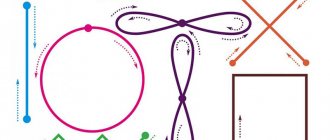
Light exercise for the eyeball helps improve visual function. Accommodation training allows you to make your vision clearer and better. Eye exercises are made possible thanks to the anatomical structure of the eyeballs. The ciliary muscle extends from the lens, which can be trained like any other muscle in the body. Eye training is recommended for both patients with ophthalmological pathologies and healthy people to prevent the occurrence of ailments.
Causes of accommodation spasm in children
With false myopia, children have poor and blurred vision of distant objects and complain of rapid eye fatigue. The cause of this condition is constant excessive visual load, leading to eye strain. It occurs in the following cases:
- discrepancy between the sizes of children's school furniture and the child's parameters;
- incorrect body position when working at the computer and doing homework at the table, neglect of a separate special place;
- insufficient lighting of the work area;
- poor or unbalanced nutrition with the necessary elements, a predominance of junk food (fast food, fast carbohydrates);
- weak, vulnerable immunity;
- insufficient exposure to fresh air, low oxygen intake;
- low physical activity, or physical inactivity;
- disturbed sleep patterns, lack of breaks between work and study;
- low muscle tone in the neck and back;
- head injuries.
Spasm of accommodation in childhood can develop due to the following provoking factors:
- physiological;
- pathological;
- artificial factor.
Physiologically caused false myopia occurs due to improper hygiene of the visual organ, especially in infants, or the use of ineffective drugs or medications prohibited for use in childhood for the treatment of eye diseases.
Some medications can temporarily lead to a spasm of accommodation. Some time after they are removed from the body, the symptom goes away on its own and does not require adjustment.
The pathological type of spasm of accommodation is a serious type that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. In their absence, there is a high risk of transition to true myopia and significant deterioration of vision.
IV. Exercises to improve blood circulation and circulation of intraocular fluid
Eye massage
Massage helps improve vision. It is recommended to do it every day for 10 minutes for a month. Massage increases blood circulation in the eyes and adjacent tissues, improves microcirculation of blood and intraocular fluid. Eye massage is performed while sitting, with clean hands.
- Relax and vigorously rub your palms together for 30-40 seconds.
- Close your eyes and place your palms on your eyelids several times, gently pressing your palms onto your eyes. Repeat 5-7 times.
- Make fists with your hands and lightly rub them over your closed eyes (like children do before going to bed).
- Walk with your fingertips with light pressure along the brow ridges, massaging the painful points more intensely for 30-40 seconds each.
- Using your fingertips, apply light pressure under the eyes, along the lower edge of the eye sockets. Massage painful points more intensely for 30-40 seconds each.
- Massage the outer corners of your eyes with your finger for 2-3 seconds, then the inner ones.
- Using two fingers, use vibrating movements to massage the bridge of your nose for a few seconds.
- Use your fingertips to massage the areas of the maxillary sinuses under the eyes, at the level of the bridge of the nose. The duration of the exercise is 30-60 seconds.
- Place your palms on your closed eyes and press firmly on them 10-12 times at intervals.
- Using your fingertips, massage your closed eyes in a circular motion, first in one direction and then in the other direction.
- Grab your eyeballs through closed eyelids with your fingertips and massage the tissue around them for a few seconds.
- Press your palms on your closed eyes 5-7 times, gradually reducing the force of impact.
During the massage, not only the eyes, but also the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle relax. To improve vision, it is useful to massage the neck and upper back.
Temperature effect
Take two large soft pieces of fabric. Immerse one piece in as hot water as your facial skin can handle. Wring out the fabric and apply it to your closed eyes for 1-2 minutes. Following this, without delay, briefly apply another piece of cloth that has been soaked in cold water to your eyes. Do this three times, then dry your eyes.
3. Exercise "Clock" to improve blood circulation in the eyes
Imagine that you are standing close to a large wall clock, the center of which is located directly in front of your eyes. At the beginning of the exercise, the gaze is directed to the central point. Then, without turning your head, look at any number on the dial, and then look at the opposite number. So go through the entire dial. At the “3, 6, 9 and 12 o’clock” points, hold your gaze for 1-2 seconds; at other points, your gaze is not fixed. It is advisable to go through the dial clockwise and counterclockwise.
Exercise "Solarization"
The purpose of the exercise is to stimulate, excite the visual cells and increase the conductivity of the optic nerve. To perform solarization, stand facing bright sunlight with your eyes closed. Now begin to freely, without tension, turn your head and body to the right and then to the left. This exercise is especially necessary in winter, when the activity of the visual analyzer decreases due to the small number of sunny days.
To prevent an adverse effect, especially in hot weather, you must remember: - the duration of solarization is regulated by the degree of comfort of your condition; in summer it is approximately 5 minutes, in winter - 15 minutes. Solarization is always carried out with your eyes closed! After solarization, it is advisable to rinse your eyes with clean cold water.
Exercise "Blackout"
From time to time it is necessary to create an artificial darkening for yourself, which can significantly speed up the process of relaxing the eye muscles and improve blood circulation.
The exercise is performed standing. Place your fingers in the center of your forehead like a visor, and then your palms will cover the eye sockets, blocking the access of light. The eyelids should move freely.
6.Exercise “Light and Shadow”
In sunny weather, you need to find a place where you find yourself on the border of light and shadow. Holding onto some support with your hands, you need to close your eyes and, breathing deeply, sway so that your face alternates between the sun and the shadow. At the same time, there is a feeling that the sun is swaying.
Symptoms
Signs of the disease may differ depending on the severity of the pathological process and the age of the child. Thus, children cannot always complain and talk about symptoms. They experience:
- asymmetry of nasolabial folds;
- the need to squint the eyes to look at an object in the distance;
- redness of the conjunctiva and tearing;
- frequent blinking, itching of the eyes.
Older children experience other symptoms:
- difficulty viewing an object in the distance - the child notes vagueness, indistinctness and indistinctness of the contours of objects, difficulties in focusing the gaze;
- redness of the mucous membrane and tearing;
- discomfort, pain;
- frequent blinking;
- burning, dryness, eye fatigue;
- headaches, lethargy, fatigue, loss of strength.
In advanced cases, the pathology may be accompanied by hand tremors and a drop in blood pressure.
Diagnostics
If at least two signs of a pathological condition appear in a child, you should visit an ophthalmologist to diagnose a spasm of accommodation, determine the provoking factor and select the correct treatment.
Diagnostics includes a number of activities:
- visual examination of the organ;
- collecting anamnesis, listening to the child’s complaints;
- checking visual acuity using tables;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- determination of refraction;
- examination of the pupil for its ability to refract light rays.
To identify the provoking factor, in some cases it is necessary to consult specialists - a traumatologist, surgeon, neurologist.
Treatment
Therapy for spasm of accommodation in childhood includes:
- elimination of the provoking factor;
- the use of special drops;
- hardware treatment;
- wearing Sidorenko glasses;
- performing gymnastics for the eyes;
- massage;
- folk recipes in the absence of contraindications and restrictions.
All methods are used exclusively as prescribed and recommended by a doctor. Self-medication for spasm of accommodation in childhood is unacceptable. It can lead to irreparable consequences - myopia, accommodation paresis, glaucoma, cataracts.
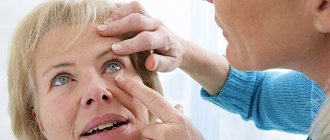
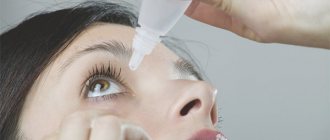
Eye drops
They are used to dilate the pupil, relieve overstrain of the ciliary or optic muscles, and prevent the progression of accommodation spasm.
Medicines used in pediatric practice:
- Irifrin - drops based on phenylephrine to constrict the vessels of the mucous membrane, improve the outflow of aqueous humor and dilate the pupil, slightly relax the ciliary muscle, prescribed from the age of 6;
- Irifrin BC - the same properties as Irifrin, no preservatives, available in disposable droppers, can be used in case of intolerance and allergic reaction to substances;
- Tropicamide, Midriacil - medications that dilate the pupil and cause paralysis of the ciliary muscle, practically not increasing intraocular pressure;
- Atropine - eliminates irritation and spasm of the ciliary muscle, can increase IOP;
- Cyclomed, Cycloptik - medications act like Tropicamide and Midriacil, are allowed by doctor's prescription from 3 years of age.
All eye drops are used in a course in recommended dosages, exclusively as prescribed by a doctor.
Hardware treatment
This type of therapy is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of a specialist. Varieties:
- acupuncture – a type of acupuncture that stimulates the ciliary muscle and helps restore vision;
- electrophoresis - for rapid delivery of medications to the back of the eye, which allows the use of medications in a smaller dose;
- magnetotherapy – to restore visual acuity and prevent the progression of the disease, special magnets with alternating current are used that affect the eyeball;
- laser therapy - to improve vision and stop the pathological process, it is rarely used in advanced, serious cases.
Hardware treatment is an addition to drug therapy.
Sidorenko glasses
The device creates low vacuum pressure on the organ of vision and emits a light pulse. With proper selection and a tight fit on the eyes, Sidorenko glasses improve hemodynamics in the tissues and relieve tension in the ciliary muscle.
The use of this treatment method is permitted in children from 3 years of age, with the exception of contraindications:
- hemorrhage in the organ of vision;
- retinal disinsertion;
- hormonal imbalances.
It is possible to combine the therapeutic method with other types of treatment - physiotherapy, ultrasound.
Gymnastics for the eyes
When performing exercises, it is important to monitor the correctness of the gymnastics and regularity. As a result, it reduces the manifestations of spasm of accommodation in childhood, prevents the appearance of eye fatigue after minimal visual load, and strengthens the body as a whole.
Before performing gymnastics for the eyes, you can do general exercises for the muscles of the neck and back - slowly turn your head to the right, left, down, up without moving your body, tuck your shoulders to your ears and straighten up.
Simple eye exercises:
- do 10 repetitions - close your eyes for 10-15 seconds, relax;
- rotating the eyeballs clockwise 8 times, then back;
- fix your gaze on distant objects, move it to nearby objects;
- draw a figure eight or a bow with your eyeballs, first clockwise 5-8 times, then in the opposite direction;
- blink quickly for half a minute;
- warm your palms, close your eyes and close your eyelids with them.
Sit in this position, quiet, relaxed for a couple of minutes.
Do this set of exercises every day, in between working at the computer and studying.
Massage
One of the reasons for the development of accommodation spasm in children is decreased tone of the muscles of the neck and back. A preventative or therapeutic massage is suitable for strengthening.
First, the specialist begins by stroking the area, then kneading to warm up the muscles, increase tone and strengthen. The massage ends with stroking.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine cannot be used as an independent method of treatment. Before using them, you should consult with a specialist to rule out intolerance to the components.
Facilities:
- ingestion of a decoction of cornflower flowers;
- eating a glass of blueberries daily to improve vision and replenish vitamin deficiencies;
- infusion of nettle and rowan;
- inclusion of carrots and juice in the diet.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, with a spasm of accommodation, traditional methods are unacceptable.
I. Exercises to prevent myopia
To prevent myopia and to stop its further development, it is recommended to perform both general strengthening exercises and special exercises for the eyes.
General strengthening exercises
All exercises are performed standing.
- Throw the ball up with both hands and catch it. Repeat 7-8 times.
- Hit the ball hard on the floor, wait until it rises and catch it with one or both hands. Repeat 6-7 times.
- Pass the ball to your partner from behind your head. Perform 10-12 times.
- Throw a tennis ball at the target, repeat 6-8 times with each hand.
- Throw the ball into the basketball hoop with both and one hand from a distance of 3-5 m. Repeat 12-15 times.
Exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back and neck
Many myopic people have poor posture, which indicates weakness in the back muscles, which can contribute to the onset and progression of myopia. It is therefore recommended to exercise daily.
- Normal walking, on tiptoes, with a small pad filled with sand on the head.
- Stand with your feet apart, hands on your waist, bend forward, back straight, shoulder blades together, look forward.
- Sit on a chair, hold the back of the chair with your hands. Push your chest forward, bend over, then return to the starting position.
- Stand up, hands clasped behind you in a lock. Pull your arms back, bend over.
- Lie on your stomach, arms along your body. Raise your head and shoulders, bend over, return to the starting position.
Exercises to relax the muscles of the back and neck
The exercises are performed while sitting on a chair with a straight back. Exercises help improve the condition of the eye muscles and relax the muscles of the cervical spine. The duration of the lesson is 3-5 minutes.
- Take a deep breath and lean against the back of the chair. Then exhale as you lean forward.
- Lean on the back of the chair and close your eyelids tightly, lean forward a little and open your eyes.
- Wrap your palms around your waist with your thumbs out and turn your head to the left several times, then to the right. Look at the corresponding elbow each time.
- Make circles with your eyes and look up.
- Stretch your arms forward and look at your fingertips.
- Raise your hands up, following your palms with your eyes and without moving your head.
On the subject: What is training to be more human
4.Special exercises for the eyes
Special exercises for the eyes involve moving the eyeballs in all possible directions: up, down, sideways, diagonally and circularly, as well as exercises for the internal muscles of the eyes. Special exercises should be alternated with general strengthening exercises. Exercises help train the eye muscles and eliminate visual strain, improve blood circulation, which helps prevent myopia in children. It is recommended to perform each exercise 2-3 times first, and then 5-6 times.
Warm-up exercises for the eyes
It is advisable to do eye exercises daily. It does not take much time, but is very useful for the prevention of visual impairment. Gymnastics is performed during breaks during prolonged eye strain or in cases where you yourself are tired or your child complains of fatigue.
- Performed while sitting. Blink quickly several times, then close your eyes for 5-10 seconds.
- Can be performed both sitting and standing. Close your eyes tightly for a few seconds, then open your eyes and look into the distance.
- Performed while standing. Draw a dot on the window glass. Look at it for a few seconds, then look into the distance, then back to the point. Repeat the exercise several times.
- Performed standing or sitting. Extend your hand forward and follow with your eyes the movement of the finger, slowly moving up and down and left and right.
- Performed standing or sitting. Make circular movements with your eyes 3-4 times, first to the right, then to the left. The pace is average.
- Performed while standing. Alternately turn your head to the right and look to the left and vice versa several times.
Special exercises for the external eye muscles
- Performed while sitting. Close your eyes tightly for 3-5 seconds, then open your eyes for 3-5 seconds. Repeat 6-8 times. Exercise strengthens the eye muscles, helps them relax and improves blood circulation in the eyes.
- Performed while sitting. Blink your eyes quickly for 1 minute (with breaks). Helps improve blood circulation in the eye area.
- Performed while standing. Look straight ahead for 2-3 seconds, hold the finger of your right hand on the midline of your face at a distance of 25-30 cm from the eyes, move your gaze away from the tip of your finger and look at it for 3-5 seconds, lower your hand. Repeat 10-12 times, alternating hands.
- Exercise reduces fatigue and facilitates visual work at close range.
- Performed while standing. Stretch your hand forward, look at the tip of the finger located on the midline of the face, slowly move the finger closer, without taking your eyes off it until the finger begins to double. Repeat 6-8 times. The exercise facilitates visual work at close range.
- Performed while sitting. Close your eyelids and massage them in a circular motion with your fingertips. Repeat for 1 minute. Exercise relaxes muscles and improves blood circulation.
Special exercises for the internal (ciliary muscles of the eye)
Exercise “Mark on glass”. A round mark with a diameter of 3-5 mm is attached to the glass at eye level. On the line of sight passing through this mark, the patient selects some object in the distance and then alternately looks at the mark and then at this object. The exercise should be performed 2 times a day for 25-30 days. The first two days the duration of each exercise should be 3 minutes, the next 2 days - 5 minutes, then 7 minutes.
Children's games for the eyes
- For children, exercise can be turned into a game
- The adult counts from 1 to 5, and the child closes his eyes, then opens them. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Invite your child to blink, imitating a butterfly flapping its wings.
- Invite your child to pretend to be a traffic light by alternately opening and closing his eyes.
- Ask your child to pretend to be a pendulum: look first to the right, then to the left, without turning his head.
- Without moving his head, the child looks up and down.
- Have your child pretend to be asleep and close their eyes for a few seconds.
- Invite your child to draw crosses with his eyes - first look up to the right, then down to the left, then look up to the left and look down to the right.
- Invite your child to look around a large circle, first from right to left, then from left to right.
- Close your eyes and lightly, without pressing, move your eyelids with your fingers.
- Have your child look at a distant object for 10 seconds, then look at a near object for 10 seconds. You can draw a dot on the window glass. Look at this point for a few seconds, then look into the distance, then again at the point. Repeat the exercise several times.
- Let the child extend his hand forward and follow with his eyes the movement of the finger slowly moving up and down and left and right.
Massage
Self-massage of the muscles on the back and sides of the neck helps improve vision. Cervical spine massage can stabilize visual function and help treat myopia. Massage is carried out 2-3 times a week. Perform it sitting on a chair, leaning on its back and keeping your head straight. Massage the neck muscles in the direction from the occipital protuberances to the shoulder girdles as follows:
- stroking with one and two hands – 20-30 seconds;
- rubbing with four fingers in a circle – 1 minute;
- kneading with one and two hands (tongs technique) – 1 minute.
The total duration of self-massage is 5-6 minutes.
Complications
If spasm of accommodation in childhood is not treated in a timely manner, there is a high probability of pathology transforming into true myopia and a stable deterioration in visual acuity.
Other complications:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- chronic eye fatigue, or asthenopia;
- trembling, or tremor of fingers and hands;
- depression;
- accommodation paresis, when it is impossible for a child to see small objects even at close range;
- glaucoma and cataracts;
- deterioration in quality of life.
III. Accommodation training
These eye exercises improve the accommodation of the lens of the eye, that is, the ability to clearly see objects at different distances. It is recommended to perform them regularly for those whose work involves eye strain and who spend several hours every day at the computer or at a desk.
- Performed while standing at the window. Look at a nearby object for a few seconds. Slowly turn your gaze to an object located at a considerable distance and look at it for several seconds. Repeat 2-4 times.
- In the same position, look into the distance, gradually, slowly moving your gaze from close objects to increasingly distant ones. Hold your gaze on each object for a few seconds so that your eyes have time to adapt to the distance and the object is clearly visible. After examining the most distant object, use your gaze to follow the path back to the closest object. Breathe deeply, evenly, and blink frequently.
- Performed while sitting. Cover your right eye with your palm. Take the calendar in your left hand and bring it close to your left eye. Try to clearly see the letters without straining your vision. Then slowly move your hand with the calendar forward from your eye. Breathe deeply and evenly, blink frequently. Slowly return the calendar to its original position without looking away and exhale. The duration of the exercise is 20-30 seconds. Repeat the exercise with the second eye. Performed 2-4 times.
- Cut out the letter C with a diameter of 10 mm from black paper and stick it on the window glass at eye level. The distance from the mark to the eye is 30 cm. Look for 10 - 15 seconds at the cut out letter C, then the same time - through the mark into the distance. On the first day, practice for 5 minutes, then add one minute every day. The maximum lesson time is 15 -16 minutes. The exercise is performed separately for each eye. The second eye is covered with the palm of your hand or a piece of paper. The eye under the palm should be open. This type of training is called a glass mark exercise . It is often recommended to be performed by schoolchildren with impaired vision. Theoretically, the exercise allows you to load the accommodation mechanism of the eye and relieve visual fatigue. However, its implementation requires constant attention and self-control. This is exactly what is difficult to expect from a child. In addition, it remains unclear how to monitor the child’s performance of this exercise. A number of devices presented on our website provide effective accommodation training. First of all, these are the “Rucheek” devices.
Prevention
Spasm of accommodation often occurs in childhood. To prevent the development of false myopia and vision deterioration, the following preventive measures should be followed:
- reduce the load on the organ of vision - find a safe alternative to gadgets, smartphones and TV, observe work and rest times, take breaks when reading, working at the computer;
- provide good lighting in the study and work area;
- under any visual load, maintain the optimal distance between the organ and the working instrument (for example, a book);
- to prevent eye fatigue and loss of vision, periodically do warm-up or gymnastics;
- purchase a comfortable, ergonomic chair or chair, table for homework, hobbies, work;
- do not read while lying down;
- sit on a chair with a straight back;
- replace gadgets with a walk in the park, football, outdoor games;
- balance your diet, saturate it with nutrients, vitamins and minerals;
- If your diet is poor, periodically, on the recommendation of a specialist, take multivitamin complexes.
If there is the slightest decrease in visual acuity, eye fatigue after reading or working at a monitor, or tearing, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
Accommodation function
Accommodation of the eye is its ability to adapt its internal optics to the distance to a visible object. Such adaptation is possible thanks to the work of the ciliary muscle, which, like any muscle in the human body, can be trained.
In the world of modern high technology, people living in cities are increasingly less likely to look into the distance. Computer, TV, tablets, smartphones, printed documents - the current human environment is at arm's length from him. And when driving a car in big cities, a person no longer needs to look at objects more than 5-10 meters away. The lack of need to look at significantly distant objects leads to relaxation of the ciliary muscle, which can cause unpleasant consequences. The situation can be easily compared to the work of a weightlifter who once lifted 150 kg, but after stopping training and playing chess for a long time, now cannot lift even less heavy weights. Something similar can happen to the accommodative muscle. Its complete atrophy in the absence of the necessary loads is, of course, impossible. But the former strength will certainly be lost or not gained at all if the child’s gaze from a very young age is “chained” to nearby objects.
On topic: Whipped eggs after a workout
Accommodation training is a completely easy task. To do this, you just need to be outside more often or just look out the window. Ordinary admiration, even of a well-known landscape, can help develop the functional abilities of the ciliary muscle. In addition, there are special exercises that will help maintain its necessary tone. Each of these exercises should be performed two or even three times daily. Not necessarily in a certain order and not necessarily at a certain time. Exercises can be alternated, and training time can be reduced or increased.
Useful video
Gymnastics to relieve fatigue and treat false myopia.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 4.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.