Structure of the eye
The human eye consists of the eyeball and auxiliary structures. Based on its operating principle, it can be compared to a first-class camera. It has a biconvex lens (lens) that can focus to different distances, a diaphragm (iris) that regulates the size of the light opening (pupil), and a light-sensitive retina that matches color photographic film. Directly behind the retina is a layer of cells filled with black pigment that absorbs excess light and prevents blurring of the image (choroid).
History and meaning of the “all-seeing eye” symbol
The all-seeing eye symbol is believed to have appeared about 6,000 years ago. The primary "basic" variations of the image were:
- an eye inside a triangle, all sides of which are equal. Rays emanate from the sides of the triangle;
- eye at the top of the triangle.
Based on information from various sources, the following values can be identified:
- an eye enclosed in a triangle protects its wearer from various ailments (both physical and mental), and also helps to cure existing diseases;
- The all-seeing eye promotes the development of insight, clairvoyance, and the ability to recognize lies.
BY THE WAY! The most universal historical meaning of the eye of Horus is knowing oneself, determining one's purpose.
The very first myth about the all-seeing eye is this. The god of chaos and war, Set, poked the god of the sky and sun Horus in the eye with his finger, causing Horus to go blind in that eye.
Some sources indicate that the eye of Horus was not pierced by Seth, but swallowed. Horus's wife, Hathor, helped her husband restore his lost eye with gazelle milk.
There is also a version that the damaged eye was buried by Horus’ brother Anubis (he was also revered by the Egyptians as a guide of souls to the kingdom of the dead), after which grapes grew at the burial site.
Horus put the renewed eye into the mouth of his father Osiris (who was killed and dismembered by his brother Set), causing him to grow together and resurrect.
BY THE WAY! In the hope of helping the dead to resurrect (as in the myth described above), the Egyptians applied wadjet to mummies.
Eye of Horus among the Egyptians
In Ancient Egypt, the wadjet was identified with Horus himself. The right eye of Horus was associated with the Sun, and the left eye with the Moon.
Thus, he had the opportunity to monitor everything that was happening in the human world around the clock. For this reason, this symbol has another name - “the all-seeing eye of Horus.”
Horus was also considered the patron saint of the pharaohs, and the current pharaohs were his embodiment on earth. The Eye of Horus (Horus) was used in magical rituals in order to learn the truth (since nothing can be hidden from the eye of Horus).
If the eye was complemented by the image of an eyebrow, then this meant an emphasis on power (of a particular pharaoh or Horus himself).
BY THE WAY! For a long time, the use of the Egyptian eye in a triangle for personal purposes was not available to “mere mortals”. Only pharaohs and clergy – priests – could have such an amulet.
The myth of the origin of Horus
The mythology of the Egyptians says the following about the origin of Horus. Osiris, the fourth of the gods ruling the earth, was killed by his brother Set in order to seize the throne.
You may be interested in: Star of David, the meaning of the symbol in different cultures and hexagrams in magic
According to information from many sources, Seth also dismembered his brother's body and scattered its fragments. Ra (Osiris's great-grandfather and first ruling god) sent Anubis (Osiris' son) to collect the scattered body parts.
Anubis collected them, swaddled them and embalmed them (which is why the Egyptians traditionally depicted Osiris as a mummy). He found all the fragments except the penis.
The wife of Osiris, who was also his and Seth’s sister, molded the missing organ from clay and attached it to the mummy.
Then, turning into a bird (falcon or kite), she sat on her husband’s corpse and, using special spells, became pregnant with his child. Thus Horus was conceived.
For a long time there were legal proceedings regarding the appointment of the legal representative of Osiris, and, in the end, Horus became this representative.
After this, Horus fights with Set, trying to take revenge on him for killing his father, and in this battle he loses his eye (as already described above).
After the miraculous restoration of the lost organ, Horus gives his eye to his father, who swallows it and is reborn.
However, having been resurrected, Osiris does not return to the human world, but remains to rule in the kingdom of the dead, and appoints Horus as ruler on earth.
The all-seeing eye of God in the Christian tradition
The symbol in question has found its niche in Christianity. Here the triangle with an eye inscribed in it is identified with the holy trinity (father, son and holy spirit).
The eye itself means the all-seeing eye of God. Moreover, this symbolism echoes the ancient Egyptian one: like the Egyptian Horus, the Christian god also sees everything.
This allows him to determine where to send people after completing their earthly journey: to heaven or to hell.
The symbol of the all-seeing eye also contains rays diverging from the sides of the triangle; they symbolize divine radiance.
It is curious that the only image of God in Christianity (in the Christian tradition it is generally not customary to depict the deity itself) is the icon “The All-Seeing Eye of God.”
BY THE WAY! Since the Christian Church prohibits the visual representation of God, on the mentioned icon he is introduced in the form of symbols. The all-seeing eye is also reflected in various denominations of Christianity, including Catholicism and Orthodoxy.
Eye of the sun star in the countries of the east
In eastern countries, the interpretation of the eyes of Horus is the opposite: the right eye symbolizes the Moon, and the left eye symbolizes the Sun.
Also, this sign in the East can be depicted in the form of a pheasant feather.
This is how representatives of different eastern countries understand the all-seeing eye:
- followers of Buddhism identify the eye with light and wisdom (analogous to the third eye of Buddha);
- Hindus also give one of the deities (Shiva) a third eye, which means penetration into one’s own consciousness and gaining wisdom;
- Iranians have a myth about the good shepherd (Yima), who has a solar eye and special knowledge that gives him immortality;
- among the Japanese, Izanagi (the first man on earth), according to some sources, with the help of his right eye, gave birth to the moon god Tsukiyomi.
BY THE WAY! In the Muslim tradition there is the concept of “the eye of the heart”, which means spirituality, intelligence and enlightenment.
Buddhist character for eye
The Buddhist tradition also has a symbol similar to the Egyptian eye of Horus. It means wisdom, the desire for true knowledge.
You may be interested in: Elephant talisman: What does the amulet mean, where to place it and how to activate it
Therefore, among Buddhists, an amulet with such an image was very common. In addition, followers of this religion believe that the eye symbol allows one to see into the future.
The bearer of this sign detaches himself from everyday life and improves himself in order to see the present and the future.
Celtic eye symbol
Among the Celts, the meaning of the all-seeing eye was very different from the meaning of this symbol among other peoples.
For the Celts, an eye inscribed in a triangle meant maliciousness, envy and joy from human suffering.
Thus, this meaning stands out from the general mass of meanings (almost all the considered religions endow the eye in a triangle with a positive meaning) and has a strong negative connotation.
Ancient Greek meaning of eye
The ancient Greeks, as successors to the traditions of the Egyptians, also adopted the symbol of the all-seeing eye.
This sign was identified simultaneously with Zeus (the thunder god) and Apollo (the sun god).
In the ancient Greek tradition, such a sign was endowed with the ability to grant access to hidden knowledge and spiritual insight.
In addition, the symbol of the eye among the ancient Greeks was considered capable of driving away evil spirits.
Muslims' all-seeing eye
In Islam, the eye is designated by the term “nazar bonjuk” (literally, “amulet against the evil eye”).
Typically done in blue glass with a lighter center with a black pupil in the middle.
Also called the "eye of Fatima". According to Muslim mythology, Fatima is the daughter of the prophet Mohammed.
Fatima gave her husband a piece of blue glass so that he could return home from a long trip.
Among the Indians of North America
The symbol of the eye also played an important role for the Indians of North America.
This sign was the embodiment of a certain great spirit who tirelessly watches over all people.
Here there is a parallel between the ancient Egyptian beliefs and the Indian ones: here, too, all the awareness of the great spirit is observed, which has the ability to observe mere mortals around the clock.
The All-Seeing Eye as a Symbol for Americans
There is a version that the Americans adopted this ancient sign in order to receive help from higher powers in the development of their state.
Actually, US citizens adopted this symbol from the Freemasons (who, according to some sources, founded the United States).
Following their predecessors, Americans believe that an eye in a triangle symbolizes wisdom and opens the door to the unknown.
The most famous image of the all-seeing eye among Americans is on the $1 bill.
BY THE WAY! The idea of an all-seeing eye on a banknote was also adopted by the Ukrainians: their 500 hryvnia bills also feature such a sign.
Freemasonry and the all-seeing eye
The Masonic sign, the all-seeing eye with rays diverging from it to the sides, is called the “radiant delta.”
Such a symbol is traditionally located in the eastern part of the Masonic lodge above the place of the Worshipful Master.
For representatives of the Masonic order, the triangle means fire and enlightenment; moreover, as traditionally in Christianity (and most Masons are Christians), it is associated with the Holy Trinity.
An open eye means the discovery of truth, truth and conscience, as well as the victory of good over evil.
In addition to decorating the lodge itself, the all-seeing eye sign is used by Freemasons on documents and in elements of ritual vestments.
Eyeball
The eyeball has a spherical shape and lies in the cavity of the orbit. It distinguishes between the anterior and posterior poles and the equator. The line connecting the poles is called the outer axis of the eyeball; Normally its length is 24 mm. The eyeball consists of an inner core and three membranes surrounding it. The fibrous membrane (outer) of the eyeball is protective. In the posterior, larger, section it forms the sclera, dense, white, in the anterior section it forms a transparent cornea, through which light penetrates the eye.
The choroid (middle layer) of the eyeball is rich in blood vessels. It has 3 parts: the choroid itself, the ciliary body and the iris. The iris - the anterior part of the choroid - has the appearance of a round plate with a hole in the center - the pupil. The color of the iris depends on the pigment content in it. A large amount of pigment causes the eyes to be brown, while a small amount causes the eyes to be blue or greenish-gray.
The size of the pupil is regulated by muscles embedded in the thickness of the iris: the muscle that constricts the pupil and the muscle that dilates the pupil. The size of the pupil changes depending on the amount of light entering the eye: the more light, the smaller the pupil, and vice versa.
The reaction of the pupil to changes in light intensity does not occur instantly, but within 10–30 seconds. Therefore, it takes some time for the eyes to get used to the darkness (when moving from a brightly lit place to a dark one) and to the light (when leaving a dark room to a brightly lit street).
Posterior to the iris, the ciliary body is located in the form of a roller. It contains the ciliary muscle, the contraction of which is transmitted through a special ligament (ciliary band) to the lens and causes a change in its curvature. Thus, accommodation occurs - the adaptation of the eye to seeing objects at different distances. When the ciliary muscle contracts, the tension of the ligament weakens, the lens, due to its elastic properties, becomes more convex, its refractive power increases and the eye is tuned to viewing nearby objects. If the ciliary muscle relaxes, then the lens, on the contrary, flattens and the eye adjusts to viewing distant objects. The ciliary body also produces a special intraocular fluid - aqueous humor - that fills the chambers of the eye.
The choroid itself, located behind the ciliary body, contains a large number of blood vessels that supply blood to the other membranes of the eyeball, and a black pigment layer that absorbs light.
The sensitive layer (inner) of the eyeball is called the retina. It has a complex structure. Here there are light-sensitive receptor cells - rods (about 125 million) and cones (6.5 million). They contain a pigment (rods - rhodopsin, cones - iodopsin), which absorbs rays with a certain wavelength of light.
By absorbing light, the visual pigment changes, which leads to the release of energy and the appearance of a nerve impulse. There are one type of rods and three types of cones. Rods are necessary at dusk; they perceive information about illumination and the shape of objects. Cones, which are 1000 times less sensitive to light, are day and color vision devices. Different types of cones respond to blue, green or red light. Other colors are perceived when two or more types of cones are simultaneously stimulated.
Rods and cones are distributed unevenly in the retina. The place of best vision in the retina is the so-called macula macula with a diameter of 1 mm, located opposite the pupil, which contains only cones. Towards the periphery of the retina, the number of cones decreases and the number of rods increases. Not far from the macula, closer to the nose, there is a blind spot - the place where the optic nerve exits the retina, which does not contain light-sensitive elements. When a specialist examines the fundus of the eye, the exit site of the optic nerve is easily determined, because This is where the vessels that supply it enter the retina.
The membranes of the eyeball surround its inner core, which consists of transparent light-refracting media: the vitreous body, the lens and the aqueous humor that fills the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye.
The lens, as already mentioned, has the shape of a biconvex lens, which can change its curvature. It is elastic, transparent and located behind the pupil. The lens refracts light rays entering the eye and focuses them on the retina. Behind the lens is the vitreous humor, a transparent jelly-like mass that fills the space in front of the retina. Light rays pass through the vitreous body, which are refracted by the cornea and lens and focused on the retina.
The space between the cornea and the iris constitutes the anterior chamber of the eye, and the space between the iris and the lens constitutes the posterior chamber. The chambers of the eye communicate with each other through the pupil and are filled with a transparent liquid - aqueous humor. Aqueous humor nourishes those structures of the eyeball that do not have blood vessels: the cornea, lens and vitreous body. Aqueous humor plays an important role in maintaining intraocular pressure, which is necessary for normal vision.
Bags and circles under the eyes
In addition to eye diseases, people can often observe the presence of circles and bags under the eyes. Where do they come from?
The fact is that the skin of the eyelids is very delicate and thin. Due to a lack of oxygen or insufficient blood supply, the blood in the capillaries stagnates and begins to become translucent. This is how dark circles appear under the eyes.
There are many reasons for their appearance. Circles can be a hereditary factor, a structural feature of subcutaneous fatty tissue, or indicate diseases of the internal organs and endocrine system. The most common causes of dark circles under the eyes are stress, chronic lack of sleep and chronic fatigue.
Puffiness and bags under the eyes often appear as a result of drinking large amounts of alcohol, tea or coffee before bed. As a result, stagnation of blood and lymphatic vessels occurs, and as a result, bags under the eyes in the morning.
In addition, bags under the eyes may indicate poor kidney function, an allergic reaction, or inflammation of the sinuses.
Accessory eye apparatus
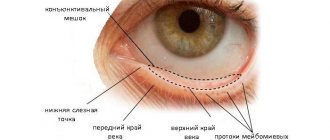
The accessory apparatus of the eye includes the eyebrows, eyelids, eyeball muscles, and lacrimal apparatus. Eyebrows serve to protect the eyes from sweat flowing from the forehead. Eyelashes located on the free edges of the upper and lower eyelids protect the eyes from dust, snow and rain. There are about 80 eyelashes on each eyelid, arranged in 2-3 rows. Eyelashes are renewed within 100 days. The basis of the eyelid is a dense plate, which is covered on the outside with skin, and on the inside with a special connective membrane - the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva passes from the eyelids to the anterior surface of the eyeball.
The lacrimal apparatus is represented by the lacrimal gland and lacrimal ducts. The lacrimal gland lies in the fossa of the frontal bone at the outer wall of the orbit. The tear washes the surface of the eyeball and flows into the medial canthus. From here, tears are drained through the lacrimal canaliculi into the nasal cavity. Tears moisturize the cornea and conjunctiva, wash away dust particles and neutralize microorganisms. Without tears, the cornea can dry out and its refractive power is impaired. The outflow of tear fluid is facilitated by blinking movements of the eyelids.
The mobility of the eyeball is ensured by six muscles that are located around it in the depths of the orbit: four straight muscles (superior, inferior, external and internal) and two oblique (superior and inferior). These muscles act in such a way that both eyes move synchronously and are aimed at the same object. The convergence of the visual axes of both eyes on the object under consideration is called convergence. This position of the eyes provides binocular vision (receiving the same image in both eyes), which is important for perceiving the size, shape, volume of an object, as well as movement, distance and depth. The muscles of the eye contract voluntarily; commands to them from the brain are carried out through three pairs of cranial nerves.
From the eyeballs, visual information travels to the brain via the optic nerves. The optic nerve is formed by processes of nerve cells lying in the retina. On the lower surface of the brain, the optic nerves cross, and only the fibers that come from the inner halves of the retina pass to the other side. After the chiasm, the nerves are called optic tracts. Each optic tract contains fibers carrying information from the inner half of the retina of the opposite eye and the outer half of the retina of the eye on its side. This creates conditions for binocular vision. The visual tract ends in the subcortical visual centers. From here, some of the fibers are directed to the center of vision in the cortex of the occipital lobe of the cerebral hemispheres (near the calcarine sulcus), where visual sensations are formed. Another part of the fibers ensures the implementation of reflex eye movements: their rotation, pupillary reflex and accommodation.
The brain perceives stimuli from the external environment and interprets them taking into account all the accumulated information. Thus, the image obtained on the retina is inverted and reduced. But a person sees objects not upside down. This happens because the activity of the organ of vision is checked by the testimony of other senses.
Some aspects of unconventional use of the eye[edit]
He can shoot with eight eyes at once!
Eye shot[edit]
An eye shot is a special seduction technique that involves re-equipping the eye with a special mini-gun, which, at the command of the brain, shoots a capsule with a love potion in the direction of the gaze. It is believed that it can awaken love, but scientific research does not confirm this. However, eye shots have been successfully used by such individuals as:
- Hermione - to seduce Ron
- Beatrice - to seduce Dante
- Gurchenko - to fool Bori Moiseev[2]
- 5678 - to excite love 1234
Common eye poker
Eye position[edit]
Eye position (lat. oculum ponere
), like an eye shot, is a special technique that serves to mark the chosen object of love, sighing, desire, desire, consisting of removing the eye from the parent device (human), and guest connecting it to another device (also human), although among woodcutters The position of the eye on trees is often observed.
A man's eye position on a woman can cause said woman to move into an interesting position. In other cases, eye position does not usually have such consequences (however, they may be erroneously attributed to this process)
Eye gouging[edit]
You can't see a thing - even if you gouge out your eyes!
~ Harry Potter about another dungeon full of Zogs invisible in the dark
Gouging out the eye is a method of counteracting evils, which consists of dismantling one of the vision devices and then piercing it with a special device (see illustration). This action shorts the fiber optic circuits of the eye, causing the eye to emit a glow that repels the zog. It is reliably known that it was with the help of gouging out his eye that Harry Potter found a way out of the dark cave.
Eyes and dust[edit]
Dust is a special nanovirus for the eyes, developed to pacify the rebellious at the behest of Medved Putinovich. The principle of operation is simple - when dust gets into the eyes, it rearranges the perception matrix, so that a person begins to see something other than what actually exists (the so-called “show off”). A short list of the main changes:
- bribe → charity
- rednecks → intelligentsia
- opposition rally → rally in support of the president
- cutting → nanotechnology
Eye diseases
Due to improper development, the eyeball can be elongated, and myopia (myopia) occurs at a young age; When the eyeball is shortened, farsightedness (hyperopia) is observed. These vision defects are corrected with glasses.
Color vision impairment is called color blindness, affecting about 8% of men and 0.5% of women. Color blindness is caused by the absence of one or more types of cones, which is associated with a genetic defect.
With age, the elasticity of the lens decreases. Together with atrophy of the ciliary muscle, this leads to a violation of accommodation, then the person sees poorly at close range. Such senile farsightedness is corrected with the help of glasses - biconvex lenses that are worn when reading. With age, the lens may lose its transparency. Cloudiness of the lens is called a cataract and is treated with surgery.
A visual impairment called astigmatism occurs when the curvature of the cornea or lens is abnormal. In this case, the image on the retina is distorted. To correct this, you need glasses with cylindrical lenses. Increased intraocular pressure is a sign of a serious eye disease - glaucoma.
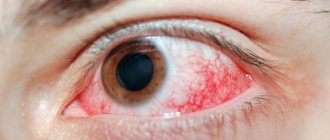
Inflammation of the connective membrane, called conjunctivitis, is caused by infection, dust or chemicals and is characterized by redness, swelling, a burning sensation and heaviness in the eyes.
In medicine, the iris is equated to a kind of scoreboard that reflects the state of the human body. The iridology method (diagnostics by the iris) allows you to establish the localization of various diseases in the human body.
Eye diseases and treatment
All eye diseases can be divided into infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious diseases arise under the influence of various microorganisms: bacteria, viruses, fungi. For these diseases, it is important to undergo an eye test and begin adequate eye treatment, otherwise the disease can lead to damage to the cornea and even loss of vision. Infectious diseases include conjunctivitis, blepharitis and stye.
Non-infectious diseases arise as a result of visual strain, hereditary predisposition, and age-related changes. The most common non-communicable diseases include dry eye syndrome, cataracts and glaucoma.
If non-infectious diseases are detected in the early stages, then eye treatment has a favorable prognosis, so it is important to undergo a vision test with an ophthalmologist every six months.
Vision prevention
The human eye is a complex optical system that requires careful attention. You should protect your eyes from mechanical influences. When reading, you need to make sure that the light falls from the left, and the distance from the eyes to the book is 35–40 cm. You cannot lean closer to the book, because Constant tension in the ciliary muscle can lead to premature development of myopia.
Excessively bright lighting also harms vision because it destroys light-receiving cells. It is not recommended to read in a moving vehicle: due to the unstable position of the book, the focal length changes all the time, which weakens the accommodation apparatus. Visual impairment can occur due to a lack of vitamin A in food, so a special diet for the eyes is necessary. It is also recommended to do eye exercises and take breaks from reading and working on the computer.
Taking good care of your eyes will help you maintain good vision and a clear view of the world around you for a long time.
Return of vision and strangeness
Now Sydney’s life will completely change, because she has had a cornea transplanted and soon she will be able not only to feel and hear the world, but also to see it. The operation went quite well, her vision has not yet fully returned, but she can already see the blurry silhouettes of those around her. Alas, all sorts of strange things were added to this.
On the very first night, the still half-blind girl observed a strange picture: some man was taking her roommate somewhere, and in the morning it turned out that she had died. The heroine did not connect these two events, but tried to find out who her eyes used to belong to. Alas, the name of the donor is kept secret, besides, what difference does it make, because now these are her eyes.
However, the better Sydney begins to see, the more strange visions she sometimes has. At night she dreams of a burning house and people in it; during the day, people appear in her field of vision that others cannot see. At the same time, the ghosts manage to leave handprints on the spilled sugar. And yes, her vision began to distract the girl from the music and she herself became more distracted.
Still from the film “The Eye”