What is an abscess of the eyelid (eye)?
This pathology refers to purulent inflammation limited to the capsule, formed as a result of the penetration of a pathogenic microorganism into the tissue.
If treated incorrectly or untimely, the disease can develop into phlegmon, characterized by a small amount of suppuration and significant spread around the source of infection.
The closer the abscess is to the head, the higher the risk of severe complications. The fact is that the “pest”, after penetrating the circulatory system, very quickly spreads through the vessels responsible for supplying blood to the brain. For this reason, do not self-medicate under any circumstances and do not delay visiting the doctor! As soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear, immediately go to the clinic for examination. Therapy is usually carried out in a hospital inpatient setting.
More about pathology
An eye abscess develops as a result of the penetration of microorganisms.
Routes of infection:
- Through damaged tissue. Infection can occur when bacteria from inflammatory elements (barley, boil, etc.) enter.
- Hematogenously (through blood). This route of infection is typical for people with reduced immunity (severe illnesses, immunodeficiency).
Eyelid abscess is classified according to stages:
- Infiltrative – the initial stage, characterized by the appearance of redness and thickening.
- Purulent-necrotic – stage of cavity formation with the formation of pus.
- The healing stage is the final stage. With large lesions, scars remain after healing; with small lesions, no traces remain.
Causes of the disease
Purulent abscesses can appear regardless of age or gender; most often, an abscess affects a fragile child’s body. The main reason for the onset of inflammatory processes is the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms (staphylococci, streptococci).
Pathology can often be caused by:
- A harmless, at first glance, insect bite;
- Squeezing out blackheads;
- Foreign body getting into the eye;
- Purulent inflammation in the sinuses or mouth;
- Improper treatment of stye or boil;
- Meibomite;
- Sepsis in ocular structures.
Infection occurs in several ways:
- Entry of a pathogenic microorganism into a wound (cut, scratch) on the skin of the eyelid. If, in addition to damage to the epidermis, there is a focus of infection (barley, squeezed out pimple), then the virus quickly “moves” there and the formation of suppuration begins;
- The pathogenic bacterium can enter the bloodstream from other sources of infection. The formation of pathology occurs against the background of otitis, sinusitis or stomatitis.
The most common cause of an abscess of the upper or lower eyelid is self-treatment of various purulent formations in the eye area.
| It is dangerous to squeeze out stye or other foci of infection, since bacteria quickly spread throughout the body and can lead to serious consequences. |
Return to contents
Causes
An abscess of the eyelid is formed due to the entry of pathogenic microbes into the body, most often staphylococci and streptococci. Often the pathology manifests itself in the presence of a concomitant illness, barley, blepharitis, furunculosis. Another reason for formation is insect bites.
Other factors predisposing to the appearance of an abscess include:
- Purulent inflammatory processes in the sinuses;
- Caries;
- Weak immune system;
- Eliminating small ulcers at home;
- Injury.
Symptoms
The disease has many specific symptoms; they appear gradually as pus accumulates. The name of the pathology translated from Latin means “big abscess,” which very clearly reflects the essence of the disease.
Symptoms do not develop as rapidly as, for example, with barley, but they are steady and gradually increase, causing pain and discomfort to the person.
The following signs indicate the formation of an abscess:
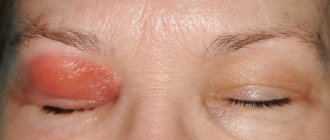
- Thickening and compaction of tissues.
- Redness and swelling of the eyelid, a feeling of tightness, at the site of inflammation the skin becomes hot due to a local increase in temperature;
- Deterioration of vision;
- The eye does not close completely (observed with sepsis of the upper eyelid);
- If the affected area is large, fever occurs (temperature rises to 39.8 degrees);
- A throbbing pain is felt in the area where pus accumulates;
- Poor health, loss of strength, migraine;
- A yellow or white spot appears at the site of inflammation; after a few days it opens and pus flows out of it.
After cleansing the wound, the patient’s well-being is significantly improved, and symptoms practically disappear. If the pus is not completely drained, a fistula forms, as a result, the signs of the disease return and the inflammation becomes more serious.
| Never open an abscess yourself, the infection can spread throughout the body! |
If the lower eyelid is affected, then there are no problems with blinking, the eye retains 100% of its functionality. But bacteria can spread to healthy tissue at any time, so you should not delay treatment of the disease.
For primary manifestations of an abscess, immediately visit an ophthalmologist. Only a doctor after an examination will be able to prescribe the correct therapy and select effective medications.
Diagnosis of the disease
The ophthalmologist makes the final diagnosis after a visual examination and collection of the necessary tests. To determine the cause of the infection, the patient is sent for x-rays and palpation is performed.
Also, to make a correct diagnosis, a puncture is taken from the patient, it is sent for bacteriological analysis, it helps to identify the source of the pathology and identify its sensitivity to antibiotics. Visual acuity is checked, the eye is examined using special instruments and a urine/blood test is taken.
The main method of removing an abscess is surgical intervention; if the capsule is opened involuntarily, then medical care cannot be avoided. A visit to an ophthalmologist will eliminate the possibility of further progression of the infection, since in most cases the pus does not come out completely. Don't try to squeeze it out yourself!
Complications and side effects
If the procedure was performed by a professional doctor, then the patient does not have to fear complications in the form of sepsis and repeated suppuration. However, people who smoke or have autoimmune diseases may experience the following side effects:
- post-manipulation pain;
- prolonged bleeding;
- the appearance of a scar.
It is better to trust even minimal surgical intervention only to professionals. In the medical department, abscesses of any category of complexity are opened. Doctors have all the necessary diplomas and regularly improve their qualifications. Make an appointment and forget about pain!
Treatment methods
Depending on the degree of development of the pathology and symptoms, the doctor prescribes outpatient or inpatient therapy. It takes up to ten days for a complete recovery if you go to the clinic in a timely manner; in case of complications, the illness can drag on for two weeks.
During the treatment period, you should avoid physical activity, avoid hypothermia, and take medications that strengthen your immune system. Return to contents
Surgery (surgery to remove an abscess)
If inflammation occurs, surgery cannot be avoided. This will help you quickly get rid of the problem and avoid possible complications. It lasts no more than fifteen minutes and is absolutely safe for the health and life of the patient.
| It is better to consult a doctor immediately after the appearance of an abscess, without waiting for the abscess to burst. |
When performing drainage, a medical professional uses local anesthesia, opens the capsule, removes the “filler,” and cleans the wound with antibacterial and disinfecting solutions. If the procedure is performed without any violations, then after the abscess heals there will be no cosmetic defects left.
A small incision is made parallel to the eyelid line to avoid scarring. To prevent the spread of infection, it is necessary to instill a 20% solution of sulfacetamide daily.
After the operation, the treated eyelid is covered with a dry sterile bandage. It must be changed several times a day, while repeating the antibacterial treatment of the eye.
Drug treatment
If an abscess develops, the doctor prescribes the following medications to the patient:
- Antibacterial agents (for example, penicillin). The medicine is administered intravenously or intramuscularly, 50-300 units up to four times a day;
- Tetracycline tablets 0.2 grams three times a day;
- Sulfadimezin 0.5 gr. eight times a day.
Additionally, it is recommended to take a course of antibiotics. The duration of treatment is determined individually for each patient, depending on the degree of development of the sepsis focus.
Maintenance therapy
After eliminating the abscess, the following procedures are recommended to eliminate the risk of relapse:
- The mucous membrane of the eye is treated with vasoconstrictor drugs (for example, 0.1% hydrochloride), they help get rid of swelling and inflammation;
- Autohemotherapy. Blood from a vein is injected into the gluteal muscle to strengthen the immune system. Ten to twelve injections are required;
- Antibiotic therapy - benzylpenicillin injections intramuscularly for five days;
- UVB of blood. A needle with an ultraviolet emitter is inserted into the patient's vein. After irradiation, all pathogenic microorganisms die, the wound healing process is accelerated, and relapse is prevented. It is necessary to complete a course of ten sessions.
| Maintenance therapy must be repeated after a year. |
Treatment with folk remedies
Some people do not trust doctors and try to get rid of an abscess with “grandmother’s recipes.” There are several safe methods for eliminating pathology at home; the best option is to apply compresses from medicinal plants.
Such procedures can alleviate the patient’s condition for a short period of time, but the consequences of self-medication are often disastrous and provoke complications.
You can find out how the source of inflammation is treated using traditional methods from the video
Return to contents
Treatment
Therapy is prescribed only after diagnosis. An ophthalmologist determines the method of treating an eyelid abscess. For therapy to be effective, the disease must first be diagnosed.
The doctor must determine whether opening the purulent formation is necessary. If there is a medical indication, then anesthesia is first performed, and then an autopsy is performed, followed by removal of the contents of the abscess. Finally, the resulting cavity is treated with an antibacterial and antiseptic agent.
If everything is done carefully, the healing process goes quickly and subsequently there is no scar left, since the incision is made along the edge of the eyelid. The autopsy procedure lasts on average 10 minutes. But you shouldn’t hope that this is the end of the treatment. The main therapy will be carried out after removal of the pus.
First of all, antibacterial therapy is carried out. Antimicrobial agents are used in the form of drops or eye ointments that are placed behind the eyelid. To prevent re-inflammation, physiotherapy is performed using the following methods:
- autohemotherapy;
- photohemotherapy (UVR).
In addition, drug treatment is also carried out:
- For severe pain, painkillers are taken.
- The use of sulfonamides is indicated
- Treat the area where there was an accumulation of pus with 70% alcohol.
- Before the abscess is opened, dry heat is applied to the site of inflammation.
- You can irradiate with a blue lamp.
While therapy is being carried out, it is necessary to follow some rules in everyday life:
- Don't get too cold.
- Cover your face from natural phenomena: rain, wind, snow and even direct sunlight.
- Avoid excessive physical activity.
- If surgical intervention has been performed, then you should not strain, even slightly, during the entire treatment period.
If the body temperature has increased, then symptomatic treatment is carried out with the use of antipyretics and drinking plenty of fluids.
The duration of therapy is on average about two weeks. At this time, a person is recommended to take general restoratives:
- herbal supplements with anti-inflammatory effects;
- vitamins;
- immunomodulators.
Even after treatment ends, it is necessary to protect the organs of vision, because in the next six months the risk of relapse is still quite high.
To reduce the likelihood of a recurrent inflammatory process, it is necessary to protect not only the eyes, but also the ENT organs: nose, ears and throat. Treatment of an eyelid abscess is always carried out in a hospital setting, since the disease can develop complications in a short period of time.
Possible complications
Patients who cherish the hope that sooner or later the eyelid abscess will go away on its own run the risk of encountering consequences such as:
- Infection of the orbit and sclera;
- Deterioration of vision;
- Inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- Phlegmon of the orbit;
- Penetration of the virus into the blood.
Complications can lead to deterioration of the condition, including disability or death.
| Under no circumstances touch the inflammation with your hands or try to squeeze it out. Use all medications only after consulting a doctor! |
How to avoid abscess formation?
The best prevention is taking care of your health and following basic hygiene rules. It is enough to follow simple recommendations so as not to end up in a hospital for a long time and get rid of a number of unpleasant sensations that cause discomfort:
- Never squeeze pimples and blackheads on your face. To remove them, use cosmetic procedures or special ointments;
- Treat even minor wounds and cuts with an antiseptic;
- If you have an infectious disease, approach treatment carefully and carefully. Do not let the disease take its course, as it can “attract” additional “sores”.
Don't forget to strengthen your immune system, take vitamins, add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
You will learn how to avoid eyelid abscess by watching the video.
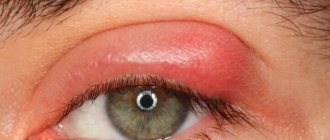
How does an abscess of the upper and lower eyelid manifest?
An eyelid abscess is determined visually and is often very similar to the manifestation of other diseases. Has distinctive symptoms.
- Increased body temperature.
- The infected area becomes hot to the touch.
- Severe redness.
- Swelling.
- Pain that increases over time. Characterized by a feeling of bursting from the inside.
- Possible drooping of the eyelid (if the abscess is localized at the top). With a lower position, it is impossible to close the eye completely.
- Upon palpation, a compacted area is detected.
If such signs are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Glucocorticosteroid for topical use in ophthalmology - instructions for Maxidex eye drops.
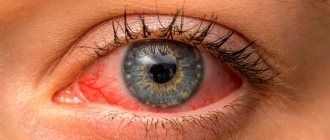
Swelling is a sign of inflammation
In serious advanced cases, the following are also possible:
- migraine;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- feeling of general malaise;
- yellowness on the affected area.
The abscess manifests itself progressively. The patient's condition worsens over time; improvement does not come on its own (only with arbitrary opening of the abscess).
Unlike a number of other diseases, in the presence of an abscess, the infected area forms at the level of the tissue. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs often do not provide relief.
You cannot perform any manipulations with the eye. It is impossible to squeeze out an abscess; there is a possibility of purulent masses penetrating into the circulatory system.
Find out when Normax antibacterial eye drops are prescribed here.
Migraine occurs when the course of an abscess is complicated
First aid in an emergency - what to do if your eyes are burned by welding.