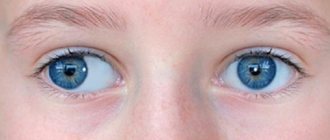
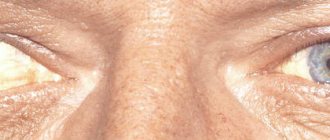
Strabismus (strabismus) is formed when the function of the extraocular muscles is disrupted. In this case, one or both eyes deviate from the midline, which leads to deterioration of vision. Glasses for strabismus are the initial stage of treatment for pathology, and they must be selected with special care.
Strabismus
strabismus Source: zrenieglaz.ru
Strabismus is an eye defect, the external signs of which are the asymmetrical arrangement of the cornea in relation to its corners and eyelids.
This disease is otherwise called strabismus or heterotropia.
With strabismus, there is an uncoordinated function of the motor muscles of the eye and a lack of connection between the visual axes on the object being viewed.
The gaze of such patients seems to be directed in different directions.
Strabismus causes the patient great difficulties in the moral and social spheres of life.
Method 1. Correct application of cosmetics.
It will not be possible to completely hide squint with makeup, but you can visually distract the attention of your interlocutor from this defect. Here are a few simple rules to follow:
- Place the main emphasis on the eyebrows. And even better on the lips.
- Do not draw arrows on your eyelids with eyeliner or eyeliner. A frame that is too bright will highlight the defect.
- Apply mascara to your eyelashes from the very roots. You can use false eyelashes or eyelash extensions, as long as they look natural.
- Use only light shades of eyeshadow, no glitter or bright ones.
Remember, excessive use of makeup can aggravate the problem, and the squint will be even more noticeable.
You may be interested in: Is it possible to cure strabismus at home?
What happens with strabismus?
When the disease occurs, each eye of the patient sends a different image to the brain than the other eye.
The visual analyzer in the cortical region summarizes the image of the two eyes and obtains an overall three-dimensional perception of the object.
As a result of various visual images obtained during strabismus, the brain cannot cope with the task and begins to ignore the image received from the diseased eye.
A long process of strabismus leads to the exclusion of this eye from visual functions. Decreased vision in this case is called “lazy eye” or amblyopia.
Childhood amblyopia develops very quickly. In a developing organism, the brain rather adapts to proposed changes in the functions of various organs.
In this case, amblyopia is reversible.
Therefore, it is necessary to take immediate measures to restore vision in order to prevent the diseased eye from completely atrophying without the possibility of recovery.
The process of developing amblyopia in adults is longer. But at the same time, the effect of duality of images appears, i.e. a person feels double vision.
To each his own: what lenses are needed for different types of strabismus
The easiest way to correct concomitant accommodative strabismus is that ordinary spherical lenses in thin and ultra-thin versions cope well with this task. If astigmatism is present, glasses with cylindrical-spherical lenses are prescribed. In order to improve the balance of convergence and divergence, individual progressive lenses made using Free Form technology are used. Computer modeling of optical surfaces based on individual eye parameters increases the chances of success of conservative treatment.
| Corrective glasses with fashionable frames will cheer up little dudes |
Double vision with non-accommodative and partially accommodative heterotropia is eliminated using prismatic lenses with the addition of the required number of diopters. The corrective effect is achieved due to the refraction of the line of sight when rays pass through glass of different thicknesses. To correct convergent strabismus, the prisms are rotated horizontally with the base outward; with a divergent shape, lenses are used that are thicker at the bridge of the nose and narrowed at the temples. With vertical heterotropia, the prisms in glasses are placed vertically.
Prismatic lenses made in Japan are considered to be the best in quality. German and French manufacturers operating in the premium segment have also proven themselves well.
The higher the degree of deviation, the thicker the prismatic lenses. In order to facilitate the design of glasses, Fresnel prisms are glued onto ordinary refractive lenses - thin elastic plates made of transparent polyurethane, almost invisible to others.
| Fresnel raster prism: will relieve strabismus and improve refraction |
It’s easy to choose elegant children’s frames for glasses with overlays that help kids overcome embarrassment and self-doubt. Fresnel prisms are also used to strengthen the extraocular muscles and to correct small residual angles in the postoperative period.
Causes and types of strabismus
strabismus_types Source: nazdor.ru
Causes of strabismus can be congenital or acquired:
- the presence of any vision pathology - farsightedness, myopia;
- presence of various types of injuries;
- existing diseases of the central nervous system;
- any infectious diseases;
- blurred vision as a result of fright.
Strabismus can be of several types:
- convergent - when one of the eyes squints closer to the nose;
- divergent - when the eye squints towards the temple;
- vertical - the eye squints up or down.
The treatment program includes the use of glasses, surgical methods, special bandages, medications.
Depending on the type of illness, it is necessary to select special glasses for the treatment of strabismus. All glasses must contain prismatic lenses.
Such lenses, having prismatic glass, have proven themselves in the process of correcting and correctly focusing vision.
Diagnostics
To determine the type of strabismus, a person needs to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures that will show the state of neglect of the disease. The ophthalmologist should:
- checking binocular vision using color test techniques;
- complete fundus examination;
- examination of the anterior segment of the eye;
- checking the nature of gaze fixation;
- determination of visual acuity with correction and in the normal state.
These parameters make it possible to accurately determine what type of strabismus the patient has. In this case, the doctor identifies the so-called primary and secondary angle of strabismus. The primary angle indicates deviations of the diseased eye, and the secondary angle indicates the deviations of the healthy eye. To identify these parameters, doctors use the “carpet test” and “Maddox cylinder” techniques.
Reference! Eyes were treated back in ancient Egypt. So in the ancient Egyptian treatises, among the 42 canonical books that were found in the tombs of the pharaohs dating back to the 15th century, 1500 BC, 6 books were devoted to medicine, and one of them was about eye diseases.
Carpet test
The purpose of this diagnosis is to identify heterotropia (true strabismus) or heterophoria (imaginary strabismus). The test shows an objective idea of the presence, severity and frequency of disease deviation.
To undergo diagnostics, the doctor sits opposite the patient and asks him to concentrate his gaze on a distant object. After this, the doctor takes turns covering the patient’s eyes with an occluder, first the left one, then the right one. This procedure is repeated several times. At this time, the ophthalmologist notes the presence and frequency of eye deviation.
An occluder is an ophthalmic medical device that blocks visual perception in one eye. It may look like glasses with one side closed or completely darkened, or like a regular patch.
When conducting a diagnosis to determine heterotropia, the doctor allows the patient to concentrate his attention on the object. If a person has signs of tropia, the eye will begin to squint in one direction.
Trophy research is a little different. The ophthalmologist applies the occluder for 1-2 seconds on each eye in turn. Thus, the possibility of focusing the gaze on the object is eliminated. If the patient suffers from heterophoria, the eye will immediately begin to squint.
For a complete study of heterophoria, they use diagnostics of the visual organ using the Maddox Cylinder.
Maddox cylinder
This technique allows you to accurately determine the type and degree of heterophoria. It allows you to assess the condition of the retina in patients with cataracts, in cases where it is difficult to view the condition of the fundus.
The Maddox cylinder is included in the ophthalmic lens trial kit. It consists of two lenses. The first lens contains red tubular cylinders with a diameter of 2-3 mm, which fill the entire lens. The second contains the linear Maddox scale, which determines the level of trophy development.
During diagnosis, the patient sits opposite the light source at a distance of either 5 m or 33 cm. Depending on this parameter, a lens with a linear scale is selected, the divisions of which correspond to the tangents of the visual angles when viewing it from a given distance. It is installed opposite one of the eyes in the socket of the trial frame.
A Maddox cylinder is placed in the second frame. To measure horizontal heterophoria, it is oriented horizontally. In this case, the patient sees a vertical red stripe with the eye in front of which the cylinder is located, and the Maddox scale with the other eye. With both eyes open, the subject is asked to indicate on which side of the light source and along which scale division the red stripe passes.
Symptoms of strabismus
A natural visible symptom of strabismus is the appearance of the eye. But this symptom cannot always serve as a reliable sign of strabismus.
There is an imaginary squint. In children at birth, this form is often observed, which is associated not with pathology, but with the structural features of children's palpebral fissures.
As a result, the impression of divergent strabismus is created.
Important!
True strabismus in children can be assumed in cases of stable deviation of one eye.
But this may not always be a sign of strabismus.
Perhaps the objects that attract the child's attention are always located on one side of the eye.
A symptom of strabismus can be squinting or forcing a person to tilt their head to a position favorable to vision.
This compensates for the inconveniences associated with impaired vision, such as headaches, double vision, and dizziness.
The feasibility of correction - is it necessary to hide strabismus at all?
There are different types and degrees of heterotropy. It is worth hiding the pathology only if the eyes are separated from each other by a decent distance.
A mild form of pathology is not noticeable to others
If the defect is minor, then there is no need to hide it. For many people, a slight deviation of the pupil from the normal axis gives it a special charm and charm.
Fact: Some stars deliberately do not eliminate slight heterotopia, as they consider it their “highlight”.
Jennifer Aniston has made a career out of having divergent heterotropia
Cosmetic correction may be needed if:
- there is obvious divergent strabismus;
- there is a severe degree of paralytic strabismus;
- the eye moved strongly to the bridge of the nose.
Convergent strabismus is more aesthetically acceptable than all other types of this disease.
If one of your pupils has moved a little towards your nose, and your vision has not deteriorated, look at it from the other side. Ask friends, acquaintances and loved ones. Perhaps this feature will even make you more attractive and charming in the eyes of other people.
Diagnosis of strabismus
diagnostics Source: medceh.ru
To correctly diagnose strabismus, a complete ophthalmological examination is performed. Computer diagnostics is widely used in the examination.
For a complete diagnosis, various tests are carried out for refraction, deviation and motor ability of the eyes, and determine binocular vision.
In addition, patients undergo a special neurological examination.
How to hide squint?
how to hide strabismus Source: bolezniglaznet.ru Pupil deviation can be externally corrected using:
- glasses;
- lenses;
- correct makeup.
Many people, faced with strabismus, begin to feel embarrassed about this peculiarity. They feel awkward when communicating with people and have complexes about how they look in photographs.
If there is no urgent need for strabismus surgery, do not be upset. It is possible to correct a cosmetic defect without the intervention of an ophthalmic surgeon.
Treatment of strabismus
Myopia, astigmatism, hypermetropia and other eye diseases that cause strabismus must be treated first in order to achieve positive results in improving the patient’s vision.
Some cases of strabismus are treated with therapeutic methods, but radical surgical methods have a greater effect.
The method of treating strabismus is selected individually based on the type and causes of strabismus.
To avoid a decrease in visual acuity of the healthy eye, treatment should be started as early as possible in the onset of the disease.
Often, correction of strabismus in children using various eye exercises aimed at strengthening the eye muscles contributes to the successful treatment of strabismus.
This is explained by the sensitivity of the children's nervous system and the ability to easily adapt.
Successful treatment of strabismus and vision correction are facilitated by glasses and special contact lenses that improve the patient’s comfort.
Taping a healthy eye to encourage the damaged one to work harder also brings the desired result in correcting vision in case of strabismus.
Therapeutic methods for treating strabismus must be carried out persistently and consistently; their duration can take several months and sometimes years.
Sometimes, if the result of the therapeutic method of treating strabismus is not successful, surgical intervention may be required.
The method and nature of the operation is selected by the ophthalmologist based on a complete examination. Surgeries to correct strabismus are currently performed in almost all eye clinics.
Their modern techniques make it possible to almost completely reduce the risk of postoperative complications and ensure rapid restoration of visual function.
How does strabismus occur and why should it be treated?
Strabismus, or, scientifically speaking, heterotropia, is a deviation of the visual axis from the direction of focus, caused by uncoordinated work of the extraocular muscles. Normally, the visual analyzer models a three-dimensional image based on information transmitted from both eyes. The picture captured on the retina of a squinting eye is at odds with the image produced by a healthy eye. The brain eliminates the contradiction by simply ignoring the problematic eye. If strabismus is not corrected, over time one should expect a functional decrease in visual acuity in the defective eye, which ophthalmologists call amblyopia.
According to statistics, heterotropia is found in 2–3% of preschool children, and in most cases the pathology is acquired. Congenital heterotropia, or strabismus, manifests itself in infancy, but diagnosis is possible only from three months. Acquired strabismus is diagnosed from the age of six months.
All types of heterotropia require correction, since the defect disrupts the formation of three-dimensional binocular vision. A child suffering from strabismus will never discover the third dimension - for him the world will forever remain flat.
Types of glasses
types of glasses Source: glazatochka.ru
It is worth recalling that the main thing in the treatment of strabismus is a timely diagnosis.
An ophthalmologist will determine the type of pathological disorder of visual function and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If your doctor has prescribed glasses, you should familiarize yourself with their variety.
There are models with:
- prismatic lenses;
- Fresnel prisms;
- red-blue filters;
- color stimulation (Sidorenko glasses).
Many patients are interested in whether there are glasses that hide heterotropia.
No glasses have yet been developed to hide strabismus.
Prismatic lenses
prismatic lens Source: en.ppt-online.org
Very often, ophthalmologists prescribe prismatic lenses to their patients because they have a unique shape.
On the one hand, such a lens will be beveled, and on the other, thicker. When worn regularly, not only the angle of vision is corrected, but also the eye muscles are strengthened.
To understand how to cure strabismus using such lenses, the doctor will first determine the characteristics of the pathology, since the choice of glasses will directly depend on this.
There are the following types of prismatic lenses:
- thick lenses at the bridge of the nose, which become thinner closer to the temples - used for divergent strabismus;
- vertical thickening of glass, which is used for the corresponding form of the disease;
- horizontal transition between prisms is necessary for convergent strabismus.
It is impossible to independently determine which glasses are best suited for the treatment of strabismus; this can only be done by an ophthalmologist after a diagnostic examination.
Glasses with Fresnel plates
Considering that more serious correction requires lenses with a wider base, such glasses become unaesthetic and quite heavy.
To solve this problem, a program is used to use Fresnel prisms, which are more elastic and lightweight compared to glass prismatic lenses.
Such prisms are plates that are smooth on one side and a whole series of identical prismatic plates on the other.
Fresnel plates are very elastic, which makes them easy to use for making glasses.
Most often, the disease manifests itself in childhood, which is why it is so important to contact an ophthalmologist for prevention and when it is necessary to prevent the disease in the first year of a child’s life.
The restoration of normal vision, focused at one point, is largely determined by the correctness and timeliness of the prescription of special glasses and whether the treatment program, which is individually selected for each patient, is carried out correctly.
Models with red-blue filters
red-blue filters Source: glazatochka.ru
Special computer programs have been developed that help treat strabismus in adults and children. Red-blue glasses are used to correct visual function.
Their operating principle is that images are shown on a computer screen, and the patient simultaneously sees different pictures with one and the other eye.
There is independent stimulation of the right and left eyes.
Some vision correction programs require blue-red filters. Therefore, these glasses are universal; you can swap filters in them.
Sidorenko glasses
Sidorenko's glasses Source: ochki-sidorenko.ru
These glasses have a positive effect on the visual nerve endings. The basis of the beneficial effect is color stimulation.
Sidorenko glasses are useful due to the following aspects:
- beneficial effect of vacuum flow on the eyes;
- the use of infrasound to improve metabolic processes in the mucous membranes of the organs of vision.
Thus, the effectiveness of treatment measures increases significantly.
Contact lenses
contact lenses Source: tribun.com.ua
The spectacle correction methods listed above are aimed specifically at treating disorders in the ocular apparatus.
To improve the quality of life and convenience, contact lenses are used for strabismus. They help to minimize the discomfort that appears as a result of deterioration in visual acuity.
Contact lenses by themselves do not have a positive effect on the eyes, but if their wearing is combined with other conservative methods of correcting pathology, then a positive result will soon be noticeable.
Important!
It is best to consult your doctor about whether a patient with strabismus can wear contact lenses.
If a person, in addition to strabismus, has other serious pathologies or disorders in the body, then this method of vision correction will be contraindicated for him.
It is also considered unacceptable to wear contact lenses in cases where heterotrophy progresses very quickly.
The choice among existing glasses and contact lenses will depend on the patient’s age, the degree of development of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body.
After you consult with your doctor and order the required product, it will need to be checked by a specialist. The patient can then begin to use them.
During treatment for strabismus, it is important to see your doctor regularly to monitor the results.
If any discomfort occurs, you should contact a specialist so that he can adjust the treatment plan.
The danger of childhood strabismus
Most often, heterotropia is diagnosed in children aged one to three years. The cause of strabismus can be:
- Prematurity of the fetus. If a child is born weighing less than 2 kg, the likelihood of developing the disease increases significantly.
- Congenital pathologies of the visual organ.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Malignant formations on the cornea of the eye.
- Cataracts.
- Eye injuries and infections.
Children's strabismus can develop in parallel with the growth of the child. In this case, there is a danger that the child will no longer be able to restore full binocular vision.
To understand the seriousness of this disease, you need to know the anatomical structure of the eye, and also understand how the visual organ develops as the child grows.
The fact is that the human visual organ is a complex optical apparatus, which consists of the eyeball and the muscles that control it.
As the child grows, the muscles develop and thicken. With strabismus, some muscles atrophy, others redistribute the load on themselves. Thus, there is an imbalance of the load on the muscular corset of the eye. At the same time, stable neural connections are formed in the child’s brain.
The longer the disease progresses, the more connections are formed. The nervous system tries to adapt to the conditions of the disease and over time begins to consider strabismus as the norm. As a result, the disease takes on a chronic form that is difficult to correct.
In addition, the child develops an incorrect picture of the world. It is more difficult for him to perceive visual images. All this is reflected in the psyche of a growing person. Children often develop feelings of inferiority. The issue arises especially acutely at school age, when the child enters his first educational institution. Ridicule from peers and difficulties that may arise when studying the school curriculum have a negative impact on the formation of the psyche.
Important! Some experts believe that a sideways glance in a child under 3 months does not mean that he is sick. But this does not exclude the fact that it can and should be shown to an ophthalmologist. It is this doctor who will help determine the development of pathology, if any, and establish the causes of the disease.
Useful tips
If glasses are chosen as a corrective method for strabismus, you must wear them responsibly and follow all medical recommendations, regardless of aesthetic shortcomings and other difficulties.
The period of adaptation to glasses for strabismus occurs differently for each child and adult, but in any case, it takes some time. Usually from two weeks to a month.
The occurrence of discomfort during addiction is a natural phenomenon.
Frames should be chosen carefully, especially for children. It should be comfortable and well fitted.
Typically, points are assigned for a specific period of time. After it has expired, you should consult a doctor again and undergo an examination.
Then it will be possible to talk about the presence of positive results, or their absence and the need to choose another correction method.
The use of the optical method in combination with other approaches gives a great chance to completely get rid of heterotropia and return normal vision.
As with any other disease, the most important thing is to see a doctor in a timely manner and start treatment.
Method 3. Wearing contact lenses.
Strabismus can also be masked with contact lenses. Choose colored lenses in dark shades.
And in case of a special form of strabismus, the ophthalmologist will select special lenses, taking into account the parameters of the deviations.
They, just like training glasses, will be able to tone the weak muscles of the eye that squints. These lenses are easy to use. Putting them on is no more difficult than regular contact lenses. The main thing is to observe the rules of personal hygiene. Wash your hands thoroughly before the procedure.
Causes
The main reason for the development of strabismus in adults is a disruption in the functioning of the nerve endings responsible for the coordinated work of the eye muscles. If the movement of the eyeballs is impaired, the visual images projected by the right and left eyes cannot be combined into one. The signal sent to the brain is completely ignored. As a result, a person seems to be observing two images at once. The brain can only accept one picture, as a result of which vision in the affected eye noticeably deteriorates.
Exotropia
The cause of the violation may be factors such as:
- genetic predisposition;
- brain injuries and diseases;
- mental trauma (fear);
- low vision or blindness in one eye;
- farsightedness or nearsightedness;
- infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever, influenza, etc.);
- paralysis of the eye muscles;
- stressful situation;
- eye diseases (cataracts, retinal detachment, etc.).
Causes of pathology
https://youtube.com/watch?v=rTjAD47SCuI
Strabismus is most common in preschool children. It cannot be considered just a cosmetic defect. The visual acuity of a squinting eye is often very reduced. With this pathology, there is no joint work of the eyes.
Strabismus negatively affects the formation of a child’s character, and in the future deprives him of the opportunity to choose many professions and reduces his ability to work. With such a vision defect, a person cannot master many professions, for example, becoming a pilot, border guard, astronaut, etc.
Acquired strabismus is primarily associated with diseases of the nervous system. In addition, very strong nervous stress, head injuries, and infectious diseases can also lead to the development of strabismus. Sometimes strabismus does not appear immediately. Its signs may be more pronounced in the evening, during the period of excitement of the child.
Often the defect is noted periodically, they think that the child is playing around, and sometimes they do not pay attention to it. And strabismus, like other diseases, requires immediate correction
Results depend on the timeliness of treatment.
Modern medicine also knows how to correct strabismus in older people. In adolescents, it occurs due to progressive myopia and growth of the bones of the facial part of the skull.
Important In adolescence, you can get by with proper optical correction, whereas after the end of growth and puberty, there is a high probability that you will have to resort to surgery. The cause of strabismus in adolescents may be a consequence of a significant decrease in vision for various reasons, including head trauma, optic nerve atrophy, and others.
In such cases, they resort to eliminating the root cause. For example, cataract removal
The cause of strabismus in adolescents can be a consequence of a significant decrease in vision for various reasons, including head trauma, optic nerve atrophy and others. In such cases, they resort to eliminating the root cause. For example, cataracts are removed.
Acquired strabismus occurs under the influence of external or internal factors. The disease can begin to develop already in the prenatal period, when a pregnant woman was diagnosed with hypoxia or suffered a severe infectious disease in the early stages of pregnancy.
Strabismus occurs due to trauma to the brain or cervical vertebrae received at birth. The acquired variant of the disease can develop rapidly or gradually.
It can be provoked by concomitant eye diseases, such as:
- astigmatism;
- myopia;
- hypermetropia.
The development of the defect is influenced by childhood infectious diseases:
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- diphtheria;
- flu.
Stress, mental disorders, and high eye strain are also unfavorable factors that can provoke strabismus. It is possible to determine the cause of strabismus in a child after a special ophthalmological examination.
The cause of a congenital disease can be:
- difficult childbirth;
- illnesses suffered during pregnancy;
- use of certain medications and drugs by the expectant mother;
- genetic abnormalities (Down syndrome);
- heredity;
- prematurity;
- congenital eye abnormalities;
- cerebral palsy;
- hydrocephalus.
Acquired strabismus develops acutely or gradually. The following factors contribute to this:
- farsightedness, myopia. In order to see objects that are far or close, the child has to strain his eyes, as a result of which strabismus occurs over time;
- past infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever, influenza);
- injuries;
- stress, severe psychological shock;
- high eye strain;
- diseases of the nervous system that lead to disruption of communication between the brain and eyes.
Necessary treatment
Traditional therapy
Seeing a doctor is necessary if such a defect is detected in a person.
When a patient has poor vision and squints, an urgent need to consult an ophthalmologist. After a comprehensive examination, the doctor will establish an accurate diagnosis and select the necessary therapeutic measures. The following manipulations are often used:
- Occlusion. In this procedure, the patient’s poorly seeing eye is covered with some kind of bandage. This technique is often used after hardware treatment to prevent complications and new progression of pathology.
- Hardware therapy. During manipulation, binocular vision is restored.
- Medications. If the eye begins to squint a little, then various eye drops or topical ointments can be prescribed, which prevent negative consequences and stop the pathological process.
- Wearing special glasses or corrective lenses.
Is traditional medicine effective?
If the patient has only one eye squinted, and visual function is not impaired, then unconventional therapeutic measures can be used. To enhance the effect, traditional treatment is combined with traditional treatment and with strengthening of the eye muscles. The following recipes from healers for strabismus are effective:
Dill seed may be effective in treating this condition.
- Dill seed. Use 10 g of the main substance, which is crushed to a powder and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Leave for 50 minutes and drop 2 drops into a healthy and squinted eye 3 times a day.
- Apple juice, onion juice and honey. The proportions are 3:1:3. It is recommended to use topically on the affected visual organ before going to bed.
- Calamus roots. Pour 10 g of the substance into boiling water and let it boil for a couple of minutes. Cover with a lid and leave for an hour. Strain and take ½ cup orally no more than 4 times a day.
Charging: how and when to do it?
If the eye squints towards the temple, the patient is prescribed special therapeutic exercises. Such gymnastics is recommended not only for therapeutic, but also for preventive purposes. When performing tasks, the healthy visual organ is covered with a hand, and the one that is mowing is loaded. It is necessary to charge as follows:
- They extend their hand forward and try to focus their gaze on the index finger.
- Slowly bring the finger closer until it is 10 cm from the nose.
- The squinting visual organ is moved to the left, then to the right.
When is surgery necessary?
The patient's problem can be corrected by recession.
The surgical intervention is selected by the attending doctor, taking into account how severely the visual organ is squinted, the age of the patient and other characteristics of the body. Radical therapy uses the following methods:
- recession;
- resection;
- tenoscleroplasty;
- surgical intervention on vertical muscles.
The manipulation is performed using local or general anesthesia, so the person does not experience discomfort or pain. If the operation is successful, the patient is discharged on the same day. To prevent complications and speedy recovery, postoperative drug therapy is required, including antibacterial eye drops and anti-inflammatory drugs.
ABOUT VISION
Strabismus is a complex topic because of the amount of background knowledge required. However, it seems to me that it is worth discussing the main points that are associated with strabismus. What is considered strabismus? Why do parents often make mistakes? Why is it not necessary to diagnose strabismus based on a photograph? Our eyes record the world around us. As soon as we pay attention to some object in the space surrounding us, our eyes are set on it so as to fix the object of attention with both eyes. If one eye deviates from the object of fixation, this is called strabismus. Strabismus is the deviation of one of the eyes from the point of fixation. Deviation from the point of fixation can be temporary, permanent, or occurring in a certain direction of gaze. Parents often make the mistake of thinking that their child has strabismus. Parents are scared by how the eyes are positioned when looking at objects at close range. In such a situation, one eye may be brought close to the inner corner of the palpebral fissure and the parents believe that the child is squinting. However, when you ask the parents to determine which object the child is fixating, the parents see that both eyes are fixing the same point in space. That is, there is no strabismus. Deviation of one of the eyes from the object of fixation is a prerequisite for the existence of strabismus. No deviation, no strabismus. And for this you need to know where the child is looking.
That's why you shouldn't judge squint from a photograph. This is a standard situation. When you convince the parents that there is no strabismus, mom takes out her phone and shows photos. To be sure that there is strabismus, two conditions must be met. 1) Know where the child is looking at the moment of determining whether there is strabismus. What does the gaze fixate on? You can actively attract attention. Then attract attention from the left, right, below, above. 2) Decide whether both eyes are directed towards the object of fixation. If yes, then there is no strabismus. If one eye in some position moves away from the point of fixation, then this is normal. Is it normal to have strabismus? Up to three months of life, the coordination of eye movements may be defective, so a short-term deviation from fixation is allowed. Slight divergent strabismus is also allowed for up to 3 months. Children with neurological delays may have longer-lasting strabismus. I would not want parents to cling to the phrase that a slight divergent squint may be a variant of the norm, because it may be misunderstood. Such strabismus may be a variant of the norm, but this is not always the case and an ophthalmologist should be seen in all cases of strabismus. It happens that the baby’s eyes do not move in a friendly manner, despite the fact that this may be a variant of the norm for up to three months, you should note positive dynamics. At older ages, normal strabismus does not occur. All strabismus is pathological. Do you always need glasses for strabismus? Convergent accommodative strabismus There is such a concept as accommodative strabismus, this is a strabismus that is associated with the accommodative reflex (it is also called the near reflex). The near reflex is that when accommodating at a close distance, the lens increases its curvature in order to focus the eye on objects located nearby. This occurs due to tension in the ciliary muscle. Both eyes turn inward, this is called convergence. Convergence is needed in order to establish the direction of gaze of each eye towards objects at close range. The pupils narrow, the depth of field increases. With emmetropia, the accommodative reflex (near reflex) is triggered when looking close. With emmetropia, when looking into the distance, the ciliary muscle does not tense and the lens is in a relaxed state.
Emmetropia is a refractive condition in which the eye is set into the distance without tension, while ensuring an ideal projection of the surrounding world onto the retina. Emmetropia is an intermediate value between farsightedness and myopia. Typically, ophthalmologists understand emmetropia as a state of weak farsightedness. This is due to the fact that the state of ideal emmetropia is unstable due to accommodation, and weak farsightedness close to emmetropia is a normal variant. Farsightedness, as a cause of accommodative strabismus, is referred to here as farsightedness to the extent that it may be a risk factor for the development of amblyopia and/or strabismus.
If the refraction of the eye is farsighted, then the tension of accommodation is constant, the ciliary muscle increases the curvature of the lens when fixating at a distance, and even more for near. This triggers excess impulses in the binocular reflex circuit. Such impulses can lead to the development of convergent strabismus. Convergent accommodative strabismus often develops in children with farsightedness. Typically, such strabismus occurs between 6 months and 2 years. With convergent accommodative strabismus, farsightedness is the main reason for its development, therefore, with this type of strabismus, glasses correction is mandatory. You can't delay wearing glasses in this case. Glasses are prescribed to correct the entire degree of farsightedness. Unfortunately, it happens that strabismus occurs, parents turn to an ophthalmologist, the doctor correctly identifies farsightedness, and prescribes glasses much lower than necessary. For example, with farsightedness +7.0 glasses, +3.0, and even accompanied by an explanation “so that the eye works.” Glasses are the most important point in the treatment of such strabismus and they should be prescribed to compensate for farsightedness as much as possible (match or be as close as possible to the refraction obtained after instillation of drops that are used to determine refraction) and these should be the first glasses that should be prescribed immediately after how complaints of strabismus appeared. Here I want to draw the attention of parents that you shouldn’t wait, you need to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist and be prepared for glasses. Undercorrection of farsightedness is possible in older children, when full correction may be poorly tolerated. Parents should be warned that sometimes squint may worsen when glasses are removed. Bifocals may be needed in cases where there is a big difference in the deviation of the eye to the nose between looking at distance and looking at near. More often, their need becomes obvious in cases where the eye squints when looking up close while wearing glasses that are prescribed for full correction.
Gymnastics, exercise machines, physical procedures for accommodative strabismus are a waste of time, and unfortunately such prescriptions can still be found in clinics. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe an occlusion, which is prescribed in order to put excess stress on the weaker eye. In most cases, timely prescribed glasses with full correction of farsightedness give good results. A good prognosis is in cases where there are episodes of normal eye position (orthophoria) with glasses and they become more frequent. If glasses do not help, the doctor decides on surgical treatment of strabismus. Divergent strabismus Divergent strabismus is less common. All children with strabismus should be examined by an ophthalmologist. Intermittent exotropia can be noticed at any age, one of the causes of divergent strabismus is often also associated with the accommodative reflex, however, with divergent strabismus, accommodation is in the opposite state, compared to what happens in cases of convergent accommodative strabismus . Accommodation is often relaxed in myopia, but cases of divergent strabismus associated with the involvement of the accommodative reflex also occur with weak farsightedness. Why some children develop divergent, unstable strabismus, while others do not, is not completely clear. In the case of divergent strabismus, parents begin to notice that one eye “goes to the temple” in cases where the child looks into the distance, into space, or is lost in thought. It often happens that when the attention of such a child is attracted, the strabismus goes away. Strabismus worsens when the child is tired or sick. Many children feel when the eye moves to the temple and can control this condition. It is typical that with divergent, unstable strabismus, children close one eye in bright light, for example on the street, if their face is accidentally turned towards the sun. It often happens that non-permanent strabismus becomes less common with age. In most cases, it does not go away completely and can sometimes appear in cases of fatigue or illness. The frequency of episodes of divergent intermittent strabismus is influenced by factors such as fatigue, stress and illness. We must try not to expose the child to stress, fatigue and illness. Treatment of divergent strabismus consists of correcting significant refractive errors, if any, and possibly prescribing occlusion. In most cases, with non-permanent divergent strabismus, visual functions are not affected. If divergent strabismus is severe and the child squints most of the time, such strabismus may affect the development of visual functions. In such cases, the doctor may recommend surgical treatment. In addition, in such cases, appearance is also a concern. In rare cases, unstable divergent strabismus may be caused by a sharp decrease in vision or even its absence in one of the eyes. In this case, the doctor may prescribe treatment depending on what led to the vision loss. Eye exercises are not helpful for divergent strabismus, but they can be effective for convergence insufficiency (which we discuss in this book), where convergence insufficiency can be confused with divergent intermittent strabismus. The difference may be that with convergence insufficiency, the eye deviation is more pronounced when focusing at a close distance.
Simulators and hardware treatment are not used in the treatment of strabismus and are not discussed in the ophthalmological information space. The widespread use of simulators and various vision care rooms is a phenomenon characteristic of some countries of the former USSR. Leave your comment
Treatment
Since with descending strabismus the work of all visual analyzers is disrupted, its treatment must be comprehensive. Basic methods:
- Pleotric therapy is aimed at increasing the load on the eyes using special applications, programs or laser.
- Glasses are selected strictly individually.
- Occlusion - stimulation of the eyes by wearing a blindfold.
- Convergence trainer – classes aimed at improving the functioning of the eye muscles.
- Stimulation – the affected eye is affected by pinpoint stimulation.
- Drops – relieve stress, relax muscles.
Magnetic stimulation in the treatment of strabismus
All procedures must be prescribed and carried out by a specialist. If conservative treatment does not produce the desired results, surgery is prescribed.
Surgery
The operation helps in cases where conservative treatment has not given the desired results. Intervention may be aimed at:
- Relieving tense eye muscles by cutting or cutting them.
- Muscle strengthening - in this case, first excision is done and then fixation.
Performing surgery for strabismus
It is possible that after a certain time the operation will need to be repeated - usually a second intervention is performed 8 months after the initial one or later (depending on the doctor’s testimony and the patient’s condition).
Gymnastics
Complex treatment of convergent strabismus also involves performing special exercises. They are aimed at optimizing muscle function, relieving tension, and improving visual function:
- Take a pencil or felt-tip pen in your hand and extend it forward at the level of the pupil. Look closely at the tip of the marker with both eyes. If you can’t concentrate, work with your eyes one at a time.
- Close one eye and try to draw the number 8 with the other. Do the exercise 10 times.
- Place a lamp or a burning candle on the table and turn off the light. Direct your gaze along your nose directly to the burning object, begin to quickly rotate your head in different directions, without taking your eyes off the lamp or candle. Do 20-40 repetitions.
- Look closely at the farthest point, then switch to a nearby object.
Gymnastics for strabismus
Other exercises are provided for children:
- Playing with a musical top - the main thing is that the child looks at the spinning figures.
- Divide a sheet of paper into large cells, draw figures in each so that some are repeated. Ask your child to find the same images.
- The child should bring a finger of either hand to the tip of the nose and touch it.
Traditional methods
- Dark chocolate is very good for the eyes - eat a few pieces of it every day.
- Make an infusion of calamus root - pour boiling water over the root, let it brew, strain and take three times a day (but not more than 250 ml per day).
- Take Chinese Schisandra tincture orally - pour 100 g of the plant with vodka or alcohol (500 ml will be enough). The product should be infused for two days. Drink 20 drops before meals, diluting them with water.