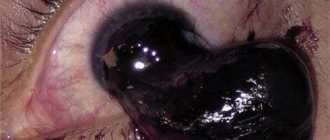
Purulent discharge, redness of the eyelids, pain and swelling - this is not the entire list of manifestations that can accompany most ophthalmological diseases. In case of suppuration and swelling of the eye in adults and children, you should seek help from specialists, since self-medication can be harmful.
Only specialists can identify the cause of the development of pathology and correctly prescribe treatment after a comprehensive diagnosis. First of all, therapy should be aimed at reducing the tumor and draining purulent accumulations in the eyes.
Causes
Symptoms of many ophthalmic diseases are purulent discharge and redness of the eyes. Often, purulent accumulation that occurs against the background of an inflammatory process is diagnosed in children with a weak immune system. Scratching the affected area should be avoided, as this may cause complications in the form of re-development of the infectious process.
Dacryocystitis
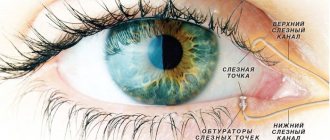
The disease is characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal sac. Purulent discharge occurs as a sign of blockage of the nasolacrimal canal. During normal functioning, tear fluid helps to moisturize the mucous membranes. When the tear duct becomes clogged, pathogenic microbes multiply on the mucous membrane. Complete or partial blockage of the lacrimal canals is diagnosed. If the specialist’s recommendations are not followed, complications may arise in the form of the development of atherosclerotic processes.
Trachoma
Chronic inflammation that occurs due to bacteria of the genus Chlamydia. Initially, the pathology affects one eye; after a week, the inflammation spreads to the second. In this case, the manifestation of the first symptoms of trachoma occurs no earlier than 14 days after infection. The first thing you notice is swelling of the eyes. Also additionally manifested:
- redness of the tissues of the eyeball;
- the conjunctiva swells;
- the quality of vision decreases;
- lacrimation increases;
- photosensitivity occurs;
- a purulent follicle forms;
- the purulent process spreads around the eyelids.
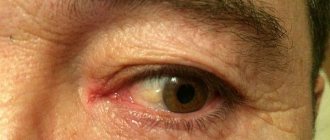
Blepharitis
In 30% of diseases that cause redness of the eye, blepharitis is diagnosed. The pathology can affect adults and children, but patients aged 40 to 70 years suffer most from it. Blepharitis affects the edge of the eyelid where the eyelashes are located. The disease occurs against the background of an inflammatory process with different etymologies of development. With complications, secondary development of conjunctivitis, chalazion, keratitis and decreased vision is possible.
Barley
Purulence and redness of the eyes are characteristic when barley develops inside the hair follicles. A small formation appears at the site of the lesion, inside which a purulent mass accumulates. The tumor causes discomfort and pain.
Most often, multiple styes develop when immunity decreases. In some cases, redness, swelling and purulent discharge may be accompanied by high fever and general malaise.
Keratitis
A disorder associated with inflammation of the cornea. The characteristic symptoms of the disease are:
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to light;
- difficulty opening eyelids;
- severe lacrimation;
- feeling of sand in the eyes;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- burning sensation, severe itching;
- decreased vision;
- redness and purulence of the eye;
- decreased sensitivity of the cornea.
Often the development of keratitis is a complication of certain diseases. In this case, there is redness and the presence of purulent discharge, which contributes to the sticking of eyelashes.
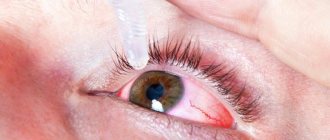
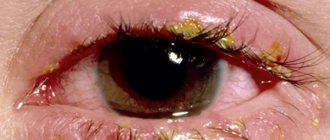
Conjunctivitis
The inflammatory process, which is accompanied by the accumulation of purulent substances on the conjunctiva, is called conjunctivitis. Pathology is divided into several forms:
- Allergic – characterized by allergic reactions that are provoked by the ingress of foreign particles onto the mucous membrane of the eyes. In each case, the symptoms appear separately - for some it is swelling of the eyelids and redness, for others it is suppuration of the eyelids.
- Bacterial - this form develops when exposed to pathogens staphylococci, gonococci and streptococci. Treatment of this pathology is carried out in a hospital setting. Infection is possible when sharing personal hygiene products and medications with a patient. In some cases, the pathogen can be transmitted by airborne droplets.
- Infectious – develops when viruses and bacteria enter the mucous membrane. The eyelid turns red and pus accumulates under it.
- Chronic - develops with constant irritation of the conjunctival membrane, vitamin deficiency or metabolic disorders.
How to treat
Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor will recommend the necessary hygienic procedures to carry out the process of washing the inflamed eye canals and removing the pus that accumulates on the eyelids. In addition, for most infectious and viral diseases of the organs of vision, the ophthalmologist prescribes pharmacological agents:
- anti-inflammatory or antibacterial ointments;
- soothing, antiseptic or antibiotic drops;
- special saline solutions for washing.
Among eye ointments, tetracycline ointment has proven its effectiveness in the fight against conjunctivitis and other inflammations of the organs of vision. This is a powerful broad-spectrum antibiotic that helps with most eye diseases accompanied by pus. Placing tetracycline ointment under the eyelid three times a day helps to cope with the symptom of purulent discharge for 5 days.
During inflammation of the ocular mucous membrane, accompanied by the formation of pus, the procedure of washing the eyelids and eyeball is especially important, as it helps relieve inflammation, reduce irritation, and speed up the healing process. It is necessary to rinse your eyes when they turn sour; you can do this with a pipette or cotton pads. For rinsing with conjunctivitis of various types, doctors recommend using a solution of chloramphenicol, furatsilin or miramistin.
- Antiviral drugs during pregnancy by trimester
- Ear drops for ear congestion
- How to wean your baby off formula and breastfeeding at night
Eye drops
Drops should be instilled into inflamed eyes oozing pus to prevent them from turning sour. Doctors prescribe Albucid drops as an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent. This is a universal remedy; when used, an allergic reaction rarely occurs; the drug can be used for antiseptic rinses. The feeling of discomfort and tingling when instilled is normal; Albucid should be instilled at least 3-5 times a day until the symptoms completely disappear.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of eye diseases accompanied by the discharge of pus should be used only as auxiliary methods in addition to drug therapy. For styes and other eye swelling, traditional healers recommend warming the eyeball with a warm boiled egg applied to the upper eyelid. For rinsing, you can use warm brewed green tea, since this plant has excellent antiseptic properties.
Calendula infusion and chamomile decoction are used as solutions for soothing lotions that soften inflamed mucous membranes. You should rinse your eyelids from pus with a solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin so that your eyes don’t turn sour, the pus stops flowing, and other symptoms begin to subside - redness, itching, burning. Some doctors recommend massage of the ocular ducts to speed up the process of suppuration and quick recovery.
Diagnostics
If redness of the whites of the eye, purulent discharge and swelling of the eyes appear, you should immediately seek help from an ophthalmologist to determine the root cause.
When examining the affected eye, a specialist may need the following diagnostic methods:
- laboratory blood tests;
- bacteriological culture of purulent discharge;
- examination of eyelashes to identify demodectic mites;
- PTC - analysis and cytology, which are used to diagnose purulent contents;
- allergic and tubular tests;
- dacryocystography.
Why do eyes fester and turn red?
Excessive discharge of brown fluid from the lacrimal sac and redness of the eyes indicate the presence of an infection. In most cases it is conjunctivitis. Also, the presence of pus causes barley, keratitis, trachoma, dacryocystitis, blepharitis and even common allergies. There are a lot of diseases with similar symptoms, so self-medication is dangerous, as it can lead to complete or partial loss of vision. Therefore, it is not advisable to do anything without the doctor’s knowledge.
Conjunctivitis
Often a viral infection is accompanied by a bacterial one.
This is the name for inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. Depending on the nature of the irritant, it can be bacterial, viral, or allergic. The first type is one of the most dangerous; it occurs when an infection enters the organs of vision and is treated with antibiotics. The second one is of viral origin, developing with a common cold or acute respiratory viral infection. The third - with the negative impact of allergens (odors, clothes, low-quality toys, products). It is quite easily transmitted, so it is necessary to carefully observe personal hygiene, wash your hands often, and do not touch your face with dirty palms. With conjunctivitis, the eye turns red, hurts, cuts, sticks in the morning, may water, swell, and fear of light appears. Purulent discharge indicates the transition of the disease to a dangerous stage and requires radical therapeutic methods.
Stye on the eye
Mostly occurs in children, but also occurs in adults. This is an inflammatory process of the sebaceous glands along the edges of the eyelids. It is there that an abscess forms, which when ripe is very painful. It is prohibited to open it yourself. Stye often does not require treatment, but a person with a weak immune system should consult an ophthalmologist. The causative agents are staphylococcus and demodicosis. The first type is a bacterium that is transmitted through dirty palms touching the face and rubbing the eyes. The second is a microscopic mite. People become infected through close contact with animals. Demodicosis settles at the beginning of eyelash growth. With prolonged exposure, the eyes itch and fester.
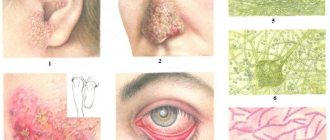
Keratitis, trachoma
A long-term inflammatory process provokes the formation of erosion of the cornea of the eye.
This is the medical name for inflammation of the cornea. The cause of the appearance may be trauma, burns, neurogenic factors, various types of infections, herpes. Associated symptoms: pain and pus in the eyes, fear of bright light, spasms, darkening of the cornea, rupture of small capillaries, watery eyes. The patient complains of loss of visual acuity, organ fatigue, and difficulty distinguishing small objects.
If the eye is red and festered, the patient may have trachoma. The causative agent is chlamydia. First, the epithelial cells of the cornea become inflamed, then the cartilage on the eyelids is involved, boils form, fluid is released, and scars appear. The disease is dangerous and can be treated with antibiotics and sulfonamides; in extreme cases, surgery is required.
Allergic reactions
The eyes become swollen, red, swollen, watery, and painful—allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva is possible. In medicine, the condition is called “allergic conjunctivitis.” With prolonged exposure to the irritant on the body, the eyes fester. Allergens include cosmetics, food, strong odors, chlorinated water and others.
Dry eye syndrome
Working at a computer for a long time creates additional stress on the eye muscles.
This is the name for severe inflammation of the mucous membrane and the edges of the eyelids of a chronic nature. A huge amount of purulent mucous fluid appears in the morning. During the day, a foreign body is felt (even though it is not there), the visual image blurs, the eye waters, turns red, and burns. Reasons for the development of the syndrome: insufficient production of tear fluid, harmful environmental factors (long stay in front of the monitor, dry air, ultraviolet radiation, low-quality contact lenses and others). If the eye is red and festering, swollen, you need to consult a doctor.
Treatment
Therapeutic therapy is prescribed individually for each patient, based on the diagnosed disease. The first step is to determine the cause of the pathology, and only then begin treatment.
If allergic conjunctivitis develops, antihistamine drops may be prescribed. In case of a bacterial disorder, agents such as Levofloxacin and Tobramycin can be used for treatment.
When redness and suppuration of one eye are accompanied by high fever, blepharitis is diagnosed. In this case, complex therapy is prescribed.
When trachoma is diagnosed, medicinal antibiotics, tablets or drops are prescribed for treatment. In some cases, if there is a complication, surgery may be prescribed to open the purulent follicles.
Treatment of children
When redness, swelling and suppuration are diagnosed in a child, different treatment methods are used. For dacryocystitis, an operation called dacryocystorhinostomy is prescribed. It helps normalize the outflow of tear fluid.
To wash sore eyes, use a decoction of calendula or chamomile. The same components are used for compresses.
Prevention
To avoid the development of conjunctivitis, keratitis and other purulent diseases in an adult, the following preventive measures will be required:
- Avoid contact with irritants that cause an allergic reaction.
- Do not use someone else’s decorative cosmetics - mascara, pencil, cream, eye shadow.
- Have a medical examination with an ophthalmologist every year.
- Follow the rules of hygiene - wash your hands and face after going outside.
- Buy lenses only after consulting a specialist.
- Immediately treat somatic diseases.
- Use only clean water to remove makeup and wash your face.
Also, the appearance of purulent deposits on the eyelids is explained by a lack of vitamins. To clarify this issue, a person undergoes tests, after which he is prescribed a vitamin complex.
To prevent the development of inflammatory processes in the eye, it is necessary to carefully monitor personal hygiene. Do not touch your eyes with dirty hands.
When the inflammatory process has already affected the mucous membrane of the eye, you should not delay treatment and use home remedies yourself. This can lead to the development of serious complications, including corneal damage. To get rid of such consequences, it is necessary to spend more than one month, or even a year.
Prevention of gonolonnorrhea in newborns requires women to be thoroughly examined for the presence of gonococcal infection during pregnancy and begin timely treatment if it is detected. As soon as the baby is born, 1 drop of sodium sulfacyl solution is dripped into his conjunctival sac. This is an excellent prevention against the disease.
The first and main preventive method to help avoid the development of pathology is to remember about personal hygiene. Do not touch your eyes with dirty hands. People who wear contact lenses should remember the need to clean their lenses in a timely manner. Violation of hygiene rules can cause irritation of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Why do my eyes fester?
During the inflammatory process, a large amount of bacterial waste products and dying cells accumulate in the eye area. They come out in the form of pus, the color of which can vary from white to dark yellow. Most often, suppuration occurs in young children and the elderly. The weaker a person’s immunity, the higher the risk of infection in the eye area.
The following can lead to various eye diseases in which pustules may occur:
- Wearing low-quality lenses.
- Violation of hygiene rules.
- Some sexual diseases.
In this case, the eyes itch, a crust appears, redness and slight swelling. The purulent discharge may severely affect one or two eyes. All this indicates the need to visit an ophthalmologist, because some inflammatory pathologies can significantly impair vision and lead to irreversible complications.