Laser eye surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that causes minimal damage to the visual organs. However, any surgical intervention can cause complications. There are also side effects after laser correction that worry almost every patient. What to do if severe pain occurs during the postoperative period?
In this article
- Laser vision correction technique
- Pain after laser vision correction: why does it occur and what to do?
- Severe pain after laser surgery - what to do?
- Displacement of the corneal flap after surgery
- Dry eye syndrome after laser surgery
- What causes keratitis after laser vision correction?
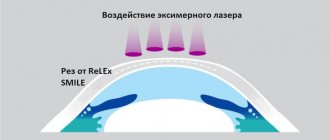
Laser vision correction technique
Laser eye surgeries to restore vision are always performed on an outpatient basis. Correction of a refractive error lasts approximately 10-15 minutes on one eye. The duration of the procedure is determined by the degree of visual pathology and the method by which the correction is performed. There are quite a lot of methods today. They are all similar in technology. Conventionally, all types of laser procedures for correcting refractive errors can be divided into operations that remove the superficial corneal layer and procedures that preserve the epithelial layer of the cornea.
In both cases, correction is accompanied by damage to the cornea. The surgeon uses a microkeratome or a laser beam to separate the upper layer of the cornea by excision or scraping to gain access to its inner layers, the curvature of which will be corrected. Next, the doctor directs a laser beam onto the eye, which vaporizes the corneal tissue and gives it the correct shape. At the final stage of the operation, the corneal flap, previously moved to the side, is straightened onto the operated area of the eye. If the flap is removed, a protective bandage lens is installed on the cornea to protect it from bacteria, which helps the damaged tissue heal faster.
Pain after laser vision correction: why does it occur and what to do?
After laser surgery, there are a number of restrictions that must be strictly observed. Thanks to this, it will be possible to avoid complications and speed up the recovery process. In the first few days after the procedure, the person operated on may experience discomfort in the form of pain, pain, burning in the eyes. They are not complications, they are side effects that disappear after 3-5 days. Sometimes they go away within the first day. It all depends on the method by which the procedure was performed and on the physiological characteristics of each patient. They need to be instilled for 14 days daily 2-3 times after surgery. Ophthalmic drops are prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
In addition to pain, after laser correction the patient may experience tearing or dry eyes, photophobia, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body on the cornea, etc. These symptoms do not pose a serious danger. In the first days after surgery, it is necessary to see a doctor who will monitor the recovery of the eyes and monitor all possible risks.
A person can see well already 2-3 days after vision correction. After surgery, some patients come to the first examination with complaints of blurred images and photophobia. However, this goes away after a few days. You should wear sunglasses when outdoors during the day. This will help get rid of photophobia, which is also accompanied by pain. You can leave the clinic on your own. It is better not to drive a car. It is advisable to stop driving for two weeks, during which you need to use the drops. Vision will finally be restored in 2-4 weeks.
The pain that bothers you during the rehabilitation period is usually moderate. Severe pain occurs for other reasons. If pain sensations are not relieved by medications, they bother you almost constantly, interfere with sleep and live fully, it is not recommended to endure them. Make an appointment right away. It is possible that laser vision correction has caused complications that need to be identified in a timely manner.
Are there any restrictions?
The choice of method depends not only on the wishes and financial capabilities of the patient, but also on a number of medical factors - the decision must be made only after a thorough ophthalmological examination and consultation with a specialist. In some cases, the operation has to be abandoned altogether.
“My situation was quite specific,” says Alexandra, “I have a genetic disease, cystic fibrosis. Because my lungs don't work very well, I cough often. After the examination, the doctors at the clinic said that “it seems that it can be done” - and this “sort of” alarmed me. The evening before the correction, I went online and watched a video about exactly how this is done. And I became scared: during the operation I had to lie still, and if I suddenly started coughing, it might ruin everything and I would be left without eyes. In general, I decided to play it safe and am still living with minus 3.5 and minus 5.5.”
In general, laser vision correction is relatively safe, if you exclude some contraindications. Simple and common, LASIK allows you to return to daily activities almost immediately, but there are situations when PRK surgery is necessary. So, for example, if the cornea of the eye is quite thin (on average it should be about 550–600 microns), the doctor may recommend flapless correction. For professions and sports where there is a risk of mechanical damage to the eyes, PRK is also better suited
But it is important to understand that any type of laser correction involves reducing the cornea by 100–130 microns, so you need to weigh the pros and cons again if your scores are, say, below 500. Severe thinning of the cornea can lead to the appearance of holes (perforations) in it. and other unpleasant consequences that will have to be treated
Severe pain after laser surgery - what to do?
Complications after laser vision correction are an extremely rare occurrence, but no one is completely immune from them. Most often they are a consequence of the patient’s failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions. Eye pain occurs with the following complications:
- displacement of the corneal flap;
- dry eye syndrome;
- keratitis.
Let's take a closer look at these complications and find out why they arise.
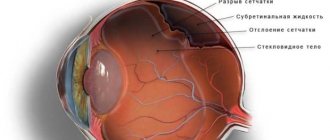
Displacement of the corneal flap after surgery
In the first two weeks after laser surgery, it is forbidden to touch your eyes with your hands, rub or scratch them. This may cause the flap to become dislodged. This often happens as a result of injury. The displacement is accompanied by pain, blurred vision, and lacrimation. This complication is treated with repeated surgery. The surgeon straightens the folds of the displaced epithelial layer, removes excess tissue, treats the eye with a solution, installs the flap in its original place and applies a bandage lens.
After this, you will have to put drops into your eyes again. When the flap is displaced, there is a risk of bacteria getting under it. Because of this, an infectious disease may occur.
Eye lens replacement: complications
The use of modern technologies (ultrasound and laser) for intraocular lens implantation operations allows us to ensure that the likelihood of complications after lens replacement is minimized.
As a rule, immediately after the procedure, patients notice a significant improvement in vision. Subsequently, it continues to improve for another six months. Since the selection of an intraocular lens is carried out individually for each patient, the result of the operation is usually a 98–100% restoration of vision. However, in some cases, complications may still occur after lens replacement.
- Clouding of the lens capsule caused by the proliferation of epithelial tissue on its posterior surface. This leads to a decrease in transparency and a gradual decrease in vision, negating the results of surgery. The problem is effectively solved by surgery using a YAG laser. The procedure is called laser dissection; it allows you to very accurately remove the clouded part of the lens capsule in the projection of the optical axis of the eye.
- Corneal edema. In general, slight swelling is quite normal, which is caused by the insertion of instruments into the eye during surgery. This swelling usually goes away within a few hours after the procedure.
- An increase in intraocular pressure, which may be caused by the insufficient ability of the solutions used during surgery to overcome the drainage system of the eye. When IOP increases, the patient may experience severe eye pain or headache.
- Hemorrhage is an extremely rare complication. To eliminate it, surgery and a course of steroid medications may be required.
- An infection of the eye that causes inflammation in the first days after surgery. It is impossible to completely eliminate the possibility of infection, however, if the equipment is completely sterile during surgery and all postoperative recommendations of the doctor, the risk of infection is negligible.
- Inability to clearly see objects at different distances from the eyes. In this case, the patient needs special glasses for reading and working.
If alarming symptoms occur, you should seek help from your doctor. It should be noted that most often complications after eye lens replacement are in no way related to the unprofessionalism of the ophthalmologist who performed the operation, but are the result of reactions caused by the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
The high professionalism of ophthalmologists and the latest equipment at the ARTOX clinic on Yugo-Zapadnaya (Vernadsky Avenue) ensure consistently excellent results from lens replacement operations. The price of the procedure is affordable and affordable. We will help you effectively eliminate the problem and enjoy excellent vision.
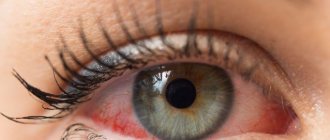
Dry eye syndrome after laser surgery
The curvature of the cornea is corrected using a laser. He vaporizes her cells. The laser effect on the eye itself lasts no more than 2 minutes, and sometimes less than a minute, but during this time the cornea receives a slight burn. The body's natural defense in case of an eye burn is an increased secretion of tear fluid, which causes its deficiency. This leads to the development of the syndrome. It usually goes away quickly. Its symptoms are relieved with moisturizing drops.
Sometimes signs of the syndrome appear a month after surgery. This happens due to the fact that a person does not follow the doctor’s recommendations and spends a lot of time at the computer or in front of the TV. In the first month after correction, it is necessary to avoid strain on the visual organs. After surgery, it is better to completely give up gadgets for two weeks.
How can you differentiate dry eye syndrome from the common side effects described above? It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- it seems to the patient that there is a foreign body in the eye - a speck, an eyelash;
- itching and burning;
- redness of the eyes and skin of the eyelids;
- lacrimation, in which tears enter the nasal cavity;
- photophobia, blurred vision;
- Pain in the eyes.
After laser surgery, the patient must visit the ophthalmologist quite often, so the syndrome is usually detected on time. It is treated with drugs that replace tears, that is, moisturizing drops.
Cataract surgery
The most common of these is cataract surgery. The newest method is phacoemulsification. During this operation, the clouded body of the lens is removed through a puncture, after which an intraocular lens made of transparent plastic is placed into the lens capsule. This technique is not only worked out to the smallest detail, but can also be carried out in a couple of minutes. But be that as it may, this is a surgical intervention, since there is complete penetration into the eyeball. And despite the fact that there are very few complications when using this method, they can still occur.
What causes complications?
The surgeon makes an incision in the cornea to clean the lens capsules from the clouded substance. And since there are no blood capillaries in the cornea, the healing of the incision is delayed. All this can lead to the fact that the spherical shape of the eye can change, which can lead the patient to develop astigmatism. This complication can be cured by keratotomy. That is, tiny incisions are made in a distant part of the cornea. This relieves the tension due to the scars that have appeared there, and gradually brings the eye back to its original shape. Well, there is a problem: such a correction is possible only 12 - 14 weeks after the operation.
It often happens that postoperative complications arise due to the lack of professionalism of the surgeon, namely, a certain amount of unremoved parts of the lens may get into the eyeball. Or, due to the invasion inside the eyeball, microscopic bleeding may occur there. Of course, they usually go away on their own after 2-6 days, but there are still cases when specialist intervention becomes necessary again.
Of course, it is more difficult when it is necessary to perform a second operation in order to treat complications. But there are cases when this is vitally necessary. For example, in the case when, after surgery, large hemorrhages or impassable opacities have formed in the eye, there are also various kinds of adhesions and scars. In this case, the surgeon must remove a portion or even the entire vitreous; it all depends on the location of the problem that reduces the patient’s vision. And in order to restore the lost transparency, the gel-like mass is gradually pumped out of it and a special solution is gradually introduced. After two days, this substance is removed from the eyeball on its own thanks to its drainage system, and protection is provided by the intraocular fluid. All this leads to the formation of a secondary vitreous body in the patient, which helps to fully restore a person’s vision.
You may be interested in Nutrition for Cataracts