How twilight vision works
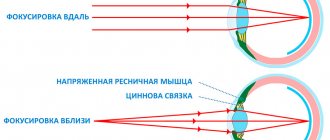
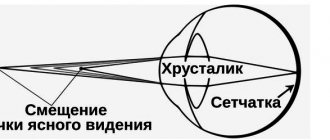
The human eye is very sensitive to external changes. Visual receptors detect light through the retina. This organ consists of rods and cones, which are responsible for the perception of color and light intensity. Night blindness occurs when the receptors have difficulty distinguishing surrounding objects at night or in the twilight. The work of rods and cones depends on the quality of lighting in the surrounding space. Therefore, there is a difference between day and night vision. All receptors are activated for better perception at dusk; light rays are caught faster in the dark.
Rhodopsin, located in rods, affects the functioning of the optic nerve. This enzyme breaks down in the light and is restored in the dark, so it takes a long time for a person to adapt to the dark. Vitamin A affects the quality of twilight vision because it is part of rhodopsin.
Problems with twilight vision occur when there is a lack of vitamin A. Dark adaptation occurs when the visual system operates at night or in twilight. The eyes operate in a black-and-white spectrum, so all visible objects appear gray.
conclusions
In cases where hemeralopia is not congenital, it can be caused by a number of reasons related to the functioning of the visual organs, as well as other diseases and the general condition of the body. The disease, caused by problems with the retina, manifests itself due to a lack of vitamins, as well as exhaustion, alcohol abuse, and diseases of the digestive system. Some forms of night blindness are explained by eye diseases: optic atrophy, glaucoma and even severe myopia.
With the development of hemeralopia, daytime vision remains normal. However, impaired twilight vision has a dangerous effect on the patient’s quality of life. This condition can have harmful consequences. For example, a person suffering from this disease practically does not see dangers on the road at dusk. This is extremely important for vehicle drivers. Also, patients suffering from hemeralopia may develop phobias associated with the dark. This causes obsessive states and other mental deformations.
Classification
Night blindness is divided into several types depending on the cause of its occurrence:
- congenital;
- essential;
- symptomatic.
Congenital is inherited from parents and manifests itself in childhood and adolescence. Genetic disorders often cause vision problems.
These include:
- Usher syndrome;
- retinitis pigmentosa, inherited.
The essential form is a functional disorder of the retina caused by a lack of beneficial microelements. Metabolism is often difficult due to various diseases.
Examples:
- liver diseases;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- rubella;
- damage by toxins;
- long exposure to bright lighting.
Symptomatic night blindness occurs with various eye diseases, disorders of the retina or nerve tissue.
Examples of diseases:
- high myopia;
- glaucoma;
- retinal dystrophy;
- atrophy of nerve tissue;
- chorioretinitis.
Ophthalmologists detect false night blindness when vision is impaired in the dark or in dim lighting due to fatigue. Working long hours at the monitor or relaxing in front of the TV have a bad effect on the condition of the receptors. The quality of vision improves after rest; severe eye strain causes serious illness.
Consequences of twilight vision impairment
When this important mechanism responsible for vision in the dark fails, a disease called hemeralopia, better known to us as “night blindness,” develops. Signs of the disorder include the following symptoms:
- peripheral vision decreases, vision deteriorates at night;
- difficulties arise in distinguishing between yellow and blue shades in the twilight;
- poor spatial orientation in the dark;
- feeling of dryness on the cornea, spots before the eyes.
The surest symptom of hemeralopia can be considered a long period of adaptation when moving from a light space to a dark one or vice versa. The eye in a normal state completes these processes in a clearly defined time, and if it is delayed, this may be evidence of hemeralopia.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods:
- visual acuity in dim lighting is determined;
- the size of the visual field is measured separately on each eye, the area that the fixed organ is capable of covering is determined;
- color perception analysis is carried out;
- ophthalmological examination of the fundus;
- electroretinographic analysis reveals nerve impulses in the retinal area;
- adaptometry is a technique that reveals dark adaptation;
- tonometry is performed to measure intraocular pressure;
- vision adaptation is determined in low light, the time during which the eye gets used to the dark is set;
- The general condition and quality of the retina is studied.
Additional examination by a gastroenterologist reveals vitamin A deficiency.
Reasons for decreased mesopic vision
In ophthalmology, night blindness is classified by type, depending on the cause. With congenital hemeralopia, which is transmitted genetically, no therapy will help. Night blindness often occurs when there is a lack of vitamins A and C in the body; it is called essential. In this case, the ophthalmologist prescribes a special diet rich in these elements, and also prescribes an additional course of vitamin preparations. Once the balance of vitamins is restored, twilight vision will also return to normal. Finally, symptomatic hemeralopia is diagnosed if a person has any inflammatory eye disease, such as glaucoma. In this case, treatment and outcome depend on the severity of the disease.
Night blindness is also dangerous psychologically: children often develop a fear of the dark to the point of panic, and adults are afraid of going blind when they are very poorly able to distinguish objects in the dark. Night blindness may also indicate the development of eye diseases that the person himself is not yet aware of (cataracts, glaucoma and other pathologies). That is why it is so important to pay attention to the state of your vision, because it often happens that negative consequences occur precisely because we do not immediately go to the doctor, citing the eternal busyness, they say, it will hurt and it will stop. But timely diagnosis in the early stages can prevent many problems.
Treatment
Therapy is possible only in a situation where night blindness is acquired. Congenital pathology cannot be treated. Therefore, first the ophthalmologist determines the cause of the disease. The doctor gives advice on changing your diet to get more vitamin A and other microelements necessary for the normal functioning of visual receptors.
Recommended Products:
- Cod liver;
- dairy products;
- egg yolks;
- corn kernels;
- legumes;
- orange fruits and vegetables.
The diet is prescribed individually to each patient; compliance with specialist recommendations affects the speed of recovery. Traditional medicine helps improve metabolism. Before using them, it is necessary to conduct an examination and identify contraindications. Since vitamin A is a fat-soluble substance, it is necessary to supplement the diet with foods containing vitamin B2.
What is twilight vision?
Twilight vision is a person's ability to see in low light, it is a cross between night and day vision. This ability depends on how much a person's pupil can dilate when lighting changes. Twilight vision is influenced by two receptors located in the retina - cones and rods.
In common parlance, twilight vision impairment is called “night blindness”; scientifically, it is called hemeralopia. This disease can manifest itself regardless of age. There are several reasons:
- consequences of rubella, diabetes, anemia, herpes, measles;
- hereditary factor in diseases such as Usher syndrome and retinitis pigmentosa;
- eye diseases: vascular pathology, retinal detachment, inflammatory processes;
- lack of vitamins A, B2, PP in the body.
To avoid problems with twilight vision, you need to include foods containing the above vitamins in your diet. Vitamin A is found in large quantities in carrots, fish oil, liver, and egg yolks. You will find B2 in peanuts, almonds, rice, buckwheat, green vegetables, and apricots. Beef liver, pork, cheese, tomatoes, legumes, dates, peanuts are rich in vitamin PP.
To identify deviations in the functioning of twilight vision, it is enough to take a short test. Cover your eyes with your hands and try to see something; if you have good vision, everything around you will be black. If there are bright flashes in front of your eyes and, for example, blue rather than black, it means that for some reason you are not able to distinguish colors that are weaker than gray. Twilight vision helps a person see black and white tones.
Often you may experience only temporary impairment of twilight vision when your eyes are exposed to intense bright light. For example, this effect can occur when a person looks at a bright smartphone screen in the dark. Light irritates the nerve endings of the dilated pupil and causes night blindness.
To prevent problems with twilight vision, the following recommendations can be given:
- include in your daily diet foods rich in vitamins A, B2, PP;
- do not use gadgets in the dark;
- try to give your eyes rest.
Congenital problems with twilight vision cannot be treated. If the disease is caused by other diseases, then their treatment will gradually lead to getting rid of night blindness.
Prevention
Adviсe:
- reduce the time spent working at the monitor and watching TV;
- additional lighting sources are installed;
- eyes rest every 40 minutes when working with documents or small objects;
- reading in the dark from electronic devices is prohibited;
- the light will be distributed evenly so that the receptors are not overloaded;
- glasses with an ultraviolet filter are used when hiking in the mountains to prevent reflected rays from blinding a person.
What happens if twilight vision is impaired?
If there is any malfunction of the mechanism of mesopic vision, a person is diagnosed with a disease called hemeralopia, or, colloquially, night blindness. The following symptoms are noted:
- deterioration of peripheral vision, narrowing of the field of vision;
- difficulty navigating in low light;
- poor discrimination between shades of yellow and blue spectrum;
- dry cornea, spots before the eyes.
The most striking sign of hemeralopia, perhaps, can be called a very long habituation when moving from darkness to a light room and vice versa. Under normal conditions, the human eye does this in a relatively short time. If the process is delayed, this is a reason to definitely visit an ophthalmologist.
Causes of hemeralopia
Violation of twilight vision is scientifically called hemeralopia, and popularly called “night blindness”. This disease is associated with dysfunction of the retina and optic nerve. It seems to a person that at dusk the entire world around him seems to be shrouded in a thick haze. Vision weakens and orientation in space is lost.
This disease not only causes inconvenience, but can also be life-threatening, for example, it increases the risk of a car accident at night. In addition, with such an illness, the field of vision narrows and adaptation to light changes. Any bright ray from the darkness can lead to disorientation in space and loss of coordination of movements. Often, those suffering from night blindness have difficulty perceiving shades of yellow and blue.
Those suffering from night blindness often suffer from phobias associated with the dark. This can even lead to obsessive states and mental deformation, which will require additional treatment from an appropriate specialist.
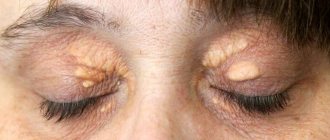
An additional symptom of hemeralopia can be dryness and keratinization of the epidermis around the eyes, and sometimes in other parts of the body, as well as brittle hair.
If a person notices such symptoms, then he should contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to reverse the loss of vision.
Representatives of both the stronger and weaker sex, especially the elderly, suffer from hemeralopia. However, ladies of Balzac's age during menopause are more susceptible to it. According to the observations of scientists, the least number of people with night blindness are among the peoples of the Far North, whose eyes have adapted to the polar night.
This disease can be congenital or acquired. The first type is rare and is diagnosed in early childhood.
The occurrence of the second type of hemeralopia depends on many reasons:
- lack of vitamin A, B2, nicotinic acid;
- physical exhaustion;
- anemia;
- eye diseases;
- childhood diseases (chickenpox, measles);
- toxic poisoning;
- alcohol abuse and drug addiction;
- sunburn of the conjunctiva;
- pregnancy.
Very often, a person begins to see poorly at dusk due to a lack of vitamin A. Its deficiency leads to deformation and destruction of photoreceptors. The lack of vitamins and microelements is most noticeable in the spring. Therefore, it is in the spring that patients with night blindness experience exacerbations.
Acquired hemeralopia is divided into essential and symptomatic. The first is characterized by problems with the retina, caused precisely by a lack of vitamins, as well as exhaustion, alcohol abuse, intestinal diseases, etc. The second type includes forms of “night blindness” caused by diseases of the visual organs, in particular, severe myopia, glaucoma, atrophy optic nerve and others.
Separately, ophthalmologists identify the so-called false form of the disease. In this case, “night blindness” occurs temporarily as a deterioration in vision as a result of prolonged work in front of a monitor screen and other serious visual stress.
How to improve twilight vision
Sunglasses
There are ways to improve dark adaptation. The first one goes back to the days of pirates. Not surprisingly, they are often depicted with an eye patch, but rarely did it cover up the missing eyeball. Pirates wore blindfolds to have one working eye when going down from the deck into the hold, where it was dangerous to use candles and lanterns.
Today, to improve dark adaptation, there is no need to wear bandages. It is enough to use sunglasses, the desired shade of gray. It has been proven that after being in the sun for 2-3 hours, it then takes 10 minutes more to fully adapt to the dark.
Don't look at the light
When in the dark, you don’t need to look at light sources. Such actions disrupt twilight vision, since rhodopsin will begin to rapidly decompose in the light. If it is not possible to avoid bright light, you need to cover one eye, maintaining dark adaptation at least in it. This way a person will not be completely disoriented if, for example, he is driving.
Red glasses
Another method is based on the fact that the rods are insensitive to red light. Previously, the army practiced this method of adaptation: soldiers wore red glasses before night guard, and the red did not interfere with the restoration of rhodopsin. Cones with red pigment did not interfere with orientation in the light, and thanks to the preservation of rhodopsin, the soldier could serve from the first minute of duty.
Diagnosis and treatment of hemeralopia
Medicine distinguishes between congenital and acquired hemeralopia. Even modern treatment methods cannot cure the congenital form.
Methods for diagnosing hemeralopia:
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus, examination of the retina, optic nerve, blood vessels);
- biomicroscopy (examination of the eye using a slit lamp);
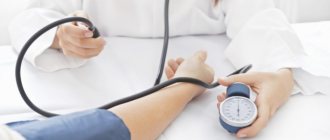
- tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
- visometry (determining visual acuity using a table);
- color vision research (the study of color perception based on color schemes).
It must be remembered that the treatment of hemeralopia is determined differently in each case, so you should not take any drugs uncontrollably. First, you need to find the cause of the disease, and the results of the examination will show what the body really lacks. Consultations from other specialists will not be superfluous.
If there is a cause for the defect, appropriate therapy is prescribed. Often these are vitamin complexes and treatment of pathologies of the visual system that provoke twilight vision disorders.
Pathologies of the visual system
When the cause of hemeralopia is myopia, therapy will consist of laser vision correction. Refractive surgeries (scleroplasty, lens replacement, etc.) can also be used.