Is poor distance vision myopia?
Myopia is a disorder of the refractive ability of the eye, in which a person can see nearby objects clearly and clearly, while distance vision
In this article
- Is poor distance vision myopia?
- Main causes of myopia
- Myopia - what is it like?
- Why is progressive myopia dangerous?
- How is myopia treated?
- Contact correction of myopia is convenient and discreet
- Laser correction - for those who want to see well without glasses and contacts
- Prevention of myopia: recommendations from experts
is blurry. In simple terms, a myopic person sees well up close but poorly at a distance. People with nearsightedness usually have no problem reading, knitting, or doing other activities close to their eyes. At the same time, it is difficult for people with this problem to read a store sign on the other side of the street or see the face of a person who is standing far from the observer without special correction means. According to statistics, myopia (another name for myopia) occurs in every third inhabitant of the Earth. Depending on the degree of the disease, it can significantly worsen the quality of life, greatly affecting vision, while in others it is almost invisible to the person himself. In any case, myopia has the ability to progress and, without proper correction, can lead to serious consequences, including critical vision loss. Therefore, as soon as you notice that your distance vision has become worse, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
What causes myopia, is it possible to prevent or stop the development of the pathology, what means are used to correct myopic vision - we will try to answer these and other questions in detail.
Prevention
Compliance with preventive measures will reduce the likelihood of vision deterioration and will always allow you to see well both at a distance and at close distances:
- sufficient amount of vitamins in the diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- good sleep;
- a break during visual work and performing eye exercises;
- work only in sufficient lighting;
- refusal to read while moving traffic;
- annual examination by an ophthalmologist.
If you notice that your distance vision has become difficult, do not put off visiting a doctor. The sooner you receive treatment, the better your quality of life will be.
In addition, you can see the top 5 eye massage methods to improve vision:
How good or bad is your distance vision? Share your feelings in the comments. Repost so that your loved ones know about the problem. Be healthy.
source
Main causes of myopia
Doctors identify two main causes of myopia:
- elongated eyeball;
- excessive refractive power of the eye.
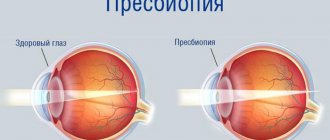
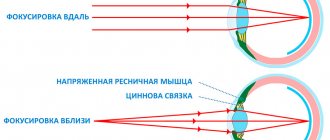
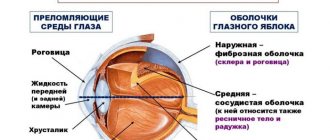
Normally, the human eyeball has such a size and shape that the rays entering the eye are focused in the center of the retina. If the anteroposterior ocular axis is slightly longer than normal, the rays do not reach the retina and are focused in front of it. Due to the shifted optical focus, a person has difficulty seeing into the distance. If the length of the eyeball increases, myopia progresses and visual impairment becomes more pronounced. Sometimes myopia is caused not by the size of the ocular axis, but by the strong refractive ability of the cornea or lens. When the optical media of the eye refract light more than necessary, the focus of the image also shifts to the area in front of the retina and this is reflected in the clarity of distance vision.
Simultaneous myopia and hypermetropia
Farsightedness and nearsightedness are the most common visual impairments. Usually a person has one of them, but it also happens that both of these pathologies are present at the same time. In this case, myopia and hyperopia can be diagnosed in one eye or in the left and right separately. How are these types of visual impairments corrected?
In this article
What factors influence the development of myopia?
Despite the fact that there are only two main causes of myopia, there are many factors that contribute to the occurrence of this disease.
- Hereditary predisposition to an elongated eyeball or strong refractive ability of the eye. The highest probability of a child developing hereditary myopia exists when both of his parents have this pathology.
- Weakened scleral tissue and increased intraocular pressure (contribute to stretching of the eyeball).
- Reduced ability of the eye to focus at different distances (this impairment is compensated by an increase in the length of the eyeball).
- Weakened immunity - due to overwork, unbalanced nutrition, various diseases (curvature of the spine, flat feet, diphtheria and other infectious diseases, allergies, birth and other brain injuries, rickets, inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx).
- Excessive visual stress - as a result of long work at the computer, reading in transport, poor lighting, incorrect sitting at the desk.
The listed factors can exist separately or complement each other. The more factors that affect a person, the higher the risk of developing myopia.
What diseases can cause a person to have difficulty seeing up close?
Deterioration of near vision in itself is already called “hypermetropia”.
Note! This pathology can manifest itself against the background of certain ailments, one of which is a violation of accommodation.
The eye can no longer focus on objects at different distances due to atrophic processes in the tissues of the lens.
Deterioration of vision at close distances may be associated with the development of the following ophthalmological diseases:
- Retinal detachment. The retina is an element located at the back of the eye. Light reflected from visible objects is focused on it, and this information is transmitted in the form of an image to the brain. In a detachment, the retina separates from the choroid to which it is tightly attached.
- Macular degeneration. The disease is a lesion of the “macula” – the area of the retina where the largest number of photoreceptors is concentrated.
- Retinal and vitreous tears.
- Diabetic retinopathy. A disease of the vascular system of the eyes, in which atherosclerotic changes develop in the capillaries. As a result, the blood supply to the optic nerve and retina is disrupted and the person begins to see worse.
Farsightedness often develops against the background of cataracts (pathology of the lens).
It is worth noting! When diseased, the lens loses its natural transparency and ceases to fully perform the work of a lens, making normal focusing of vision impossible.
Myopia - what is it like?
Since there are many causes and factors contributing to the development of myopia, there are different types of myopia. Due to its occurrence, myopia is divided into the following types:
- axial (associated with an increased length of the anteroposterior axis of the eyeball);
- refractive (caused by excessive refractive power of the ocular media);
- mixed (in which both the size of the eyeball and the refraction of the eye optics are higher than normal);
- combined (dimensional and refractive indices of the eye are within normal limits, but are poorly combined).
Based on the time of occurrence, myopia is divided into congenital and acquired. In the first case, a child is born with a refractive error, in the second, myopia develops during life under the influence of external factors, visual stress, injuries, and diseases. The congenital form of myopia is less common than the acquired form, but is often accompanied by complications and abnormal development of the visual organs. The acquired form of the disease can be represented by both minor and more serious visual impairment. According to statistics, every year there are more and more people with acquired myopia.
According to the degree of development, myopia is divided into three types:
- weak (up to -3 diopters): a person with such a visual impairment sees distant objects a little blurry;
- medium (from -3.25 to -6 diopters): when it is difficult to see at a distance without glasses or contact lenses, but close objects can be clearly seen if they are no further than 30 cm from the face;
- high (from -6 diopters): with severe myopia, a person can see even closely located objects only when they are close to the face.
Causes of farsightedness
Farsightedness, caused by a short longitudinal axis of the eye, is usually inherited from parents to children. After 40-45 years, due to age-related changes in the body, the refractive ability of the lens begins to deteriorate in many people, and then “senile farsightedness” occurs.
What happens?
In order for the eye to see normally, the image of objects must be focused on the retina. With farsightedness, this point of the ideal image moves away and is located, as it were, behind the retina. As a result, a person sees the picture in a slightly blurred form.
The rays coming from distant objects are parallel, and those coming from nearby objects are divergent. Farsighted eyes cope poorly with the latter. Thus, a person sees worst of all at close range and much better at distance.
There are two reasons why light rays are focused too far in case of farsightedness: a shortened eyeball or insufficient refractive power of the eye's optical system. It is also possible to have a combination of these defects in one person.
The main manifestations of farsightedness:
poor near vision; increased eye fatigue when reading; headaches, burning eyes.
Farsightedness, if ignored, is fraught with such unpleasant complications as:
strabismus; frequent inflammatory eye diseases (conjunctivitis); Amblyopia (“lazy” eye) - the eye is healthy outwardly, but sees poorly and cannot be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
The progression of farsightedness can lead to disturbances in the outflow of intraocular fluid and, as a consequence, the development of glaucoma.
What symptoms may indicate myopia?
Myopia is a condition when a person can see objects close to him, but has difficulty seeing objects that are far away. Accordingly, the main symptom of the disorder is reduced distance vision.
But, in addition to this main symptom, other symptoms may indicate developing myopia:
- blurred image contours;
- increased eye fatigue;
- squinting when looking at distant objects;
- headaches, a feeling of tightness in the temporal zone and bridge of the nose, dizziness;
- “spots”, blind spots before the eyes, loss of visual fields (may be symptoms of complicated myopia);
- large eyeballs and wide pupils (a characteristic external sign for people with a high degree of myopia).
Causes
Not everyone develops refractive errors (astigmatism, myopia). Therefore, the reasons are better called predisposing factors. When you have difficulty seeing distant objects, eye pathology may have developed due to:
- regular excessive loads on the visual apparatus;
- increased IOP;
- structural changes in the eye.
The risk of distance vision impairment increases:
- in children born to myopic parents or astigmatism;
- in those who have previously undergone vision correction surgery;
- in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- in those suffering from diseases of the immune system.
The development of cataracts is most often caused by age-related changes, less often by traumatic factors. Possible congenital cataract.
What diseases cause poor distance vision?
Most often, poor long-distance vision develops against the background of:
- vascular disorders of the eyes;
- spasm of accommodation;
- injury or hardening of the lens;
- thickening of the cornea.
If you find that you have trouble seeing into the distance, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will determine whether this is a plus or a minus, identify the cause, select glasses or refer you for surgery.
Why is progressive myopia dangerous?
If myopia progresses, it poses a serious threat to vision. Stretching of the eyeball becomes pathological, leading not only to a decrease in visual acuity by more than one diopter annually, but also to disruption of the nutrition of the eye tissues, ruptures, detachments and degenerations of the retina, and opacification of the vitreous body. With complicated progressive myopia, a person sees worse and worse, and any hard work or sudden movement can lead to damage to the retina and, as a result, a sharp fall or complete loss of vision.
That is why one of the most important tasks of ophthalmology is the stabilization of myopia.
Five signs that your vision has become worse
It often happens that a person goes to the ophthalmologist only when the lines on the monitor blur, and friends complain that you can’t recognize it from a distance of five steps! But signs of decreased vision and the very serious diseases that lie behind it can be recognized in advance, when the problem can still be quickly solved.
1. Change in vision clarity throughout the day
In the morning you can see perfectly, but in the evening the outlines of objects begin to blur. To restore clarity to them, you need to either rub your eyes hard or press on your eyeballs. walk clearly, but in the evening everything starts to blur. This may be a sign of myopathy. This disease damages the small blood vessels in the eyes. Myopathy often accompanies type 2 diabetes.
2. You lose dexterity
Do you start bumping into people in the corridor every now and then, can’t really see the surrounding cars in the mirror, are you constantly hitting objects standing to the side of you? This may be due to decreased peripheral vision. Usually a person does not associate this problem with the eyes: they do not hurt, they are not tense, and you can clearly see objects far and near. But not from the side. Meanwhile, loss of lateral vision may be the first symptom of such a serious disease as glaucoma.
3. The appearance of a “blind spot”
Does it happen that a dark spot or a “blind spot” appears in your field of vision for a couple of seconds? Then it just as suddenly goes away. This could be a sign of age-related molecular degeneration, the most common cause of vision loss in people over 50, reports EurekAlert. Another obvious symptom of this disease is a periodically arising illusion, when obviously straight lines appear wavy.
4. Study in brown tones
Do you feel like you are looking at the world through brown glasses? Or is it like a film shot with special filters—as if antique? After a few seconds, the colors of the world return to normal. This could be a sign of cataracts. The lens of the eye becomes cloudy, which in the future can even lead to partial or complete blindness. But now the cataract is successfully operated on, and after replacing the lens, vision is restored.
5. Small flashes
Do you sometimes see many sharp small flashes before your eyes? For example, when you do some heavy physical work, carry heavy objects, or bend over suddenly? This condition may indicate a threat of retinal detachment. If this happens, you should urgently consult an ophthalmologist.
BY THE WAY
Apricots and fresh cabbage will help protect your eyes from the sun
The bright July sun often causes your eyes to become watery and strained. Ophthalmologist Nadezhda Arutyunova advises:
— To prevent the mucous membranes of your eyes from drying out, buy “artificial tear” drops at the pharmacy. There are quite a few such moisturizing solutions; you can choose by price and size of the bottle.
— Eat apricots, since the season is in full swing! Their pulp contains many substances that are beneficial for the eyes - zeaxaltin and lutein. They prevent your eyes from getting tired and filter UV rays that hit the retina.
— A glass of carrot juice a day is enough to provide “fuel” to the retinal cells. Carrots contain a lot of vitamin A, which is essential for nourishing the eyes.
— Lotions made from infusions of chamomile, mint, and linden blossom will help put sore eyes in order. The simplest thing is to hold cotton swabs soaked in strong cold tea on your eyelids for about ten minutes.
— Do you come home from work with bleary eyes? Make an eye mask from a mixture of 2 teaspoons of grated raw potatoes, 2 teaspoons of flour and 2 teaspoons of milk. The remedy is simple, but effective.
— Compresses made from finely chopped fresh cabbage leaves will help relieve swelling from tired eyes.
How is myopia treated?
Despite the fact that myopia is a widespread phenomenon and affects more than 1 billion people around the world, today there are no treatment methods that could restore the eye to normal refraction with a 100% probability. The methods used in the treatment of myopia are aimed at solving several main problems:
- vision correction;
- stabilization of myopia (stopping or slowing down its progressive development);
- elimination of factors that contributed to the onset of the disease.
The choice of therapy depends on the cause, degree of myopia, patient's age and other factors. The ophthalmologist decides which treatment regimen will be effective in each specific case. All methods of combating myopia can be divided into several groups.
- Medicines (mainly affecting the functioning of the accommodative apparatus and reducing intraocular pressure).
- Vision correction with glasses, soft or orthokeratological lenses.
- Hardware techniques.
- Surgical treatment (scleroplasty, lens replacement, phakic lenses).
The development of myopia often begins in childhood, so the most important role in combating this problem is played by disease prevention, timely diagnosis and early treatment in children.
What to do: treatment approaches
What to do if you encounter this symptom and near vision becomes poor? If near vision deteriorates, treatment is prescribed depending on the cause of the disorder and the severity of farsightedness, as well as the age of the patient.
Keep in mind! Options range from conservative therapy (in mild cases) to surgical intervention.
General approach
Conservative treatment in this case includes the use of corrective optics .
Moreover, if farsightedness is slight, you can wear glasses or contact lenses only when performing activities that require visual concentration (reading, watching TV, working on a computer).
In childhood, the tissues of the eye are still quite elastic, and instead of such auxiliary means, you can try to get rid of refractive errors with the help of special eye exercises.
If the examination reveals farsightedness of more than +3 diopters, you cannot do without constantly wearing corrective glasses or lenses.
Additionally, computer-based treatment can be used.
If this combination does not produce results, surgical or laser treatment is prescribed.
Surgical treatment
The following surgical options are possible:
- laser correction;
- laser thermokeratoplasty (the cornea is affected by thermal radio waves, as a result of which the shape of the cornea changes and, accordingly, its refractive characteristics);
- lensectomy (removal of a poorly functioning lens and its replacement with an artificial implant, mainly relevant for age-related visual impairment);
- keratoplasty (replacement of a clouded area of the cornea);
- lens implantation, in which the organ is not removed, but the lens is installed directly in front of the lens;
- radial keratotomy (applying incisions to the cornea that help correct its refractive power);
- thermokeratocoagulation (spot treatment of the cornea with a needle heated to a certain temperature).
Each method has its own indications, different effectiveness and rehabilitation period. The choice of treatment method depends on the results of a preliminary examination of the patient.
Drug treatment of myopia - strictly as prescribed by the doctor
Medicines in the treatment of myopia are used infrequently and strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
When indicated, ophthalmologists sometimes prescribe atropine, which can slow the progression of myopia in children. However, experts still do not have complete data on the possible side effects of long-term use of this drug, so it is prescribed in rare cases.
In addition to atropine, tropicamide, which relaxes the ciliary muscle and blocks accommodation, can be used in the complex treatment of myopia. Sometimes doctors prescribe antihypertensive medications, believing that increased pressure inside the eyes can worsen myopia. However, at the moment, ophthalmologists have little evidence of the relationship between increased IOP and the progression of myopia, so many doctors consider it inappropriate to prescribe such treatment to patients.
Who undergoes scleroplasty?
This method refers to surgical methods for treating progressive myopia. As a rule, it is prescribed to adult patients when the level of eye refraction exceeds -6 diopters. The main goal of the operation, which is performed under local anesthesia and takes about 15-20 minutes, is to strengthen the outer layer of the eye (sclera) to prevent further increase in the length of the eyeball and deterioration of distance vision. Doctors note that scleroplasty, in addition to strengthening the eye shell, has another positive effect - it helps to increase the number of vessels through which nutrition flows to the posterior pole of the eye, and thus improves its blood supply. During scleroplasty, the ophthalmic surgeon inserts special implants into the sclera through microscopic incisions, which form a frame that prevents stretching. You should not expect that after scleroplasty a person will be able to see well into the distance. But this procedure will stop further vision loss by fixing the refraction values at the level they were before surgery. To restore visual function, optical or laser correction will be required.
Treatment
It is impossible to cure such symptoms exclusively. The doctor must identify the cause of their development. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the etiology. Its symptoms will disappear on their own. In most cases, patients experience poor vision in only one eye.
Typically, ophthalmologists prescribe conservative treatment. It consists of the following methods:
- use of computer programs;
- a bandage is put on the healthy eye to stimulate the function of the damaged organ;
- physiological procedures.
Drug therapy is prescribed individually to each patient. Self-medication can lead to serious consequences. Then poor vision will be present constantly. Only timely diagnosis provides a favorable result. In most cases, visual acuity can be restored. Surgical intervention is used in severe situations.
Glasses will help you see near and far equally well.
One of the popular methods of vision correction for myopia and the most common in children is glasses. The principle of their operation is based on reducing the refractive power of the eye to such values that the focusing of light rays falls exactly on the retina. Myopia glasses have negative power lenses that help shift the focus to the retina, allowing the eyes to see far and near with equally good clarity. Often, a patient is diagnosed with astigmatism along with myopia. In this case, ordinary monofocal glasses will not be able to restore the necessary clarity of vision; special astigmatic models with “cylinder” lenses will be required. For myopia, the doctor may prescribe glasses for constant or periodic wearing, depending on the goals of correction, the degree of myopia, the patient’s age and other factors.
The main advantage of spectacle correction for myopia is its versatility, ease of use, and accessibility for people of any age and occupation. However, not everyone likes how glasses change their appearance, and teenagers may even be ashamed of their “bespectacled” image and refuse the necessary correction. In this case, you should consult your doctor about the possibility of switching to contact lenses.
Which glasses to choose for farsightedness: plus or minus?
→ Home treatment → Eye diseases → Farsightedness
Farsightedness is a special condition of the eye that is often contrasted with myopia. With farsightedness or hypermetropia, the focus of the image when looking at an object falls not on the retina, but behind it.
The farsighted eye is usually shorter than the healthy eye. People who suspect they have this disease often wonder whether farsightedness is a minus or a plus? The choice of glasses and treatment in general depends on this.
- Features of the disease
- What is the difference between farsightedness and nearsightedness?
- Glasses for farsightedness: plus or minus
- Treatment of farsightedness
Features of the disease
Hypermetropia is not as common a disease as myopia. It is believed that the main symptom of this condition is poor near vision, but it is worth noting that poor distance vision also occurs. Farsightedness is often an age-related problem; most people experience its symptoms after 30–40 years.
However, due to congenital structural features of the eye, hypermetropia can occur in children. In this case, it is imperative to immediately engage in vision correction; in children, such a pathology can lead to more serious problems, for example, strabismus.
In addition to decreased near visual acuity, farsighted people are plagued by a number of other symptoms that are not always immediately associated with eye problems. People with hypermetropia often experience the following symptoms:
- a feeling of tension, burning in the eyes, especially after a busy day at work;
- fatigue, periodic rather severe headaches;
- Difficulty reading small texts and looking at nearby objects.
All these phenomena are consequences of farsightedness. Without correction, this disease can begin to progress and cause more and more difficulties. The following degrees of hypermetropia are distinguished depending on the number of diopters by which vision has deteriorated:
- first degree, weak, up to +2 diopters;
- the second degree, more serious, stands out from + 2 – 2.5 to + 4.5 diopters;
- the third degree is the most severe, starting from +4.5 diopters.
In the first stages of the disease, the patient does not feel any serious difficulties; pain in the eyes may begin to appear from working for a long time. If farsightedness is detected at the first degree, the patient often only needs specialized reading glasses, which help to better distinguish small print without unnecessarily causing eye strain.
In later stages, serious discomfort may appear, and it will become extremely difficult to distinguish small fonts and nearby objects. In the third degree of the disease, visual acuity decreases not only near, but at a distance.
Important! Farsightedness almost never occurs at an early age
What is the difference between farsightedness and nearsightedness?
The main difference between these diseases is where the images inside the eye are focused, and this is where the rest of the differences between the two conditions come from. With farsightedness, the image is focused behind the retina, the rays of light are collected literally behind the eye.
With myopia, light rays are focused without reaching the retina. Therefore, with hypermetropia, a person better sees objects located far away, and with myopia, objects located close to them are better. In this regard, glasses for vision correction should be selected with different signs; each disease requires its own diopters.
Glasses for farsightedness: plus or minus
For hypermetropia, glasses with positive diopter values are required. With this disease, the optics of the eye are too weak; there are not enough plus diopters to focus the image on the retina, and not behind it.
Properly selected glasses with “plus” lenses will literally help to pull the focus of the image back onto the retina, and the patient will begin to see better. Therefore, with farsightedness, only diopters with a “+” sign can help.
It is also worth mentioning that specialized reading glasses are common for people with farsightedness. Many people with this disease are forced to move books and any other printed texts away from them at arm's length; with reading glasses, this problem is easily solved.
“Plus” glasses can be easily identified by their appearance. When worn on a person, they visually increase the size of the eye. Today, glasses for farsightedness are the most effective non-surgical method of vision correction.
Contact correction of myopia is convenient and discreet
Today, contact optics are in great demand, and the choice of soft optical lenses for correcting myopia is quite large.
Contact lenses operate on the same principle as glasses, that is, due to the “minus” in diopters, they move the focal point onto the retina.
But, compared to spectacle correction, contact correction has several advantages:
- does not produce peripheral image distortion;
- eliminates the possibility of eye injury if the product is damaged;
- invisible to prying eyes and does not affect appearance;
- allows you to lead an active lifestyle without regard to vision problems.
Modern contact lenses not only correct myopia, farsightedness and other refractive problems well. They are manufactured using technologies that make them easy to wear, comfortable and safe for the eyes. Popular contact lens models that are often prescribed to correct myopia include ACUVUE Oasys, Dailies AquaComfort Plus, Biofinity and others.
Orthokeratology lenses - night vision correction
Night lenses, otherwise called orthokeratological lenses, are an option for those who, for one reason or another, are not suitable for conventional contact lenses. Such products should be used during sleep and removed during the day. Overnight, an orthokeratology lens changes the shape of the cornea so that light rays begin to fall directly on the retina. Having removed optical products in the morning, a person can see clearly both near and far. This effect lasts for several hours, so during the day the user sees clearly without any means of optical correction. By evening, the cornea takes on its original shape, so at night it is necessary to wear orthokeratology lenses again.
What is hypermetropia?
Hypermetropia is the opposite disorder of myopia. Its other name is farsightedness, and it is not difficult to guess that in this case a person sees well at long distances, but poorly at close range.
IMPORTANT! In relation to hypermetropia, the term “close” refers to objects that are up to 30 cm away from the eyes.
With hypermetropia, the image is focused behind the retina.
Why is it developing?
All children are born farsighted. This is explained by the immaturity of the ocular apparatus, so by the age of 4, as it develops, the eye begins to function normally.
Farsightedness is caused by various injuries, surgical interventions and disorders that change the shape of the eyeball. Another common cause of hypermetropia is a change in the curvature of the lens, which is common in older people.
Hardware techniques - safe treatment of myopia in childhood
When a child has difficulty seeing distant objects, along with optical vision correction, the doctor may prescribe hardware treatment to improve the functions and condition of the visual system.
Infrared laser therapy.
The eyes are exposed to infrared radiation, which helps normalize metabolism and relieve spasm of accommodation.
Vacuum massage.
The procedure helps improve the hydrodynamics of the visual organs, blood supply, and normalizes the functioning of the ciliary muscle.
Electrical stimulation.
The child’s visual organs are exposed to low-intensity current, which improves the conduction of signals in the optic nerve. When necessary, the doctor may prescribe other hardware techniques. This is, for example, laser therapy or special video-computer training.
Methods for diagnosing pathologies
To diagnose any visual impairment, standard ophthalmological procedures are used:
- visual acuity test;
- determination of refraction;
- measuring the length and width of the eye;
- measuring corneal thickness;
- fundus examination.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic methods, such as measuring intraocular pressure.
Laser correction - for those who want to see well without glasses and contacts
Today there are several methods of laser correction of myopia. They are united by a common principle of execution. Using a laser beam under the control of modern high-precision equipment, an ophthalmologist changes the shape of the cornea according to a person’s individual parameters. This allows you to achieve correct refraction and see clearly without the use of aids.