Classification of retinal dystrophy
Retinal dystrophy is divided into two large types. These are hereditary and acquired forms of the disease. If we talk about hereditary dystrophies, then destruction occurs at the level of receptors that allow vision in the twilight. The following types of hereditary lesions are distinguished:
- Generalized - degeneration of the pigment type, congenital blindness or lack of night vision, impaired or absent color perception.
- Peripheral - retinal separation due to the characteristics of chromosomes, damage to connective tissue, dysfunction of the rod and cone systems.
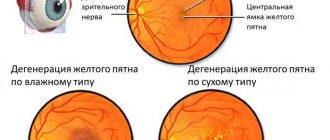
- Central - hereditary macular degeneration with the appearance of spots or yellow lesions, dystrophy against the background of age-related changes.
If we talk about the secondary (acquired) form of retinal dystrophy, it is also divided into peripheral and central. The disease of the central type is in turn divided into wet and dry manifestations of dystrophy. In the first case, the formation of new vessels is observed in the affected area. They are very fragile, so elements contained in the blood leak through them. As a result, edema forms and the light-sensitive elements of the visual organs are damaged. This disease is severe, so increased attention is paid to its treatment.
Dry central retinal dystrophy occurs in 90% of cases. It becomes the result of a metabolic disorder. In this case, accumulations of products involved in metabolism form between the retina and the vessels.
Peripheral dystrophy
This manifestation is typical for myopic people and very often leads to retinal detachment. There are two types of peripheral dystrophy: chorioretinal and vitreoretinal. Peripheral chorioretinal dystrophy (PCRD) affects the membranes of blood vessels. Peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophy (PVCRD) affects the condition of the cornea. In addition, peripheral dystrophy can be cystic, frost-like and lattice.
Retinal detachment - what is it?
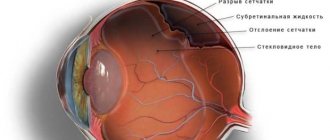
Retinal detachment is a dangerous condition in which, under the influence of many factors, its pigment layer is separated from the neuroepithelium (rods and cones). This process can be painless. Therefore, sometimes the patient does not suspect eye pathology for a long time. This is what leads to irreversible loss of vision.
Restrictions that remain after the recovery period
To avoid recurrent retinal detachment, it is necessary to adhere to a number of restrictions even after the end of the recovery period. In particular, sports involving jumping, pushing, hitting, and sudden movements are contraindicated. These include horse riding, running, long and high jumps, and almost all types of martial arts. There is no ban on swimming, but you must use safety glasses while swimming.
In some particularly difficult cases, even after a period of rehabilitation, the ban on bending and lifting heavy objects remains. In addition, it is necessary to regularly visit an ophthalmologist and monitor the condition of the eyes to prevent re-detachment.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Causes of retinal dystrophy
The causes of dystrophic changes in the retina can be the following factors:
- Scar formation as a result of disruption of the vascular system or decreased local immunity.
- Non-compliance with diet and consumption of unhealthy or low-quality food.
- Bad habits, in particular smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Negligence in the treatment of infectious diseases.
- Presence of chronic diseases. This could be diabetes, blood pressure surges, diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
- Eye surgeries.
- Obesity as a result of metabolic disorders.
These manifestations worsen the condition of the circulatory system and slow down metabolic processes. Because of this, the retina is affected. Here's what they say about the causes of retinal dystrophy on the Internet:
Types of retinal detachment
There are central and peripheral retinal detachments.
- With peripheral or marginal vision, deterioration and loss of vision begins around the circumference, that is, from the edges. In the morning the symptom is usually mild and intensifies in the evening.
- Central is characterized by the loss of words, letters, and entire parts from the text being read.
It can also be mobile and rigid.
- Mobile – a milder condition in which, with bed rest for several days, the detached part fits into place.
- Rigid is an unfavorable form of the disease in which such adhesion is absent.
Symptoms of retinal dystrophy
Common signs for all types of retinal dystrophy are the following manifestations:
- Absence or decreased color perception.
- The appearance of image defects (floaters, lightning, flashes, fog).
- Loss of central vision.
- Perception of objects located to the side as a fuzzy picture.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Loss of sense of movement. An object at rest is difficult to distinguish from one that is moving.
- Need for excessive light while writing or reading.
If we talk about individual forms of the disease, peripheral dystrophy is expressed by the appearance of flashes and dots before the eyes. Damage to the macula is accompanied by curvature of the visible lines. Dry retinal dystrophy distorts visual images. The patient cannot work with small objects and fonts. He has difficulty seeing in the dark and distinguishing faces.
Here is one example of the development of retinal dystrophy and its treatment:
In most cases, the manifestation of symptoms is characteristic of one eye. In addition, the initial stages of retinal dystrophy occur unnoticed. Having discovered the first signs indicating the onset of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Retinal dystrophy during pregnancy
During pregnancy, retinal dystrophy occurs due to decreased blood flow to the eyes as a result of low blood pressure. If the development of the disease is not stopped in time, it can lead to retinal rupture or detachment. To avoid such consequences, a planned caesarean section or laser coagulation procedure is performed. Laser coagulation is prescribed before the 35th week of pregnancy. The procedure involves creating a reliable connection between the choroid and the retina. The result of such an intervention is to reduce the risk of complications on the visual organs during natural childbirth.
What symptoms may indicate detachment?
In order to notice the beginning of detachment in time and consult a doctor, you need to know the symptoms of this disease:
- Black flashing spots and dots before the eyes that persist even after a long sleep.
- Bright flashes before the eyes. May appear as light spots or lightning.
- Retinal detachment can lead to image distortion. People with this diagnosis often see straight lines as curved, and perceive stationary objects as shaking or blurry.
- Visual acuity decreases, deterioration progresses quickly over a short period of time. If the detachment is massive, complete loss of vision can occur in a matter of hours.
- Fog before the eyes, dark spots and lines can also indicate detachment. Blind spots are the detached areas of the retina, which has stopped transmitting light impulses to the brain. If a person does not see a doctor immediately, dark spots in the field of vision gradually expand.
- Reduced visual field. This symptom can manifest itself as a so-called marginal detachment, when vision loss begins from the periphery.
- Letters and words falling out of the visual field when reading. The sign indicates that the detachment has affected the central zone of the retina.
If you notice even one of the listed symptoms, do not delay visiting a doctor. There are no conservative methods for treating retinal detachment; in any case, you will need surgery. But with early diagnosis, treatment will be simpler, and the chances of maintaining vision will be higher.
MagazinLinz.ru team
How is retinal detachment diagnosed?
Only an ophthalmologist can determine retinal detachment. One of the most important methods for diagnosing retinal detachment is the following:
In the photo (top left, clockwise) are examples of diagnosing retinal detachment: computer perimetry, tonometry, electrophysiological study (EPI), ophthalmoscopy
- Determination of visual acuity - to determine the center of the retina.
- Using computer perimetry, we examine visual fields and determine peripheral vision.
- We perform tonometry - we measure the patient's intraocular pressure.
- Electrophysiological study - to determine the viability of retinal and optic nerve cells.
- Direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy - an ophthalmologist examines the fundus of the eye, which allows you to determine the location of the ruptures, their number, and detect thinned areas in order to avoid further retinal ruptures.
After carrying out all diagnostic methods, the ophthalmologist can make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Identifying dystrophy and making a correct diagnosis involves conducting the following studies:
- Checking visual acuity (visometry).
- Identification of the visual field (perimetry).
- Check for distortion of visible lines - Amsler test.
- Detection of abnormal deviations in the refraction of light rays (refractometry).
- Biomicroscopy.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Determination of the degree of color perception.
- Electroretinography.
- Determination of the degree of adaptation of visual functions in the dark (adaptometry).
- Finding affected areas.
- Retino- and coherent tomography.
- Ultrasonography.
- Collection of analyses.
Depending on the clinical picture, the patient is prescribed a consultation with doctors of other specialties.
Operative methods
For rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, the following methods are used:
- Extrascleral. These include ballooning and filling.
- Endovitreal - vitrectomy.
- Cryocoagulation of ruptures.
- Laser treatment.
Extrascleral methods are effective only if the rupture, which resulted in a detachment, occurred recently (up to 1 month).
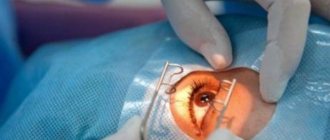
Ballooning is an operation that is performed on the surface of the tunica albuginea (sclera). The essence of the method is as follows: the surgeon identifies the location of the rupture and, accordingly, the detachment. After this, he sews a balloon made of elastic material to the tunica albuginea. This small container is then filled with gas or liquid. Gradually, an indentation area forms on the eyeball. Thanks to this, the membranes come together, resulting in the elimination of rhegmatogenous detachment. The operation is effective if no more than 1 of the 4 quadrants of the retina is affected.
Filling is a type of surgical intervention that is also performed on the surface of the tunica albuginea. At the diagnostic stage, the doctor determines the location, shape and size of the exfoliated area. Based on this information, a filling is made, consisting of a biocompatible material. As a rule, sponge silicone is used in ophthalmology clinics.
In case of retinal detachment, the operation is performed as follows: the surgeon makes an incision in the conjunctiva, through which a seal is applied to the site of the tear. After this, it is fixed with sutures. If the pathology is accompanied by severe swelling, drainage is performed. The final stage is suturing the conjunctival incision.
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure during which the vitreous body is partially or completely removed. Instead, a substance with similar properties is introduced. This method is considered minimally invasive, since a minimum of perforations are made during the operation.
Cryocoagulation of fractures involves the use of low temperatures. The operation algorithm is as follows: the doctor drops an anesthetic drug into the patient’s eyes, while it begins to act, the surgeon lowers the cryoapplicator into liquid nitrogen. The latter is then placed on the eyeball. Through the use of ultra-low temperatures, a high penetration rate is achieved, while there is no effect on the tunica albuginea and muscle tissue. Cryocoagulation can be considered both as an independent and as an auxiliary method of treating rhegmatogenous detachment.
Laser treatment is also carried out under local anesthesia. This is a modern method, which is considered the safest due to the minimal risk of complications. In case of retinal detachment, the operation is carried out according to the following algorithm: the doctor directs a high-precision laser beam to the lesion, which promotes the fusion of the vascular and nerve membranes. The doctor monitors the progress of the operation using a microscope. Its duration is about 20 minutes, after it the patient can immediately begin his daily activities.
Treatment and prevention of retinal detachment
Surgery is the only correct method of treating retinal detachment, the effectiveness of which increases significantly if the intervention is carried out in the early stages of the pathological process. In this case, the likelihood of restoring trophism and, accordingly, vision increases. The main task of the doctor performing the surgical process is to block the existing gaps as much as possible and thereby contribute to the restoration of lost connections between the separated areas. If, as a result of an accident, a head injury occurs, as well as damage to one or two organs of vision, contacting a medical facility in order to prevent retinal detachment should be immediate. There are several types of operations aimed at eliminating the problem: extrascleral, endovitreal and laser.
Extrascleral surgical intervention means the surgeon’s work purely on the surface of the sclera (methods of extrascleral filling and ballooning).
Endovitreal methods for repairing retinal tears involve manipulations performed inside the eyeball, during which the gelatinous transparent substance is partially or completely removed, allowing the surgeon to gain access to the posterior wall. The removed vitreous is subsequently replaced with a hypoallergenic, non-toxic, long-term material that has the necessary strength and viscosity - in most cases, bubbles with gas or oil, special saline solutions or artificially created polymers are used.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy
The standard treatment regimen for dystrophy using medication looks like this:
- Drugs that strengthen and dilate blood vessels. The dosage of Complamin, Noshpa, Papaverine or Ascorutin is selected individually for each patient.
- Medicines to prevent blood clots. This may be Aspirin, Ticlodipine or Clopidogrel.
- Vitamin B, administered intramuscularly, and a complex of other vitamins in tablet form.
- Medicines that prevent the formation of new painful blood vessels (Lucentis).
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs.
- Means for improving metabolism inside the eye. Injected intravenously or directly into the structure of the visual organs.
- Retinalamin, injected into the lower eyelid or eye shell for 10 days.
- Eye drops that speed up the healing process and metabolism.
Conservative treatment is complemented by physiotherapy. The patient is prescribed procedures such as photo- and electrical stimulation, electrophoresis, and magnetic therapy. If we talk about the use of small doses of laser radiation, they are used to influence the retina and blood.
Laser treatment
The laser beam extends its effect directly to the affected areas of the visual organs. They are exposed to irradiation in order to stimulate and start the metabolic process. The laser is able to strengthen blood vessels through their coagulation and separate affected areas from healthy ones, thereby stopping the spread of the disease. This process involves soldering defective tissues.
Surgery
If conservative and laser treatment methods do not help to cope with retinal dystrophy, the doctor decides to prescribe surgery. Depending on the complexity of each case, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- Revascularization – restoration of blood vessels.
- Vasoconstruction is a narrowing of the spaces between blood vessels.
- Vitretomy is complete or partial removal of the vitreous.
After surgery, it is necessary to take measures to help quickly restore visual functions. You need to make sure that your eyes are not overstrained, wear sunglasses outside, and take vitamins. In addition, it is necessary to stop smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Traditional methods of treating retinal dystrophy
Traditional medicine recipes for dystrophy should be used in conjunction with the main treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor. The following remedies have a good effect:
- Goat milk diluted with boiled water in equal proportions. Within a week, the resulting solution is dripped into the eyes, then covering them with a dark cloth. As a result, the process of retinal detachment will stop.
- For a month, drink half a liter of decoction per day. To prepare it, take 5 parts of pine needles, 2 parts of rose hips and onion peels. They are poured with boiling water and cooked for 10 minutes.
- A decoction of cumin and cornflower flowers is instilled into the eyes 2 times a day.
- For a month, a decoction of celandine is instilled into the eyes 3 times a day.
- Tinctures of birch, horsetail, lingonberry, and mustard are taken orally.
- Wheat grains are left to germinate in a warm place. The embryos grind and eat the resulting mixture.
- For 9 days, a decoction of mumiyo and aloe juice, boiled in proportions of 5:1, is dripped into the eyes.
Before using folk remedies, you need to consult a doctor and make sure that the components of the decoctions do not cause allergic reactions.
Please note: If, when a disease is detected, you refuse the help of a doctor and self-medicate, the disease may develop to a severe stage. It can lead to complete loss of vision, which is characterized by the irreversibility of the process.
Types of surgical intervention
The disease can be cured with laser, filling, or open surgery. The intervention is carried out immediately.
The main goal is to restore the structure of the membrane by bringing light-sensitive cells closer to the pigment epithelium. No retinal replacement is required.
Vitrectomy (removal of the vitreous)
It involves partial or complete removal of the vitreous body and replacing it with an artificial material (silicone, gas or solution). Microsurgery is indicated for retinal tears, retinopathy due to diabetes, and total retinal detachment.
The intervention proceeds as follows:
- make 3 small incisions;
- install an irrigation system (a device for circulating fluid);
- the vitreous body is removed;
- carry out tamponade;
- apply a suture.
Vitrectomy is contraindicated in cases of high intraocular pressure (glaucoma), malignant tumors, and coagulopathy.
Vitrectomy is one of the types of surgical intervention in the treatment of retinal detachment.
Extrascleral filling
It involves a mechanical effect on the retina with a filling (sponge). Filling can be radical, circular and sectoral. It is contraindicated in case of hemophthalmos (accumulation of blood in the eye), vitreous opacification. Preparation includes regional anesthesia or general anesthesia (in the secondary form of the disease).
The operation requires:
- silicone sponge;
- suture material;
- microsurgical scalpel;
- powerful lamp.
First, an incision is made, then the muscles are fixed and marking is carried out using the coagulation method. The filling is fixed with a mattress suture.
The most gentle method is laser coagulation
Patients ask whether it is possible to restore the retina with laser. Yes, laser coagulation is used.
This is a minimally invasive procedure. Indications: peripheral dystrophy and rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.
Contraindications include gliosis (layering of cells), clouding of eye structures, cataracts, and hemorrhages. The doctor installs the lens, focuses the rays and applies coagulates.
Pneumatic retinopexy using a gas bubble
During the procedure, the doctor introduces an air bubble into the eye, which causes the retina to be pressed and secretions to leak out. A laser or freezing device is then used to seal the gap.
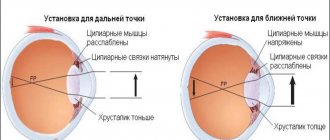
What causes farsightedness in children
Children's farsightedness, along with strabismus and amblyopia, is one of the most common vision disorders. Children are born farsighted, but this problem usually corrects over time.
How is hypermetropia treated in children, does it create any restrictions?
Characteristics of farsightedness
According to ICD-10, each disease and disorder has its own code. Hyperopia – code according to the international classification system ICD-10 – H52.0.
Farsightedness - what is it? First of all, it is important to know that hypermetropia is not a disease. This is a disorder characterized by changes in the shape and size of the eyeball. The most common is axial childhood farsightedness, which is characterized by a deviation in the anteroposterior axis of the eye. We can say that farsighted visual organs are considered as not fully developed and are characterized by a delay in their growth.
At birth, almost every person is equally farsighted, and as the entire body grows, the sagittal length of the organ of vision increases. In newborns, the average eye length is about 18 mm, at two or three years old it is already 23 mm. From 4 years to 14 years of age, a child's growth slows down by about 0.1 mm per year. The length of the eyeball in older age is about 24 mm, which does not apply to hypermetropia of both eyes - in this case the length is shorter. The deviation value determines the degree of disorder. Degrees in children and adults are classified as follows:
- low degree hyperopia (plus 2 diopters, +2D);
- moderate hyperopia (plus 5 diopters, +5D);
- high degree hypermetropia (plus 5 diopters and above).
The treatment of farsightedness in children and the choice of correction method depend on the degree of the disorder (the first degree, as a rule, does not require correction; special exercises are used).
The shortening of the anteroposterior axis of the eye rarely exceeds 2 mm. A decrease in length of one millimeter represents a change in refraction of about plus 3 diopters.
Important! Improvement in vision (in most cases) during childhood distinguishes hyperopia in children from age-related farsightedness, called presbyopia.
Farsighted newborns and vision development
Natural farsightedness in children is associated with the shape of the eyeball. Newborns have imperfect vision at birth. Their eyes are immature and they do not perceive the outside world clearly. Therefore, there is no point in talking to them at a distance greater than 25 cm - they will see you blurry. Gradually, slowly, the baby builds eye contact with the people around him. Soon he can look at the offered toy, and at about 2 months he will begin to follow it with his eyes. Sometimes it happens that one eye squints, but for 6 months there is no need to worry - during this time, children's eyes develop, the interaction of both eyes and the visual centers in the brain. Thus, farsightedness in children under one year of age does not require correction. If a one-year-old child continues to have some degree of impairment, some restrictions on eye strain are needed. Doctor E.O warns about this. Komarovsky, who also recommends spending time with your baby outside more often - this will help speed up the improvement of vision.
At the age of six, a small person can see as well as an adult. Before this time, however, errors may occur that can disrupt the normal development of vision. During their stay in the maternity hospital, newborns are screened for cataracts as part of a general examination. The critical period for visual development is the first year of life, when binocular vision begins to form.
As mentioned, congenital farsightedness in children is normal. In only about 6% of young patients, hypermetropia values remain elevated, which can lead to strabismus and amblyopia in later life. These disorders are usually diagnosed before age 8. Vision development is completed during puberty, around 15 years of age.
Development of the disorder
In the case of farsightedness in children, the eye is unable to focus vision at close range. In general, this disorder manifests itself in such a way that a person has no problems contemplating distant objects, but cannot focus his vision on close objects. Farsighted people may have problems with reading and writing, cutting, gluing...
Farsightedness in children 1 year of age is most often caused by congenital shortness of the anteroposterior axis of the eyeball. Light rays are refracted behind the retina, not on it.
Important! Since the eyes are able to partially compensate for this problem by increasing accommodation, farsightedness may not be obvious in children under 3 years of age.
The disorder causes increased fatigue and headaches from excessive accommodation. Defective vision, like any ophthalmological disorder, can cause slow psychomotor development. Therefore, parents with farsighted children should consult an ophthalmologist. If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe a correction.
What causes hypermetropia
Genetic predisposition is responsible for many cases of refractive disorders, which include hypermetropia. But people also suffer from farsightedness of any degree, without having a genetic predisposition to this disorder.
In addition, environmental factors play a certain role in the development of farsightedness and its degree. However, heredity remains the best known cause, especially for the higher forms of this disorder (as well as other ophthalmic diseases).
The following factors involved in the formation of farsightedness are:
- flat cornea;
- insufficient refractive value;
- small lens thickness;
- congenital small visual organ (microphthalmos);
- short length of the sagittal axis of the eye;
- exposure to certain medications;
- injuries.
Farsightedness can also be caused by certain diseases (cancer, retinal detachment, etc.). In older people, provoking factors are decreased lens refraction and diabetes. Backward displacement of the lens due to illness or injury, aphakia (lack of an intraocular lens - lens) can also cause hypermetropia.
How to determine farsightedness in a baby
All parents should be attentive, especially in families where there is a history of visual impairment. There is a high probability of inheriting an ophthalmic disorder. Many parents, however, focus on the disorder when children start school, and problems with schoolwork may arise.
Farsightedness in a 2 year old child can be expressed as follows:
- while playing, he brings objects closer to his eyes, changes the viewing distance;
- when drawing, tilts his head over the table;
- the baby has an unnatural head tilt - in this way he can compensate for strabismus;
- periodically closes one eye;
- farsighted children quickly get tired when performing activities at close distances;
- they do not focus on details (pictures, toys);
- sit as close to the TV as possible;
- mistakenly determine the location of objects.
Important! If in any doubt, consult your pediatrician or ophthalmologist. He will assess the presence and extent of the disorder at an early age, and recommend opportunities for improvement.
How to help your baby
Below are some tips that you can follow to help maintain your eye health and vision.
- Daily Exposure to Natural Daylight – Scientific research indicates that everyone should spend at least 30-60 minutes a day outdoors in natural daylight. This rule does not mean direct exposure to sunlight!
- Limit watching TV and playing on the computer. They are sources of artificial light, which directly affects the quality of impaired vision. The maximum period for TV/computer is 30 minutes/day in total.
- Include physical activity in your daily routine. The type of activity does not matter - oxygenation of the body is important, preferably in the open air.
- If your child already wears glasses for farsightedness, let him take them off whenever possible.
- Provide a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Include as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible (especially leafy green vegetables - spinach, cabbage, lettuce, etc.). Avoid white sugar (sweets, carbonated drinks) - it can be replaced with cane sugar. Make sure you stay hydrated.
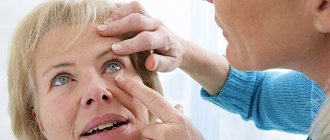
Contact lenses and glasses
At what age can you wear contact lenses? Age is not a limiting factor in the use of contact lenses, it is a personal matter, depending on the particular child, his motivation, responsibility and ability to use contact lenses. Treatment of farsightedness in young children involves wearing glasses; children in the older age group can use lenses.
Lenses are usually worn throughout the day. The mode of wearing glasses is determined by the doctor depending on the specific condition. Usually, with low degrees of farsightedness, you can wear glasses only at school; in cases of moderate or severe impairment, you may have to wear them constantly. An important role is played by the presence of associated strabismus, amblyopia or astigmatism - for these disorders, correction is mainly permanent.
Farida Yukelson
Before classes: macular degeneration of the right and left eyes, progressive retinal detachment of the left eye.
After: the macular spot in both eyes is normal, the retinal fit is normal.
Lesson period: 3.5 months.
I have never worn and do not wear glasses; I am a dentist by profession. Now I am a pensioner, I’m almost 80. Last September my eyesight began to deteriorate significantly. When I went to see an ophthalmologist, he sent me to a doctor who examines the fundus of the eye, a retinadictor (20 years ago I left Russia and live in Chicago). Here in America, doctors have a very narrow specialization and each deals with their own range of issues.
He diagnosed macular degeneration in both eyes and said that moisture had already begun to accumulate in the left eye. This is a very serious signal (retinal detachment has begun, editor’s note) and I was offered injections in my eyes. At first I didn’t agree, but since my vision was deteriorating and I didn’t want to lose it, I went for injections for three months, starting in September. I didn’t feel any particular results and didn’t go for the injection in December. I went to the doctor in January, and he said that nothing was changing and that without injections my vision might disappear.
Since I did not feel the effect of the injections and was concerned about the prospect of losing my vision, I began to act.
I have taken at least six or seven online courses related to eyes. It's just with the eyes! I went through Zhdanov, Peychev, Shvedova and everything else that is on the Internet. In my opinion, there is nothing left. Norbekov, of course, it all started with him. And you know, something was missing everywhere. They all had some twist that I liked, but I wasn't happy with the overall results.
Then I made an appointment with Fedor and decided to study here again. I did qigong in January, February, March and I really liked it, it turned out to be interesting and no one had it.
And for the first time, if before I only supported my vision, here I got an improvement!
Firstly, I really liked working with energy and working with entities (a type of exercise, editor’s note). Somewhere in May we talked, I said that there was such a problem and Fedor suggested starting to stand in a pillar for 30 minutes (one of the qigong techniques, editor's note). I really did this and other exercises throughout May. When I went to see the doctor in June, they were shocked! He says: “You have no moisture in your eye!”
With your compatriots in our amateur musical theater Welcome
It all depends on the person. Any exercise can be effective only when a person himself strives and believes, and water does not flow under the lying stone.
If you don’t do anything yourself, you won’t get anything! The doctors are surprised: “I don’t know, they say what you’re doing, but we’ll see!”
Prevention of retinal dystrophy
In order to reduce the risk of developing retinal dystrophy, you must follow these rules:
- Make sure your work area is properly lit.
- Any load on the visual organs should be accompanied by periodic rest.
- It is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist once a year.
- The diet should consist of foods containing vitamins and microelements necessary for normal metabolism.
- You need to give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
Massage and exercises strengthen the visual organs and normalize blood flow to them. Watch your health. Contact your doctor at the first signs of the disease to begin treatment on time.
The role of nutrition in strengthening the retina
Solarization, laser therapy, gymnastics - all these means can improve vision, but at the same time you need to monitor the health of the entire body as a whole.
In particular, to strengthen the retina, it is necessary to adhere to a balanced diet that ensures the supply of vitamins and elements:
- Blueberry. Blueberries should be included in your diet. This berry is considered one of the most effective preventatives for preventing cataracts and glaucoma. It protects retinal cells from age-related and physiological changes. This is possible thanks to the anthocyanidins contained in the berries. Blueberries relieve eye fatigue and allow you to see better in low light. It contains antioxidants that strengthen the retinal capillaries. They also play an important role in preventing or treating macular degeneration.
- Omega-3. Omega-3 fatty acids have a positive effect on eye health. This is due to the fact that retina contains docosahexaenoic acid. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in large quantities in fish. Based on experiments, it has been proven that patients who use it several times a week are less likely to encounter the problem of weakened vision. You can also compensate for the lack of fatty acids with the help of nuts and olive oil.
- Ginkgo biloba. Ginkgo biloba helps get rid of free radicals in the retina, and therefore strengthen it. Taking this drug 2 times a day can increase visual acuity and improve its quality, increase blood circulation in the optic nerve.
- Vitamin A. Vitamin A, which is one of the elements of the visual pigment of the retina, is also important for eye health. It is found in large quantities in red palm oil - 5 mg in 1 teaspoon. Sources of vitamin A are also sorrel, carrots, and fish oil.
Development mechanism
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is a multifactorial disease. This is a primary pathology resulting from rupture of nervous tissue.
There are two main mechanisms for the development of the disease:
- The occurrence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment against the background of thinning of this layer. As a rule, this condition appears during the natural aging process of the body. For many people, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, but at the same time it can pose a health hazard. Over time, end-to-end defects form on the retina, through which fluid from the vitreous body begins to penetrate under it, causing detachment. In addition, often zones of dystrophy appear after injury to the eye.
- The occurrence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment due to tension. The vitreous body is a gel-like substance that is 99% water. It is very tightly connected to the retina at the base of the latter, most weakly in the areas of localization of large blood vessels. During the natural aging process of the body, the vitreous body liquefies and the retina stretches. As a result, detachment occurs, which is not always accompanied by tissue rupture.
Since the disease is multifactorial in nature, in most cases both mechanisms are detected in patients at once. The risk of rhegmatogenous eye detachment increases significantly under the influence of provoking factors.
Causes of retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is a rapidly progressive process, usually starting in the peripheral part and accompanied by a decrease in the clarity of lateral vision. Due to the characteristics of the initial stages of the disease, it is quite difficult to diagnose it at an early stage. However, if you do not seek help from specialists in time, the detachment can gradually spread to the macula (the center of the retina), as a result of which central vision will be impaired.
Retinal detachment is a serious problem faced by many people around the world. Ophthalmologists note a systematic increase in the number of patients with this disease from year to year. This pathology involves a loss of connection between the retina and the choroid. The trophism of the retina is provided by the vessels located underneath it. In the case of detachment, nutrition and oxygen supply are forced to stop, which leads to varying degrees of disruption in the functioning of the visual apparatus.
Without proper treatment, retinal detachment progresses from minor to obvious symptoms. A negligent attitude to the problem can lead to blindness, and the corresponding changes occur in just a few days, and sometimes a couple of hours are enough. As a rule, a patient diagnosed with this disease is offered surgery. Otherwise, there is a risk of loss of vision in the affected eye.
There are cases when retinal tears do not require any immediate surgical or laser intervention. For example, with age, small microdamages can form in it, which are not so dangerous and do not imply subsequent partial or complete detachment of the retina. They may appear due to vitreous pressure. In this case, a person often complains of floaters or flashes before the eyes. In other cases, when the resulting microdamages are not associated with traction of the vitreous, the risks of detachment are minimal. The most dangerous are ruptures, which are accompanied by clinical symptoms.
In most cases, retinal rupture is the main cause of retinal detachment. After the retina is detached, fluid from the vitreous body begins to seep under it, resulting in cavities that are filled with this content. As a result of such undesirable processes, complete blindness can occur. Retinal detachment cannot be treated with medication; it seems possible to get rid of this anomaly only through surgery. If the patient previously had a corresponding pathology in one eye, doctors warn about the increased risks of the situation repeating in the other. There are several signs by which ophthalmologists recognize detachment when examining a patient.
Retinal detachment: symptoms
- A veil has formed before the patient’s eyes, which does not disappear even when blinking;
- Visual acuity has decreased significantly (especially in cases where the person has not previously encountered such
- problems and no visual pathologies were detected in him);
- The patient complains of unexpectedly appearing “spots” or floating spots before the eyes;
- Decreased lateral vision abilities;
- Visual change in the size and shape of objects.
This pathology may arise as a result of external factors. The following causes of retinal detachment and the progression of this pathology are identified:
- Diabetes;
- Hypertension;
- Pregnancy;
- Atherosclerosis of retinal vessels;
- Various types of injuries;
- Failure to comply with occupational visual hygiene (we are talking about excessive visual stress);
- Other causes of detachment.
Possible complications
Without timely intervention in angiopathy, a reversible change in the retina, tissue hypoxia and hemorrhage can be expected. The retinal vessels themselves also undergo changes. In turn, they become severely deformed and lose blood conductivity. In some cases, complete loss of vision is possible.
Complications can be caused by various bad habits, high blood pressure, hereditary vascular diseases, obesity, and high cholesterol.
Risk factors
Risk factors include both external and internal causes. There is a high probability of ruptures in persons diagnosed with myopia, when an enlarged eyeball causes thinning and rupture of the membrane. In old age, pathology is provoked by structural dystrophic changes in the vitreous body, leading to overstretching of the retina.
Pathological changes in the fundus, straining during childbirth, hypertension, diabetes mellitus and vascular diseases increase the risk of OS. All of them are associated with excessive tension and thinning of the retina. Serious ruptures are observed under the influence of traumatic factors and surgical interventions. During inflammatory processes, excess fluid accumulates in the subretinal zone, putting pressure on the retinal layer.
IMPORTANT! Every fifth child born prematurely suffers from retinopathy. In premature babies, the underdeveloped retina tends to rupture.
Laser coagulation
This method is considered one of the most effective. Laser retinal strengthening is used both for serious diseases that can lead to complete loss of vision, and for the prevention of complications. Coagulation is part of complex treatment for diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension. Most often, laser therapy is used for moderate and high myopia. This method helps prevent retinal detachment and progression of pathological changes.
Before the procedure, drops are placed in the patient's eyes. The laser beam is exposed through a lens with a reflective coating installed on the eye. Thanks to the drops, it is possible to reach even hard-to-reach areas. The laser beam penetrates into the eyeball, causing an increase in temperature in certain areas of the retina, resulting in coagulation. This means that the tissues coagulate and are tightly attached to the choroid. During the procedure, a specialist monitors the process using a stereomicroscope.
The advantage of laser coagulation is that such an operation does not require additional preparation and does not cause pain to the patient. The procedure usually lasts no more than 20 minutes and general anesthesia is not used. However, there are a number of contraindications for the operation, for example, insufficient visual acuity.