The concept of central and peripheral vision
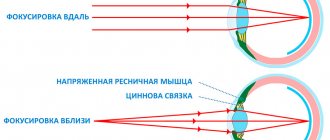
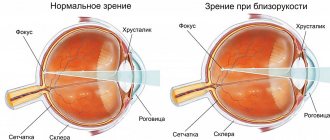
In the first case, we are talking about the visibility provided by the central area of the retina. With its help, a person gets the opportunity to examine small elements in detail. Eye acuity depends precisely on the work of this area.
Peripheral vision is not only objects located to the side of the visual apparatus, but also objects located around it (for example, a moving car, blurry things). For this reason, side view is extremely important, because with its help a person orients himself in space.
In women, peripheral vision is slightly better developed than in representatives of the stronger half of humanity. Men, on the other hand, can boast of central vision. The side viewing angle is approximately one hundred and eighty degrees horizontally and one hundred and thirty degrees vertically.
Determination of central and peripheral vision is carried out using simple and complex techniques. In the first case, the Sivtsev ophthalmological table is most often used. The poster contains letters of different sizes in several lines, and the patient needs to name the one the doctor points to. The norm is to read the symbols indicated in the ninth row.
| To analyze the lateral view, perimetry is usually prescribed. In this case, the patient's participation in the procedure is minimal. All he needs to do is put his head on the device, all measurements are carried out automatically. |
Measurement methods
In ophthalmology, the boundaries of lateral vision are measured in degrees using a device called a perimeter.
Perimetry allows you to evaluate peripheral vision and identify areas of loss of parts of the visual field (scotoma).
Diagnosis is carried out on patients to identify diseases leading to partial or complete loss of vision:
- glaucoma;
- retinal pathology;
- damage to the optic nerve (mechanical, inflammatory).
Kinetic perimetry – the use of a Förster arc with an angle of 180°. The inside of the arc is covered with black paint, and on the outside there is a scale that determines the viewing angle. The patient's head is placed motionless on a stand in the center of the hemisphere, one eye is closed. The gaze should be fixed on the white mark. By moving the mark, the boundaries of the field of view are schematically established. Can also use a colored marker. In this case, the border of view is considered not when a person saw the mark, but when he clearly identified its color.
Statistical computer perimetry – study of the boundaries of peripheral vision without movement. The patient is subjected to several stationary tests, where the brightness and size of the marks change. When a person clearly sees the control marker, he presses a special button. At this moment, the device fixes the field boundary.
The duration of diagnostic studies does not exceed 10–15 minutes.
Types and causes of peripheral vision impairment
Deviations can be of different types. Numerous studies and detection of pathologies in the lateral viewing area have revealed a number of causes and forms of deviations:
- Glaucoma. Increased intraocular pressure damages the optic nerve and causes a decrease in visual acuity. Peripheral vision is also affected, and the risk of blindness is high. At the initial stages, the deviations are not too noticeable, but in the absence of therapy, the narrowing of the boundaries of vision occurs irrevocably.
- Poor blood circulation in the vessels of the optic nerve.
- Damage to the retina leads to blindness, narrowed vision, and decreased visual acuity.
- Poor circulation in the brain, lack of oxygen in the vessels, increased cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the main organ of the central nervous system, stroke - all this negatively affects peripheral vision.
- A jump in intracranial pressure.
These are the most common factors causing impairment of lateral vision. Each deviation has serious complications, so it is important to detect them promptly and treat them correctly.
Diagnosis and treatment
The patient is examined by an ophthalmologist; if abnormalities in the area of the optic nerves are detected, a neurologist is involved in the examination. Diagnostics of the lateral view is carried out using perimetry. The procedure is divided into two types:
- kinetic;
- static.
Computer perimetry is gaining increasing popularity; with its help, visual fields can be analyzed as accurately as possible.
Kinetic inspection uses a moving object. Most often, a light spot of constant size and shade is used for testing. It is set in motion, and along the trajectory the patient must understand where the pendulum is located. Depending on where the patient sees the light, the lateral viewing angle is determined.
| Static perimetry is characterized by the fact that the objects on which the subject focuses his attention are motionless. The ophthalmologist first announces where the object is located, and the patient must examine it from a certain point in the room. The analysis is carried out in different places along the wall to confirm or refute the development of the disease. |
Also, to make a correct diagnosis, doctors sometimes prescribe campimetry. The procedure is performed using a large screen (2*2), the surface of which is illuminated. The patient sits at a distance of two meters from the device, closes one eye, and looks with the other through a small slit in the center of the monitor. The doctor moves a small square along it.
A person needs to inform the doctor when he sees the figure. Testing is carried out several times in opposite directions.
As such, the concept of “treatment of peripheral vision” does not exist, since the deviation is not an independent pathology and develops against the background of other ailments. Depending on the root cause, the doctor selects a course of therapy. This could be medications or surgery.
Traditional medicine recipes for treatment are not included in the prohibited category. But under no circumstances use them without first consulting your doctor.
How can you train the reader's point of view?
Schult tables
- randomly located numbers (or other objects). Tables are usually used for research, training and development of the pace of information perception, including the speed of visual search movements. Searching eye movements are the basis of fast reading. Schulte tables allow you to expand the reader's field of view. A wide field of view significantly reduces the time it takes to detect text fragments needed by the reader.
Some information about human vision
- The maximum field of vision for a person is 35 degrees. The zone of clear vision is 14 degrees. The area of best vision is 1.4 degrees. The field from which information is retrieved, as studies have shown, can be significantly expanded, for example, by using Schulte tables.
- When a person's gaze moves, the greatest visual acuity occurs in the central zone of the retina - the zone of clear vision. Everything that lies outside this zone of clear vision, on the periphery, is seen by a person as if in a fog. A wide field of view reduces the time it takes to search for informative text fragments.
- Working with the Schulte table trains volumetric attention. The main thing is not to roam around with your eyes, the main thing is to concentrate your gaze on the center of the Schulte table to see the upper, as well as the lower left and right numbers.
With regular use of Tables, peripheral vision increases and this allows you to increase reading speed by covering a larger space of the readable text, and by mastering the one-time mode of analyzing printed characters.
Rules for working with Schulte tables.
- The time of study should be chosen so as not to overwork.
- When searching for consecutive numbers, the eyes are allowed to fixate in the center of the table. Horizontal eye movements are prohibited. The distance from the table to the eyes is as usual.
- You need to find numbers by silent counting in ascending order from 1 to 25 (without skipping). Found numbers are indicated only by sight. As a result of such training, the time for reading one table should be no more than 20 seconds.
- The gaze is fixed in its center of the table in order to cover the entire table.
- When working with Schult tables, you should remember that training is not the main goal here. It is important to expand your field of vision.
Is it possible to develop lateral vision?
It needs to be trained because it increases the performance of the brain. In addition, with good peripheral vision, a person orients himself in space much better and faster, and the skill of speed reading develops.
The workout includes a number of simple exercises that will take a few minutes:
- Take a newspaper and look for a narrow column in it. In the central part of the article, draw a bright vertical line. Peer at the line and try to read the words included in the peripheral area.
- Fix one object in front of your eyes. Look at it and select an additional object using your peripheral vision. Then grab another item. The training continues until the person is able to fix his gaze on seven objects simultaneously.
Video training from the course: How to correctly complete Schulte Tables
Subscribe, and new useful exercises will always be at hand: VKontakteInstagramZenFacebookTelegramYoutube
Training on texts
Also try to use your peripheral vision (peripheral) when reading normally. At first you can take in, for example, 2 or 3 words, but then there will be more. And after some time you will be able to read entire lines, especially if they are small.
Also, some people have learned to read 2 or more lines at once or even entire paragraphs and pages. I was able to read in paragraphs and at one time even in short pages, but my eyes still moved across the page from top to bottom.
Now, for example, read this text line by line, looking strictly at the center of each line:
Just two words per line are easy to read and very fast. Interesting exercise. And the main thing is simple.
The text above is easy to read, the eyes do not move along the line, now let’s take a more difficult example (also read, looking strictly at the center of the line):
This text is more complex and also easy to read; the lines have become longer. The longer the line, the more difficult it is to read while looking at the center of the line. However, you are already training and making your first progress!
Still easy to read, but may be difficult. With a little practice it becomes easy.
Now try to read the same text, but a little wider (also read while looking strictly at the center of the line):
This text is more complex and also easy to read, although the lines have become longer. The longer the line, the more difficult it is to read while looking strictly at the center of the line. However, you are already training and making your first progress!
Yes, you already know this text and therefore it is easier for you to practice reading it, which is very good! Because this makes it easier for you to train your peripheral vision, try reading already known and completely new texts this way, alternate them, experiment!
Now read another text, from approximately the same long line:
This text is even more difficult than the previous one, but you are already a little trained, which helps you read this text with ease. This is exactly how you need to train, gradually, step by step, increasing the width of the line! Your skill just got better!
Most likely, even from such a small training you have already started the process, and reading such texts line by line has become easier!
Try reading the same text, only this time the line will be even longer (look strictly at the center of the line):
This text is even more difficult than the previous one, but you are already a little trained, which helps you read this text with ease. This is exactly how you need to train, gradually, step by step, increasing the width of the line! You are wonderful and your skill has become even better!
Thus, by increasing the line width you can develop excellent peripheral vision !
For this, it is very convenient to change the width of the browser window (if the site adapts to small mobile screens) or simply paste the text into a regular notepad on the computer, put in a font convenient for you, screen width and read.
Now try to completely take in this square with your gaze, looking at the very center of it:
Speed reading development course
Our Speed Reading course in 30 days will help you develop and synchronize both hemispheres of the brain. With synchronized, joint work of both hemispheres, the brain begins to work many times faster, which opens up much more possibilities.
The course contains a large number of exercises for training the brain, because with a fast reading speed you still need to have time to understand, remember and sometimes even think about information!
Sign up for a courseFree lesson
Side view training
Peripheral vision can be developed with the help of special gymnastics. Also, such exercise is useful for the brain; it allows you to maintain its functions for a long time. The training is recommended for drivers, teachers, police officers, wax workers, etc.
The exercises will not take much time and do not require special skills. The main condition is regular implementation.
- Fix your gaze on any object located in front of you. Then, without moving your pupils, try to look at objects on the sides.
- Select an observation object on the wall that is located at a distance of three meters from the organ of vision. Then take two pencils and hold them out in front of you. Slowly spread your arms in different directions, while not taking your eyes off the point on the wall.
- Take a picture with large symbols, sit comfortably on a chair and place it in front of you. The image must be in the area of peripheral vision, i.e. so that you can make out what is written on it. Slowly move the pictures to the sides, expanding the viewing angle.
- Stand near the window and find the object behind the glass. Without moving your pupils, name objects that are located near the selected point.
- Open a magazine or book, find any word and focus on it. Then try to read what is nearby.
| When walking outside, pay attention to soil defects by directing your gaze forward. Performing such gymnastics is easy and it brings maximum benefits to vision. |
Prevention
To avoid problems with peripheral vision, you should follow simple recommendations:
- Visit your eye doctor regularly for preventative checkups.
- Treat chronic pathologies in a timely manner.
- Take action if glaucoma or retinal detachment is detected. Don't ignore such illnesses!
- Protect your head and visual apparatus from injury.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle (especially after sixty years).
- Perform special exercises regularly.
Like any organ, eyes require attention and care. Monitor their condition carefully, avoid infections and treat any diseases that are detected. This will help avoid a large number of health problems.