Disability loss of eye
To initiate the process, you must draw up a statement of claim, submit it to the court of jurisdiction, attach supporting documents, and then attend court hearings. To increase the likelihood of a successful resolution of the issue, you can do this with the help of a lawyer.
4.2. Good afternoon It is not clear the grounds for denial of disability. The issue of establishing disability is resolved during an examination at the Bureau of Medical and Social Examination (MSE). A referral for medical examination is issued by the medical institution where the patient is being observed. If a citizen has medical documents confirming violations of body functions, a referral can also be obtained from pension authorities and social protection authorities.
Who is given disability for glaucoma: basic criteria
This group is not a working group. There is a narrowing of the fields to 20°, complete dysfunction of the optic nerve or a marginal depression of its disc. Vision in the more sighted eye is 4-10%. The presence of scotomas cannot be excluded - a lack of visual perception, when in a limited area of the eye the visual function is maximally reduced (distorted) or absent.
When and who assigns a group for glaucoma?
The issue of disability due to glaucoma worries many, since there is a tendency for the incidence to increase not only among the elderly, but also among people of working age. After all, the ability to conduct everyday affairs disappears. The disability group for glaucoma is not at all what patients strive for, but many have to deal with it.
The determination of disability is entrusted to the medical and social examination of the ITU; citizens with blindness in one eye remain socially unprotected: – they do not have the opportunity to get a decent job because they are considered unfit for this profession; – loss of previous profession by decision of the EEC; – the possibility of being left without means of subsistence; – unsatisfactory emotional state of a person. A person, faced with the complete loss of blindness in one eye, has problems with official employment; recognition of him as a group 3 disabled person will allow him to receive a pension.
- a person has a health disorder, which is characterized by a disorder of certain body functions. Regarding this disability, we are talking about complete or partial loss of vision;
- citizens are completely or partially unable to move independently and navigate in space. Moreover, a person cannot study normally due to the lack of opportunity to read the educational material;
- a person who has vision problems is in dire need not only of government support, but also of rehabilitation.
Criteria for assigning visual disability
According to WHO estimates, there are about 40 million completely blind and 250 million visually impaired people in the world. In general, approximately 4% of the world's population experiences vision problems. The main reasons for registration of primary disability in Russia are glaucoma (37%), diseases of the retina and optic nerve (34%), myopia (12%), problems with the lens and cornea (8%).
According to the law, visual disability is not separated from other options. However, the commission takes into account frequent cases of restoration or, conversely, a sharp deterioration of vision, so the registration takes into account not only the current level of development of blindness, but also positive/negative dynamics.
Who is eligible for visual impairment?
- the first disability group assumes complete blindness or visual acuity with correction of no more than 0.04 diopters with a bilateral decrease in the boundaries of the visual field of 10–0;
- group 3 is given to persons with vision 0.1–03 in at least one eye with a decrease in the visual field of 40–20.
the second group means visual acuity in the seeing eye of 0.05–0.1 with a bilateral reduction in vision of 20–10;
The third degree of severity of the disease occurs when a person cannot do without the care of loved ones under any circumstances. This usually occurs with complete blindness, in which a person can navigate at the level of detecting light and shadow. In some cases, he is able to see silhouettes. In the worst case scenario, one eye cannot see at all. Such a person cannot take care of himself, his communication with others is disrupted. And if this disorder appeared at birth, his ability to learn is lower than that of others. Depending on the severity of the disease, different groups of visual disabilities are distinguished.
Do they give you disability if one eye cannot see?
What is disability? It is rather an established set of symptoms, diseases and norms for which state benefits are provided, as well as exemption from various jobs.
Or work under special conditions. Taking into account the severity and capacity of a person, disabilities are divided into three groups.
Let's look at each one in terms of eye conditions, because very often they give a specific group based on vision.
First group
Let's start with the heaviest group. Bilateral narrowing of the boundaries of the visual field from ten degrees from the point of fixation.
The first vision group is given in cases where a person cannot see 99% or at all. The reasons for this can be very diverse. Starting from congenital degradation of the lens or retina, ending with acquired, past diseases and physical effects.
Very often the problem arises due to careless handling of various objects or chemicals. For example, during welding, construction, and work in chemical laboratories.
That is why safety precautions are very important, without which rapid partial or complete loss of vision is quite acceptable.
Sometimes blindness is not due to local problems (specifically in the eyes), but to a general lesion of the central nervous system or certain brain centers responsible for visual perception. Or there are problems in the connections between the brain and the eyes themselves.
For example, with cysts or tumors in the brain, it can put severe pressure on the centers responsible for vision. It begins to fall as the tumor grows. Sometimes it happens that the tumor is removed, but vision is no longer restored.
In this case there will also be the first disability group.
This also includes visual acuity of no more than 0.04, corrected for the better eye.
Second group
This group is a little “lighter”. It may be given for certain eye diseases. For example, glaucoma or cataracts in complex forms may be indications for registration in the group.
In this case, the visual acuity of the better eye is from 0.05 to 0.1, and the narrowing of the boundaries is from 10 to 20 degrees. Operation is possible only under certain conditions.
Third group
In this case, the main indicators will be visual acuity from 0.1 to 0.3 and a narrowing of the boundaries of more than 20 degrees, but less than 40.
The 3rd group also includes people whose one eye does not see at all, and the second sees with a slight deviation.
But at the same time, there are a number of additional conditions, including: loss of legal capacity, the ability to self-care, or the need for rehabilitation and social protection.
From here we can conclude, answering an important question, if one eye does not see, while the second has 100%, as well as the normal physical condition and functioning of other body systems, the disability group is not assigned. In this case, the person is not considered incompetent.
Therefore, if in your case one eye does not see (by the way, this can also be for a variety of reasons), it is best to consult an ophthalmologist. Because only a specialist can give a qualitative assessment of the condition, on the basis of which a group can be obtained.
It must be said that there are a number of vision problems for which a person does not fall under the group. Moreover, it is capable of working in almost any conditions. Of course, there are certain types of activities that will simply be impossible for him to do on his own, or his condition may worsen.
In this case, the person will not be allowed to work after passing the commission. One simple example is work at heights. Due to pressure changes, people suffering from chronic eye diseases are not always allowed to see them.
Therefore, to obtain a permit for industrial climbing and high-altitude work, it is necessary to pass a medical commission. And special attention is paid to vision.
This is also important when driving a car. With the 3rd disability group, you can get a license, but at the same time the person must prove his full legal capacity to drive a car.
Therefore, if you are registered, you must mention this when passing the medical examination. Because licenses can be issued even to a person with one eye not functioning.
But again, here you need to prove the full functionality of the other eye.
Procedure and rules for registering visual disability
Having collected all the necessary documents and attaching an application of the established form to them, you must contact the federal bureau at your place of residence and submit this entire list. After accepting the application and documents, they will set a date to appear at the commission.
- original and copy of identity card (passport);
- original referral to the commission;
- a copy of the work record book, which must be certified by a notary (if the person previously carried out work activities or was registered with the employment center);
- medical card;
- extracts from all clinics where the patient received treatment for his disease;
- application for disability status.
Is disability given for loss of vision?
- the ability to move independently without assistance;
- ability to communicate;
- free orientation in space;
- behavior control;
- ability to learn;
- opportunity to carry out work.
This usually refers to children who, seeing their peers making fun of their glasses-wearing classmates, do not tell their parents about the problem, deepening the loss of visual function. Often, several reasons lead to deterioration in visual perception, and the more serious they are, the more significant their impact on the eyes. Criteria for assigning a visual disability On average, every year about 55 thousand Russians receive a visual disability group.
When is a visual disability granted?
- absolute blindness of both eyes without the possibility of recovery;
- if the acuity of visual function decreases (both eyes), while the acuity of the dominant eye is less than 0.03;
- if surgery is performed, but vision does not improve.
It should be noted that the process of obtaining a group cannot be called quick. First of all, a person who has poor vision should visit an ophthalmologist and take a referral to undergo a full medical examination at the medical center at his place of residence. At this stage, information is collected about the general condition of the body and the presence of diseases.
Lack of one eye disability
The legal topic is very complex, but in this article we will try to answer the question “The absence of one eye is a disability.” Of course, if you still have questions, you can consult with lawyers online for free directly on the website.
- disabled people of group 1 who have this status from the moment of birth, as well as disabled children - 12,730.82 rubles monthly;
- persons whose physical capabilities have been partially limited since childhood in group 2, as well as disabled people of group 1 who became disabled in adulthood - 10,609.17 rubles;
- disabled people of the second group, with the exception of those who have had this status since childhood - 5,304.57 rubles monthly;
- third group – 4,508.92 rubles per month.
It is worth noting that the patient has the right to independently choose where to go. You can go to a paid clinic, or you can go to a municipal one.
Pension amount
According to current legislation, vision that is no more than 0.03, or the presence of complete blindness, is a key reason for recognizing the degree of disability on a permanent basis. In simple terms, you won’t need to go through the commission again every year.
If the patient cannot see in one eye, the doctor will assess the condition of the second and may refer him to disability. Patients with a high degree of myopia (from -6 D) ask the doctor “at what disadvantage can they give a group.” Persons with a 0.1 visa apply for registration of disability against the background of correction. With myopia, the doctor takes into account not only how many diopters the patient’s examination will show.
The ophthalmologist will evaluate the condition of the retina, the possibility of surgical and pleoptic treatment that improves the prognosis, the persistence of disorders, and the patient’s social status. In practice, group 3 is assigned to the patient at minus 12–15 D.
What do you pay attention to when registering for a visual disability?
The organs of vision are responsible for communication with the outside world. It is through this analyzer that a person receives more than 80% of the information. Complete or partial dysfunction leads to difficulties in movement, communication, learning, work, and performing everyday tasks. Social isolation sets in.
- Contact the attending physician at the hospital for a referral for a comprehensive examination and a commission.
- Collection of documentation.
- Filling out the application form for ITU.
- Submission of documents to the commission.
- Setting a date and time for the meeting to be held.
- If the commission members do not have any questions based on the examination results, the patient is given a visual disability.
“No eye? Not disabled!
The Investigative Committee will take up the case of a four-year-old girl who was deprived of her disability. The corresponding instruction was given by the Chairman of the Investigative Committee, Alexander Bastrykin. The child was born without one eye. But at the last medical examination, the experts considered that the existing eye was enough to see well. On this basis, the girl’s disability was removed, and with it all the entitlement social payments and benefits. Read more from Vesti FM columnist Boris Beilin.
Julia was born without one eye. At 4 months, doctors installed a prosthesis for her. It needs to be changed 2 times a year as the child grows. This was done for free - the girl received a disability. Now Yulia is 4 years old. In addition to vision problems, the child has some developmental delays. However, all this did not prevent experts from recognizing the child as actually healthy during the next medical examination and removing Yulia’s disability. Now the girl and her mother do not receive the required benefits, preferential medications and free eye prostheses.
Julia is raised by her mother alone. She cannot work because the child requires constant care. As a result, the family lost more than half of their funds. And she is forced to live on 12 thousand rubles a month - this is benefits and alimony - while a prosthetic eye costs 10 thousand rubles.
It's all about changing the system for defining disability. Once upon a time, a medical and social commission made decisions based on diagnosis. According to the new rules, experts must calculate the percentage of impaired body functions. If the result is a loss of 40 percent, disability is considered. If less, then no. Yulia has one healthy eye. On this basis, experts considered that the child had object vision. Overall visual impairment was estimated at 30 percent. This means there is no disability. It’s time to change such an examination system, says Alexander Lysenko, general director of the National Center for Disability Problems, ONF expert.
LYSENKO: Until 2004, all children with one eye were diagnosed with disability. Then, including on the basis of international experience, this rule was canceled. For 15 years now, children with one eye have not been diagnosed with a disability. Even if corrected vision in a healthy eye is better than 0.3. You and I understand that something is not right here. After all, the absence of one eye leads to impairment of binocular vision, which we really need in everyday life. I am deeply convinced that a mistake was made then – 15 years ago.
I would like to note that Yulia has problems not only with her eyesight. She also has a 30 percent impairment of psychological functions. But this is not enough to receive benefits. The percentages of losses for vision and general development do not add up.
Now Yulia’s mother is trying to challenge the results of the examination in court and return her previous benefits. The Investigative Committee also got involved in the case. But this, of course, is not an isolated case. There are many such children. Thousands.
The problems of people with a missing paired organ were discussed at the end of last year at a meeting of Vladimir Putin with members of the Human Rights Council. The president was then given the conclusion of a medical and social examination: “The absence of a paired organ is not a basis for prolonging disability.” “So if one arm is missing, the person is no longer disabled?” – Putin asked. And having received an affirmative answer, he noted that this was “nonsense” and gave instructions to deal with this problem.
Who is entitled to a visual disability and how to get it
After studying the documentation and considering these issues, the commission makes a decision to assign disability or refuse to obtain status. If the answer is negative, the patient has the right to go to court to confirm the diagnosis and obtain the registration of a group.
Third
Loss of vision in one eye is not considered a basis for disability. During the ITU, the commission relies more on the condition of the second eye. If he sees 100%, then the person will be considered legally capable, so he will be denied government financial support.
Starting from congenital degradation of the lens or retina, ending with acquired, past diseases and physical effects. Very often the problem arises due to careless handling of various objects or chemicals.
Visual disability: eligibility criteria and groups
It often happens that after the appearance of vision problems, a person’s quality of life and ability to work significantly deteriorate.
Therefore, to support people who have partially or completely lost the ability to see, pensions and social benefits are provided in Russia.
But in order to achieve payments, you first need to figure out how to get a visual disability and what documents are needed for this.
Receipt criteria
Disabled status is granted to people with complete or partial loss of vision if they meet the following criteria:
- The patient is unable to move without assistance.
- The patient cannot read or study educational materials independently.
- A person needs to systematically undergo a course of therapy and rehabilitation.
- Due to loss of ability to work, the patient needs financial support from the state.
In addition, the causes of loss of vision are taken into account - congenital pathology or injury, as well as age at the time of the disease.
In each specific situation, it would be best to contact your treating ophthalmologist so that he can explain what type of vision is required, with what disadvantage, and also in what cases a disability can be assigned.
Groups
During the meeting, the medical and social commission (MSC), when considering each individual case, takes into account various factors, taking into account the degree of visual impairment. Important indicators include visual acuity - it is checked every time at an appointment with an ophthalmologist and visual fields - they show the space that is visible to the eye with a fixed gaze.
Judging by these and some other medical parameters, the patient is assigned one of three disability groups.
First
Installed for patients who need outside help due to the loss of the ability to care for themselves. As a rule, this is associated with blindness - at best there is minimal visibility of silhouettes, and at worst there is complete blindness in both eyes. Visual acuity in such patients does not exceed 0.05, and the visual fields are narrowed to 10 degrees.
Second
This group involves the emergence of restrictions in work and the creation of special living conditions. Sometimes people with this level of visual impairment may need help from others. This also includes cases of hemorrhage in one or both eyes and retinal detachment. The maximum visual acuity here is 0.1, and the visual field is narrowed to 20 degrees.
Blindness in one eye
Loss of vision in one eye is not considered a basis for disability. During the ITU, the commission relies more on the condition of the second eye. If he sees 100%, then the person will be considered legally capable, so he will be denied government financial support.
Decor
The procedure for obtaining disabled status involves the following sequence of actions:
- Contact the attending physician at the hospital for a referral for a comprehensive examination and a commission.
- Collection of documentation.
- Filling out the application form for ITU.
- Submission of documents to the commission.
- Setting a date and time for the meeting to be held.
- If the commission members do not have any questions based on the examination results, the patient is given a visual disability.
At the end, the patient is given a certificate of group assignment and a rehabilitation program. After this, the certificate must be submitted to the pension fund - without fulfilling this requirement, it will not be possible to receive the required payments and benefits.
Medical examination
To apply for disability, you must undergo a medical examination with a referral from an ophthalmologist. Based on the results of hardware vision tests, a conclusion will be issued indicating the disease. In fact, this will be the basis for conducting a medical and social examination.
It is important to know that the pension fund and social services can also refer citizens to undergo MSA.
Collection of documents
To receive a group, the patient needs to collect a package of documentation. In addition to the passport and its photocopy, it includes:
- SNILS insurance card;
- work book or its certified copy;
- outpatient card with all certificates of examinations and treatment completed;
- referral from an ophthalmologist to a commission;
- statement.
Commission
After collecting a package of documents, the patient is sent to the ITU, where members of the commission will consider the following issues:
- Causes of partial or complete loss of vision.
- Date of detection of pathology and diagnosis.
- There is a need for social support and help from outsiders.
- The patient's ability to work.
After studying the documentation and considering these issues, the commission makes a decision to assign disability or refuse to obtain status. If the answer is negative, the patient has the right to go to court to confirm the diagnosis and obtain the registration of a group.
Deadlines for obtaining status
Permanent disability is assigned only to those whose visual acuity is no higher than 0.03. Also, lifelong disabled status can be obtained by patients who undergo examination for 10 years and each time the diagnosis is confirmed or worsened - in this case, an indefinite group will be established for the 11th year.
For all others, an annual re-examination is required, where it is necessary to document stable and irreversible changes in the visual system. A disabled child must also undergo re-examination after reaching adulthood.
Benefits and pension
After receiving disability, the patient may qualify for the following government benefits:
- reduced land tax rate;
- free travel on local transport;
- undergoing treatment in sanatoriums at the expense of the budget with free travel there and back;
- exemption from property tax;
- receiving a list of medications free of charge.
The size of disability pension payments in 2021, as always, depends on the assigned category - for disabled people of group 1 the pension is 9838 rubles, for group 2 4325 rubles, for group 3 4153 rubles. The largest allowance is paid to disabled children - 11,646 rubles each.
In addition to monthly payments, every year adults with disabilities and children receive a one-time benefit, the amount of which also depends on the group:
- first - 3238 rubles;
- second - 2341 rubles;
- third - 1824 rubles;
- disabled children - 2191 rubles.
All pension payments for people with disabilities are indexed annually.
The process of registering disability for people with vision problems is fraught with various difficulties. To do this, you will have to undergo many examinations, collect all the documents and prove your incapacity to the commission. But this is necessary in order to receive monthly financial assistance from the state, since in conditions of loss of ability to work this is very important.
Disability in the absence of 1 eye
- contacting an ophthalmologist at your place of residence; if there is no effect of treatment, the doctor will refer you to other specialists;
- examination by doctors of other specialties; if any violations are detected, additional examinations are prescribed;
- providing the results to an ophthalmologist, after drawing up a conclusion and collecting documents, a referral to an ITU is issued;
- registration of documents for examination;
- visiting the commission, receiving a decision/refusal to assign a group.
How to register for a visual disability
- Federal Law No. 181 of November 24, 1995 - “On the social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation”;
- Federal Law No. 46 of March 28, 2021 - “On Amendments to the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.”
What kind of vision is required for disability? Depending on the degree of blindness, group 1, 2 or 3 may be assigned. The classification is presented in the table.
How to get a visual disability group
If your vision is severely impaired, which has become a problem for everyday life, you should first contact an ophthalmologist at your place of residence with complaints. Perhaps the prescribed treatment will solve the problem. If this does not happen, you should indicate in your application that you want to receive a referral to ITU to determine your disability group. It should be remembered that the basis for this should be visual acuity lower than 0.1.
- Step two. The attending physician will issue a referral to other doctors. This will have to be done even if there are no other diseases. If complications or other diseases are detected, additional examinations may be prescribed.
- Step three. The results of the examinations completed must be provided to the doctor who referred you. He will do the following:
We recommend reading: Should there be communications on the site for large families in the Krasnodar TerritoryEstablishing a disability group for myopia in accordance with Art. 8 of the “Law on Social Protection of Disabled Persons of the Russian Federation” dated November 24. 95 181-FZ is made based on the degree of vision loss, taking into account all of the above aspects.
All about visual impairment
- number;
- date of inspection;
- Full name, date of birth of the patient, place of registration and residence;
- conclusion about the degree of disorder;
- conclusion about violation of vital functions of the body;
- assigned group;
- cause of disorders, diagnosis;
- validity;
- date of re-inspection;
- the degree and time of loss of ability to work;
- list of issued documents;
- list of documents under consideration;
- position and signature of all expert specialists;
- position and signature of the head of the medical organization where the examination is carried out;
- date of;
- seal.
Who is considered disabled
In addition, doctors must record the fact that there is no forecast for improvement in the near future. The causes may be, for example, chronic myopia (farsightedness), astigmatism, glaucoma, inflammation or detachment of the retina, myopia.
- a referral signed by the head physician of the medical center for the ITU;
- a person’s written application for certification of rights to receive a group;
- passports (original and photocopy);
- photocopies of the work record book (must be notarized);
- outpatient medical record with all necessary extracts and stamps;
- an act that confirms an injury received during work.
Visual disability is assigned in cases where decreased vision in the eyes has resulted in disruption of a person’s life. Previously, a person is examined by an ophthalmologist to determine how much he can see, and receives a referral for a medical and social examination (MSE). After confirming the diagnosis of “partial or complete blindness,” a group is assigned. Social authorities pay state assistance in the form of pensions. The size of the pension depends on multiple factors, including the group of visual disability.
How to register for a visual disability
- acuity index and visual field coefficient (one and second eye);
- basic physiological indicators (one and second eye);
- presence of secondary pathologies;
- degree of efficiency (the amount of material payments depends on this).
If the attending physician refuses to issue such a certificate, you should contact the head of the department or the deputy chief physician for clinical expert work of the institution. Specialists from the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise conduct an examination of the citizen and, based on its results, draw up a program for additional examination of the citizen and implementation of rehabilitation measures, after which they consider the question of whether he has any disabilities.
Is there a disability without one eye?
If a person does not agree with the decision of the ITU bureau: a) you can request clarification from the bureau’s specialists, primarily from the head. In accordance with paragraph 5 of the Procedure for the organization and activities of federal state institutions of medical and social expertise; /approved by order
Is missing one eye a disability?
A disability can be determined only if the remaining eye has lost visual acuity, if its field of vision is significantly reduced. If this leads to limited ability to work, then the person has the right to contact the medical institution at his place of residence to determine his disability.
Is disability given for missing one eye?
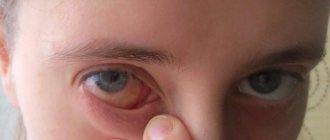
Complete loss of one eye is a condition in which it is possible to consider receiving a disability group.
But at the same time, doctors assess the consistency of the functioning of the visual organs as a whole.
What matters here is the severity of the patient’s condition and his ability to work. After a full examination, the commission comes to a conclusion: to grant or not a disability of a certain group. If the patient is refused, it is possible to file an appeal, in which the case will be reconsidered.
↑ Criteria for establishing disability groups
One of three disability groups
is established based on the severity of health impairments, the degree of persistent functional disorders and limitations in life activity, as well as the need for social protection and assistance measures.
•Disability of the first group
determined in cases of health impairment with a persistent, significantly expressed disorder of body functions, leading to limitation of the main categories of life activity of the third degree. For persons with visual impairments, the first disability group is established in the presence of practical or absolute blindness in both eyes (IV degree of visual impairment), which, in combination with other medical and social factors, causes restriction of the main categories of life activity of the III degree.
•Disability of the second group
established in cases of health impairment with a persistent pronounced disorder of body functions, leading to limitation of the main categories of life activity of the 2nd degree and (or) the ability to learn and work of the 2nd or 3rd degree. In case of visual impairment, the indication for determining the second disability group is the presence of a high degree of low vision in the only or better seeing eye or in both eyes (III degree of visual impairment), which, taking into account social factors, leads to II degree of restrictions on the ability to carry out the above types of life activities.
• Disability of the third group
are determined in case of health impairment with a moderately severe functional disorder, leading to a limitation of the ability to work of the 1st degree or a limitation of other categories of life activity of the 1st degree. For persons with visual impairments, disability of the third group is established when the ability to work professional activities is limited to the first degree, caused by moderate vision impairment (second degree of visual impairment) or, in special cases, of a small degree (I degree of visual impairment), which in combination with social characteristics determine the limitation of several other categories of life activity of the first degree.
Is there a disability status if one eye is missing?
If the patient is missing one eye completely, but the other is present, consider the degree of visual acuity of the remaining organ of vision. If its functionality is fully preserved, it is impossible to obtain disability.
Obtaining a group is possible if visual acuity in the second eye decreases, if its functionality in glasses fluctuates within the following limits:
- 0-0.04 – give the first group;
- 0.05-0.1 – give the second group;
- 0.2-0.3 – give the third group;
- 0.4 – awarding of any group is impossible.
The commission additionally considers the following factors of human life:
- inability to work;
- inability for self-care: movement, cooking, hygiene procedures, communication, use of various devices;
- the need for additional treatment and rehabilitation methods;
- the need to receive social protection in the form of certain benefits and cash benefits.
If a person lacks the functionality of one eye, but the other sees well, all of the above additional factors must be present to obtain the group.
Otherwise, the patient is not entitled to disability. He will not be able to receive benefits, since he is able to perform various jobs.
If a patient’s absence of an eye is not congenital, but acquired, and the medical commission decides to limit his work activity, but not to issue benefits, this may mean that the patient will lose his job. With this type of disorder in the body, the following types of activities cannot be performed:
- drive a vehicle;
- work in an enterprise where binocular and lateral vision is necessary;
- working in an enterprise using various chemicals or toxic substances;
- work that involves lifting a person to a height (climber, builder), since in this case the intraocular pressure may rise, which will lead to complications.
There are cases when a temporary disability is issued; it is permissible if a person has lost an eye and at that time performed the following activities:
- pilot;
- driver (the ban on driving a vehicle must be confirmed by a driver’s commission);
- dispatchers of various vehicles;
- military;
- police officer.
The benefit received is not for life. It is given only for the time during which a person must study and get a new job. Most often this period takes one year. After this, the patient’s disability group is taken away and all social protections associated with it are deprived.
Temporary disability is not granted to persons whose activities are related to the mental process. In this case, a person can apply for disability, but he will lose his job.
Дают Ђи онвалидность, если один глаз не ввдит
Отсюда можно сделать вывод, отвечая РЅР° важный РІРѕРїС ЂРѕСЃ, если РѕРґРёРЅ глаз РЅРµ РІРІРґРёС‚ , РїСЂРё этом Сѓ второго 100%, Р° также нормальное физическРѕРµ SЃРѕСЃС‚РѕСЏРЅРёРµ Рё функцРеонирования остал СЊРЅС‹С... систем организма, РіСЂСѓРїРїР° инвалидности РЅРµ RїРѕР»РѕР¶Р µPSP°. R' SЌS‚РѕРј SЃР»СѓС‡Р°Рµ S‡РµР»РѕРІРµРє RSRµ SЃС‡РёС‚ается RSRµРґРµРµСЃРїРѕСЃРѕР±РЅС ‹Рј.
We recommend reading: Where to work for lawyers
Также важно это РїСЂРё вождении автомобиля. РЎ 3-Р№ РїСЂСѓРїРїРѕР№ мнвалидности права получить RјРѕР¶РЅРѕ, РЅРѕ РїС ЂРё этом S‡РµР»РѕРІРµРє должен доказа S‚СЊ SЃРІРѕСЋ полную дееспособность РІ вождении авто. Поэтому, если РІС‹ стоите РЅР° учете, РїСЂРё прохождении РјР µРґРєРѕРјРёСЃСЃРеРё РѕР± этом обязательно нужно SЃРєР° зать. Потому что права РјРѕРіСѓС‚ быть выданы даже S‡РµР»РѕРІРµРєS ѓ СЃ нефункционирующим RѕРґРЅРёРј гла R·РѕРј. RќРѕ RѕRїSЏS‚СЊ-таки, R·РґРµСЃСЊ нужно RґРѕРєР°Р·Р°С‚СЊ RїRѕR»РЅСѓСЋ S„ункциR ѕРЅР°Р»СЊРЅРѕСЃС‚СЊ РґСЂСѓРіРѕРіРѕ глаза.
What to do in case of refusal
If a person believes the committee made the wrong decision, they can appeal. His case will be re-examined. He will undergo additional medical examination. But if the second organ of vision has fully retained its function, there will be no disability.
If a person is missing one eye, but the other is in a healthy condition and the medical commission has not given a disabled group, the person may lose his job. This is due to the fact that some activities require binocular and lateral vision. A patient with an absent eye does not have such functions. In this case, the person will need to mentally and physically prepare to look for a new job. He must get used to living with only one eye.
Obtaining disability in the absence of one eye is a rather difficult process. This is due to the fact that the functionality of the second organ of vision can be completely preserved; the medical commission considers not the absence of one eye, but vision as a whole. In case of refusal, the person can demand from the medical commission an explanation of why this verdict was made. You can appeal it to higher authorities or court. To do this, you need a written application to the organization that conducted the medical examination.
What visual impairments give disability?
Vision loss can occur in a person from birth or be a consequence of an injury or illness. There are four main criteria for determining visual disability:
- complete or partial blindness;
- inability to move without assistance;
- inability to obtain information without outside help;
- need for rehabilitation measures.
If a person has two of the listed criteria, he can count on receiving disability.
Criteria for assigning visual disability
According to WHO estimates, there are about 40 million completely blind and 250 million visually impaired people in the world. In general, approximately 4% of the world's population experiences vision problems. The main reasons for registration of primary disability in Russia are glaucoma (37%), diseases of the retina and optic nerve (34%), myopia (12%), problems with the lens and cornea (8%).
Obtaining the status of a visually disabled person
Visually impaired people are one of the most common groups among people with disabilities. This is due to a number of reasons:
- Fragility of human vision: even minor injury or illness can cause permanent loss;
- Relative ease of obtaining: as soon as the level of vision drops below a certain level, the group is given without any questions;
- Age-related problems: the majority of disabled people (about 78%) are elderly, gradually losing their vision.
Citizens of the Russian Federation who have completely lost their sight or who suffer from a decrease in function to the point of being unable to live and work without additional assistance have the right to receive the status of a disabled person.
- 181-FZ, a guarantee of social protection for all categories of disabled citizens;
- 46-FZ, fundamental rights of persons with disabilities;
- Government Decree No. 95 on the conditions of recognition;
- Order of the Ministry of Health No. 535 on the procedure for conducting MSA.
In addition, when determining visual impairment, the commission is guided by the latest revision of the ICD.
According to the law, visual disability is not separated from other options. However, the commission takes into account frequent cases of restoration or, conversely, a sharp deterioration of vision, so the registration takes into account not only the current level of development of blindness, but also positive/negative dynamics.
This can either help with registration or cause an unexpected refusal.
Benefits for the visually impaired
Every disabled person has the right to receive the following benefits:
- free travel on suburban and international transport, if used to get to the place of treatment;
- free medications if they are required for treatment;
- free treatment at resorts and sanatoriums;
- there is no need to pay property tax;
- reduction of land tax.
Helpful: The full list of benefits depends on the disability group and related factors.
Every year, 45,000 citizens in Russia receive the status of a visually disabled person. About half of these people are completely blind. Older people often go blind due to the development of a disease called cataracts. Approximately 50% of citizens become disabled at working age.
Among the causes of vision problems, doctors identify the following:
- excess weight;
- bad environment;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- lack of microelements and beneficial vitamins;
- aging.
The earlier deviations are identified, the greater the chances of slowing down the process or completely preventing it.
Criteria for dividing visual impairment into groups
In general, receiving a visual disability is no different from the usual registration procedure, except that in this case the help of a trusted person or close relative is much more often used.
The disability group will be given according to the following criteria:
- The first group is defined in people who are unable to perform normal activities due to complete blindness. Includes blindness in both eyes, a decrease in visual field of up to 10 degrees, or a visual acuity of the “strong” eye of 0.04 after correction;
- The second group means the inability to live and work without outside help and aids. The field of visibility is limited to 20 degrees, the quality of vision of one eye should not exceed 0.1 from normal;
- The third group is the ability to independently carry out most activities, some with the help of additional funds. A healthier eye shows visual acuity up to 0.3, visual field up to 40 degrees.
Simply put, Group 1 has no vision at all, Group 2 has very little vision and wears glasses, Group 3 has consistently poor or deteriorating vision but can still see with some limitations with glasses or contacts.
In addition to state criteria that help identify a person into a system of three groups, there is also a medical classification.
According to it, the degrees of visual impairment are divided into four categories:
- Absolute blindness – acuity from 0 to 0.04;
- Serious deviations – from 0.05 to 0.1;
- Moderate violations – from 0.1 to 0.3;
- Small (insignificant) deviations – from 0.4 to 0.7.
How to register for visual disability and in what cases it is granted
According to WHO estimates, there are about 40 million completely blind and 250 million visually impaired people in the world. In general, approximately 4% of the world's population experiences vision problems. The main reasons for registration of primary disability in Russia are glaucoma (37%), diseases of the retina and optic nerve (34%), myopia (12%), problems with the lens and cornea (8%).
Obtaining the status of a visually disabled person
Visually impaired people are one of the most common groups among people with disabilities. This is due to a number of reasons:
- Fragility of human vision: even minor injury or illness can cause permanent loss;
- Relative ease of obtaining: as soon as the level of vision drops below a certain level, the group is given without any questions;
- Age-related problems: the majority of disabled people (about 78%) are elderly, gradually losing their vision.
Citizens of the Russian Federation who have completely lost their sight or who suffer from a decrease in function to the point of being unable to live and work without additional assistance have the right to receive the status of a disabled person.
Obtaining a group for visually impaired and blind citizens is regulated by the following laws:
- 181-FZ, a guarantee of social protection for all categories of disabled citizens;
- 46-FZ, fundamental rights of persons with disabilities;
- Government Decree No. 95 on the conditions of recognition;
- Order of the Ministry of Health No. 535 on the procedure for conducting MSA.
In addition, when determining visual impairment, the commission is guided by the latest revision of the ICD.
According to the law, visual disability is not separated from other options. However, the commission takes into account frequent cases of restoration or, conversely, a sharp deterioration of vision, so the registration takes into account not only the current level of development of blindness, but also positive/negative dynamics.
This can either help with registration or cause an unexpected refusal.
Criteria for dividing visual impairment into groups
In general, receiving a visual disability is no different from the usual registration procedure, except that in this case the help of a trusted person or close relative is much more often used.
The disability group will be given according to the following criteria:
- The first group is defined in people who are unable to perform normal activities due to complete blindness. Includes blindness in both eyes, a decrease in visual field of up to 10 degrees, or a visual acuity of the “strong” eye of 0.04 after correction;
- The second group means the inability to live and work without outside help and aids. The field of visibility is limited to 20 degrees, the quality of vision of one eye should not exceed 0.1 from normal;
- The third group is the ability to independently carry out most activities, some with the help of additional funds. A healthier eye shows visual acuity up to 0.3, visual field up to 40 degrees.
Simply put, Group 1 has no vision at all, Group 2 has very little vision and wears glasses, Group 3 has consistently poor or deteriorating vision but can still see with some limitations with glasses or contacts.
In addition to state criteria that help identify a person into a system of three groups, there is also a medical classification.
According to it, the degrees of visual impairment are divided into four categories:
- Absolute blindness – acuity from 0 to 0.04;
- Serious deviations – from 0.05 to 0.1;
- Moderate violations – from 0.1 to 0.3;
- Small (insignificant) deviations – from 0.4 to 0.7.
Anything above 70% of ideal vision is considered normal and is not a basis for determining low vision.
It should be remembered that the visual acuity indicator quite weakly intersects with the “minuses” and “pluses” that determine the distortion of the lens. You should not assume that significant myopia or farsightedness will be the basis for the design of the group: the key parameters are visual acuity and viewing angle.
Pension and daily allowance for vision in 2021
There are no additional payments for visually impaired people in 2021; the size of social pensions and daily allowance coincides with the national average.
| Pensioner category | Payment amount | EDV |
| Group I disabled children, disabled children. | 12432 rub. | 3627 rub., 2590 rub. |
| Disabled children of group II, disabled people of group 1 | 10360 rub. | 2590 rub., 3627 rub. |
| Disabled people of group II | 5180 rub. | 2590 rub. |
| Disabled people of group III | 4403 rub. | 2073 rub. |
Fringe benefits
In addition to payments and monetary assistance, a disabled person should be provided with free means for adaptation to society.
For the visually impaired, this list includes:
- Special aids for orienteering (glasses, lenses, guide dog);
- Assistance in education and training (literature for the blind, Braille reading courses);
- Prosthetic products (eye prostheses).
In addition to assistance in adaptation, a visually impaired person can count on a number of standard benefits, such as priority receipt of a site for housing construction or repair of rehabilitation equipment without waiting in line on preferential terms.
Details should be clarified when receiving a rehabilitation program or from Pension Fund specialists.
Getting a group for the blind in one eye
When receiving disability, the performance of one eye with the highest visual acuity is taken into account, so the loss of half of vision as a result of physical injury or illness is not a sufficient reason for assigning a group. Even when at a previous job a perfect eye was required, and the loss of an eye was the reason for dismissal.
This is a standard approach for all ITUs in Russia - the loss of a paired organ is not considered a critical health risk if the second one is working normally. In this case, it will be possible to register a disability only if the second eye sees at a level of 0.4 and below.
If they become disabled, people with eye loss can count on a standard package of benefits for the visually impaired and an eye prosthesis from the state. There are no additional benefits as part of the pension.
How to register for a visual disability
The design does not differ from the standard scheme. In case of complete blindness, a citizen can use the services of a trusted person to draw up documents: in this case, you will additionally need a power of attorney officially certified by a notary and an identity card from the attorney.
The first step will be to receive a referral for an examination or an official refusal from a specialized doctor. Any of the documents is the basis for launching the ITU procedure. Next, you need to submit an application with copies of documents to the nearest office of the bureau.
Sample application
This is what a standard sample application for adults for an examination looks like, after submitting which the bureau will begin the examination procedure. You can also download one of the suitable versions of the form (for example, for a child) on the GBMSE website in Moscow.
How and where does the ITU pass for recognition of visual disability?
If you are planning to pass a commission for visual disability, you should find out the criteria for passing from ITU specialists. The examination itself is carried out in regional branches of the bureau. If additional examinations are necessary, the citizen will be sent to specialized institutions with the necessary equipment.
It should be remembered that all examination procedures are free.
After receiving opinions from certified doctors, it is necessary to undergo an interview with a council of BMSE specialists who will determine the need for social assistance in a particular case. They will also make a decision on assigning a group in the prescribed manner.
What documents need to be collected
To register a disability, five documents are required:
- A referral for an examination from any ophthalmologist or a certificate-notification of refusal to provide it;
- Application for conducting an ITU, filled out in person or by an authorized representative;
- Identity card (original passport, copies of all pages with information);
- Employment history;
- Medical card with a list of activities carried out and the history of the disease.
In addition, the commission may require additional examinations or documents if it considers that they are relevant to the issue under discussion.
Can they refuse to establish disability, how to appeal the decision
Refusals to grant a visual disability occur quite often. What the average person considers a critical injury that affects his entire future life (for example, a drop in vision to 0.5 or the loss of one eye) for MSE is just a cosmetic inconvenience or a minor problem.
The reason for refusal may be a temporary decrease in vision, for example, after surgery or a serious illness. In such cases, the examination prefers to wait or give a lower degree with re-certification after a year.
The group can be lowered even if the indicator is stable on the border between the two categories, as well as rehabilitation procedures have been fully carried out. As a rule, if the indicators are exactly in the middle of the two groups, the ITU will try to give the lower one in order to meet internal quotas and restrictions.
The important thing here is to argue why a higher panel is necessary in this case and to use medical records to make the evidence stronger.
You can appeal the decision both in the examination of a higher authority (city, regional, federal bureau) and directly in court. It is worth going to court after at least one attempt to protest the decision of the district branch or in case of serious violations of the procedure.