Blepharitis and chalazion are two fairly common eyelid diseases. Moreover, the second is often a consequence of the chronic course of the first. These diseases are accompanied by inflammation of the eyelids and have similar symptoms. Let's look at the features of these eye diseases and find out how they are treated.
In this article
- What is blepharitis and why does it occur?
- Symptoms of blepharitis
- Types of blepharitis
- How is blepharitis treated?
- Complications of blepharitis
- What is a chalazion?
- Symptoms
- How is chalazion ?
What is blepharitis and why does it occur?
Blepharitis refers to various ophthalmological pathologies in which the edges of the eyelids become inflamed. In most cases, such inflammations take a chronic form and periodically worsen. An inflammatory process occurs after microbes, viruses, fungi or mites enter the meibomian glands. In some cases, blepharitis develops due to allergies. Pathogenic microorganisms are the direct causative agents of a disease. There are also internal reasons that can be called disposing factors:
- avitaminosis;
- mechanical injuries to the eyes and eyelids;
- infectious and viral systemic diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- refractive errors;
- dry eye syndrome;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- weak immunity.
Most often people suffer from blepharitis:
- children;
- women who use cosmetics;
- allergy sufferers;
- patients with serious illnesses, such as diabetes;
- people with poor vision.
Often, inflammation of the eyelids is detected in users of scheduled replacement contact optics who do not care for them well. In principle, anyone can get blepharitis. A person is more vulnerable during a period of weakened immunity.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention; there are a number of general recommended rules, the observance of which will help prevent the disease.
Preventive measures:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Timely treatment of all chronic infections - blepharitis, caries, barley, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, sinusitis.
- If you are prone to stagnation in the meibomian gland ducts, give yourself a preventive eye drainage massage.
- A balanced diet, a sufficient amount of vitamins in the diet.
- If the cause is a chronic disease of the body, you need to fight it directly.
Now you know how to deal with chalazion. Save the article to bookmarks so as not to forget and share the information with your friends on social networks, they may also find it useful, be healthy.
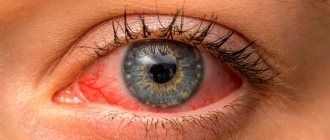
Symptoms of blepharitis
The symptoms of the disease depend on its type. First, let's list the general symptoms:
- itching and burning;
- redness and swelling of the eyelids;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- mucous and purulent discharge from the eyelids;
- heaviness in the eyes.
These are typical symptoms not only for blepharitis, but also for many other eye diseases. You cannot self-medicate. An incorrectly selected drug can cause complications.
Types of blepharitis
Depending on the causes and symptoms of inflammation, several types of the pathology in question are distinguished:
- Scaly, or seborrheic. A characteristic feature is scales on the eyelashes, which are desquamated particles of the epidermis. Symptoms such as very severe itching, redness of the conjunctiva, and hardening of the edges of the eyelid are also observed. When the disease is severe, the eyelashes turn gray and fall out.
- Ulcerative. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the follicles of the cilia. Pus flows in large quantities from the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands. Crusts form on the eyelids, which subsequently cause scars. There is a disturbance in the growth of eyelashes and their loss.
- Demodectic. This blepharitis is caused by Demodex mites. It is almost always found on the skin of the face, but does not pose a danger if a person maintains hygiene, his immune system is strengthened and he monitors his health. Ticks that have entered the meibomian glands can begin to multiply due to hypothermia, a cold or a viral disease. Reproducing parasites feed on the secretions of the sebaceous glands. Mite waste products cause inflammation.
- Meibomian. This type of disease is accompanied by severe thickening and redness. When bacteria enter the excretory ducts of the eyelids, increased secretion production begins, but due to blockage of the glands, it does not come out. This leads to the development of inflammation.
- Acne. This disease is also called ophthalmic rosacea. It is characterized by the presence of rashes on the skin of the face and eyelids. Pink acne spreads quickly and causes discomfort in the form of burning and itching.
- Allergic blepharitis is the only type of pathology that is not caused by microbes and viruses, and therefore is not contagious. The allergy manifests itself in severe itching, profuse lacrimation, increased photosensitivity, and swelling.
It is possible to accurately determine the cause and type of blepharitis only after an examination, during which allergy tests are taken, laboratory tests of discharge and other procedures are performed.
How is blepharitis treated?
Treatment of this disease is carried out with the help of medications - eye drops, ointments, gels. The type of medicine is determined by the causes of inflammation. The general principles of therapy are:
- maintaining hygiene;
- performing rinses;
- eyelid massage;
- instillation of solutions based on natural tears;
- diet.
As for drugs, antihistamines, antimicrobials, antiseptics, glucocorticosteroids, and sulfonamides can be prescribed.
It is possible to eliminate inflammation and improve blood circulation in the eyelids and eyeballs during physiotherapy. If medications do not help, the patient is sent to:
- UHF therapy - treatment with a high-frequency electromagnetic field;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation therapy;
- darsonvalization - exposure of the affected tissues of the eyelids to high-frequency pulsed current;
- irradiation with Bucca rays - ultra-soft x-rays.
Complications of blepharitis
This disease is rarely accompanied by complications; it often develops into a chronic form, which, as a rule, occurs due to incorrect, untimely started therapy or its complete absence. Blepharitis can cause conjunctivitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, keratitis and other ophthalmic pathologies. In other words, the inflammation spreads to the eyeball - the conjunctiva, cornea, etc. Chronic blepharitis can lead to the formation of a chalazion, which sometimes has to be treated surgically. Let's take a closer look at this disease.
Expert opinion
Experts in the field of ophthalmology are inclined to believe that the level of personal hygiene plays a decisive role in the formation of a chalazion. This means that, other things being equal, the disease is more likely to develop in those who neglect hygiene requirements.
Therefore, it is important to keep your facial skin clean, use specialized products when washing your face, accustom yourself to regularly wash your hands, and refuse to use other people’s personal items (cosmetics, towels, etc.)
What is a chalazion?
A chalazion, or hailstone, is a benign compaction in the thickness of the cartilage of the eyelid. Its formation occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands. This disease is quite common. It is diagnosed in 7% of patients with inflammation of the eyelids. People of all ages suffer from it, but it is more often detected in people over 30 years of age. This is due to a decrease in the production of secretions responsible for lubrication of the conjunctiva.
The main cause of chalazion is blockage of the excretory ducts of the glands. Because of this, the lipid contents do not flow out, but accumulate in the lumen of the duct, which leads to tissue inflammation and the formation of a nodular seal. It often occurs against the background or as a result of the following diseases:
- barley;
- chronic blepharitis;
- rosacea;
- seborrhea.
Factors also predisposing to chalazion are:
- hypovitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- viral diseases;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- diabetes;
- poor hygiene, including when using contact lenses.
Diagnostics
In some cases, a chalazion may not require treatment. The outflow from the gland will be restored within a few weeks, but conditions for subsequent relapse will remain.
Diagnosis is based on external examination and clinical picture. As a rule, chalazion is easy to treat, but you should not delay a visit to an ophthalmologist and rely on self-medication, so as not to miss the symptoms of a more serious disease, for example, meibomian gland cancer.
The earlier the diagnosis is made, the easier the treatment will be. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is required.
If, while following all medical recommendations, the disease reappears, the doctor prescribes additional examinations: histology, culture for staphylococcus, blood tests for sugar, infections, and others.
Squeezing out a chalazion or opening it with a needle is strictly prohibited. This leads to infection and the risk of complications.
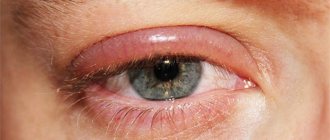
Symptoms
When a chalazion develops, a round-shaped compaction forms under the skin of the eyelid. It is located in the thickness of the cartilage. This does not cause pain. The seal slowly enlarges and can grow up to 5-6 mm in diameter. The swelling becomes pronounced.
A visible cosmetic defect occurs. In some cases, a patient develops several chalazions on the upper and lower eyelids.
This pathology may also be accompanied by:
- lacrimation;
- itching;
- redness of the conjunctiva.
As the hailstone increases in size, it begins to affect the quality of vision, causing diplopia and image distortion. Often the chalazion opens spontaneously. Its contents flow out and the swelling immediately subsides. If this does not happen, the lump turns into a cyst with mucus inside.
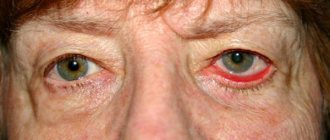
Chalazion can also occur in a more severe form, with suppuration. In such cases, the following symptoms appear:
- throbbing pain;
- redness of the eyelids and skin around the eyes;
- swelling;
- increased body temperature;
- softening of hailstones.
How is chalazion treated?
At an early stage, drug therapy is used. The patient is prescribed eye drops and ointments. Eyelid massage, heat compresses, and UHF therapy can also be used in treatment. In case of severe inflammation, injections with corticosteroids are given. The drugs are injected into the compaction cavity, which leads to rapid resorption of the contents of the chalazion.
Surgery is prescribed in extreme cases when the disease does not go away and begins to affect vision. Hailstone removal surgery is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthetic. After excision of the formation, sutures are placed on the eyelid, and a tight pressure bandage is placed on the eye. For 5-7 days, the patient instills drops and applies ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect.
Today, laser methods for chalazion removal are also used. First, the hailstone capsule is dissected, after which its contents are evaporated by a laser. This treatment is less traumatic. No stitches are needed.
So, blepharitis and chalazion are common diseases with similar symptoms. In this case, sometimes inflammation of the edges of the eyelids leads to the formation of hailstones. These ailments can be treated quickly. It is important not to neglect them and start treating them when the first signs appear.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is important to remember that traditional methods can only be used after consulting an ophthalmologist: otherwise, you risk causing damage to your health. In particular, it is important to determine exactly what type of neoplasm has appeared on the eyelid: stye or chalazion.
Why is it necessary to know an accurate diagnosis? A simple example can be given: in the first stages of chalazion development, a hot compress can achieve an excellent effect. If the patient has barley, compresses and any other heating are contraindicated.
In the first stages of the disease, you can successfully use a regular chicken egg for warming. The egg should be boiled, wrapped in a clean cloth and applied to the affected eyelid. You can replace the egg with table salt, which retains heat perfectly.
Light massage of the affected area can prevent the development of inflammation.
There are other methods for treating chalazion at home:
- aloe treatment. It is known that aloe is an excellent natural antiseptic. Aloe juice should be applied to the affected eyelid several times a day. You can replace aloe with Kalanchoe;
— flaxseed oil helps to cope with chalazion, which also needs to be applied to the eyelid several times a day. Before application, the oil should be slightly warmed in a water bath;
— Figs help cope with inflammation and boost immunity. Regular consumption of dried fig decoction is an excellent way to cure chalazion on a child’s eye. It is enough to pour several fruits with a glass of hot milk and drink this drink every morning before breakfast.