Not every person can boast of good eyesight. Eye diseases are increasingly affecting young people under 40 years of age. Blurred vision, stretched objects, a dot that looks like a line or an oval, are often attributed to fatigue, prolonged use of the computer, or migraines. In reality, this is astigmatism, as seen by a person suffering from visual pathology, how to recognize the signs of the disease and go to an ophthalmologist in a timely manner, whether there are methods of prevention and treatment of refractive dysfunction of the visual apparatus, let’s try to figure it out.
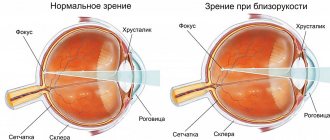
How do the visual organs of healthy people work?
The eyes are a paired visual organ consisting of:
- Rainbows;
- Transparent thin cornea (cornea);
- Anterior chamber, the area between the iris and cornea filled with moisture;
- Ciliary muscles;
- Retina;
- Ciliary body;
- Lens (participating in the refraction of light rays from the lens);
- Vitreous body (jelly-like consistency);
- Choroid;
- Muscles that move the visual organ;
- Sclera;
- Optic nerve;
- Eyeball.
Light penetrates through the optical apparatus of the visual organ and hits the retina. On the inner lining of the eyeball, the lens collects the image. Light rays are converted by the retina into signals that transmit a picture of an object to the brain.
The degree of roundness of the eye lens is controlled by the muscles of the eyes, making the pattern as clear as possible.
In healthy people, the beam of rays is concentrated at a single point. Refraction is measured in diopters. 1D or diopter (diopter) = refractive power of a lens with a focal length of 1 m.
Causes of pathology
The causes of astigmatism can be divided into congenital and acquired. Violations of the refractive system of the eye in the fetus occur even during the mother’s pregnancy. This is facilitated by disorders of the lens or cornea. In most cases, this happens at 3-7 weeks of gestation, when many women do not even suspect pregnancy.
REFERENCE. A high probability of developing astigmatism is present with congenital circulatory disorders in the retina, albinism and fetal alcohol syndrome.
The acquired form develops against the background of:
- corneal injuries;
- conjunctival burn;
- eye operations on the sclera;
- scar on the cornea;
- eyelid lesions;
- the presence of postoperative sutures on the cornea or sclera;
- inflammatory keratitis.
Any violation of the integrity of the cornea is fraught with a change in its optical properties. Even small deformations in its shape lead to a change in the refraction of light rays.
Sometimes astigmatism occurs due to large styes that put pressure on the cornea.
In some cases, the defect occurs as a result of previous dental pathology, which resulted in a complication in the form of deformation of the walls of the orbit. Optic nerve hypoplasia, eyelid ptosis and keratoconus occur as concomitant diseases with astigmatism.
Expert opinion
Danilova Elena Fedorovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest qualification category, Doctor of Medical Sciences. Has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating eye diseases in adults and children.
Most often, astigmatism is hereditary. Doctors recommend conducting examinations at a child’s early age in order to promptly identify the defect. Along with it, the patient may have myopia or farsightedness.
Astigmatism does not occur or be aggravated by poor lighting, reading, or watching TV at close range.
Astigmatism
The name “astigmatism” comes from the Greek stigme (translated as point) and the negative particle “a”. Objects are distorted by an optical apparatus due to the fact that the refraction of rays in different parts of the light beam does not occur equally. As a result, the image becomes not sharp, all points of the object are displayed as blurry ellipses.
3 degrees of the disease are diagnosed:
- Weak stage up to 3 D.
- The average degree of the disease is from 3 to 6 diopters.
- Strong stage over 6 D.
Astigmatism of 1 - 1.5 D is usually not noticed by people; it does not affect the clarity of vision, being a physiological norm.
Symptoms and degrees of astigmatism
The angle of inclination of the rays can change in adults, and pathology also occurs at birth. In both cases, the signs are not always immediately visible. The picture appears depending on what stage its development is at.
Degrees of astigmatism
A mild degree of illness does not interfere with a normal perception of reality. Your vision does not need correction, but you should not refuse to visit a doctor. Since the angle by which the meridians deviate can increase from 0.75 diopters, which is the norm, to 1, and after crossing this border they already resort to therapy.
Further change signals a serious problem, manifested by:
- double vision;
- skipping lines while reading;
- blurry image from close and far distances;
- headache, which haunts the patient more and more often.
The angle of inclination can increase to 6 diopters. The pathology enters the middle stage , in which astigmatism in children and adults is corrected by wearing glasses.
When the degree is advanced, a person suffers from:
- from severe tearing;
- the appearance of burning and irritation in the eyes;
- from pain in the eyebrow area;
- due to the lack of normal focusing from any distance.
At this stage, the level of refraction (changes) exceeds 6 diopters . Wearing lenses and glasses is no longer of much use. Only surgery can improve vision. In adults, astigmatism is treated using laser correction.
The pathology may be accompanied by myopia, when the main optical focus is in the space between the retina and the lens, and myopia appears.
When these two disorders accompany each other, myopic astigmatism . Doctors believe that the cause of the development of this phenomenon is a hereditary factor, infection in the eye, or injury to the cornea.
Classification
Ophthalmologists classify astigmatism according to various parameters. For example, the disease can be lens, cornea, depending on the location of the pathological area.
According to the method of refraction in the main meridians, there are 3 types of disease:
- Direct (genetic form of the disease). Deviations appear along vertical meridians;
- With oblique axes (usually an acquired disease);
- Reverse astigmatism. Increased refraction occurs horizontally.
There are physiological and pathological astigmatism. The first form of the disease is characterized by dysfunction in the area of one diopter; in the second, the patient experiences discomfort all the time, objects do not look sharp, with blurred edges.
Astigmatism can be either independent or accompanied by farsightedness or myopia. It is divided into the following types:
- Simple, when one meridian has normal vision, and the second has farsightedness or myopia.
- Complex, with deviations in 2 meridians at the same time and is accompanied by farsightedness or myopia.
- Mixed - on one meridian there is farsightedness, and on the second there is nearsightedness.
Based on how people with astigmatism see, there are 5 types of dysfunction:
- Simple myopic (M). A combination of myopia in the 1st meridian with correct vision in the other.
- Simple hypermetropic (H). In one meridian there is farsightedness, in the other there is clear vision.
- Complex hypermetropic (CH). Farsightedness on the main meridians of the eyeball.
- Complex myopic (CM). Accompanied by myopia in the horizontal and vertical main meridians.
- Mixed (NM and MN). It is distinguished by farsightedness in one meridian and myopia in the other.
What causes astigmatism
The disease can be congenital or acquired. The reasons influencing the development of these two forms of pathology are different.
Causes of congenital astigmatism:
- Pathology of the formation of refraction of the organs of vision during the intrauterine formation of the fetus. Appears due to a violation of the genetic code or under the influence of external factors.
- Heredity. If relatives have astigmatism, the child may inherit the disease.
- Low birth weight of newborns may occur in premature infants.
Causes of acquired astigmatism:
- Injuries to the lens. Appear due to blows, rupture of the ligaments of the lens or its subluxation, penetrating wounds of the visual organ.
- Keratitis. Inflammatory diseases that cause clouding of the cornea, ulceration, and deformation.
- Corneal injuries associated with damage from foreign objects.
- Keratoconus. Not an inflammatory disease that causes thinning, but in a severe stage degeneration of the cornea of the eye.
- Pathologies and diseases of the dentofacial apparatus. Incorrect bite, inflammatory processes, and ingrown teeth can cause changes in the shape of the walls of the orbit.
- Surgical intervention. Eye surgeries, errors in suturing, increased intraocular pressure during these manipulations.
- May develop against the background of diabetes mellitus or arterial hypertension. In this case, vision correction is usually not required, since patients with astigmatism see almost clearly or the symptoms of the disease appear from time to time.
Can astigmatism be cured?
To cure astigmatism, you need to create conditions under which the correct optical focus is formed on the retina.
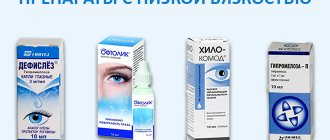
- The simplest and cheapest way that allows a person to see objects clearly, and not in a distorted image, is to wear contact lenses and glasses .
This method does not allow changing the properties of refraction and the angle of refraction. However, it is quite accessible. There are no practical contraindications; no complications occur during use. Using this traditional method, parameters are adjusted.
Contact lenses are not only invisible to others, but also make it possible to see objects in their actual size, in an unlimited field of vision.
Adults can wear glasses and lenses for astigmatism when they start working. In children, the pathology can result in complications; there is no need to remove them.
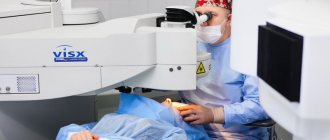
- By resorting to refractive surgery, the functions performed by the lens and cornea are changed. Thanks to this, the correct refraction angle is formed.
The most gentle intervention is laser correction of astigmatism . The price of a service may vary even in clinics of the same city. They offer to do it for a cost of 25 thousand rubles and more, up to 35. However, the operation on only one eye will result in this amount.
How does a person see with astigmatism?
How a person with astigmatism sees depends on the characteristics of the disease. According to unconfirmed data, every fourth inhabitant of the earth suffers from this pathology.
An astigmatic person sees objects a little fuzzy and blurry due to the fact that the rays of light passing through the retina of the eye are not focused at one point.
People with round-shaped eyesight are not susceptible to the disease; astigmatism develops with oval-shaped eyes.
Patients with this disease find it difficult to read for a long time; their eyes have difficulty focusing on text. Prolonged stay in a room with poor lighting provokes weakening of vision. At night, color blindness and impaired stereoscopic vision may appear. All this can result in irreversible consequences, so it is necessary to recognize alarming symptoms in time and consult an ophthalmologist.
Where does astigmatism come from?
The shape of the cornea and lens is an individual feature of a person. For some, astigmatism is congenital: such people may not even realize that there is something wrong with their vision, because from infancy they are accustomed to seeing a “blurred” picture.
For others, astigmatism develops as they age. Most often this occurs after illness, eye injury or surgery on the organs of vision.
But the idea that astigmatism can appear or worsen if you read at dusk or watch TV too close is a myth.
Symptoms of astigmatism
With all types of astigmatism, vision deteriorates; this is due to the focusing of the image not at one point, but in different parts of the retina.
Main symptoms:
- Deterioration of vision;
- Distortion of the appearance and contours of objects;
- The eyes get tired quickly;
- Squinting.
Associated conditions:
- Feeling of discomfort in the eyes;
- Migraines, pain in the frontal part of the head and the back of the head;
- Dizziness.
The main symptoms of the disease are constantly present in the life of an astigmatic person; concomitant conditions usually appear after prolonged eye strain (long reading, working at a computer). The headaches that occur differ in duration, regularity and are pulsating in nature.
If you discover one of the symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Astigmatism: types of treatment and principles of therapy
Astigmatism is a serious disease, and it is very important to begin its treatment in a timely manner. At the first symptoms, you need to contact an ophthalmologist and sign up for a diagnosis.
Treatment, or more precisely, corrective actions, are always prescribed on an individual basis, but three correction methods are usually offered:
- Glasses. The best option for children. If the degree of astigmatism is high, then the glasses will be difficult for the patient to tolerate - the head will begin to feel dizzy and the eyes will hurt.
- Lenses. A more convenient and aesthetic option, suitable for people who are predisposed to wearing them, as well as those who are able to care for them (definitely not for children).
- Operation. This is a method that does not correct vision for astigmatism, but treats it.
You can talk about the last method in more detail. The patient may be offered the following options:
- Keratomy. Suitable for eliminating mixed or myopic astigmatism.
- Thermokeratocoagulation. It is used to treat hypermetropic astigmatism.
- Laser correction. Innovative, effective technology with which you can cure almost any type of astigmatism. As a rule, it is performed on adult patients, but if a child’s pathology progresses too quickly, then the procedure may be prescribed for him.
We must remember that each case is absolutely individual. The operations are simple and almost always occur without complications. After the procedure, vision is completely restored, the patient does not have to face any restrictions - he can lead a full, active lifestyle, being the owner of healthy eyes.
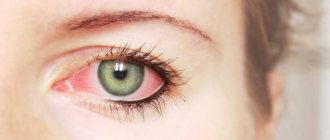
The sooner treatment is started, the better. Ignoring astigmatism is fraught with a sharp deterioration in vision and strabismus. Plus, the disease is often accompanied by pain, pain in the eyes, lacrimation, as well as chronic blepharoconjunctivitis, manifested by redness and inflammation of the eyes and eyelids.
What is the danger of a progressive disease?
Congenital astigmatism is asymptomatic in children for a long time. The picture changes when the child starts going to school. As visual stress increases, fatigue, intolerance to bright light, headaches appear, vision deteriorates, and its sharpness decreases in poor lighting.
In adults, in the initial stages, objects become slightly fuzzy, their contours blurred.
The main danger of the disease is that many people attribute small deviations in the visual image to fatigue, taking it for granted and not understanding the seriousness of the problem.
The appearance of additional signs, accompanying conditions, the inability to focus on the boundaries of an object, increased blurriness of objects indicate that the disease has begun to actively progress and it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
In the early stages, the disease can be corrected and treated; lost time can lead to strabismus, decreased vision and blindness.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease has a number of nonspecific symptoms. At the first stage, only slight blurring of vision can be observed, which can easily be mistaken for eye fatigue.
As the pathological process develops, the following symptoms begin to appear:
- burning;
- lack of clarity of vision;
- redness of the eyes;
- frequent headaches;
- double vision during prolonged visual work;
- pain;
- curvature of visible objects.
Headaches with astigmatism are pulsating in nature. If the defect occurs in a child, then while reading he may confuse similar letters or complain of a feeling of “sand” in his eyes. He may squint, turn or tilt his head to see an object.
At dusk, the quality of vision deteriorates. It is especially dangerous for such patients to drive after sunset.
REFERENCE. Increased sensitivity to light is accompanied by pressure on the eyes, which interferes with leading a normal lifestyle.
If the first symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor. He will conduct an examination and select the appropriate correction method. Particular attention should be paid to the behavior of a young child who cannot report vision problems.
Diagnostics
The final diagnosis is made by an ophthalmologist based on comprehensive studies of the state of visual functions of the eye. Modern techniques are used to identify the disease, its type and stage.
- Visometry. The most common type of diagnosis to check visual acuity. The person being tested is fitted with a diagnostic frame in which one eyepiece is covered with a light-blocking material. Cylindrical lenses of different refractive powers are placed opposite the open eye, and the one at which vision will be as sharp as possible is selected.
- Shadow test or skiascopy. A method for determining the degree of refraction using cylindrical and spherical lenses, illuminating the pupil and studying the light reflex on it.
- Refractometry. Accurate measurements of the refractive power of the eye and refractive errors with an automatic computer refractometer.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye. It makes it possible to identify pathologies of a dystrophic, inflammatory and post-traumatic nature.
- Ophthalmoscopy. Examination of the fundus in detail, making it possible to visually assess the degree of transparency of the optical components of the eye.
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision. It is carried out using devices with high-frequency sound waves. Allows you to identify pathologies and neoplasms.
- Computer keratotopography. Determines the presence and degree of corneal astigmatism and keratoconus.
Based on the examinations of the patient, the doctor determines what exactly caused the disease, makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
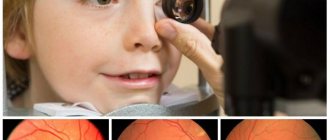
Clinical diagnosis of astigmatism in children
Only an ophthalmologist can diagnose a visual impairment such as astigmatism in a child during a face-to-face appointment. Diagnostics is carried out using devices such as a cylindrical lens and an autorefractometer. Together with the cylindrical lens, special plates are used, which depict various symbols. Of course, this is an extremely dubious method for diagnosing astigmatism in infants, but at 3-4 years old a child will already be able to say that he does not see some images on the tablet.
If the visual impairment is natal in nature, that is, the child sees poorly from birth, the diagnosis can be complicated: he doesn’t even know that he should see the world differently. And at the same time, time in this case is not an ally at all: congenital disorders can worsen with age. That is why it is necessary to adhere to the schedule of visits to the ophthalmologist and not neglect unscheduled visits if something bothers you. The child should visit the doctor for the first time at 2 months, and then the schedule of examinations is as follows:
- 6 months;
- 1 year;
- 3 years;
- Then once every 2-3 years for prevention.
If a child is diagnosed with astigmatism (or any other mild visual impairment that does not require surgical treatment), he will have to start wearing glasses. In this case, the next appointment with the ophthalmologist will be scheduled in a couple of months to assess how well the glasses made are suitable for the child and how the body responded to the change in vision.
If there is no improvement, the doctor may prescribe a pleoptic. This is a hardware vision correction procedure that should be performed 2-4 times to achieve a lasting result.
Further, if astigmatism is diagnosed, the child’s vision should be checked every 3-6 months to monitor changes until the body is fully formed (18-20 years).
To diagnose astigmatism, a specialist will need to check:
- Intracranial pressure
- Visual acuity without glasses (with selection of glasses)
- Eye length (to determine the degree of myopia)
- Refraction of the eye and degree of myopia
If refractive surgery was performed, diagnostic methods are supplemented with procedures such as ophthalmoscopy, keratopachymetry, abberometry, and keratotopography.
To determine the presence of astigmatism, an ophthalmologist collects an anamnesis and then conducts a comprehensive vision assessment, performing the following procedures:
- Examines the eye and its structure;
- Performs skiascopy (shadow test, for which spherical and cylindrical lenses are used);
- Performs refractometry (a procedure for which it is necessary to dilate the pupil artificially using drops);
- Performs ophthalmometry (measures the length of the eye);
- Performs biomicroscopy (a procedure that helps determine the cause of astigmatism and its degree);
- Performs ophthalmoscopy (procedure to examine the vitreous body)
In some cases, an ultrasound of the eyes or a visit to other specialists (neurologist, surgeon, etc.) is required.
Treatment of astigmatism
To treat astigmatism, the patient is prescribed lenses or glasses; in difficult situations, laser or microsurgical correction is performed.
- Glasses. They do not have a therapeutic effect, but provide clear visualization of objects. Correction consists of personal selection of glasses with suitable lenses. Usually prescribed in the initial stages of the disease for simple myopic and hypermetropic astigmatism.
- Lenses. They have the same functions as glasses, but have a number of advantages. Thanks to their tight fit to the surface of the eye, they improve both central and peripheral vision, allowing you to see the image brighter and clearer than glasses.
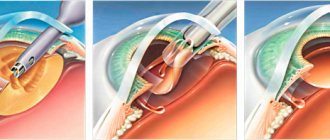
- Surgical intervention. Replacement of the lens with artificial contact lenses of toric (spherocylindrical) or spherical shape. It is performed in case of mechanical damage, pathology or deformation of the lens.
- Laser correction. The affected areas of the cornea are removed using a laser, its refractive power is corrected, and an artificial lens is implanted. Micro-incisions are applied to the cornea, weakening the strong meridian along the periphery. The most common LASIK technique. The surface layer of the cornea is separated with a laser, smoothed, and placed in its original place. This method is the least traumatic and is rarely accompanied by complications. Vision improves 2-3 hours after completion of the correction.
Treatment
The treatment method is selected depending on the results of the diagnostic examination. For this, modern equipment is used, which allows you to accurately determine the degree of deformation and other damage.
At the initial stage, correction without surgery will be sufficient.
This may include wearing glasses, contact lenses and performing a set of exercises using special devices.
Glasses and contact lenses are not a treatment option, but a visual correction. It is impossible to cure astigmatism without surgery.
An ophthalmologist prescribes wearing glasses with complex cylindrical lenses. They correct corneal pathology by refracting light rays only in the place where the astigmatism is located. This type of correction product is prescribed for mild cases.
In more complex cases, spherocylindrical lenses are selected. They allow you to get rid of several ophthalmological problems at once.
Wearing them can cause dizziness and pain in the eyes. A high-quality product must fully comply with the characteristics of the cornea. Otherwise, you can only make the situation worse.
Initially, the specialist selects weaker glasses so that the patient can quickly get used to them and not suffer from side effects. After 4-5 months, they need to be replaced with stronger ones, and only then products for complete correction are prescribed. The doctor should take into account the following indicators:
- cylinder axis according to the Tabo scale;
- the strength of glass;
- optical power of the cylinder.
It is quite difficult for an adult to adapt to such glasses. It is especially difficult if the cylinder strength exceeds 2 diopters. The brain will have great difficulty perceiving the resulting images. It takes quite a long time to get used to.
If previously only rigid contact lenses were used to correct astigmatism, now flexible ones are used.
REFERENCE. When wearing contact lenses, it is recommended to undergo regular examinations to monitor the dynamics of the development of the defect.
Pros of contact lenses:
- possibility of correction of high corneal astigmatism;
- minimal distortion and change in the field of view;
- creating conditions for normal vision with both eyes;
- minimizing optical aberrations and prismatic effect.
Despite the many benefits, contact lenses can cause inflammation. Tonic products have increased thickness. The addiction process takes longer and unpleasant sensations may be present.
Chronic oxygen deficiency can aggravate myopia. Many patients who wear tonic lenses experience changes in the shape of the cornea.
Exercise for the eyes
Astigmatism affects the structure of the eye; it is not possible to completely restore vision with physical therapy, but you can slow down the rate of progression of the disease. How do astigmatists see? When trying to see an object, the eyes are subjected to high loads, pain and burning occur in them. Some eye muscles are subject to excessive stress, while others do not participate in the process at all.
Eye exercises are designed to compensate for the imbalance, give the tired people the opportunity to relax, and load unused muscles with work.
Bates method
It is used for diseases accompanied by farsightedness or myopia.
- The patient is shown a card with a letter written on it;
- Then close your eyes completely with your palms for 10-20 seconds and relax all the facial muscles. It is necessary to mentally imagine the letter;
- The eyes open and look at the card again. The letter will look clearer;
- The exercise is performed several times, first for two eyes, then for the left and right eyes in turn.
Gymnastics for the eyes, borrowed from yoga
It is done for most types of disease.
- Close your eyelids, relax your eye muscles and imagine a rainbow;
- Concentrate separately on each color of the rainbow, imagining it for at least 2 seconds. You must try to see all 7 colors bright and saturated.
Eye movements
- Close your eyes tightly for 2-3 seconds;
- Blink quickly for 60 seconds; if dizziness begins, you can reduce the time to a quarter of a minute;
- Look alternately right, left, up and down;
- Look at objects close up, look into the distance;
- Slowly make rotational movements with your eyes, first counterclockwise, then clockwise;
- Close your eyelids, relax your eye muscles for 3-5 seconds;
- Repeat the exercise several times.
To prevent and alleviate the symptoms of astigmatism, eye exercises are combined with a healthy lifestyle. Long walks in the fresh air promote good hydration of the mucous membranes of the eyes, preventing dryness, discomfort, and burning in the eyes. A balanced diet helps supply the visual organs with substances important for normal functioning.
Health is in your hands
Having understood how people see with astigmatism, we can conclude that this is a serious pathology of the visual organs, which leads to strabismus, visual impairment or complete blindness. The danger of the disease is that it develops asymptomatically for a long time, and then quickly begins to progress.
Regular examinations by an ophthalmologist and contacting specialists when the first alarming symptoms appear will help avoid tragic consequences. The combination of proper treatment, a healthy lifestyle and regular eye exercises recommended by doctors will help preserve your vision and see the world around you clearly and clearly in all its colors.