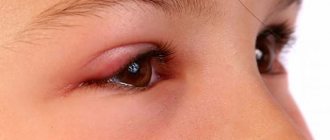
Many patients complain to an ophthalmologist that their eyelids are red and swollen. Such nonspecific symptoms may occur due to excessive accumulation and impaired outflow of fluid from the intercellular tissue space around the eyes. There are unilateral and bilateral swelling of the eyelids. In some cases, the disorder occurs without additional symptoms; sometimes itching, pain, and lacrimation may occur. At the first warning signs, it is recommended to refrain from self-medication and seek qualified help.
Causes
Most often, redness and swelling of the eyes are associated with direct damage to the eyelids. Similar symptoms are observed when the organs of vision are irritated by household dust, cigarette smoke, prolonged exposure to a computer or monitor screen, overwork, and stress. However, this can also be a symptom of systemic damage to the body. Most often, this clinical picture is observed against the background of progression of the following pathological processes:
- allergic, infectious conjunctivitis
- demodicosis
- hypothyroidism
- Quincke's edema
- dermatitis
- allergies
- flu, sinusitis, rhinitis, sore throat
- bronchial asthma
- diabetes mellitus
Swelling and redness are often observed during pregnancy, as well as in cases of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, pathologies of the kidneys and endocrine system. It is important to take into account the overall clinical picture and history in order to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the root cause of the disorder.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with an ophthalmologist online
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a bilateral recurrent inflammatory process that affects the edge of the eyelid. Accompanied by redness, swelling, itching, and a feeling of heaviness in the eyelid area. It is more difficult for the patient to tolerate bright light, the eyes quickly get tired, and eyelashes fall out. This is a common disease that occurs more often in people aged 45-75 years. The main predisposing factor to the development of such a disease is staphylococcal infection, as well as foci of chronic infection in the tonsils, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, and skin. Blepharitis is accompanied by redness and swelling of the eyelids, itching, increased fatigue, sensitivity to bright light, wind, and cold.
Blepharitis is often accompanied by:
- symptoms of conjunctivitis
- dry eye syndrome
- keratitis
- acute chalazion
- barley
- significant decrease in vision
There are complaints about the formation of a tear film, due to which vision becomes blurry and unclear. Associated symptoms depend on the form of blepharitis: scaly, ulcerative, demodectic, seborrheic. With rosacea-blepharitis, the formation of grayish-pink nodules and ulcers on the surface of the eyelids is observed.
Ethmoiditis
Ethmoiditis is one of the least common types of sinusitis that affects the ethmoid sinus. It develops due to a decrease in the protective properties of the body due to the influence of chronic ENT pathologies, developmental anomalies, and traumatic injuries. Catarrhal, purulent, edematous-catarrhal, and polyposis forms of the disease are noted. Accompanied by redness and swelling of the eyelids, pain in the bridge of the nose, which intensifies when the patient tilts his head.
There are complaints about:
- impaired sense of smell
- nasal discharge
- nasal congestion
- increase in body temperature
- deterioration in general health
- apathy, weakness, decreased ability to work
- sleep disorders
- increased irritability
The disease transforms into a chronic form if the expected therapeutic effect is absent for 3 months. Children aged 5-8 years with a history of scarlet fever are at risk. Exacerbation of chronic ethmoiditis is observed mainly in the autumn and winter seasons.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process that affects the conjunctiva. One of the most common ophthalmological pathologies that develops under the influence of viral, bacterial infections, chlamydia, fungi, metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiency, as well as when exposed to external irritants: dust, chemicals, ultraviolet radiation, tobacco smoke. Depending on the root cause that caused the disorder, the following symptoms develop:
- redness, swelling of the eyelids
- sudden pain, pain in the eyes
- swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane
- itching, burning. Watery eyes, feeling of a foreign body, “sand” in the eyes
- intolerance to bright light
- blepharospasms
- decreased visual acuity
- discharge of mucous, purulent secretion from the organs of vision
If conjunctivitis is triggered by the toxic effects of aggressive chemicals, it manifests itself as intense pain when trying to look sideways, blink, open or close your eyes. In the subacute form of the disease, the symptoms are less pronounced. Lack of therapy is fraught with transformation of the disorder into a chronic form, which is characterized by a persistent, long-term course.
Barley
Barley is an acute purulent inflammatory process that affects the hair follicle of the eyelashes and sebaceous glands. In 98% of cases, the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus. The disease manifests itself against the background of a decrease in the body's defenses, for example, during a cold. Styes are accompanied by painful, limited swelling of the eyelids, swelling, and redness. After 48-72 hours, a yellow crust forms on the surface of the swelling. The eyelids become red and swollen, in some cases the formation of 2 or more styes is observed.
In severe cases of the disease, symptoms of general intoxication appear:
- headache
- swollen lymph nodes
- increase in body temperature
- complaints of weakness, fatigue
- increased sweating
Under no circumstances should the pus be squeezed out: this can provoke a rapid spread of the infectious process.
Chalazion
Focal swelling most often indicates a chalazion. This is a chronic inflammatory process, which is accompanied by the formation of benign tumor-like compactions in the thickness of the eyelids due to blockage and chronic inflammation of the meibomian glands. With chalazion, nodules and swelling appear on the eyelids, excess pressure occurs on the eyeballs, and the mucous membrane of the eyes becomes irritated. The formed abscesses spontaneously open. Patients aged 35-55 years are at risk.
With chalazion, the eyelids become red and swollen, and there are complaints of itching, watery eyes, and increased sensitivity to touch. As the chalazion grows, compression of the cornea is observed with the subsequent development of astigmatism and visual distortion. If the chalazion does not open for a long time, cysts filled with mucus form in its place. The process of suppuration is accompanied by local redness of the eyelids, swelling, throbbing pain, and softening of the nodules. In some cases, body temperature rises and blepharitis occurs. Spontaneous opening of the chalazion with subsequent discharge of pus is possible.
Allergy
Most often, swelling of the eyelids is caused by an allergic reaction: local and systemic allergies. In the second case, angioedema, itching, and allergic rhinitis are observed. If redness and swelling of the eyelids are caused by an allergic reaction, it is recommended to stop contact with the allergen, replenish the deficiency of B vitamins (particular attention is paid to vitamin B6), and improve the functioning of the liver and gall bladder. To reduce clinical manifestations, antiallergic medications are used for local and systemic effects.
ARVI
ARVI is a group of infectious pathologies that occurs when DNA and RNA viruses infect the respiratory tract. With ARVI, there is an increase in body temperature, runny nose, cough, sore throat, and lacrimation. Pronounced swelling and redness of the eyelids are symptoms of acute inflammation, which are often combined with pain and pain in the eyes, decreased visual acuity, severe lacrimation with mucous discharge, and damage to the cornea.
To prevent damage to the organs of vision during ARVI, adhere to the following recommendations:
- use disposable paper tissues
- refrain from scratching the eyes to prevent the spread of infection
- replace contact lenses with glasses
- observe the rules of personal hygiene: wash their hands with soap after contact with nasal secretions and sputum
- at the first alarming symptoms from the visual organs, refrain from self-medication and seek advice from an ophthalmologist
ARVI is often accompanied by enlargement and pain in the lymph nodes and neck. Visual symptoms, including unilateral conjunctivitis affecting the lower eyelid, are one of the most common symptoms of adenovirus. The earlier treatment begins, the less likely it is to develop complications from the visual organs.
Eyelid dermatitis
An inflammatory process affecting the skin of the eyelids. There are complaints of burning, itching, redness and swelling of the skin, pain, and discomfort. Dermatitis of the eyelids often develops as a complication of infectious pathologies such as herpes, chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever. It may also be a side effect caused by medications.
The clinical picture depends on the underlying factor that provoked the disease:
- itchy skin
- burning around the eyes
- tightness, dry skin
- formation of blisters, ulcerative lesions
- vesicular, bullous rash
- increased sensitivity, thickening of the skin of the eyelids
- in severe cases - angioedema, which spreads throughout the face, to the lips, cheeks
The eyelids swell, turn red, and softening of the skin in the corners of the eyes is observed. The eyes may swell so much that the patient cannot open them. With allergic dermatitis, there is itching near the edge of the eyelashes, which gradually spreads to the wings of the nose, lips, forehead, and head.
Demodicosis
Demodicosis of the eyelids is a pathological process that develops due to the activity of the acne mite. The causative agent of the pathological process belongs to the representatives of opportunistic microflora. Located at the mouth of the hair follicle, it negatively affects visual acuity. The disorder is manifested by redness of the edges of the eyelids, itching, loss of eyelashes, a feeling of dryness, and purulent discharge. Patients often complain of a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, and the eyelids swell significantly.
Hypothyroidism
Diseases of the thyroid gland often cause damage to the organs of vision. Redness and swelling of the eyelids is a common sign of hypothyroidism. Peripheral edema often indicates a progressive decline in thyroid function at the cellular level. Protrusion of the eyeballs and a feeling of fullness in the eyes are common. Swelling affects not only the eye sockets, but also the eyelids, which leads to the formation of “bags” under the eyes. The disease is accompanied by photophobia, as well as damage to the muscles of the eyeballs. Symptomatic therapy in this case is ineffective. To cope with swelling and redness of the eyes, it is necessary to restore the functional state of the thyroid gland.
Ophthalmic rosacea
Ophthalmic rosacea is an inflammatory process that causes redness, swelling, and a burning sensation in the eye area. Patients aged 35-55 years with a history of rosacea are at risk. In some cases, ocular rosacea is the first warning sign of rosacea. Symptoms from the visual organs appear most often; the disorder is accompanied by:
- dry eyes
- burning, tingling
- lacrimation
- swelling, redness of the eyelids
- vasodilation
- blurred vision
- intolerance to bright light
- sensation of a foreign body in the eyes
The disorder occurs under the influence of hereditary predisposition, deficiency conditions, and unfavorable environmental factors.
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a pathology of the endocrine system that develops due to a lack of the hormone insulin. This leads to an increase in the level of glucose in the blood plasma, which cannot enter the cell. As a result, hyperglycemia develops. Such a violation negatively affects the condition of blood vessels, organs of vision, and liver. General clinical picture:
- blood pressure increases
- sensitivity in the upper and lower extremities is impaired
- there is a characteristic smell of acetone
- headache, dizziness
- long wound healing process
- eyelids become red and swollen, visual acuity decreases
Swelling can occur not only on the face, but also spread to the lower extremities and throughout the body. This is an alarming symptom that indicates a malfunction of the urinary system, in particular the kidneys, as well as the cardiovascular system. In case of asymmetrical edema, it is necessary to exclude the development of diabetic microangiopathy.
Treatment of safe causes of swelling and redness of the eye
When asking the specific question of what to do if your eye is swollen and red, you need to understand that the most important thing is to find out the cause of this condition. Without this, you cannot use any folk remedies, and especially medicines. But if you are sure that this is an isolated case that will not lead to a number of complications, then you can resort to the following recommendations:
- If your eye is swollen and alcohol or other foods are to blame, eliminate them from your diet. This list also includes sparkling water and any salty or overly spicy foods, coffee drinks,
- If the visual organs are swollen from small foreign objects (dust, dirt and the like), rinse them with warm water while removing the problematic item (it is better to do this with a cotton swab). After some time, the red tint will subside, as will the swelling. Until this moment, do not rub your eyes (there may be a false sensation of foreignness on the membrane),
- If the root lies in other everyday problems, you can use a number of remedies that have been proven over the years:
- Chamomile based decoction. 2 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the raw materials, when it cools down, strain and make lotions. If more than one procedure is required, then for each subsequent time you need to prepare a fresh decoction,
- Grated raw potatoes. Wrap the product in gauze and apply to the problem area for 25 minutes,
- Brewed tea bags are often used. The most effective is black tea, which will help get rid of the disease in 10-15 minutes.
If redness and swelling of the eye is not a consequence, but only a symptom of a disease, the listed remedies will not help, and may even worsen the situation.
Possible complications
Lack of timely treatment for visual disorders is fraught with complications:
- ethmoiditis: purulent masses can spread to the orbital cavity, which is fraught with retrobulbar abscess, phlegmon of the orbits, and narrowing of the visual field. If the pathological process spreads into the skull, the likelihood of developing purulent meningitis, brain abscess, encephalitis, arachnoiditis, and thrombosis of the venous sinuses increases;
- complications of conjunctivitis: blepharitis, keratitis, dry eye syndrome, violation of the integrity of the cornea, decreased visual acuity;
- barley: squeezing out the purulent contents is fraught with the spread of the infectious process to the orbits with the subsequent development of phlegmon, thrombosis, meningitis;
- diabetes mellitus is complicated by diabetic neuropathy, edema, pain in the upper and lower extremities, trophic ulcers, gangrene, fluctuations in blood pressure, coma;
- chalazion is fraught with the formation of fistula tracts, around which foci of granulation form;
- ARVI: tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia;
- eyelid dermatitis can be complicated by conditions such as blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis;
- severe blepharitis can cause chalazion, conjunctivitis, keratitis, and blurred vision.
The earlier therapy begins, the better the prognosis. Self-medication is unacceptable, as it may not have the expected therapeutic effect. The disease continues to progress, and the likelihood of complications increases.
Which doctor should I contact?
At the first alarming symptoms from the visual organs: redness, swelling of the eyelids, it is recommended to seek help from an experienced ophthalmologist. Depending on the underlying condition that causes such symptoms, concomitant consultation with a dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, allergist, therapist, neurologist, cardiologist, dentist, otolaryngologist may be required.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with an ophthalmologist online
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the patient, asks about lifestyle, habits, and concomitant diseases. The doctor clarifies when exactly the symptoms first appeared, whether they were preceded by a traumatic injury: an insect or animal bite, or contact with an allergen plant. Pays attention to the course of the pathological process: unilateral, bilateral, as well as the accompanying clinical picture (pain, itching, headache, dizziness, blurred vision, discharge from the eyes).
Additional research is being carried out:
- General and biochemical blood test
- ophthalmoscopy
- biomicroscopy of visual organs
- determination of visual acuity
- puncture
- radiography
- anterior rhinoscopy
- bacteriological examination
- microscopic examination of eyelashes
During a general examination, attention is paid to possible manifestations of intoxication that indicate an infectious lesion: increased body temperature, increased sweating, general weakness, fatigue, dizziness, headache, decreased ability to work, irritability. If swelling affects not only the eyelids, but also the limbs, then this indicates a systemic disorder. Particular attention is paid to accompanying symptoms in the form of impaired mobility of the eyeball and its protrusion, a significant decrease in visual acuity.
Viruses
Sometimes swollen eyes are a manifestation of a virus, such as herpes. It is this virus that can provoke conjunctivitis. In addition to swelling, you may notice soreness.
On the forums, many recommend fighting this syndrome at home like this. Prepare a lotion from tea leaves. For this you need freshly brewed tea, always warm. Of course, the tea lotion will not affect the virus, but it can relieve pain and inflammation. This method cannot be considered the main method in treating the virus. And when it is because of a virus that the eye is swollen, only a doctor can tell you what to do. Antiviral medications are usually prescribed.
Treatment
Therapy of the visual organs requires an integrated approach: lifestyle correction, the use of medications for symptomatic therapy, and an impact on the primary condition that provokes such symptoms. Depending on the root cause of the violation, the following recommendations are followed:
- ethmoiditis requires complex therapy using antibacterial drugs, vasoconstrictors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines, multivitamins, immunomodulators, and physiotherapy. The chronic form of the disease is an indication for surgical intervention;
- conjunctivitis: antibacterial, antiallergic drugs, Gentamicin, Erythromycin ointment, painkillers, systemic administration of antimicrobial drugs;
- stye: in most cases, specific therapy is not required; warm compresses and eye ointments with an antibacterial effect are used to relieve symptoms. Purulent abscess is an indication for surgical intervention;
- Chalazion: disinfectant eye drops, dry heat compress, UHF treatment, massage of eyelids and clogged glands, corticosteroids. If conservative measures are ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated; an alternative to surgery is laser treatment;
- ARVI: in addition to antiviral and symptomatic therapy, the use of ophthalmic drugs that include dexpanthenol is recommended;
- eyelid dermatitis: antiviral drugs for local and systemic effects based on Acyclovir, immunomodulators, antihistamines, corticosteroids, zinc, vitamin C, D preparations;
- eye demodicosis: alcohol tincture of calendula, metronidazole, eye drops with antibiotics, antiseptics, antiallergic active substances;
- for blepharitis, it is recommended to sanitize foci of chronic inflammation and use antiparasitic drugs. It is necessary to carefully observe eyelid hygiene and massage them. Depending on the form of the disease, Sulfacyl ointment, the use of brilliant green solution, corticosteroids, antibacterial drugs, artificial tears, antiallergic drops and tablets are indicated.
The described medications are not intended for self-medication and can be used only after confirmation of the diagnosis, as prescribed and under the supervision of the attending physician.
What can cause a burning sensation around the eyes?
Around the human eyeball there are many tissues that are very susceptible to infections and irritations. These include eyelids, tear ducts, and thin, sensitive skin... The causes of unpleasant, painful sensations in this area can be different.
Burning and redness of the eyelids and/or skin under and above the eyes can occur as a result of an allergic reaction to decorative or care cosmetics: eye shadow, eyeliner, mascara, any cream, etc.
Therefore, if you observe similar symptoms in yourself, then the first thing you need to do is wash off your makeup and not apply any cosmetics until the exact cause is determined and the problem is completely eliminated.
Another cause of burning around the eyes may be the skin disease demodicosis. It occurs as a result of the activity of a tiny mite – demodex. This parasite, entering the human body, chooses as its habitat the ciliary follicles and cavities of the sebaceous glands on the skin of the eyelids and under the eye.
Demodex (its other name is the iron mite) can “sleep” for quite a long time without showing itself in any way, but then it “wakes up” due to any changes in the functioning of the body (for example, malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract, or liver disease, or the consequences of taking antibiotics, etc.). When activated, demodex causes both burning and itching.
A burning sensation in the skin around the eye can also be caused by a mechanical effect - for example, a thermal or chemical burn. With an ordinary burn (caused by hot water, steam or touching a hot object), in general, everything is clear - you should apply ice and immediately consult a doctor (especially if the eye itself is also damaged). Do not lubricate the burned area with fatty compounds, fermented milk products, do not apply any lotions, etc., before examination by a doctor.
But chemical burns caused by exposure to any toxic substances, especially acids, are almost impossible to treat at home - you need to immediately take the person to the hospital. Such accidents occur when working with various chemicals in factories or laboratories, when caustic household chemicals come into contact with the skin of the face near the eyes, etc.
Itching around the eyes and burning in the eyes – together, these are signs of some diseases of the eyeball. In particular, this is how acute conjunctivitis and blepharitis occur. In addition, the cause may be the flu or an acute respiratory infection - but then it is necessary to treat not the eyes or skin separately, but the disease itself in all its manifestations.
Since redness and burning around the eyes are only symptoms and not a diagnosis, you should consult a dermatologist to find out the diagnosis and begin treating the patient. Sometimes tests are taken for this (for example, for demodicosis).
How is burning around the eyes treated if it is associated with infectious diseases? Treatment usually involves instilling antiviral or antimicrobial drops that fight the pathogen. But in these cases, it is not the dermatologist who should make his appointments, but the ophthalmologist.
Itching around the eyes and burning associated with an allergic reaction to cosmetics usually goes away on its own if you wash off the offending product and do not reapply it.
But if it is a food allergy or one of the symptoms of hay fever, then you should take some anti-allergenic medication. However, it rarely happens that due to a food allergy or reaction to plant pollen, only the eyes and the area around them suffer - usually there is also a runny nose, lacrimation, itching and redness of the wings of the nose, etc.
The site podglazami.ru does not recommend turning to untested folk remedies if you want to relieve the feeling of “burning” or itchy skin around the eyes. Do not lubricate the skin with fatty creams, oils, decoctions or infusions of any herbs, etc. (especially when it comes to treating a burn). Also, you should not steam your facial skin during the treatment period (no matter which of the reasons described above is caused by the problem).
In addition, exclude the use of any cosmetics, even decorative ones - no matter how much you want to mask the redness of the eyelids or other external manifestations of the problem. It is especially undesirable to use scrubs and soaps with exfoliating ingredients.
You should not rub the skin, eyelids and corners of the eyes - although, of course, with a strong burning sensation, this is exactly what you involuntarily want to do.
But it is possible and even, in some cases, necessary to rinse your eyes and gently wash the area around them with clean water. This temporarily suppresses itching and other irritating sensations.
Prevention
To prevent swelling and redness of the eyes, ophthalmologists suggest following these recommendations:
- review your diet: exclude smoked, pickled, fried, overly salty foods
- adhere to the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle
- give up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol
- observe the work and rest schedule
- go to bed on time: go to bed no later than 23:00, sleep at least 7-8 hours
- eliminate the source of stress
- regularly carry out general detoxification of the body: take baths with sea salt, visit a bathhouse, sauna, use medicinal herbs to normalize the outflow of bile and liver function
- limit exposure to aggressive irritants: chemicals, tobacco smoke, allergens
- observe the drinking regime: the daily norm can be calculated using the formula 30-50 ml multiplied by body weight
- promptly treat emerging disorders: both systemic and visual.
- refrain from prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, do not freeze
- care for the delicate skin around the eyes: use masks, patches, compresses based on decoctions of medicinal plants (chamomile, cornflower, lavender)
- undergo regular preventive examinations with a doctor
- To prevent demodicosis of the eyelids, it is recommended to refrain from using feather pillows, as well as cosmetics that were used before infection with the mite
The prognosis depends on the patient’s age, individual characteristics of the body, and the degree of spread of the pathological process.