Sinusitis
When there is no runny nose, but the bridge of the nose hurts, one should not exclude the occurrence of sinusitis, or, as it is also called, maxillary sinusitis. Of course, many people are accustomed to the fact that this disease is often accompanied by profuse nasal discharge, but this is not always the case.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
Symptoms of sinusitis without a runny nose include:
- Pain in the bridge of the nose, eye socket, forehead, which radiates to the jaw;
- Feelings of strong pressure in the bridge of the nose when tilting the head;
- Heat;
- Nasal changes in voice;
- Impaired sense of smell;
- Insomnia;
- General malaise.
Treatment options
To treat sinusitis without a runny nose, which causes pain on the bridge of the nose, doctors use antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, nasal glucocorticosteroids and rinsing sessions.
Causes of pain in the bridge of the nose and forehead
Pain is a symptom of many diseases.
If it is localized in a certain place, this indicates that this particular part of the patient’s body is affected. Headaches appear due to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems of the body, diseases of the ENT organs, teeth, and so on.
When the bridge of the nose and forehead hurt, the doctor first of all looks for the cause in damage to nearby organs and blood vessels. Let's look at the most common causes and nature of pain.
Neuralgia
A fairly harmless etiology of pain in the forehead and bridge of the nose is neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve.
Patients under 35-40 years of age are most susceptible to this pathology. A person feels discomfort, pain in the sinuses, forehead, eyes. Nature of pain:
- quite strong, and when acutely manifested, can cause night awakenings. They often appear at night;
- pressing, with this pathology the pain presses on the bridge of the nose, forehead, and there is a feeling of fullness from inside the head.
Additional symptoms:
- the pathology affects the eyes: they may turn red, lacrimation appears, and sometimes the nutrition of the cornea is disrupted;
- pulsation in the frontal region;
- Nasal discharge appears, the nasal mucosa swells, and turns red.
Complications of acute respiratory infections, dental ailments, ENT diseases affecting nerve endings, including a deviated nasal septum, and other causes can lead to this pathology.
Injuries to the bridge of the nose
In patients of all ages, headaches in the bridge of the nose are caused by injuries.
A blow to the nose can be caused by an unsuccessful fall, attack, or active children's games. The consequences of injuries are soft tissue bruises, cartilage damage, swelling and redness in the affected area, and abrasions. If a nasal fracture occurs, this is a reason to immediately contact an otolaryngologist. Restoring the nasal septum and the patency of the nasal passages will relieve the patient of discomfort and pain.
Acute sinusitis
With sinusitis, the patient suffers from severe pain, which is especially intense in the morning or evening. This disease can be suspected when pain radiates to the bridge of the nose when turning the head, touching the skin of the face, and discomfort is felt in the area of the eye sockets and forehead.
Chronic pathologies of ENT organs
Periodically occurring runny nose, swelling and nasal congestion indicate the presence of a focus of inflammation in one of the ENT organs. Chronic pathologies are diagnosed quite often.
The first sign of an inflammatory process in the ENT organs, which occurs in a chronic form, is a headache.
It is accompanied by general weakness and tingling in the bridge of the nose. With provoking factors, the disease worsens. These factors are:
- severe physical fatigue of the patient;
- decreased immunity;
- overheat.
Rhinitis
Acute rhinitis is also sometimes accompanied by bursting, pressing pain in the nose. With this pathology, a discharge of watery mucus appears, acquiring a thick consistency over time.
Swelling appears, and a focus of infection appears in the nasal cavity. In the absence of adequate treatment, rhinitis can become complicated or become chronic.
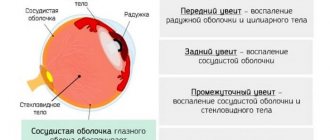
Sinusitis
When acute sinusitis does not go away within a week, it can be assumed that the inflammation has spread to the maxillary sinuses - sinusitis develops.
This pathology requires immediate intervention by an otolaryngologist, as it can lead to serious consequences. With sinusitis, the patient feels a severe headache, pulsation, which sometimes radiates to the temple area.
The symptom complex is also complemented by pain in the forehead and bridge of the nose; there may be no exudate in the first days. Then the patient notes the release of yellow thick mucus and an increase in temperature. Some people experience migraines; intoxication of the body is externally manifested in general weakness and increased fatigue.
Frontit
This is an inflammation of the frontal sinuses - the frontal sinuses. The pathology manifests itself as pain in the forehead, the area between the eyebrows, and the bridge of the nose. When a person tilts his head, mechanical pressure occurs on the inflamed area, and the pain will intensify. The pathology is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the area of inflammation.
Ganglionitis
The disease occurs due to inflammation of the pterygopalatine nerve ganglion. Signs indicating the presence of this pathology:
- severe pain in the bridge of the nose, forehead;
- dizziness, cephalgia;
- eye sockets hurt;
- the pain intensifies if you press in the area of the eye sockets.
Unpleasant sensations also radiate to different areas of the head, especially to the upper jaw, rarely to the shoulders and shoulder blades.
Ethmoiditis
Features of the pathology are severe headache, nasal congestion, a feeling of fullness in the bridge of the nose, impaired sense of smell, and low-grade fever.
Pathology occurs as a complication of a runny nose, inflammation of the frontal and maxillary sinuses. The causative agent is a viral or bacterial infection. These are the main causes of discomfort in the lower part of the forehead, the bridge of the nose.
Pathologies of the ENT organs or neurological ailments require special treatment. But often patients turn to a doctor when the process has already gone too far. Therefore, it is important to know under what conditions it is necessary to urgently see a specialist.
Ethmoiditis
Many people are interested in the question of why the inside of the nose hurts, where the bridge of the nose is, but there is no runny nose . The result of such manifestations is often ethmoiditis - an inflammatory process caused by viruses or bacterial infections. This disease is rarely diagnosed, as it has similar symptoms to other diseases.
© shutterstock
Signs of ethmoiditis
The disease manifests itself:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Pain in the bridge of the nose;
- High temperature;
- Loss of appetite;
- General malaise.
Without proper treatment, there is a risk of adenoid overgrowth.
Treatment options
Ethmoiditis can be cured using conservative methods, including:
- Antibiotics;
- Drugs that constrict blood vessels;
- Painkillers;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
In rare cases, surgical intervention is performed.
Why does nasal congestion and headache occur?
In humans, anatomically, the facial part of the skull contains air cavities - frontal (frontal), maxillary (maxillary), sphenoid, and ethmoid bone cells. The nasal passages with the upper, middle, and lower conchae are distinguished separately.
Each structure is lined internally with mucous membrane. Under the influence of an inflammatory or allergic agent, their thickening and swelling occur, which leads to breathing problems.
Reasons why you get a headache from a runny nose:
- Signs of intoxication triggered by toxic breakdown products.
- Oxygen deficiency. Blocking the lumen of the sinuses reduces the volume of incoming air. Brain tissue suffers from deficiency.
- Forced intense intake of air leads to an increase in pressure.
- Complications due to the addition of damage to the inner ear (otitis), the membranes of the brain (meningitis).
Allergic form of rhinitis
Pollen, odors, and food products cause individual intolerance. It is manifested by swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasal concha (rhinitis) and eyes. Therefore, a headache may occur from an allergic rhinitis. When the factor is eliminated, the nose begins to breathe, and the head stops bothering you.
Interesting: Why does your head hurt after you cry?
Frontit
A runny nose and headache often accompany each other with inflammation of the frontal sinuses. It develops less frequently than sinusitis, but is dangerous due to its complications. The hardest thing is meningitis.
Frontitis can be inflammatory and post-traumatic. Often, after a fracture of the facial skull bones, an infection from the external environment occurs, which requires surgical intervention. The operation is aimed at closing the bone defect.
Ethmoiditis
In the deep parts of the nose there are cells of the ethmoid bone. Their inflammation is called ethmoiditis. It accompanies pansinusitis or can be an independent process.
Sinusitis
If your head continues to hurt after a runny nose, the cause should be sought in the maxillary sinuses. Sinusitis is classified according to several criteria:
- Type of mucosal thickening:
- uniform;
- polypoid;
- cystic.
- Presence of liquid:
- infiltrative;
- exudative;
- mixed.
- Degree of sinus closure:
- total;
- subtotal;
- partial.
- Affected side:
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- bilateral.
Neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve
Pain in the bridge of the nose and forehead without a runny nose is caused by neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve. In medicine, the disease is also called Charlin's syndrome, which is often diagnosed in young people, mostly females.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
The disease has a variety of symptoms, manifested:
- Pain in the bridge of the nose and eyes;
- No runny nose;
- Tearing;
- Swelling of soft tissues;
- Photosensitivity;
- Hyperemia;
- Sharp pain when pressing on the bridge of the nose or eyes.
Treatment options
The course of treatment for the disease includes:
- Antibiotics;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Vasoactive drugs;
- Painkillers;
- Medicines that dilate blood vessels;
- Vitamin complex.
How to reduce headache pain?
If you have a paroxysmal headache due to congestion, you should consult an otolaryngologist. The doctor will prescribe additional studies to differentiate between inflammatory and allergic origins.
If there is an assumption that the nose is blocked under the influence of external or internal allergens, then consultation with a specialist will be required. The allergist will make adjustments to the treatment regimen in the form of detecting and eliminating factors that trigger thickening (hyperplasia) of the mucous membranes of the paranasal sinuses.
Complex impact
Headache from a runny nose must be treated comprehensively - eliminate the cause, reduce clinical manifestations. For this purpose, medications for the common cold (tablets, drops, sprays) and physiotherapy are used. Physician supervision is required to adjust the regimen, introduce additional therapeutic measures, and replace medications in case of individual intolerance.
The danger of self-medication
Sinusitis is fraught with the spread of infection along the physiological bone canals of the head. The following development of the infectious process is possible:
- the bacterial infection has spread to the inner ear;
- damage to the mucous membranes led to otitis and mastoiditis (inflammation of the cells of the mastoid processes);
- connection with the cranial cavity leads to infection of the meninges (meningitis).
This option is more typical for children, because the immune system is weak. But it is also possible for adults. If the secreted mucous component has changed color (green snot), the headache is unbearable, the temperature has risen, then self-medication will not help. On the contrary, it will worsen the situation. Only a doctor will help not only remove pain in the head, but also stop the infection and prevent serious consequences.
Interesting: Why glasses cause headaches: causes and treatment
Drug treatment
Edematous mucous membranes are treated with the following means:
- cleansing sprays – Aquamaris, Marimer;
- vasoconstrictor drops (3-4 days, so that addiction does not develop) - Nazivin, Tizin;
- antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs – Vibrocil.
If your head continues to hurt after a runny nose, you can add antispasmodics - Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is included in the complex therapy of rhinitis and sinusitis:
- magnetic therapy;
- inhalation;
- electrophoresis;
- washing with saline solutions.
They should be carried out in a course (about 10 procedures) until the pathological manifestations completely disappear.
Pain in the head is reduced by acupressure, it improves blood flow and promotes accelerated discharge of the exudative component.
Vasomotor rhinitis
Another cause of pain on the bridge of the nose is vasomotor rhinitis, due to which the nose becomes blocked due to infection, during colds or allergies.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
Vasomotor rhinitis manifests itself:
- Increased tear production;
- Pain in the head and bridge of the nose;
- No runny nose;
- Itching and slight swelling of the nose;
- Frequent sneezing.
Treatment options
To get rid of rhinitis without a runny nose, doctors prescribe:
- Antihistamines;
- Vasoconstrictor drugs;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Ganglioneuritis
Pain in the bridge of the nose without a runny nose is caused by ganglioneuritis - damage to the ganglia and associated nerve trunks.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
The main symptom of ganglioneuritis is pain, which is localized on the bridge of the nose, eyes, and jaw. The person’s reflexes also decrease, and swelling of the disturbing area is observed.
Treatment options
You can get rid of the disease using:
- Antibiotics;
- Analgesics;
- Antiviral drugs;
- Physiotherapy.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause headaches and nasal congestion. This is influenced by various factors, including hormonal changes during pregnancy.
Rhinitis is common during pregnancy. In this case, sneezing and runny nose are also observed. If you are pregnant, tell your doctor about any symptoms.
Treating nasal congestion and headaches
Your doctor will recommend safe medications or therapy to treat headaches and nasal congestion. You can also try the following methods:
- try yoga for pregnant women;
- maintain good posture;
- ask for a neck and shoulder massage;
- get more rest;
- eat well;
- apply a cold compress to relieve tension headaches;
- Place a warm cloth over your eyes and nose if your headache is caused by sinus pain.
Injuries
A common cause of pain on the bridge of the nose with the absence of a runny nose is an injury, which can be either long-standing or newly acquired.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
With various injuries, the pain is girdling in nature and can be strong, pulsating, and sharp.
Treatment options
If the injury is minor, the pain goes away on its own after a certain time. But when the nasal septum is severely damaged, the only way to get rid of the pain is through surgery.