Methods for treating eyelid edema or what needs to be done?
Treatment options
When the upper eyelids of the eyes swell, according to ObaGlazaPy, doctors look for the causes and select the appropriate treatment. It is dangerous to tidy up swollen eyelids without medical advice using various lotions and rinses. Therefore, you first need to establish what is causing the swelling on the eyelid. When it becomes clear that there is nothing dangerous, you can move on to symptomatic treatment.
The body's allergic reaction requires treatment, which usually consists of taking antihistamines and using eye ointments to relieve itching.
To consolidate the result, doctors advise including more fruits and vegetables in the diet, which will strengthen the immune system.
In some cases, the skin around the eyes can be restored using cosmetic procedures:
- Mesotherapy;
- Dermatonia;
- Lymphatic drainage massage of the temporal region;
- Electrical stimulation.
Eye swelling is reduced by stimulating blood circulation, thereby improving the overall condition of the skin.
Inflammatory processes require an integrated approach and the use of medications. Traditional treatment, consisting of analgesics, antibiotics and antiviral agents, is combined with rinsing and physiotherapy.
In case of injury, the area around which the swelling is located is first treated with antiseptic agents, which reduce the risk of infection and infection. Cold can also be applied, says OglazaRu.
Secrets of our grandmothers (folk recipes)
Such a phenomenon as swelling of the upper eyelid of the eye occurs quite often among all cases of inflammation of the eyelids. Therefore, in addition to traditional methods of treatment, there are many folk recipes that it is time to mention.
All of them are time-tested, but they can only be used as additions to the main therapy prescribed by a specialist, ObaGlaza notes.
You can cope with swollen skin around the eyes and upper eyelid with the help of:
- Parsley. The plant has anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. All parts will come in handy; from roots to seeds. Finely chopped parsley roots and stems (5 plants), add water (1 liter) and add a little sugar (2 tablespoons). The mixture is placed on low heat for 30 minutes, cooled and consumed 3 times a day, 100 ml. If there is no fresh herb, obaglazaRu believes, you can brew dried parsley stems: 2 tablespoons per 200 ml of boiling water. The mixture is passed through a sieve and one tablespoon of infusion is drunk four times a day.
- Flax seeds, which have an antibacterial and diuretic effect. For 1 liter of water you will need 4 teaspoons of seeds. After boiling for 15 minutes, the mixture is cooled and consumed three times during the day, 100 ml each.
- Carrots with their diuretic properties, as well as anti-inflammatory, laxative and carminative effects.
- Teas infused with mint and linden blossom.
- Fresh cucumbers. Sliced vegetable slices are placed on the eyes and left for 10-15 minutes.
- Masks based on sour cream or cottage cheese.
Cosmetic preparations
On sale, according to OglazaRu, you can easily find a cream or gel that helps relieve swelling. As a rule, the manufacturer places information about this property of the product on the product label.
Cosmetic preparations with a lifting (tightening) effect also help to remove swelling of the upper eyelid.
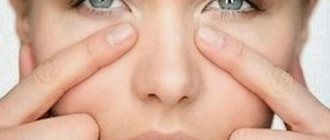
Symptoms of eyelid edema
The appearance of the eyelid and the unusual sensations in it will help determine the beginning of swelling. You need to be wary if:
- the skin changes its natural color (reddens, turns pale, appears cyanotic);
- there is a feeling of tension;
- the skin becomes thinner and its surface begins to shine;
- blood vessels become clearly visible on it;
- a rash appears in the form of small dots;
- the palpebral fissure decreases until it closes completely;
- touching the eyelid is painful;
- parotid lymph nodes are inflamed;
- upon palpation, it is revealed that the tissues around the eyes have become dense;
- the skin itches, tingles, there is a burning sensation or irritation.
Symptoms
The appearance of swelling of the upper eyelid against the background of an inflammatory process is accompanied by:
- Swelling.
- Redness.
- Tissue compaction.
- An increase in local temperature.
- Soreness to touch.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction appear quickly and are accompanied by:
- Soreness.
- Itching and burning.
- Pale skin. In rare cases, cyanosis may appear.
Depending on the general condition of the patient, the pathology may be accompanied by other symptoms: irritation, general weakness, and a slight increase in temperature.
The appearance of reactive edema of the eyelids is most often the body’s response to an allergic reaction or Quincke’s edema. There is limited or widespread swelling that can spread lower down the face. There is no significant pain during its formation; the patient may feel severe itching and tissue tension. After a short time, the swelling disappears. However, if the allergen is not eliminated, the negative symptom may periodically recur or take a more severe form, involving other membranes of the eye in the pathological process.
Diseases in which symptoms may be observed
If swelling constantly appears, the cause of this condition should be sought in the development of some disease. The most common causes of this condition are:
- Blepharoconjunctivitis. The pathology combines inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye and the edge of the eyelid.
- Hemophthalmos. Hemorrhage into the vitreous body caused by damage to the blood vessels located in the upper eyelid.
- Conjunctivitis. The most common disease of the ocular mucosa. Is it infectious or non-infectious in nature. The skin around the eyes turns red and the eyelids swell. Additional symptoms depend on the nature of the disease that caused the appearance of this lesion.
- Trachoma. An infectious disease caused by the presence of chlamydia. Swelling appears at the last stage of the disease.
- Tuberculosis of the eye. Infectious pathology caused by the presence of Koch's bacillus. Rarely develops independently, more often it manifests itself against the background of pulmonary pathology.
- Endophthalmitis. Inflammation of the internal structures of the organ of vision, characterized by the accumulation of pus in the tissues of the eyes. The disease causes blurred vision, leads to severe swelling, hardening and redness of the tissues.
Swelling of the bridge of the nose in a child
Observing swelling in a child is a good reason to immediately consult a doctor. Among the main reasons for the manifestation of pathology are:
- the appearance of recurrent pimples and acne in the sinus area;
- the formation of hollow cystic formations and inflammatory granulomas, in which swelling spreads to the cheek);
- disturbances in the functioning of the adenoids.
Swelling can also be the result of an injury or frostbite after a long walk outdoors in severe frost. An allergic reaction to flowering or pollen is also no exception when diagnosing the cause of swelling in a child. Timely assistance will help to avoid complications and quickly restore full breathing.
Types of swelling of the eyelids
According to clinical symptoms, as well as the reason that caused the swelling of the eyelid, it is divided into several types:
- Inflammatory. The condition occurs due to the penetration of viruses, infections, and parasites into the eyes. Swelling is formed due to the accumulation of interstitial fluid secreted by the endocrine glands.
- Not inflammatory. In the absence of inflammation, the patient's symptoms are less pronounced. Swelling of the eyes is detected in the morning, immediately after waking up, and spreads to both eyes. The cause may be kidney disease, liver disease, or impaired water-salt metabolism.
- Allergic. The condition can form seasonally, for example when plants bloom. An allergic reaction can also form under the influence of a negative factor that suddenly appears in front of a person. This condition is detected with an increased reaction to animal fur, medications, and contact lenses. The condition is often accompanied by severe redness, itching, increased production of tear fluid, and photophobia. This is the most severe type of eyelid swelling.
For inflammatory and allergic edema, similar drugs are used, the therapy differs slightly. If the cause is not inflammatory, but is formed as a result of internal disorders and diseases, complex therapy for the primary condition is required.
Swelling of the upper eyelids
There are cases when the swelling extends only to the upper eyelid area. The condition is detected in the following cases:
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular and urinary systems;
- the presence of a benign and malignant tumor in the body;
- allergic reaction to external factors or food products;
- accumulation of adipose tissue in the eye tissue on the upper eyelid.
For the first 3 conditions, complex treatment is required. Fat deposits can be removed through surgery.
Swelling of the lower eyelids
Otherwise, this condition is called bags under the eyes. Most often they form in the morning, immediately after waking up. Swelling appears immediately in 2 eyes, due to the influence of non-inflammatory factors.
The following conditions and diseases may be the causes:
- endocrine pathologies;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and urinary systems;
- consumption of nicotine, alcohol, drugs, medicinal substances;
- use of low-quality cosmetics.
Puffiness and bags under the eyes can occur due to a hereditary factor. That is, the characteristics of the physiological structure are transmitted in the genetic material from parents to child.
Swelling of the eyelids in the morning
This condition can occur in patients in a single case or systemically. Most often it manifests itself in the following conditions and diseases:
- drinking large amounts of liquid and salt before bed;
- alcoholism;
- low fluid intake during the day;
- severe body tension, stress, overwork, sleep disturbance;
- using fatty creams before bed.
To eliminate the phenomenon, it is enough to adjust the fluid intake regimen and use gentle diuretics. Also, recently the use of patches under the eyes to eliminate swelling has become fashionable.
Swelling of the eyelids after tattooing
Many women do not want to apply cosmetics to their eyes every day. In this case, they resort to eyelid tattooing. The cosmetologist applies a dye under the skin, which then remains there for many years. Immediately after the procedure, severe swelling of the eyelids may occur. Normally, it should go away within a few days. But there is also an increase in the rehabilitation period due to the influence of the following factors:
- low-quality pigment for tattooing;
- increased reaction of the immune system, leading to allergies to pigment;
- excessively deep introduction of pigment;
- increased sensitivity and irritability of the skin of the eyelids;
- hypersensitivity, allergic reaction to anesthesia;
- violation of hygiene rules, due to which an infectious agent spreads inside the wounds.
If the procedure is successful, the swelling should go away within 3-4 days. If there are complications, the patient will need therapy, after which the swelling of the eyelid will go away on its own.
Pathological causes
There are diseases that can cause darkening of the bridge of the nose:
- mechanical damage, trauma, bruises occurring in this area, for example, a broken nose, accompanied by internal hemorrhage;
- lack of oxygen in the air due to vasospasm, coronary artery disease, prolonged absence of walks on the street;
- use of nicotine, alcohol, drugs, illegal drugs;
- serious pathologies of internal organs (cardiovascular system, kidneys, liver);
- serious hormonal disorders.
Treatment of such conditions should be started only after a complete diagnosis. This will identify the true cause in order to prevent a relapse of the condition.
Treatment depending on the causes
Before treating a swollen eyelid, you need to determine the cause of the problem. Regardless of the disease, it is recommended to use external decongestants - creams or ointments that can quickly eliminate swelling. However, symptomatic treatment alone is not enough. Depending on the pathology that caused the negative symptoms, medications are prescribed.
For conjunctivitis
Various forms of the disease provoke the appearance of edema of varying severity. The greatest swelling of the upper eyelid is caused by the bacteriological form. If the eyelid of one eye is swollen, the use of bacterial and decongestants is prescribed.
For blepharoconjunctivitis
When treating eyelid swelling in one eye, it is recommended to use local remedies and medications. The treatment regimen may include corticosteroids and drugs with antihistamine, antibacterial and antiviral effects. In addition, it is recommended to regularly wash your eyes with antiseptic solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs.
For trachoma
For treatment, antibiotics of the sulfonamide group are used in different forms: drops, ointments or combinations thereof.
If follicles appear, they are excised or squeezed out. This can only be done in a hospital setting. If swelling persists, a second course of treatment may be prescribed.
Conservative therapy
For infectious processes, it is recommended to use broad-spectrum antibiotics and antiviral drugs in the form of tablets, ointments or drops. For allergy symptoms, drugs with antihistamine, anti-inflammatory action, which include synthetic steroid hormones, are used. These drugs help cope not only with swelling, but also itching, redness, and eliminate discomfort.
Non-inflammatory swelling can be eliminated with proper rest, reducing fluid and salt intake, and giving up bad habits. If the problem persists, you need to check the functioning of the kidneys, endocrine and cardiovascular systems.
Cosmetical tools
If the swelling is the result of cosmetic procedures, then in order to cope with the problem, you can use special ointments, creams or masks that help remove swelling of the eyelids above the eyes. Good results are obtained by using physiotherapeutic procedures: electrical stimulation, mesotherapy, manual, roller or vacuum massage. They have a beneficial effect on the condition of tissues, help remove excess fluid, and normalize lymph flow.
Folk remedies to eliminate swelling of the eyelids
Traditional medicine to combat swelling in the upper eyelid recommends using products with anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties that can remove excess fluid, improve blood flow and lymph outflow.
The most effective remedy is parsley. Its decoctions are used for lotions and compresses, and taken orally as a diuretic. An infusion of birch leaves has the same property. Flaxseed decoctions act as an antibacterial and diuretic. Chamomile infusion helps relieve inflammation and reduce the manifestation of an allergic reaction.
As first aid for swelling, you can use pieces of ice, slices of raw potatoes or fresh cucumber. They should be applied to the affected areas of the skin for 10-15 minutes.
Prevention of edema
In order to have a good morning and the reflection in the mirror does not spoil your mood for the whole day, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- Don't drink a lot of water before bed. It is recommended not to drink water 2 hours before bedtime.
- Healthy, full sleep (7-8 hours).
- Limit your intake of salty foods and avoid artificial sweeteners.
- In summer, use sunscreen and avoid being in direct sunlight for a long time. Wear highly protective sunglasses.
- When working with dangerous tools, follow safety precautions (for example, wear a protective mask when carrying out welding work).
- Minimize or completely avoid coffee, alcohol, and carbonated drinks.
- Whenever possible, avoid contact with people suffering from infectious diseases.
- If your eye becomes swollen and constantly itches, then you should not put off visiting a doctor and do not try to solve the problem yourself.
By following simple rules, this problem will bypass you. If the eye is swollen, and the upper eyelid has significantly increased in size, then it is best to seek help from a doctor to diagnose and treat the disease.
Eyelids are swollen after tattooing: what to do?
Permanent makeup allows a woman to always be “at her best” and significantly saves both time and money on purchasing decorative cosmetics. However, the tattooing procedure does not always go smoothly, and swelling of the eyelids is one of the most common phenomena when applying a design to the eyelids and eyebrows.
Swelling can be a natural reaction of the body to multiple micropunctures and the introduction of dyes under the skin. In this case, the swelling will go away on its own, and within a day there will be no trace of it left.
To minimize the negative consequences of permanent eye makeup, immediately after the procedure the eyelids are lubricated with Hydrocortisone ointment.
Hydrocortisone ointment for swelling after eye tattoo
If after tattooing your eyelids are not just swollen, but also darkened or covered with crusts, severe itching appears, your eyes turn red and begin to water, consult a doctor. This is an abnormal condition that can only get worse.
Treatment of swelling of the bridge of the nose
The causes of swelling and swelling of the bridge of the nose can be different, so before starting treatment for swelling, it is necessary to establish the provoking factor.
If the cause is a runny nose, then it is treated with drops. But when swelling develops for unknown reasons, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After establishing an accurate diagnosis, therapy using medications or folk remedies is selected individually.
Traditional therapy
After the examination, the doctor will tell you how to remove the swelling of the bridge of the nose. They fight a runny nose with the help of vasoconstrictors: Sanorin, Nazivin, Mezaton. You can use the drops for no more than one week. In addition to these remedies, in official medicine, a runny nose is treated using physiotherapeutic procedures. If the runny nose does not go away, additional examination may be required.
If the cause is an allergy, then therapy is carried out with antihistamines. The course of treatment is 10 days. They use Tavegil, Zyrtec, Cetrin. For viral diseases, antiphlogistic agents are used: Sinupret, Cinnabsin.
Causes of swelling of the upper eyelid
Inflammatory tumors
Severe inflammation can be a consequence of bacterial or viral diseases. Redness, tearing and swelling of the eyelids are observed with conjunctivitis and blepharitis. They may swell due to an abscess and blockage of the meibomian gland.
In this case, patients experience a high body temperature, and the swollen eye becomes very red. Most often, the tumor forms on one eyelid, the disease is accompanied by purulent discharge. Patients experience photophobia, itching and discomfort.
Allergic reaction of the body
When a person comes into contact with allergens, the eyelids may swell so much that the eye lumen will be closed. They begin to swell at the same time, and the process develops unexpectedly and quickly. All kinds of medications, foods, chemicals, cosmetics, fungi, etc. cause an allergic reaction.
| In order to remove severe swelling, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen and take an antihistamine (drops, tablets). |
If you do not suspect what caused such a reaction in the body, you need to contact a specialist to conduct appropriate tests for allergens and prescribe treatment.
Systemic diseases of the body
The eyes become swollen due to other ailments, and in this case it will not be easy to relieve severe swelling. It is necessary to treat exactly the cause that caused the symptom. The eyelids may swell due to vascular diseases, problems with the heart, kidneys and liver, due to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract or thyroid gland.
The cause may be cancer. Pathological processes of lymph flow disturbances and tissue fluid retention cause pastosity. This type of skin appears due to problems with blood supply and improper distribution of intercellular fluid.
Swelling can be caused by diabetes mellitus, problems with the immune and nervous system, liver dysfunction and respiratory tract pathologies. The specialist prescribes complex therapy to treat the disease causing swelling.
Wrong lifestyle
Proponents of a healthy lifestyle rarely complain about the swollen appearance of their eyelids; this happens to them in case of lack of sleep or severe fatigue. Eyes may become swollen and painful from working at a computer for long hours.
| But such swelling above and below the eyelids often occurs in people who abuse alcohol. Lack of a balanced diet leads to the same results. |
The eyelids take on a swollen appearance after eating foods with a high salt content. In order to avoid unsightly swelling, you should limit it in your diet, drink enough water and avoid drinking alcohol. Adequate sleep will be your ally in maintaining healthy skin.
Physiological reasons
These include age-related changes that inevitably occur in the human body and mechanical effects on the facial area. The eyelids “drop” down, and their sagging often resembles swelling. In this case, only plastic surgery will help eliminate the defect.
What is inflammation of the meibomian gland?
Blockage of the canals causes gradual inflammation of the eye tissues. Fat is not removed on time, pathogenic organisms begin to accumulate, which lead to the formation of a tumor on the eyelid. This is a painful process that forces a person to seek help from an ophthalmologist.
Is it possible to squeeze out barley?
If staphylococcus enters the body of a person with a weakened immune system, a stye may form on the eye. The body temperature rises, the tumor grows in size until the abscess opens and its contents are released.
After this, the patient feels better, and the small wound heals and the swelling decreases. You cannot squeeze out the barley yourself. If a large tumor has formed on the eye, the accumulated fat can be removed in the hospital under local anesthesia.
In this case, dangerous bacteria that can lead to serious complications are prevented from entering the body.
Injuries
Injuries in the area of the nose or eyes cause the formation of hematoma and swelling. If a bruise occurs during sports or outdoor activities, you should apply ice to the site of the impact and then consult a doctor for an examination.
Excessive fluid intake
Uncontrolled consumption of water and drinks leads to swelling in different parts of the body, and the eyes are the first to suffer in this case. To solve the problem, you may need not only an examination by a specialized specialist, but also a consultation with a nutritionist. Swelling occurs after drinking heavily in the evening, so you should reduce your fluid intake before bed.
Causes and corresponding symptoms
Since the causes of edema can be very different, the symptoms of their manifestation differ from each other. Thus, the pathology itself can be provoked by:
- Sinusitis, in which swelling is observed not only on the bridge of the nose, but also on the wings of the sinuses and near the eyes. When pressing on swollen areas, the patient may feel increasing pain. The main reason for this is the accumulating pus inside the sinuses themselves.
- Rhinitis (in the acute form of an infectious lesion), in which the nasal cavity may become completely swollen. In this case, the patient himself experiences pain in the nose, excessive lacrimation, sneezing attacks, and an increase in body temperature. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the formation of boils and painful cracks.
- The presence of formations (benign or malignant). These can be either hollow cystic formations with internal liquid contents or tumors producing cancer cells. Often, in addition to swelling, the disease is accompanied by pain only in the later stages of development of the pathology (when the tumor increases in size and puts pressure on neighboring tissues and organs).
- One or more boils , which are the result of inflammation of the sebaceous glands or hair follicles. In such cases, timely surgical intervention is necessary. The presence of boils may be accompanied by itching and pain when pressed.
- Excessive acne in the nasal area, accompanied by itching and pain.
- The presence of numerous herpes rashes , characterized by painful tingling in the affected area.
- The entry of a foreign object into the nasal sinuses, which in turn causes the accumulation of purulent discharge and pain when pressing on the swelling itself.
- Inflammations around the eyes, for example styes, which if left untreated can cause swelling.
- Syphilis, which is dangerous due to the risk of destruction of the bone base of the nasal cavity, accompanied by painful inflammation.
- Rhinosinusitis, which is characterized by loss of smell, increased body temperature and the presence of mucopurulent discharge from the nose.
- The manifestation of an allergic reaction of the body to cosmetics, pollen, flowering, which is complemented by increased tearfulness, difficulty breathing and redness in the eye area. The presence of an allergy to anything from the environment is not accompanied by pain, which is its distinguishing characteristic when diagnosing the disorder itself.
- Anatomical features of the structure of the nasal sinuses and bridge of the nose, as well as possible previous injuries, such as bruises and fractures. Often occurs precisely after a blow to the bridge of the nose. In such cases, pain in the damaged area is often observed, as well as the inability to breathe properly.
- Impaired kidney function. In such cases, changes in the color and volume of urine excreted, pain in the lumbar region, and an increase in body temperature are typical. The patient himself may also complain of lack of appetite.
Swelling can be caused by uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops, hormonal dysfunction, disturbances in the cardiovascular system, and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Often, temporary swelling on the bridge of the nose is observed after rhinoplasty (plastic surgery to correct or restore the nose).
With this pathology, the patient may often complain of excessive dryness and burning in the nose and loss of sensitivity to smells.
What to do for treatment?
Swelling can be eliminated by using decongestants, but first of all it is necessary to identify the cause of this disorder.
Medicines
For allergies, antihistamine and hormonal drops and ointments are used to relieve swelling, including:
- opatanol;
- hydrocortisone ointment;
- lecrolin;
- dexamethasone;
- cromohexal and others.
Next, antibacterial drops and ointments are used to eliminate pathogenic microflora, the presence of which contributes to the intensification of this symptom.
Such antibiotics are prescribed by the attending physician based on the patient’s age, the causative agent of the disease and the stage of the disease.
For blepharitis and barley, such drugs include ointments for external use or for placing under the eyelid (ophthalmic drops in such cases are ineffective).
Treatment lasts approximately a week, with ointments being applied up to three times a day.
As a disinfectant for swelling, you can use a solution of boric acid: 5 grams of this product is diluted in 100 grams of boiled water and used for rinsing two to three times a day.
It should be noted! Additionally, you can take decongestant tablets Claritin, Zodak, Zyrtec, Tavegil orally.
Traditional methods
Along with standard treatment, it is possible to speed up the removal of swelling using traditional medicine methods.
But such therapy should not be the main one and all of the listed recipes should be used only after agreement with the attending physician:
- 20 grams of finely chopped fresh parsley are brewed in a glass of boiling water. The product must additionally be kept on the fire for five minutes and then left to infuse for 30 minutes. This medicine is taken orally, three times a day, dividing the glass into three equal portions. If it is necessary to use such a remedy in the following days, a new portion of the infusion is prepared every morning.
- A decoction of plantain, chamomile, calendula and mint is frozen in cubes in the refrigerator. In this case, the concentration and combination of herbs is not important - the more herbs in the composition, the better. Such ice cubes are wrapped in gauze or a clean cloth and the finished compress is applied to the eyes for about five minutes three times a day. Such cold compresses help relieve swelling and help restore normal skin color. You should not keep the cubes for longer than the specified period, as this can lead to hypothermia and damage to blood vessels.
- A medium-sized apple of any variety is crushed on a fine grater and placed in gauze, which is placed over the eyes. The gauze needs to be rolled up in no more than two layers so that the apple juice can seep through it. It is enough to apply the compress once a day for fifteen minutes.
- Grate carrots and fresh parsley in equal proportions. The mixed ingredients without cloth and gauze are placed on closed eyes once a day for 15 minutes. After this time, you can wash off the compress with regular cool water.
- Mix ten grams of cottage cheese and grated raw potatoes. The mixture is salted with a pinch of salt and applied to the eyes for twenty minutes. It is better to remove the mixture with cold water to completely remove the remaining starch released by the potatoes.
Note! A good way to relieve swelling is a cucumber-honey mixture, but this method can only be used if you are not allergic to honey.
10 grams of honey are mixed with 20 grams of cucumber juice. The resulting thick composition is applied to the eyelids for ten minutes.
Possible diseases
- Eye infections. These are demodicosis, keratitis, sinusitis, and conjunctivitis listed above. They will be accompanied by the flow of pus, copious release of tear fluid;
- Urolithiasis, renal failure are combined with difficulty urinating, pain in the excretory tract;
- Diabetes;
- Often swelling occurs against the background of flu, sore throat, and colds. Then there is fever, redness of the eyes, and general malaise.
In each case, the symptoms will be different. Therefore, it is necessary to distinguish the signs of one disease from another.
Morning swelling of the eyelids
During the night, the fluid accumulated during the day stagnates in the body. Swelling is caused by drinking large volumes of water in the evening and eating spicy foods. If this is the case, then the symptoms will go away on their own within half an hour. And the next morning the swelling will not happen again.
| When it is repeated every day without taking plenty of liquid the day before, this indicates diabetes mellitus and kidney problems. |
Eye diseases
Myopia, astigmatism, cataracts, glaucoma, and retinal pathologies are common. These diseases occur inside the eye and do not have pronounced external symptoms. Only injuries are expressed in the redness of the white and the formation of a bruise in the periorbital area. But this is a sign of injury, not illness.
Accordingly, swelling will occur only with conjunctivitis, sinusitis, demodicosis, which are treated with antibiotics in the form of drops, Taufon for the blood vessels of the eye, Albucyt to remove the infection.
Diseases of other organs
Kidney disease, diabetes, and vascular problems can lead to swelling of the eyelids. If diabetes or renal failure is diagnosed, there is increased intracranial pressure, hypertension, then these diseases need to be treated.
You should take Lasix, Saparal, Regulton, and install “systems” in a day hospital setting. This will keep the pressure at the desired level. For blood pressure, take Diuretics or Rinin to remove excess fluid from the body.
Causes
The etiology of the development of subcutaneous seals can be various diseases or mechanical damage (a bump on the bridge of the nose after an impact). Most often, this symptom occurs due to the development of the following pathological processes:
- Lipoma. In common parlance it is called wen. It does not cause pain, and appears as a consequence of lipid metabolism disorders in the body, when eating unhealthy foods or when hormonal balance is disturbed. In addition to a cosmetic defect, the number of wen may increase with eyelashes growing into them.
- Papilloma. It can develop on any part of the face. The bump on the bridge of the nose, which has a stem at the base, looks especially unsightly. In the pathogenesis of the development of this compaction, the main role is played by the human papillomavirus.
- Cystic compaction. It is formed inside the skin; upon palpation, a dense consistency is felt. Tends to become inflamed, causing the contents to come out.
- Abscess. It is a formation that is filled with purulent secretion inside. Occurs due to the penetration of bacterial pathogens under the skin. Accompanied by an increase in body temperature, and can cause the spread of infection throughout the body (sepsis). As it increases in size, it causes throbbing pain.
- Barley. The disease often begins with the appearance of a bump on the bridge of the nose near the eye (in the corner near the lacrimal punctum). The cause may be an inflammatory process in the eyelash follicle or in the meibomian (sebaceous) gland. In this case, the patient experiences the following symptoms: severe hyperemia and swelling around the eye; stabbing pain; feeling that a foreign body has entered the eye; sudden increase in body temperature; symptoms of malaise and loss of strength appear.
- Hemangioma is characterized by a dense consistency. Its surface may have varying degrees of red tint. There are no painful manifestations.
- Oncological neoplasms. A distinctive feature is that, despite the completeness of the treatment process, the lump does not go away for a long time. It tends to periodically fester, and in advanced forms is accompanied by a persistent painful syndrome.
- Furuncle. Initially appears as a small ball in the center, which has a yellowish dot. Its cavity is filled with purulent contents, and as a result of “ripening” it opens. Subsequently, a scar forms in its place. The lump is painful and can cause swelling of the face due to inflammation.
- Chalazion. It is a consequence of blockage of the sebaceous glands. It is often a complication of untreated stye. The resulting capsule has a dense structure, and touching it causes pain. The danger of this formation is that suppuration can come out with the formation of a fistulous tract.
Why does swelling occur?
There are many reasons why this symptom appears. To accurately determine the nature of the pathology, the doctor focuses on additional manifestations of the disease.
Inflammatory processes
Most often, the upper eyelid swells due to ophthalmological disorders. This occurs much less frequently in other pathologies not related to the organ of vision.
Main ocular causes:
Viral conjunctivitis.
This disease leads to swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye and its eyelids. It appears due to the introduction of viruses into the conjunctiva and the development of an inflammatory process there. The patient complains of a feeling of sand in the eye, lacrimation, photophobia, and decreased visual acuity. It happens that the patient cannot open his eyes due to increasing swelling. Most often, one eye is affected first, and after a few days the infection spreads to the other.
Blepharitis.
The infection affects the edges of the eyelids, causing them to become hyperemic and swollen. Severe itching and discomfort appears. The cause of the disease is an inflammatory process caused by bacteria and mites.
Barley.
The disease develops acutely with inflammatory damage to the hair follicle of the eyelid. Over time, a swelling forms, which gradually turns into a “bump”. It contains purulent contents. After a few days, the formation opens with the release of pus. The patient's eyelid is locally hyperemic and swollen.
Chalazion.
It is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margin, affecting the meibomian gland and cartilage. It develops when a duct becomes blocked. A secretion begins to accumulate in it, which is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microbes.
As a result, a dense round formation is formed in the thickness of the cartilage, painless on palpation. The chalazion becomes noticeable from the skin and creates an aesthetic defect.
Dacryoadenitis.
This is an acute inflammation of the lacrimal gland. The causative agents of infection are viruses or bacteria. Most often this is a secondary process. It develops against the background of other diseases - acute respiratory infections, mumps, tonsillitis, measles, rotavirus and others.
The patient has severe swelling of the upper eyelid. The pathological area is hyperemic and painful. Severe, continuous lacrimation appears.
Other inflammatory causes are acute respiratory infections, frontal sinusitis.
What is Dacryoadenitis:
Non-inflammatory causes
Most often, swollen eyelids cause the following disorders:
- cardiovascular pathology (heart failure);
- kidney diseases (amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis, heavy metal poisoning, renal failure);
- thyroid function disorder;
- violation of the outflow of blood and lymph;
- oncological neoplasms of the eye;
- excessive salt intake;
- bad habits;
- visual strain;
- lack of sleep.
Attention! Most often, swelling forms in the morning immediately after waking up. It is not accompanied by hyperemia, pain or local fever
The skin of the eyelids is cool and pale.
Allergic reactions
Usually the pathology develops acutely. Its additional symptoms are severe itching, redness, discomfort, lacrimation with photophobia, and nasal congestion.
Swelling of the upper eyelid appears due to the development of an allergic reaction. It can be triggered by:
- food products;
- cosmetical tools;
- household chemicals;
- pollen of flowering plants;
- insect bites: midges, mosquitoes;
- animal fur.
Swelling of the upper eyelid occurs as allergic dermatitis or Quincke's edema. In the first case, the symptom is not so intense, but always occurs with hyperemia and itching.
Quincke's edema is especially dangerous because it can spread to the organs of the respiratory system. Its manifestations are very pronounced. The patient is unable to open his eyes due to severe swelling.
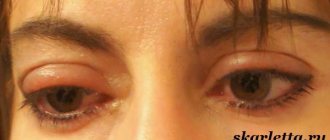
What is eyelid swelling
This is a symptom that represents an excessive accumulation of fluid in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the eyelids, resulting in their swelling. The common cause of this pathology is various diseases of a local or general nature. Swelling of the upper eyelid is most common, but sometimes it also occurs in the lower eyelid. The attack can be single or recurrent. Edema can develop at any age, but men and women over 30 are more prone to it.
In general, the eyelid is a fold of skin that protects the eyes from possible dangers, such as dust and bright flashes. It consists of two layers:
- Anterior, or superficial . This is the musculocutaneous layer that provides blinking. The muscle includes two parts: palpebral and orbital.
- Posterior, or deep . This is the conjunctival-cartilaginous layer. The cartilage of the eyelids consists of dense connective tissue located under the eye muscles.
Most of the human body is fluid. It occupies almost 70% of the total volume. Part of the fluid is located inside the cells, the rest is in the space between them. Swelling of the eyelid in one eye develops when the amount of water in the intercellular area becomes above a critical value of 1/3 of the total volume. Depending on the reason it happens:
- membranogenic - develops due to increased permeability of vascular walls to water and molecular substances;
- hydrostatic – associated with a decrease in the pressure of the same name inside the capillaries and tissues;
- hypoproteinemic - is a consequence of a decrease in colloid osmotic pressure.
Depending on the location, swelling is divided into bilateral and unilateral (on the right or left eye). These types are practically no different. Swelling of the lower eyelid is observed less frequently; swelling of the upper eyelid occurs more often. In the first case, cardiovascular diseases may be a serious cause. Taking into account the cause, edema is classified into:
- Inflammatory . Accompanied by pain, redness, and hyperemia of the skin. This type of inflammation is characteristic of eyelid swelling in one eye.
- Allergic . Also called angioedema. The eyelid doesn't hurt, it just itches. There are no other symptoms. When a child's upper eyelid is swollen, the most common cause is allergies.
- Non-inflammatory . The skin color remains normal or pale, there is no pain, as well as a local increase in temperature. Swelling of this type is often bilateral and occurs mainly in the morning.
- Traumatic . Characteristic of the condition after tattooing, in which pigment is driven under the skin to create a makeup effect. The cause can also be other trauma to the eyelids, for example, microtrauma when wearing contact lenses.
Inflammatory edema
This type of deviation is associated with infectious lesions of the eyes, and less often with other diseases, such as acute respiratory viral infections, sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammations of the sinuses. Such pathologies are accompanied by:
- burning;
- itching;
- tingling;
- photophobia;
- tearfulness.
Similar symptoms in the case of colds develop more often in both eyes. If only one eyelid is swollen, then the likely cause is infectious pathologies of the organs of vision. The list of such diseases includes:
- Barley . It is formed after pathogenic bacteria, most often Staphylococcus aureus, enter the surface of the eyeball. The infection is an inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelashes. The eyelid turns red, swells, and hurts when pressed.
- Conjunctivitis . Inflammation develops in the mucous membrane of the eye. Redness appears. There is a feeling of a foreign body or sand in the eye. There is photophobia and discharge of pus or clear fluid.
- Blepharitis . This is a chronic disease accompanied by inflammation of the edge of the eyelids, which swells.
- Dacryocystitis . Characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal sac. Dacryocystitis is indicated by pain, redness, and swelling of the eyelids. Symptoms are localized closer to the inner edge of the eye.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases . These include abscess and phlegmon of the orbit, which develop as a result of bacteria entering the wound. In this case, the eyelid swells and hurts very much. In more severe cases, body temperature rises, general weakness and headache appear.
- Erysipelas lesions . This is a serious infectious disease that causes general intoxication of the body and inflammatory skin lesions. It can also cause swelling of the eyelid in one eye.
Allergic swelling of the eyelids
The clinical picture of allergic edema of the eyelid in one eye differs from inflammatory edema. Symptoms develop suddenly. Itching and swelling appear on the eyelid, it turns red. A person feels discomfort in the area of the affected eyeball. Skin rash, nasal congestion, and tearfulness also indicate the allergic nature of the disease. This reaction can be caused by:
- household chemicals;
- cosmetical tools;
- animal hair;
- plant pollen;
- insect vinegars;
- food products;
- hygiene products.
Allergic edema is classified into two types based on the symptoms and their severity. Based on these characteristics, the following are distinguished:
- Allergic dermatitis . Accompanied by not very strong swelling. Characteristic symptoms are itching and redness.
- Quincke's edema . Unlike the previous type, on the contrary, it causes severe swelling, which does not even allow a person to open his eyes. There are no other signs. This condition is dangerous because it can spread to the respiratory system.
Traumatic edema
Due to the soft and very delicate tissue, the eyelids are easily injured. Swelling may appear as a result of a burn, bruise or other mechanical stress. No specific treatment is required. Therapy is aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing purulent complications. This requires maintaining eye hygiene. There are other causes of traumatic swelling:
- Tattoo procedure . Involves driving pigment under the skin. Swelling develops due to too deep exposure. If the procedure is carried out correctly, the symptom disappears on its own after a day.
- Anatomical structure of the organs of vision . If the membrane between the fat layer and the skin is too thin, then it can swell under any negative influence.
- How to get rid of an annoying admirer. Advice from psychologists - how to beautifully send off an obsessive man
- How to weave macrame bracelets
- Bread in a slow cooker - step-by-step recipes with photos. How to bake delicious homemade bread with and without yeast
Non-inflammatory edema
This type of deviation is most often observed in the morning after waking up. In this case, swelling of the eyelids above the eyes is accompanied by severe pain, redness and hyperemia of the skin. At the same time, the external skin looks pale and cool. The cause of this complex of symptoms may be:
- oncological eye diseases;
- violation of lymph outflow or blood circulation;
- systemic diseases of the thyroid gland, vascular system, kidneys, digestive system;
- abuse of salty foods;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- lack of sleep;
- eye strain.
Swelling of the eyelids in the morning
At night, fluid gradually fills the space between the cells. This occurs due to prolonged exposure to a horizontal position. Then the swelling goes away throughout the day. The main causes of pronounced swelling after sleep, which occurs regularly, are:
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- abuse of pickles and alcohol the day before;
- first use of a new cosmetic product.