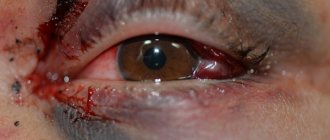
Chemical burn of the eyeball - this diagnosis sounds so frightening and distant .
It seems that only people in certain professions whose activities involve hazardous chemicals can get such an injury.
But, in fact, most injuries occur everyday life - during meals, medical procedures, cleaning , etc.
What to do if alcohol gets into your eye ? How to help yourself at home ? Is it possible to do without medical help? Read our article.
Symptoms
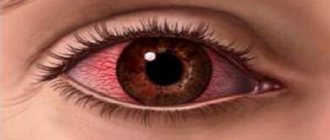
Reference! A chemical burn of the mucous tissue of the eye is difficult to confuse with anything else. The first symptom is severe discomfort, pain, and in some cases, painful shock.
The degree of destructive effect of an alcohol-containing substance depends on its quantity, concentration and duration of stay on the surface of the eyeball.
The following clinical picture is typical for an alcohol burn of the eye:
- sharp, cutting pain;
- redness of the white of the eyeball, protruded capillaries;
- swelling of the eyelids, swelling;
- photophobia, tearfulness when changing lighting;
- decreased visual acuity, myopia;
- high intraocular pressure;
- white veil over the eye.
How does it manifest?
The severity of a chemical burn depends on many factors. Among them are:
type of chemical (acid, alkali, etc.);- the amount of substance that has reached the surface of the eyes;
- concentration of the chemical (the more diluted it is, the less harm the burn will cause);
- temperature of the substance (the higher it is, the more complex the consequences);
- duration of exposure to the eyes.
The favorable outcome of treatment is also influenced by the patient’s age (the younger the person, the faster the recovery), as well as how timely and high-quality first aid was provided.
There are several degrees of eye damage from chemicals, which differ in the severity of the damage and are manifested by specific symptoms. There are 4 degrees of chemical burns:
The first is considered the mildest degree of burn. Its main features:
- sudden onset of pain;
- cloudiness in the eyes (vision problems);
- the appearance of red blood vessels in the whites of the eyes (hyperemia);
- conjunctival edema (chemosis);
- cloudiness of the fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye.
Manifestations of violation
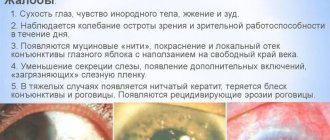
Signs of a violation largely depend on how long the irritating factor has been in effect. Most often, patients complain about:
- acute pain that is present for a long time;
- swelling formation;
- redness of the mucous membrane and skin;
- swelling of the eye apparatus;
- profuse lacrimation;
- high sensitivity to natural and artificial light sources;
- the appearance of a white film on the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- violation of intraocular pressure indicators, which manifests itself in corresponding discomfort.
The listed manifestations should not be taken as the only ones possible, since a person may complain of other symptoms. They appear against the background of concomitant diseases of the eye apparatus and other characteristics of the body. Also, if you burn yourself with alcohol, the pressure area may narrow.
A few days after the burn, all symptoms disappear, but this does not mean that the violation has passed without a trace. The pathology will progress regardless of whether there are external signs of a disorder or not. Conservative treatment in this case helps to avoid the development of serious complications and slow down the pathology. Unfortunately, it is not possible to improve visual acuity with medication alone; this will require surgical intervention.
Precautionary measures
To prevent chemical burns, you should:
- use personal protective equipment - rubber gloves, safety glasses, respirator;
- store ammonia in a glass container with an airtight lid;
- thoroughly ventilate the room after using the drug;
- refrain from wiping the skin and mucous membranes with the drug.
It is strictly not recommended to use ammonia for rinsing your mouth. When treating skin diseases, it is better to give preference to safer antiseptics - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
source
How to provide first aid at home?
Keep in mind! Alcohol, ammonia, lotions, perfumes - all this can cause severe burns to the organs of vision.
This is an extremely dangerous situation in which it is important to navigate in time and provide first aid.
How to help an adult?
The following instructions will help you provide first aid to the victim or yourself if you are faced with a problem alone.
- Call an ambulance . A chemical burn to the eye is a serious injury. If you are unable to provide first aid to yourself and then go to the hospital yourself, call an ambulance. Remember - the sooner you receive qualified help, the higher the chance of maintaining eye health.
- Rinse eyes with plenty of water . To do this, you can use an enema or a large syringe without a needle. Direct a stream of warm water from the outer edge of the eye to the tear duct, being careful not to touch the eyelid with your hands. Water should flow freely down your face and into a sink or basin. Rinsing must be carried out for quite a long time - from 15 to 25 minutes. In the absence of the above devices, you can use a sterile bandage or gauze soaked in water or saline solution.
- After rinsing the eye, keep yourself or the victim at rest. Take a horizontal position and wait for paramedics to arrive.
Alcohol has a detrimental effect on the cornea and, if treatment is delayed, you can partially or completely lose your vision.
How to help a child?
Many adults panic when it comes to helping a child. The baby cries, screams, rubs his eyes with his fists and it seems that there is simply no time to find a solution.
Need to know! The first thing you should do is call an ambulance.
The instructions for providing first aid are exactly the same as in the case of injury to adults - it is necessary to act despite the spasm and acute pain.
To alleviate the child’s suffering before the arrival of medical workers, it is permissible to give him a painkiller.
First aid
When the skin is damaged by ammonia, acute pain occurs. Alkaline burns are dangerous due to bacterial complications, so the victim needs to be given first aid:
- Neutralization of ammonia. Clothes soaked in the preparation are removed or carefully cut with scissors. To neutralize alkali, use a 5% solution of boric, citric or acetic acid. To prepare it, add 5 g of powder to 100 ml of water.
- Washing. The skin wound is washed with running water for 15 minutes. Blot with a clean towel or sterile gauze.
- Cooling. Apply a cold pack or ice bag to the burn.
- Anesthesia. The victim should be given oral analgesics to relieve pain. They prefer non-steroidal ones - Ibuprofen, Ketorolac.
- Treatment of the wound. When treating chemical injuries, you need to treat damaged tissues with Pyromecaine ointment.
A doctor is consulted only for serious burns, which are accompanied by the death of large areas of the skin. For grade 1 and 2 injuries, treatment is continued at home with wound-healing ointments.
More dangerous are burns of ammonia alcohol to the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by damage to the mucous membranes. In this case, you need to provide urgent primary assistance:
- Washing. If liquid gets into the eye, rinse with running water for 15-20 minutes. In a hospital setting, 0.5% solutions of acetic or boric acid are used. After neutralizing the alkali, a 0.5% Dicaine solution is instilled.
- Rinsing the mouth. In case of a burn to the oral mucosa, treatment is carried out with a 1% solution of citric or boric acid.
Non-narcotic analgesics do not always completely relieve pain caused by a burn with ammonia. To enhance their effect, take an additional 1-2 tablets of Sedalgin.
Medicines
Due to the ingress of caustic liquid, hyperemia and infiltration are observed in the affected area. Drug therapy can reduce the severity of symptoms and accelerate the regeneration of tissue structures. Groups of drugs prescribed:
- Antibiotics in the form of drops. To eliminate possible infection, drugs with a bacteriostatic effect are prescribed.
- Anesthetics. Pain relief occurs with instillation of medications based on lidocaine or novocaine.
- Antiseptic medicines. Ointments are prescribed to prevent scars, on the basis of which an overlay is made for the damaged organ of vision.
- Regenerants and reparants. This group of drugs is prescribed to accelerate the regeneration of tissue structures of the organ of vision.
To speed up recovery, it is possible to use traditional medicine methods, but only after consulting an ophthalmologist.
Further therapy
A combustiologist treats burns of the skin, mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and ENT organs. The principles of treatment depend on the severity of the injury and the area of damage.
If ammonia gets into your eyes, you should immediately consult a doctor. Exposure to the composition may cause the patient to lose vision.
For skin lesions, ammonia is used:
- Olazol is a combination medicine that has an antimicrobial and analgesic effect. Used in the treatment of infected skin wounds and non-healing burns.
- Pantestin is a gel with miramistin and provitamin B5, which stimulates the regeneration of the epidermis and prevents infection from entering the wound. When treating burns, apply under a bandage 2-3 times a day.
- Panthenol is a spray with provitamin B5 that accelerates the healing of the skin. Used in the treatment of extensive wounds up to 5 times a day.
- Povidone-Iodine is a topical antiseptic that kills most known bacteria, fungi and protozoa. Prevents purulent inflammation of the skin, stimulates healing.
- BoroAyur is a disinfecting cream with calendula that has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Apply under a bandage to treat superficial burns.
When inhaling ammonia fumes, the nasal cavity is washed with a weak solution of boric acid. In case of severe irritation of the respiratory mucosa, the following are used:
- Eufillin is a bronchodilator that prevents swelling of the airways and bronchospasms. Used in the treatment of burns of ENT organs to prevent suffocation.
- Prednisolone is a hormonal drug with an anti-inflammatory effect. It also has an antioxidant and anti-shock effect in case of burns of the respiratory tract.
- Decasan is a disinfectant solution for inhalation that has antimicrobial and antifungal properties. Prevents abscesses in the ENT organs, bacterial pneumonia, etc.
To treat wounds in the oral cavity, wound healing ointments, disinfectants and astringent solutions are used. The soft palate, gums and tongue are treated with Metrogil Denta gel. It prevents infectious and inflammatory pathologies and purulent complications. To disinfect the mucous membrane, rinse the mouth with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine.
Serious injuries require hospital treatment. Inhalation of concentrated ammonia fumes is dangerous due to suffocation and severe intoxication. To stabilize the condition of patients, they resort to oxygen therapy. It provides for the inhalation of gaseous mixtures with a high oxygen content - more than 21%. This treatment stimulates metabolism in the body and increases the regenerative properties of tissues.
When should you go to the hospital for help?
Regardless of the circumstances , an alcohol burn to the eyeball requires emergency medical care .
The patient is required to be admitted to an ophthalmological hospital , where, under the supervision of doctors, jet rinsing with saline solution continues.
Do not try to independently select medications to improve the condition of the eyeball and mucous tissue of the eyelid.
Note! This can be extremely dangerous because it is unknown how such treatment will affect vision.
Symptoms
Depending on the location of the affected areas of the body, different signs of burns with ammonia may be observed:
- swelling of the mucous membranes, painful nasal congestion;
- the appearance of ulcers on the affected surface of the epidermis;
- irritation, itching;
- deterioration of health, headaches;
- increased sweating;
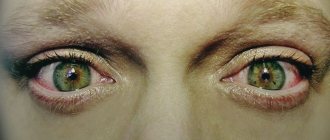
- lacrimation, photophobia, inflammation of the mucous membranes, temporary or irreversible loss of vision (if the eyes are damaged);
- difficulty breathing, cough, hoarseness (if the throat and larynx are injured).
When the esophagus is burned, severe pain and vomiting with blood appear. This condition is especially dangerous due to the high risk of perforation.
After the first symptoms appear, the victim must receive first aid as quickly as possible and begin special treatment, which will prevent the development of tissue necrosis.
What consequences might there be?
Alcohol burns to the eye are classified in several areas of damage: eyelid skin, cornea, conjunctiva, eyeball, adnexa.
There are four stages of burn :
- Initial stage . It lasts for one or two days. During this period, the patient feels acute discomfort in the eye and suffers from tearing. It is at this stage that tissue death occurs.
- Second stage. Duration from two days to several weeks (depending on the individual characteristics of the body). The cornea swells, severe trophic disorders occur, which can cause irreparable damage to vision.
- Third stage. Takes another 4 – 16 weeks. Hypoxia begins. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues of the eyeball, trophic processes begin, and the vessels of the cornea grow.
- Fourth, final stage. It may take several years. The mucous membranes become scarred due to excessive production of collagen by the body.
Stay up to date! For vision and health, this is fraught with the following consequences:
- Decreased visual acuity. Initially, this may be due to epithelial damage, swelling or cloudiness caused by lacrimation. It is worth considering that vision may not deteriorate immediately - some consequences of burns become apparent only after a while. Most often, myopia caused by an injury of this kind is irreversible.
- Increased intraocular pressure. Caused by deformation and shortening of collagen in the trabecular apparatus. In the future, it can provoke inflammatory processes in the anterior part of the eye.
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva . This disease is possible even with a mild alcohol burn. It causes severe discomfort and makes the eyes more sensitive to light.
- Corneal perforation . A rather rare phenomenon that occurs only in severe chemical burns, when the ability for natural tissue regeneration is significantly reduced.
- Scarring of the eyelid/conjunctival surface. Leads to serious problems, complications and inflammation, especially if the scar prevents the proper closure of the palpebral fissure (closure of the eyelids).
Main characteristics of injury
A chemical burn is an injury to the eye caused by exposure to aggressive chemicals. First of all, there is damage to the conjunctiva - a thin connective membrane that covers the outer surface of the eye and the back surface of the eyelid. It performs an important function because it releases a special liquid that lubricates the eye and prevents it from drying out. Its damage often leads to impairment and even loss of vision.
Damaging substances
Chemical burns of the conjunctiva are not uncommon these days. According to statistics, 10% of all eye burns are of chemical origin. Most often, damage occurs when aggressive substances come into contact with the ocular surface. Among them are:
Acids. Most often, burns occur with the following acids:
- hydrochloric acid (HCl);
- sulfuric (H2SO4);
- acetic (HC, COOH);
- hydrofluoric(HF).
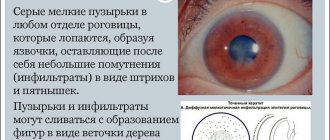
An acid burn is similar to a thermal burn. It affects the conjunctiva and cornea without spreading into the eyeball. The degree of damage is influenced by the concentration of acids and the duration of their exposure. At the site of acid entry, a necrotic area appears, which is separated from healthy tissue (coagulation). In this case, a very strong pain syndrome appears, since the optic nerves are irritated.
Alkali. The most common alkalis that cause burns are:
- ammonia (ammonium hydroxide);
- caustic soda (sodium hydroxide);
- magnesium hydroxide;
- potassium hydroxide;
- slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
Burns from alkaline substances are considered more dangerous because the damage extends deep into the eye, from where it is not easy to remove. At the same time, the time of negative impact increases.
This occurs due to the fact that alkali provokes liquefaction necrosis in the proteins, which leads to their melting (myomalacia) and spreading throughout the eye. In this case, the optic nerves are damaged by alkali, which leads to their loss of sensitivity. That is why a person with alkaline burns practically does not feel pain. This often leads to underestimation of damage.
Risk factors
How do chemical eye burns occur? This occurs through direct contact with acids or alkalis, when, due to carelessness or failure to comply with safety measures, these aggressive substances first enter the area of the conjunctiva of the eye, causing its necrosis (death). Among the risk factors contributing to the occurrence of such burns are:
- Construction or repair manipulations. These types of work often use chemicals that can cause burns.
- Using aggressive substances in everyday life without following safety rules. For example, improper or careless use of ammonia, household chemicals containing dangerous acids or alkalis. It is also risky to leave such substances within the reach of children.
Work involving frequent use of chemicals. This may be the production of concentrated acids and alkalis or other types of work where such substances are used.- Careless behavior with car batteries that contain sulfuric acid concentrate. This is especially true for car enthusiasts who do not have professional skills in working with cars.
- Alcohol abuse. In this state, very often people do not follow safety rules, which leads to unpleasant consequences.
Any type of burn is potentially dangerous. Therefore, first of all, a person needs emergency care for a chemical burn to the eyes.
The sooner it is provided, the more favorable the forecasts will be.
What should be done for subsequent treatment?
In most cases, the doctor prescribes the patient regenerating eye ointment and drops that emit the chemical composition of “living” human tears.
You should know! In case of serious violations, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotic drugs. Physiotherapy and eyelid massage may be prescribed at the same time.
Surgery is performed only if there is a risk of complete loss of vision.
Treatment of thermal burns
The primary task before the arrival of doctors is to eliminate the damaging effect. Then you should cool the eye. There should be no problems with eliminating a weld or other hot element, but for cooling it is worth using the following algorithm:
- A bandage is applied to the fingers and they are wrapped with it.
- The person opens his eyelids as much as possible.
- To cool, you need to turn on a small water pressure from 12 to 18 ° C and keep your eye on for 20 minutes.
An alternative for refrigeration is any frozen or chilled item. You can simply fill a container with water and apply it to the organ. The fastest way to cool the organ is by immersing your entire face in a container of cold water. Underwater you need to blink sometimes. Plain cotton wool will also help cool the eye; you need to wet it and move it from the temple to the eyelid, then move the nose using smooth movements (do the same with a piece of ice).
When the preparatory procedures are completed for a burn of the cornea of the eye, treatment is selected with drops with an antiseptic effect, for example, Levomycetin, Albucid. The damaged eye is covered with a napkin and an analgesic tablet can be taken.
It is necessary to contact a specialist if during the day:
- pain is present or intensifies;
- there is a feeling that there is a foreign object in the eye;
- other symptoms are noticeable that indicate infection in the eye: swelling, hyperemia, mucus secretion;
- the quality of visual function is reduced.
Healing procedures
For a chemical burn to the eye, first aid involves a set of certain actions. It must be provided on an emergency basis. It’s good if there is a person nearby with a medical education or basic knowledge in this area. But even an ordinary person can help.
First aid
So, what to do for chemical eye burns? There are several stages of emergency assistance:
First, it is urgent to rinse the affected eye (no later than 30 minutes after contact with the chemical). To do this, use a physiological solution of sodium chloride 0.9% (table salt) or a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). They have antiseptic properties.
If nothing is available, rinse the eyes with plain water from the inner corner of the eye to the outer corner to avoid chemicals getting into the healthy eye. If there are solid particles of the chemical (lime) in the eye, they should be removed with a dry cotton swab before rinsing.
- When it is known exactly what substance caused the burns, it can be neutralized. In case of an alkaline burn, the eyes should be rinsed with water and vinegar or 2% boric acid. A few drops per 500 ml of water is enough. If the burn is caused by acid, you need to treat your eyes with a weak soda solution.
- To avoid infection, antiseptic eye drops are dripped into the eye. A solution of furatsilin or sodium sulfacil is suitable for this purpose.
- local anesthesia for the purpose of carrying out manipulations to remove aggressive substances (Lidocaine);
- antitetanus serum;
- antibiotics to prevent infection (drops containing ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin eye ointment);
- cycloplegic drugs that reduce pain and prevent scarring (atropine sulfate solution);
- tear fluid substitutes (Lakrisin);
- drugs that reduce intraocular pressure (Timolol, acetazolamide solution);
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) are prescribed when inflammation occurs.
After all these manipulations, you should cover the affected area with a clean bandage, give the patient a sedative and send him to the hospital, where appropriate treatment will be carried out.
It depends on the severity of damage to the eyeball and the presence of concomitant conditions (inflammation, pain shock and others).
Further therapy
Medical centers offer these procedures to treat eyes damaged by chemicals. First of all, medications are used. Among them:
Burn with ammonia (ammonia): how to treat
Ammonia (ammonium hydroxide) is an aqueous solution of ammonia that has a local irritant and antiseptic effect. Used in medicine to disinfect wounds, as well as stimulate breathing during loss of consciousness.
Many people use it to kill bacteria in the mouth. In everyday life, ammonia is used as a stain remover, cleaning agent, and dye. A burn with ammonia is one of the most common household injuries.
The prognosis of treatment depends on the duration of contact with alkali, the extent of the damage, and proper first aid.
Why is ammonia dangerous?
Ammonia solution is a toxic substance that contains alkaline components. An ammonia burn is a chemical injury that causes severe damage to the mucous membranes and skin. Therefore, doctors categorically do not recommend using the drug to treat oral problems.
Burns from ammonia can cause damage to the deep layers of the dermis. Unlike acids, ammonia does not cause tissue coagulation. Therefore, scabs do not form in the damaged areas, which could prevent the drug from penetrating deep into the tissues.
Degree of skin damage
When ammonia gets on the skin and mucous membranes, swelling and weeping wound surfaces with a whitish coating occur. Treatment methods depend on the depth and extent of the damage. More often, only the first three degrees of burns with ammonia occur:
- first – slight swelling, redness, moderate pain in the affected areas of the body;
- second - ulcers form on the mucous membranes, and watery blisters form on the skin;
- third - a weeping wound with a whitish coating and a red edging around appears in the affected area.
With short exposure to tissue, relatively minor wounds occur. Treatment of 1st and 2nd degree burns is carried out at home with local medications - antiseptics, regenerating ointments, analgesics. If the drug is swallowed, treat only in a hospital setting.
Symptoms of chemical burns
An ammonium hydroxide burn always causes severe pain, so treatment begins with painkillers. The following symptoms indicate skin damage by the drug:
- burning pain;
- swelling;
- redness;
- small bubbles.
In 90% of cases, ammonia provokes only 1st and 2nd degree burns. But when large areas of the body are affected, sometimes the deep layers of skin and muscles are destroyed. If the wound area is more than 30% of the total skin surface, a burn disease occurs. It is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication - nausea, weakness, vomiting, kidney or liver failure.
If ammonia gets into your eyes, you should immediately consult a doctor. Exposure to the composition may cause the patient to lose vision.
When inhaling ammonia fumes, the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, pharynx, lungs, etc. are affected. A burn of the ENT organs is indicated by:
- hacking cough;
- sore throat;
- burning in the nose;
- overexcitement;
- hallucinations;
- labored breathing.
The greatest health hazard is caused by internal burns caused by ingesting ammonia. When the gastrointestinal tract is damaged, the following symptoms occur:
- pain along the esophagus;
- labored breathing;
- pressure behind the sternum;
- burning in the epigastrium;
- strong thirst;
- persistent diarrhea;
- severe weakness.
Third degree burns are uncommon. Treatment of such injuries is carried out only in a hospital or burn center. The seriousness of the injury is indicated by damage not only to the skin, but also to tendons, muscles, and bone tissue.
Due to damage to sensory receptors, pain sensations are dulled. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, aggressive ammonia penetrates deeply into the tissues and systemic bloodstream.
This is fraught with burn shock, intoxication, and renal and hepatic failure.
First aid
When the skin is damaged by ammonia, acute pain occurs. Alkaline burns are dangerous due to bacterial complications, so the victim needs to be given first aid:
- Neutralization of ammonia. Clothes soaked in the preparation are removed or carefully cut with scissors. To neutralize alkali, use a 5% solution of boric, citric or acetic acid. To prepare it, add 5 g of powder to 100 ml of water.
- Washing. The skin wound is washed with running water for 15 minutes. Blot with a clean towel or sterile gauze.
- Cooling. Apply a cold pack or ice bag to the burn.
- Anesthesia. The victim should be given oral analgesics to relieve pain. They prefer non-steroidal ones - Ibuprofen, Ketorolac.
- Treatment of the wound. When treating chemical injuries, you need to treat damaged tissues with Pyromecaine ointment.
A doctor is consulted only for serious burns, which are accompanied by the death of large areas of the skin. For grade 1 and 2 injuries, treatment is continued at home with wound-healing ointments.
More dangerous are burns of ammonia alcohol to the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by damage to the mucous membranes. In this case, you need to provide urgent primary assistance:
- Washing. If liquid gets into the eye, rinse with running water for 15-20 minutes. In a hospital setting, 0.5% solutions of acetic or boric acid are used. After neutralizing the alkali, a 0.5% Dicaine solution is instilled.
- Rinsing the mouth. In case of a burn to the oral mucosa, treatment is carried out with a 1% solution of citric or boric acid.
Non-narcotic analgesics do not always completely relieve pain caused by a burn with ammonia. To enhance their effect, take an additional 1-2 tablets of Sedalgin.
Further therapy
A combustiologist treats burns of the skin, mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and ENT organs. The principles of treatment depend on the severity of the injury and the area of damage.
If ammonia gets into your eyes, you should immediately consult a doctor. Exposure to the composition may cause the patient to lose vision.
For skin lesions, ammonia is used:
- Olazol is a combination medicine that has an antimicrobial and analgesic effect. Used in the treatment of infected skin wounds and non-healing burns.
- Pantestin is a gel with miramistin and provitamin B5, which stimulates the regeneration of the epidermis and prevents infection from entering the wound. When treating burns, apply under a bandage 2-3 times a day.
- Panthenol is a spray with provitamin B5 that accelerates the healing of the skin. Used in the treatment of extensive wounds up to 5 times a day.
- Povidone-Iodine is a topical antiseptic that kills most known bacteria, fungi and protozoa. Prevents purulent inflammation of the skin, stimulates healing.
- BoroAyur is a disinfecting cream with calendula that has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Apply under a bandage to treat superficial burns.
When inhaling ammonia fumes, the nasal cavity is washed with a weak solution of boric acid. In case of severe irritation of the respiratory mucosa, the following are used:
- Eufillin is a bronchodilator that prevents swelling of the airways and bronchospasms. Used in the treatment of burns of ENT organs to prevent suffocation.
- Prednisolone is a hormonal drug with an anti-inflammatory effect. It also has an antioxidant and anti-shock effect in case of burns of the respiratory tract.
- Decasan is a disinfectant solution for inhalation that has antimicrobial and antifungal properties. Prevents abscesses in the ENT organs, bacterial pneumonia, etc.
To treat wounds in the oral cavity, wound healing ointments, disinfectants and astringent solutions are used. The soft palate, gums and tongue are treated with Metrogil Denta gel. It prevents infectious and inflammatory pathologies and purulent complications. To disinfect the mucous membrane, rinse the mouth with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine.
Serious injuries require hospital treatment. Inhalation of concentrated ammonia fumes is dangerous due to suffocation and severe intoxication. To stabilize the condition of patients, they resort to oxygen therapy. It provides for the inhalation of gaseous mixtures with a high oxygen content - more than 21%. This treatment stimulates metabolism in the body and increases the regenerative properties of tissues.
Consequences of chemical burns
Chemical damage to soft tissues with ammonium hydroxide is dangerous due to purulent complications. Possible consequences of careless handling of ammonia include:
- scarring of the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- internal bleeding;
- dehydration;
- pain shock;
- lymphadenitis;
- bloody diarrhea;
- skin abscess.
Aqueous ammonia absorbs moisture and instantly destroys the protein components of tissues. If it gets into the eyes, it reduces visual acuity. In case of delayed treatment, it destroys the cornea and iris. Clouding of the lens and necrosis of the conjunctiva are possible. Victims complain of constant lacrimation, spasms of the eye muscles, and photophobia.
A burn of more than 30% of the body leads to internal poisoning. The accumulation of tissue breakdown products in the body leads to acute liver and sometimes kidney failure.
Precautionary measures
To prevent chemical burns, you should:
- use personal protective equipment - rubber gloves, safety glasses, respirator;
- store ammonia in a glass container with an airtight lid;
- thoroughly ventilate the room after using the drug;
- refrain from wiping the skin and mucous membranes with the drug.
It is strictly not recommended to use ammonia for rinsing your mouth. When treating skin diseases, it is better to give preference to safer antiseptics - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
Emergency measures
Lotions, vodka, and perfumes can cause severe alcohol burns to the eye. This is a dangerous situation in which most of the damage occurs on the cornea.
Immediate measures can prevent complications:
- First, you should immediately rinse your eye with plenty of clean, cold water.
- Keep the victim calm and place him in a horizontal position.
- Do not delay and contact an ophthalmologist.
- Do not rub your eyelids under any circumstances, even if itching or burning occurs.
When vodka gets into the eye, ethyl destroys the cornea; if treatment is delayed, you can partially lose vision.
Symptoms of chemical burns
An ammonium hydroxide burn always causes severe pain, so treatment begins with painkillers. The following symptoms indicate skin damage by the drug:
- burning pain;
- swelling;
- redness;
- small bubbles.
In 90% of cases, ammonia provokes only 1st and 2nd degree burns. But when large areas of the body are affected, sometimes the deep layers of skin and muscles are destroyed. If the wound area is more than 30% of the total skin surface, a burn disease occurs. It is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication - nausea, weakness, vomiting, kidney or liver failure.
If ammonia gets into your eyes, you should immediately consult a doctor. Exposure to the composition may cause the patient to lose vision.
When inhaling ammonia fumes, the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, pharynx, lungs, etc. are affected. A burn of the ENT organs is indicated by:
- hacking cough;
- sore throat;
- burning in the nose;
- overexcitement;
- hallucinations;
- labored breathing.
Welding eye burn treatment
Burns to the cornea of the eye caused by welding are especially dangerous to treat due to exposure to rays of 280–300 nm, which are able to penetrate the body without any obstacles. This phototrauma should be a compelling argument for contacting a doctor, who will assess the level of damage to the eye.
Before contacting a doctor, it is necessary to relieve the symptoms:
- Sunglasses are put on the eyes, the amount of light in the room is limited by means of dark curtains. Light is replaced by night lamps;
- anti-inflammatory drugs with an analgesic effect are used;
- natural tear preparations are instilled.
Protecting your eyesight from strain is especially important in the first 24 hours after the injury. During this period, photophobia is most pronounced and blepharospasm is very noticeable. At the same time, wearing bandages somewhat slows down the restoration of vision, so wearing them is not recommended.
Burns of the cornea of the eye by welding are effectively treated with painkillers: Nimesil, Nurofen, Diclofenac. The method of use makes no difference. If the drug is in tablets, it should be taken 1 piece at a time. 2–3 times a day. Most effective after eating. Eye burns caused by welding are treated symptomatically for 3 days.
Treatment of eye burns from welding often involves the use of natural tear medications, which accelerate the epithelization of the eye and prevent the onset of dryness. It is necessary to instill the drugs in 1-2 drops at regular intervals of 2 hours.
Treatment is selected by an ophthalmologist. Predominantly prescribed:
- antibiotics in the form of drops prevent the occurrence of an inflammatory reaction due to microbes;
- anesthetic solutions, Dicaine or Lidocaine are suitable for topical use;
- novocaine blockades of the perivasal type - the technique is used only in the hospital;
- burn of the cornea of the eye, treatment with drops involves the use of drugs to dilate the pupil.
Folk remedies are highly effective for burns, so at home you can supplement therapy with homemade recipes.
Welding eye burn treatment with folk remedies:
- Raw potatoes have beneficial effects. It is necessary to cut a regular-sized potato in half and apply the cut to the eyelids. The pain will go away gradually and if the potato is quickly removed, the pain will return. To normalize the condition, you should hold the vegetable for 2 hours. For easier use, you can prepare a paste and put it under the bandage.
- Ultraviolet eye burns are often treated with tea leaves. To treat eye burns with ultraviolet radiation, it is recommended to brew 2 sachets in boiling water and then apply them to the eyelids. The advantage of this method is the quick effect, it only takes 10 minutes, the disadvantage is that it stains the skin. You can replace the bags with tea leaves wrapped in gauze.