Retinal detachment is the process of the eye rejecting retinal tissue, resulting in loss of vision. Treatment can be carried out in different ways: both folk remedies and medications with possible eye surgery are used.
Be sure to take into account diet and some home therapy recipes, since it is known that the properties of certain products containing the necessary vitamins have a positive effect on the visual system and can strengthen the general condition of all membranes of the eye.
Depending on the type of healing measures performed, a person is given time restrictions. For example, after surgery, for several days you will not be able to read, write, or do work that involves eye strain. If you do not follow the recommendations, the treatment may not have the expected effect.
Why does the retina of the eye detach?
Retinal detachment after surgery - what not to do Source: habr.com
At an advanced stage of the disease, complete loss of vision develops, irreversible changes form in the visual center of the brain. Pathological changes can be observed in hemorrhages, traumatic injuries, hereditary pathology of the structure of the vascular and nervous systems.
In old age, the cause of detachment is degenerative-dystrophic disorders associated with impaired nutrition and blood supply against the background of secondary degenerative-dystrophic diseases. Increased retinal tension is formed in hypertension due to increased pressure inside small capillaries.
There are secondary and primary detachments. The primary form develops for rhegmatogenous reasons. The secondary form is exudative, traction. The occurrence of the above nosological types is caused by provoking factors:
- Anomalies in the structure of blood vessels;
- Myopia;
- Diabetes;
- Hypertonic disease;
- Degenerative conditions of the fundus of the eye;
- Astigmatism;
- Pregnancy;
- Operations on the eyes.
With rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, pathological damage to blood vessels and nerve fibers gradually increases. Hemorrhages and swelling lead to separation of the choroid and retina. Such changes develop under the influence of traumatic brain injuries (in athletes, boxers), with excessive physical stress, and periodic hypertensive crises.
Such varieties belong to a number of traumatic options. Exudative variants appear against the background of certain diseases:
- Tumors;
- Occlusions;
- Inflammation;
- Diabetic retinopathy;
- Sickle cell anemia;
- Intoxication, toxicosis.
During exudation, infiltration occurs inside the eye, which increases local pressure. Pathology leads to the development of secondary eye diseases - glaucoma, cataracts. Traumatic types of detachment are formed due to eye injuries. They can only be eliminated by surgical methods.
Self-healing is impossible. Conservative remedies do not help either. Scientific literature points to another cause of retinal detachment - genetic defects. In practice, this type occurs in several family members, but the location of the abnormal genes has not been established.
People with a high degree of myopia often experience rhegmatogenous detachment. Symptoms are associated with the penetration of fluid from the vitreous body through tears under the membrane. The increased risk of the disease in people with high degrees of myopia is due to stretching of the intraocular tissues.
Retinal stretching is a provoking factor leading to complete loss of vision without surgical treatment. Symptoms of exudative detachment are observed when the vitreous changes, when the connective tissue interferes with normal functioning.
Scars stretch the retina, change its morphological properties, but breaks do not occur, bleeding and tissue swelling appear. In the traumatic type, fluid accumulates excessively on the side of the choroid due to damage to the arteries.
Similar morphological changes provoke tumors of intraocular tissues. If there are severe symptoms of complete detachment - loss of vision, bleeding, swelling inside the eye, only surgical intervention helps restore visual function.
It is important to identify early symptoms of detachment:
- Flashes that are localized on the side of the temporal bone in the area of the affected eye;
- Veil on the injured side when moving the head. Progression leads to an exacerbation of this symptom, so the person gradually loses visual function;
- The accumulation of a large number of “flies” is the main manifestation of the disease. It is formed against the background of hemorrhages, leading to retinal tears and swelling of the vitreous body.
The listed morphological changes lead to a decrease in visual acuity. When looking at surrounding objects, a person sees distorted, moving outlines. The contours of the object are blurred. During sleep, swelling decreases as the eye rests.
Vision improves, so the patient thinks that the loss of visual function in the evening is the result of fatigue during the day. The temporary nature of the loss of visual acuity as the disease progresses leads to permanent symptoms.
If you have this condition, you cannot use folk remedies or eye drops, so if you identify the first signs of pathology described, you should immediately consult a doctor. To prevent progression in an outpatient setting, strict bed rest is recommended.
To prevent blindness, it is necessary to promptly identify early manifestations of nosology. In addition to clinical symptoms, clinical and instrumental methods are used to verify pathology:
- Ophthalmoscopy;
- Ultrasound scanning.
Ophthalmoscopy helps to identify swelling and hemorrhages inside the fundus. Domestic ophthalmologists have several diagnostic methods - indirect ophthalmoscopy, a lens of three mirrors. European specialists have a somewhat wider arsenal of methods.
An ultrasound examination of the eye is prescribed for a cloudy lens. The impossibility of ophthalmoscopy in cases of vitreous lesions necessitates an alternative diagnosis using ultrasound.
For timely diagnosis of detachment, experts from the World Health Organization recommend forming groups of patients with a high probability of detachment. The disease is often observed in people with severe myopia and hypertension.
The assessment of the viability of intraocular tissues to predict possible pathological disorders in the future is carried out by electrophysiological examinations. Modern methods for diagnosing retinal detachment:
- Tonometry shows a decrease in intraocular pressure, below 16 mm. Hg Art.;
- Perimetry – reveals deviations in lateral vision;
- Electrophysiological examination determines the functionality of the optic nerve and nervous system;
- Study of visual acuity;
- Ophthalmoscopy – helps visualize areas of retinal defects;
- Ultrasound examination shows the extent of destruction, opacification of the lens and cornea, which are often combined with pathology.
European clinics have the capabilities to thoroughly examine the condition of the intraocular fundus. Such equipment makes it possible to identify pathology at an early stage.
Mechanism of retinal detachment
Due to a number of reasons, damage to the retina of the eye occurs, under which part of the liquid contents of the eyeball gets trapped. This leads to detachment of the choroid plexus and disruption of retinal nutrition. As a result, the cells of this layer of the eye (rods and cones) die. Dead cells are not restored.
There are three types:
- Rhegmatogenous, the most common, is associated with a retinal tear.
- Traction , in which the retina is not injured, but is pulled back as a result of cicatricial changes in the eyeball itself.
- Exudative , its cause is the accumulation of fluid (blood, pus, exudate) between the retina and the vitreous body.
Causes
The main cause is traumatic damage to the eyeball. However, there are others:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the visual organs, such as uveitis, retinitis. Uveitis is an inflammation of the vascular network of the eye. Retinitis is inflammation of the retina.
- Tumors of the vascular membranes.
- Age-related changes in tissues, the occurrence of macular degradation, especially in persons over 45 years of age.
- Decreased vision due to general diseases, for example, diabetic retinopathy.
Separately, there are risk factors that can cause detachment:
- genetic predisposition;
- retinal detachment of the neighboring eye;
- constant increased physical activity, especially heavy lifting.
The risk group includes: weightlifters, boxers, people with high myopia, and people with diabetes.
Stages and symptoms of pathology
The early stage of the disease may not manifest itself at all, or is characterized by minor pain and periodic visual defects. However, after sleep, symptoms most often disappear.
Over time, the disease progresses and enters an advanced stage, which is accompanied by pain and partial and then complete loss of vision.
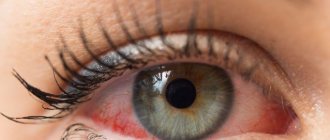
This pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- decreased field of view;
- photopsia is accompanied by the appearance of flashes, sparks and lightning in the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity, especially in the evening.
- the occurrence of defects in the visual image in the form of flickering flies, floating dots, as well as the appearance of a veil before the eyes.
- The objects in question change color, size or shape.
- Periodic pain in the eye and discomfort.
Important! If, with such symptoms, washing the eyes or instilling drops does not bring results, then you should immediately consult a doctor for examination.
Short-term normalization of vision after sleep is possible due to the resorption of fluid accumulated under the retina.
Useful video
Is it possible to restore the retina of the eye?
Symptoms
The initial symptom of retinal detachment is often photopsia (“flashes,” “lightning,” “sparks” in the field of vision).
Their appearance is due to the fact that impulses in the retina are formed not only when light enters, but also when there is a mechanical effect on it. Vitreoretinal adhesions stretch the retina, irritating photosensitive cells, which leads to this phenomenon.
Retinal detachment may be accompanied by the appearance of floating “floats”, “threads”, “dots” in the field of view. However, this symptom is not specific, it is very common and does not require treatment; in most cases, it is caused by destruction of the vitreous body.
Sometimes a round cloudiness (Weiss ring) appears in the field of view, indicating detachment and tearing of the posterior hyaloid membrane at the site of attachment at the optic disc. This condition also does not require treatment.
Along with this, the sudden appearance of black floating spots, “cobwebs” in the field of view may indicate retinal detachment, being caused by hemorrhage into the vitreous from damaged vessels due to rupture or traction of the retina.
Important
The patient may also notice loss of a portion of the visual field, which appears as a “veil” or “curtain” in front of the eye. This occurs due to detachment of the sensory layer of the retina and, as a result, disruption of the processes of visual perception in it.
In this case, the detachment is localized in the part of the retina opposite to the presence of the defect: i.e., if the visual field defect is noted from above, then the detachment occurred in the lower parts, etc. If the process affected the sections located anterior to the equator of the eye, then this symptom will not appear.
Patients may notice a decrease or absence of this symptom in the morning and reappearance in the evening, which is associated with spontaneous absorption of subretinal fluid. Detachments of the upper parts of the retina progress much faster compared to the lower ones.
The fluid accumulating in the subretinal space, in accordance with the laws of physics, gradually falls down and exfoliates the underlying sections. Whereas inferior detachments can exist asymptomatically for a long time and are detected only when they spread to the macular area.
The duration of the decrease in visual acuity, as a consequence of damage to the macular area, affects the prognosis for the restoration of central vision.
The patient may notice a decrease in visual acuity, distortion of the shape and size of objects, curvature of initially straight lines (metamorphopsia), the severity of which depends on the degree of damage to the macular and paramacular parts of the retina.
The appearance of this symptom is also possible after a head or eye injury, removal of a cataract, foreign body, intravitreal injections, vitrectomy, scleral filling, PDT, laser coagulation. In this regard, when metamorphopsia occurs, a thorough examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis is necessary.
All of the above symptoms are more characteristic of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. The symptoms of exudative detachment are usually scant, since this type of detachment is not associated with retinal traction. Tractional retinal detachment also develops slowly and asymptomatically in most cases.
Visual field defects may worsen (increase) gradually or not progress at all for months or even years. Only when the macula is involved in the pathological process does the patient begin to experience a noticeable decrease in vision.
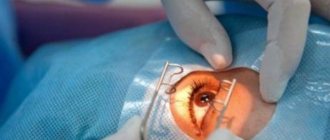
Operation process
Depending on the type of surgical intervention, certain stages of detachment elimination are carried out. With laser coagulation, the course of the operation is determined by:
- the patient is seated in a chair;
- administration of drops with an anesthetic effect 5 or 10 minutes before the start of the procedure;
- instillation of medications that dilate the pupil;
- a lens in the shape of an eyepiece from a microscope is put on;
- A bonding procedure is performed in which the patient only feels flashes of bright light.
The results of the intervention can only be judged after 10 days or 2 weeks. Among the side effects due to manipulation are dizziness or short-term nausea.
Filling using the extrascleral method proceeds according to the following stages:
- The surgeon cuts the conjunctiva.
- Using a diathermocautery, pressure is applied to the sclera.
- Measuring the area where the filling needs to be placed. Silicone is used for its manufacture, as it is elastic and malleable.
- Silicone is applied to the gluing site and pressed for a few seconds. Due to manipulation, the 2 layers are glued to each other.
- The seal is sewn on. The fluid that has accumulated at the site of the tear should resolve on its own. If this does not happen, additional incisions are made to remove it.
Vitrectomy to eliminate detachment is carried out according to the rules:
- the patient is transferred to a hospital;
- administer anesthesia;
- the surgeon makes an incision in the sclera;
- Scissors and tweezers are inserted into the vitreous body and the area is excised;
- Gas or silicone oil is introduced into the resulting space;
- the patient is advised to look down during the procedure;
- The conjunctiva is sutured.
The results of surgery can be judged after at least 2 weeks.
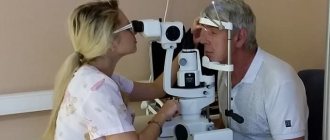
Diagnostics
If retinal detachment is suspected, a complete ophthalmological examination is necessary, since early diagnosis can avoid irreversible vision loss. If there is a history of TBI, the patient must be consulted not only by a neurologist, but also by an ophthalmologist to exclude ruptures and signs of retinal detachment.
The study of visual functions in case of retinal detachment is carried out by checking visual acuity and determining visual fields (static, kinetic or computer perimetry). Loss of visual fields occurs on the side opposite the retinal detachment.
Using biomicroscopy (including using a Goldman lens), the presence of pathological changes in the vitreous body (strands, destruction, hemorrhages) is determined, and peripheral areas of the fundus are examined.
Tonometry data for retinal detachment are characterized by a moderate decrease in IOP compared to a healthy eye. The key role in recognizing retinal detachment belongs to direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy.
The ophthalmoscopic picture of retinal detachment allows us to judge the location of the breaks and their number, the relationship of the detached retina with the vitreous body; allows you to identify areas of dystrophy that require attention during surgical treatment.
If it is impossible to perform ophthalmoscopy (in case of opacities in the lens or vitreous body), an ultrasound of the eye in B-mode is indicated. The diagnostic complex for retinal detachment includes methods for studying entopic phenomena (the phenomenon of autoophthalmoscopy, mechanophosphene, etc.).
To assess the viability of the retina and optic, electrophysiological studies are carried out - determining the threshold of electrical sensitivity and lability of the optic nerve, CFSM (critical flicker fusion frequency).
Contraindications
General contraindications to surgical intervention are:
- history of allergy to anesthetic;
- inflammatory process in the active stage;
- caries;
- the presence of diseases of the respiratory system.
Contraindications to vitrectomy are:
Extrascleral filling is not performed if the patient has:
- vitreous opacities;
- pathological condition of blood vessels;
- protrusion of the sclera.
Laser coagulation is not recommended if there are contraindications:
- vitreous opacification;
- pathological conditions of blood vessels;
- high degree of retinal dissection;
- hemorrhage in the fundus of the eye.
Treatment options
Retinal detachment in any form always requires immediate treatment, otherwise it will result in complete blindness of the eye. During an old detachment that is ignored for a long period, ocular hypotension often occurs because fluid is constantly leaking and the pressure is unstable.
Cataracts, subatrophy, chronic iridocyclitis and blindness, which cannot be cured, are all consequences of an advanced form of retinal detachment. The key task for treatment is to force the boundaries of the gap to come closer together, which eventually becomes blocked.
There are the following basic microsurgery methods for treating detachment:
- Extrascleral - the whole process occurs on the surface of the sclera.
- Endovitreal - the action is carried out in the eyeball itself.
The most advanced modern method is vitrectomy - the vitreous body is removed, and a silicone substance or gas is introduced in its place to ensure complete adhesion of the exfoliated parts.
Endovitreal microsurgery includes operations performed in the cavity of the eyeball itself. Access is provided through three incisions on the sclera, which do not exceed 1 mm in length. The clarifier, the instrument itself, and a solution are injected through them to maintain the shape of the eye in good shape.
Sometimes prolonged vitreous tamponade is simply necessary. For this, a special gas or silicone substance is also used. The gas bubble resolves on its own within a couple of weeks after the procedure, or a month at most.
The area with an artificial liquid substitute gradually decreases in volume, as the voids are immediately filled with natural material. It is more difficult with silicone oil - it is removed after at least 2 months, sometimes later.
The symptoms of detachment are even so specific that they appear suddenly and cannot go unnoticed. Therefore, you should not be negligent about your own vision, but it is better to immediately seek help from doctors.
Indications for surgery
Depending on the course of the detachment process, as well as the level of the already exfoliated area, several types of operations are performed. Coagulation is necessary for soldering along the edges of the detachment:
- for minor damage;
- in case of peripheral tissue detachment.
Surgical filling of the edges of the retina is performed in case of damage to large areas or detachment of the neuroepithelium and pigment layers. Indications for vitrectomy are damage to the vitreous body, which can be eliminated by introducing substances of helium consistency into it.
The procedure is prescribed if:
- ingrowth of blood vessels into the body of the retina;
- extensive damage to the visual organ;
- bleeding into the vitreous cavity.
Modern methods
The main idea of treatment for retinal tears is to close the defect. For these purposes, laser cauterization or cold exposure is used. Under the influence of the procedures, scarring of the defect occurs.
Integrity is restored more quickly when a silicone filling is suspended to bring the choroid closer to the detached retina. The following procedures are used for surgical intervention:
- Laser coagulation to thin and limit areas of rupture;
- Vitrectomy - to remove the altered vitreous body, introduce liquid silicone, saline solution. To improve fluid properties, perfluorocarbon is used to bring the choroid closer to the retina;
- Circular filling;
- Installation of local fillings – in case of partial detachment.
The choice of method is determined by the surgeon individually based on diagnostic data and the nature of the disease in each individual person.
Surgery for retinal detachment
If you treat your health irresponsibly and do not consult an ophthalmologist in a timely manner at the first signs of retinal detachment, then the further development of the disease may result in:
- Hypotony of the eye;
- Subatrophy of the eyeball;
- Chronic iridocyclitis;
- Incurable blindness.
Before the operation, the patient undergoes a number of special diagnostic procedures and passes the necessary tests. The retina and fundus are examined, the main indicators are identified, visual acuity is checked, and a slit lamp examination is performed.
Since each case is individual, additional studies may be prescribed. Sometimes a chest x-ray and an ECG may be needed.
The patient must inform the attending physician about the presence of allergic reactions (if any) and about the constant use of any medications in order to avoid possible complications.
In this case, a week before the date of the scheduled operation, you must stop taking medications that thin the blood. 6 hours before the operation you should refuse food, unless there are contraindications, for example, with diabetes. In this case, the doctor will advise you on how to prepare for the operation.
During the operation, general or local anesthesia is used. The choice of anesthesia depends on the method of treatment, the general health of the patient, his age, weight, and the presence or absence of complications. The duration of the procedure is about 2-4 hours.
Important
After the operation is completed, you may experience slight pain in the eye area and a feeling of nausea. Most often, the patient can go home almost immediately, but it is better to agree in advance with relatives or loved ones about accompanying them, since weakness may occur.
For some time after the operation, you will need to follow the doctor's recommendations for a quick recovery. Immediately after all procedures, a sterile bandage is applied to the eye, which can only be removed with the permission of the attending physician, usually 24 to 36 hours after surgery.
For a month after surgery, the patient is not recommended to visit the sauna, and should also avoid rooms with high levels of humidity and high temperatures. During this period, it is necessary to ensure that water does not get into the eye and avoid heavy physical exertion.
You should strictly follow all the recommendations of your doctor and undergo a re-examination to avoid complications and speed up the process of restoring impaired visual functions. Depending on the doctor’s instructions and compliance with all recommendations, you will be able to return to work within 1-2 weeks after the operation.
General recommendations from doctors
General recommendations include the following rules:
- try not to get water in your eyes during the first week;
- do not tilt your head too far back while taking a shower;
- do not use cosmetics for the first 2 weeks after surgery;
- use sunglasses with ultraviolet protection;
- If you have difficulty reading, do not panic, this will continue for several weeks;
- do not use glasses or contacts;
- Avoid staying in smoky and dusty places during the first month of rehabilitation.
Possible complications
In rare cases, complications may occur after surgery. They are usually associated with cataracts and glaucoma. the general poor health of the patient. The most common complications include:
- Recurrent retinal detachment, which will require new surgical intervention;
- Increased scarring of the retina (ie, proliferative vitreoretinopathy). In this case, repeated operational measures are also carried out;
- The development of endophthalmitis as a result of infection in the eye.
You should immediately consult a doctor if there is discharge from the eyes or fever. chills, if swelling and redness appear, shortness of breath, cough. pain in the chest area.
Folk remedies for retinal detachment
Source: dvaglaza.ru
Together with medications and surgical methods, folk remedies are used that improve the healing process, but they cannot be used for monotherapy of pathology. Honey contains many natural substances (microelements, vitamins), enzymes, and flavonoids.
Clinical studies show that lubricating the eyes with honey leads to normalization of trophic properties, healing of traumatic defects, and promotes the resorption of inflammatory foci.
The product contains antibacterial, antiviral drugs, and antifungal agents. In folk medicine, honey was used to relieve inflammation of the eyes and treat tuberculous lesions of the conjunctiva.
Eye honey is not a product that beekeepers collect. Only with the industrial production of drugs do specialists have the opportunity to create the desired medicinal form.
For these purposes, pharmaceutical companies raise special bees from which honey is taken in small quantities over a long period. The complexity of preparing the drug determines the high cost, but the costs are justified by the medicinal qualities.
If the retina of the eye is detached, you cannot self-medicate. Small tears do not lead to significant loss of vision, but the size of the detachment gradually increases. The progression of the pathology leads to irreversible changes and complete blindness.
Retinal detachment is one of the most serious diseases of the visual system, which can lead to complete loss of vision. Unfortunately, the mistrust or doubts of some patients regarding the capabilities of official medicine often leads them to search for alternative treatment methods.
Therefore, in the ophthalmologist’s office you can often hear the question: are there folk remedies and methods for treating retinal detachment? In order to answer this question correctly and as clearly as possible, it is necessary to clearly explain the mechanism of retinal detachment.
At its core, retinal detachment is a separation of the retina from its underlying tissue, mechanical damage, an open wound that cannot be treated in any way other than surgery.
The only difference in surgical techniques lies solely in their complexity and the final results. Even the most miraculous compresses, vitamin drops, aloe juice, decoctions and other remedies available in the arsenal of traditional medicine will not allow the damaged retina to “grow back” to its original place.
Special gymnastics and eye exercises, which are presented by various healers as time-tested oriental techniques, will also be powerless. Any assurances of the benefits of traditional methods of treating retinal detachment and beliefs in their effectiveness are fundamentally incorrect and criminal.
Minor improvements when using such alternative methods may be observed only in the early stages of the disease. But this effect is temporary, which can only be explained by a sharp activation and mobilization of the regenerative reserves of the eyes, but this does not eliminate the main cause - the physical detachment of the retina.
Important
Even officially approved, certified and most expensive eye drops cannot replace the effectiveness of surgery to restore a detached retina. Sooner or later, the patient will still have to see an ophthalmologist for surgical measures.
And it’s better if it’s early than late, when the disease reaches an advanced stage. Therefore, at the first symptoms, you must immediately consult a doctor. Any delay caused by experiments with traditional medicine and alternative treatments only greatly increases the risks of complete loss of vision.
Treatment and prevention of retinal detachment
Surgery is the only correct method of treating retinal detachment, the effectiveness of which increases significantly if the intervention is carried out in the early stages of the pathological process. In this case, the likelihood of restoring trophism and, accordingly, vision increases. The main task of the doctor performing the surgical process is to block the existing gaps as much as possible and thereby contribute to the restoration of lost connections between the separated areas. If, as a result of an accident, a head injury occurs, as well as damage to one or two organs of vision, contacting a medical facility in order to prevent retinal detachment should be immediate. There are several types of operations aimed at eliminating the problem: extrascleral, endovitreal and laser.
Restrictions
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that requires immediate surgical intervention. Attempts to do without surgery can lead to complete loss of vision in the shortest possible time.
However, even after successful treatment, a number of restrictions remain, some of which must be observed throughout life. The most important prohibition regarding retinal detachment is that you should never try to cure this disease yourself, using so-called “folk” methods.
When the first symptoms appear - spots or sharp flashes before the eyes, sudden deterioration of vision, vibrations of visible objects - you need to consult a doctor. After all the necessary studies have been carried out to clarify the diagnosis, surgery is prescribed.
After surgery to restore the integrity of the retina, the patient wears a bandage on the operated eye for the first day. If pain occurs, you can take painkillers - a specific drug, the regimen of which will be recommended by your doctor.
The next day, the bandage can be removed and the eyelids (not the eye itself!) treated with a solution of chloramphenicol or furatsilin. What not to do during the recovery period:
- overexert yourself, engage in any kind of sports, lift weights;
- expose the eye to any radiation (especially ultraviolet radiation) and heat - it is advisable to refrain even from cooking food on the stove yourself;
- make sudden movements of the head, bend over;
- rub the eye or subject it to any other mechanical stress.
It is highly undesirable to use decorative cosmetics for two months after surgery. Particular care must be taken when washing and performing other hygiene procedures: water, soap and other products should not get into the eye. To do this, you can cover it with a sterile napkin secured with an adhesive tape.
In addition, you should be especially careful about your general health: even a minor cold accompanied by an increase in temperature can lead to a deterioration in the condition of the retina.
Unfortunately, even a successful operation does not guarantee that the retina of the eye will not exfoliate again or that tears will not occur in it. Therefore, observing certain restrictions only during the recovery period may not be enough: some of them will have to be adhered to throughout your life.
Thus, it is extremely undesirable for people with a similar disease to engage in sports, especially those associated with sudden movements, jolts, jumps, and impacts. All martial arts, horse riding, running, and diving are prohibited.
However, swimming and morning exercises, consisting of a set of simple exercises, will only be useful. In some cases, the ban on heavy lifting remains for life. In addition, it is prohibited to perform any work that requires bending, as well as to stay in the hot sun for a long time.
Rehabilitation period
The recommendations below are general recommendations developed for most patients. If the course of the postoperative period is individual, the doctor will offer an individual treatment regimen, as well as a schedule of examinations of the patient. His recommendations must be clarified at each visit!
- Mode. A specific postoperative regimen can have enormous therapeutic value. Therefore, you should strictly follow the recommendations for compliance on the first postoperative day that you receive from the surgeon. In the future, the features of postoperative behavior should be clarified during regular examinations.
- Hygiene. When washing your face, you should avoid getting soap or water in your eyes. Washing your hair should be done with your head tilted back. If, nevertheless, water gets into the operated eye, rinse it with an aqueous solution of 0.02% furatsilin or an aqueous solution of 0.25% chloramphenicol (sold in a pharmacy).
- Don't miss your doctor's appointment!
- During the first postoperative days, it is recommended to wear a bandage (“blind”) on the operated eye to protect it from dust present in the air and the effects of bright light. This bandage is made of two-layer gauze and is attached in front of the eye to the forehead using an adhesive plaster, like a “curtain”. It does not put pressure on the eyeball.
- Eye drops are recommended in the postoperative period for better healing, as well as to prevent infectious complications. Often, after surgery, the surgeon recommends instilling several drugs: anti-inflammatory drops (Naklof, Indocollir, etc.), disinfectant drops "Ciprofloxacin", "Tobrex", (Floxal, etc.) or combined agents (Maxitrol) , "Tobradex"). Drops, as a rule, are prescribed according to a decreasing scheme: four times a day - the first week, three times a day - the second week, twice a day - the third week, once daily - the fourth week, then they are discontinued.
FAQ
Retinal detachment is a fairly common disease. Its danger is that progression causes other pathologies: glaucoma, cataracts, blindness. It is important to detect the disease in a timely manner. To do this you need to know the symptoms.
However, they can be different: a veil before the eyes or black dots, the appearance of “lightning” and “flashes” in front of the visual organs. Symptoms may vary depending on the stage and the reasons that led to the detachment, but all symptoms are accompanied by deterioration of vision.
Therefore, if this is detected, you should make an appointment with an ophthalmologist, who, after a thorough diagnosis, will make a diagnosis and determine the degree of development of the disease. In addition, the doctor will determine the causes of the detachment and tell you what needs to be done before and after the operation.
What should you not do if you have a retinal detachment?
Before the surgical procedure, the patient must:
- avoid intense physical activity, as this is one of the causes of rupture and detachment of the retina;
- avoid traumatic situations;
- wear sunglasses during the day and in bright sunshine;
- Beware of various types of intoxications.
Also, the occurrence of complications can be affected by childbirth in the presence of this pathology. Before giving birth, a woman must undergo laser coagulation.
What should you not do after retinal surgery?
- Firstly, the patient should follow all the ophthalmologist’s recommendations. He will tell you what is contraindicated and can cause relapse or complications.
- Secondly, you will have to limit yourself in sports and other heavy activities. Swimming or running, for example, are not prohibited, but lifting weights is strictly contraindicated.
- Thirdly, you should not tilt your head down: tie your shoelaces, sleep on your stomach, or work in your dacha on a plot of land.
- Fourthly, thermal procedures (baths, saunas, solariums) are prohibited.
Even in the absence of complaints, the patient must appear for an appointment with an ophthalmologist after one month. The patient should also avoid excessive sun exposure and public places in the early postoperative period to avoid infectious diseases.
In addition, it is important to take all medications that your doctor prescribes. They will help the retina recover faster. If you experience any symptoms, such as spots before your eyes, you should go to the hospital immediately.
Late rehabilitation
At this stage, you will need to visit an ophthalmologist one month after surgery. Follow all rules followed during early rehabilitation.
It is important to prevent eye injury and blockage. If foreign bodies get in, wash with solutions prescribed by the doctor for such cases. Then be sure to visit an ophthalmologist.
The use of cosmetics is not recommended. These compounds irritate the mucous membranes of the eye and can cause infection if used incorrectly or accidentally in contact with the eye.
Drops and other medications continue to be used until the retina is completely healed. Your doctor will tell you to stop taking it.
Forecast
Detection of pathology requires immediate surgical treatment. Delay in treating this pathology is fraught with the development of persistent hypotension and subatrophy of the eyeball, chronic iridocyclitis, secondary cataracts, and incurable blindness.
The main goal of treating retinal detachment is to bring the layer of photosensitive receptors closer to the pigment epithelium and create an adhesion of the retina with the underlying tissues in the area of the rupture.
In surgery for retinal detachment, extrascleral and endovitreal techniques are used: in the first case, the intervention is performed on the scleral surface, in the second - inside the eyeball. Extrascleral methods include filling and ballooning of the sclera.
Extrascleral filling involves suturing a special silicone sponge (seal) to the sclera, which creates an area of scleral depression, blocks retinal breaks and creates conditions for the gradual absorption of fluid accumulated under the retina by capillaries and pigment epithelium.
Options for extrascleral filling for retinal detachment can be radial, sectoral, circular (circlage) filling of the sclera.
Ballooning of the sclera in case of retinal detachment is achieved by temporarily suturing a special balloon catheter into the area of projection of the rupture; when inflated, an effect similar to filling occurs (a shaft of scleral depression and resorption of subretinal fluid).
Endovitreal treatments for retinal detachment may include vitreoretinal surgery or vitrectomy. During the process of vitrectomy, the altered vitreous body is removed and special preparations (liquid silicone, saline solution, special gas) are introduced instead, which bring the retina and the choroid closer together.
Gentle methods of treating retinal detachment include cryocoagulation of breaks and subclinical retinal detachments and laser coagulation of the retina. allowing to achieve the formation of chorioretinal adhesions.
Cryopexy and laser coagulation of the retina can be used both for the prevention of retinal detachment and for therapeutic purposes alone or in combination with surgical techniques.
The prognosis depends on the duration of the pathology and the timeliness of treatment. Surgery performed early after the development of retinal detachment usually promotes a favorable outcome.
In most cases, retinal detachment can be prevented. For this purpose, patients with myopia, retinal dystrophy, diabetes mellitus, head and eye injuries need regular preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist.
An examination by an ophthalmologist is included in the standard of pregnancy management and helps prevent retinal detachment during childbirth. Patients at risk for retinal detachment are contraindicated in heavy physical activity, heavy lifting, and playing certain sports.
When areas of retinal dystrophy are identified, cryopexy or laser coagulation of the retina is performed for preventive purposes.
Types of retinal surgery
All surgical methods of treatment on the retina of the eye are carried out through punctures using microsurgical instruments. Under the control of a microscope, a gas mixture is injected into the eyeball, abnormal films are excised, the vitreous body is removed, the retina is cauterized with a laser or exposed to cold. Most often, operations in case of detachment or rupture of the membrane must be performed on an emergency basis to prevent loss of vision.
If the operation is planned, then it is preceded by an ophthalmological examination (diagnosis of visual acuity, perimetry, electroretinography) and general clinical diagnostics (blood tests, urine tests, biochemistry, coagulogram, ECG and fluorography). Many procedures require general anesthesia. The anesthesiologist measures basic hemodynamic parameters, administers anesthetics, sedatives and hemostatic drugs.
The first stage of operations in most cases is the destruction and removal of the vitreous body - vitrectomy. In case of slight clouding of the ocular media, vitreolysis is prescribed - evaporation of abnormal inclusions with laser radiation. After this, the treatment begins directly. For this use :
- “soldering” of the retina to the epithelial layer using laser coagulation;
- freezing to connect the retina and choroid (cryopexy);
- installation of a silicone filling (extrascleral filling);
- pressing the retina with a balloon (extrascleral ballooning);
To improve tissue nutrition, implantation of eye muscle fibers and episclera is used, which stimulate the formation of new vessels to nourish the membranes and nerve structures. If there are membranes that reduce vision, they are excised.
Operation extrascleral filling for retinal detachment
The final stage is the introduction of silicone oil, a gas mixture or a perfluoroorganic substance into the location of the vitreous body (during vitrectomy).
Injections of antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications are made under the conjunctival membrane, the eye is covered with a bandage, and the patient is transferred to a ward for further observation. The maximum duration of operations is 3 hours; with laser coagulation or cryopexy it lasts about half an hour.
We recommend reading the article about angiopathy of the retina or both eyes. From it you will learn about the types and causes of the disease, signs and symptoms, as well as the treatment and prevention of retinal angiopathy. And here is more information about retinopathy of premature babies.