory substance. If your eyes are damaged due to contact with hot, hot oil or grease, the eyes should be washed. The injured area is covered with a napkin for a while, and a cold compress is applied on top. If there is severe pain, you can take an analgesic.
Burns of infrared and ultraviolet origin are treated with drops with an anti-inflammatory effect, and then cold is applied to the damaged area. In case of a penetrating wound, the eyes are given rest, and the injury site is covered with a napkin. In case of bleeding, the bandage is sealed with cotton wool.
If a foreign object is stuck deeply, then the eye should be kept motionless and the head should be fixed. In the periorbital area, remove all foreign bodies lying on the surface, without affecting the injured part.
For emergency treatment of eye damage, drops such as Levomycetin, Sodium Sulfacyl and Albucid are used. Together with the drops, you can use tetracycline ointment, Floxal. If the wound is large, then a medical eye patch should be applied to both eyes. If a foreign body is present, an antitetanus injection is given and antibiotics are prescribed.