Dexa-Gentamicin eye drops are a complex ophthalmic agent for topical use that has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. The medication is prescribed to relieve unpleasant signs of an inflammatory process in the organ of vision. Sometimes it is used for the prevention and treatment of allergic conjunctivitis to eliminate swelling and redness.
pharmachologic effect
The active substance gentamicin is an antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action from the group of aminoglycosides. The component is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The maximum concentration of gentamicin in the corneal stroma and in the anterior chamber of the eye is observed 5-6 hours after instillation. Damaged corneal epithelium does not facilitate the penetration of the substance into the systemic circulation.
Dexamethasone is a hormone that has antiallergic and anti-inflammatory properties. Due to this, symptoms such as itching, burning, swelling, redness, pain, and foreign body sensation are eliminated. Dexamethasone quickly penetrates the conjunctiva and cornea. Damage to the mucosa enhances penetration.
Dexa-Gentamicin belongs to the group of glucocorticosteroid drugs for topical use. The drops have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiallergic effect.
Gentamicin injections: instructions
Gentamicin in ampoules is prescribed for injection - intramuscular or intravenous. It can be in the form of a solution or powder for its preparation. During the day, 2 to 4 injections are prescribed. A single administration of the drug is possible, 1 time per day. The course of treatment usually does not exceed 10 days.
The injection dose is prescribed by the doctor based on the severity of the infection, the course of the disease and the diagnosis. The maximum dose of the drug is for severe sepsis in newborns. Medium doses - for the treatment of inflammation of internal organs. In this case, the dose is calculated based on the weight of the child or adult. For an adult, the permissible dose should not exceed 5 mg/kg of weight, for a child under 2 years of age - no more than 6 mg/kg of weight.
The injection solution has the highest concentration of the active substance, 40 mg of sulfated antibiotic in 1 mg of solution or 4%.
What else should I add? Internal treatment with Gentamicin is carried out by injections or droppers (intravenously). The drug takes a long time to be absorbed through the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Therefore, gentamicin is not produced in tablets due to the low effectiveness of treatment.
Main indications
The instructions for use indicate the following conditions for which the use of drops is indicated:
- conjunctivitis, including allergic;
- keratitis;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- blepharoconjunctivitis;
- iritis;
- iridocyclitis;
- barley.
Read more Instructions for using Timolol eye drops
Thus, the main indication for use is eye diseases accompanied by inflammation and infection.
The medication is prescribed to prevent infection after ophthalmic surgery. Drops also help to quickly recover from burns and eye injuries.
Using eye drops
The instructions for Gentamicin eye drops regulate their use for any eye inflammation:
- Conjunctivitis (infection of the lining of the lining called the conjunctiva);
- Blepharitis (infection of the eyelid margin);
- Dacryocystitis is an infectious inflammation of the lacrimal sac;
- Keratitis is an infectious inflammation of the cornea;
- Barley or meibomitis - inflammation of the hair follicle along the edge of the eyelid;
- Injuries to the retina with infection - burns, surgical interventions (antibiotics are often used as a prophylaxis to prevent infection).
Contraindications
Dexagentamicin complex drops have a wide list of contraindications, so only a specialist should prescribe them. The ophthalmic agent should not be used in the following cases:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- increased eye pressure;
- damage to the organ of vision of a viral or fungal nature;
- dendritic keratitis of herpetic type;
- ocular tuberculosis (extrapulmonary form of tuberculosis);
- period after cataract removal;
- purulent or erosive lesions of the cornea;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- age under 18 years.
Use the drug with caution in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, because There have been no reliable studies in this area. There is also no information available for use in young children and adolescents. Drops are prescribed to children when the potential benefit is relevant despite the perceived risk. For children, use the drug strictly according to indications.
Use of gentamicin
Preparations containing gentamicin treat eye infections - conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis. They also treat infected purulent wounds and burns. Internal administration and injections are prescribed for the treatment of kidneys, lungs, ureters, bone tissue and joints. Because this antibiotic has serious side effects, it is used only when other treatments do not provide noticeable improvement.
For eye inflammation, external forms of the drug are prescribed - drops and ointment. They are used in combination - the solution is instilled into the corner of the eye, after which the ointment is placed under the lower eyelid.
Ointment forms of the drug are used in ophthalmology and dermatology. Ointments are prescribed for skin inflammations - impetigo, boils, infected acne. For secondary bacterial infections associated with allergies, viral or fungal infection, injury.
Note: the price of Gentamicin ointment often becomes the reason for its self-prescription, without consulting a doctor. This is fraught with complications and problems.
Injections and administration through a vein are prescribed for serious infections of internal organs, blood poisoning, and sepsis. And now - in more detail about the various forms of drugs and the diseases that they treat.
Side effects, overdose
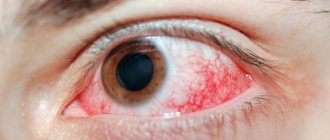
Common negative effects from using gentamicin eye drops:
- allergic manifestations;
- burning, itching of the eyes;
- herpes simplex keratitis;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- secondary glaucoma;
- eyelid ptosis;
- perforated corneal ulcer;
- pupil dilation;
- neuritis (inflammation of the auditory nerve).
Steroid glaucoma and cataracts are dangerous complications that arise as a result of non-compliance with dosage and prolonged therapy. If the listed symptoms appear during treatment with Dex-Gentamicin drops, you should stop using them and consult a doctor.
When used topically, an overdose is unlikely.
Read more Trilactan eye drops: instructions for use and reviews
When is gentamicin injection prescribed?
Gentamicin injections are prescribed for serious infections of internal organs and tissues, namely:
- Urinary tract infections – pyelonephritis (kidney inflammation), cystitis (bladder infection), urethritis (urethral infection in men);
- Sexual and sexually transmitted infections - for example, gonorrhea (purulent inflammation of the ureters, the causative agents of which are sexually transmitted);
- Respiratory tract infections - bronchitis and pneumonia, pleurisy, as well as accumulation of pus in the lungs (abscess or empyema);
- Bacterial infections of the digestive organs - acute bacterial cholecystitis (inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder) and cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts);
- So-called surgical infections - peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity, often accompanies acute appendicitis), surgical wound infection, sepsis;
- Skin infections - boils (ulcers), trophic ulcers, and other slow-healing wounds.
Interaction with other drugs
An increase in intraocular pressure can be provoked by the combined use of Dex-Gentamicin and cholinergic medications (for example, Atropine). Combining the following local ophthalmic medications with drops can lead to complications:
- Heparin;
- Amphotericin B;
- Sulfadiazine;
- Cloxacillin;
- Cephalothin.
Special Recommendations
When using Dex-Gentamicin eye drops, the following features of the drug should be taken into account:
- It is not recommended to use the medicinal solution without a doctor's permission for more than two weeks. Long-term use threatens the addition of a secondary infection of the organ of vision
- To avoid the development of edema, the frequency of use should not be increased more than 5 times a day.
- The tip of the dropper should not touch the mucous membrane of the eyes and other surfaces to prevent infection of the solution.
- Before the procedure, any contact lenses (hard, soft) are removed. You can put on the ophthalmic device after 15 minutes.
- In some patients, the drops affect the clarity of vision. Therefore, immediately after instillation, you should not drive a vehicle or engage in potentially dangerous work that requires precision.
- Patients predisposed to increased eye pressure should have their pressure monitored regularly. Especially when the treatment is long-term.
After using Dex-Gentamicin, it is recommended to add or drip other local ophthalmic drugs after 20-30 minutes.
Gentamicin eye drops
Gentamicin is a drop that is prescribed to treat eye inflammation. The concentration of the active antibiotic in them is 0.3%. This is enough to treat eye tissue.
Note: the concentration of the antibiotic gentamicin itself is 0.3% or 3 mg per 1 ml. The antibiotic is added to the medicine in the form of sulfate. In this case, to obtain 3 mg of antibiotic, 5 mg of gentamicin sulfate is introduced into the solution.
The solution is instilled into the conjunctival sac every 4 hours, except at night. For extensive purulent conjunctivitis, eye drops are instilled more often, every 1-2 hours. Important: the frequency and dosage of Gentamicin is prescribed by a doctor. Typically, the patient is prescribed 1-2 drops per eye (children - 1, adults - 2). But there are exceptions.
The effect of gentamicin drops is quite strong. Therefore, the drug is used for purulent conjunctivitis that cannot be treated with other weaker antibiotics.
When drops are instilled into the eyes, sharp painful sensations may occur. Burning, stinging, pain in the eyeballs, photophobia and painful reaction to light. At a minimum, there is redness of the sclera and short-term fogginess before the eyes.
The painful sensation is the reason why they try not to prescribe the drug to children. The modern pharmaceutical industry offers a choice of less aggressive antibiotics that are used in pediatric ophthalmology.
Advantages of Gentamicin eye drops over other antibacterial drugs:
- Gentamicin solution has low absorption into the lens tissue;
- Gentamicin quickly forms a therapeutic concentration in inflamed tissues. Already 30 minutes after instillation, its amount in the tissues reaches the required level, at which it remains for at least 6 hours.
Analogs
There are no structural analogues of Dex-Gentamicin. Combined eye drops with a similar effect:
- Dexapos. The therapeutic effect is achieved through direct contact of the active substance with histamine receptors. The drug belongs to the group of glucocorticosteroid anti-inflammatory and antiallergic medications.
- Colbiocin. Rolitetracycline, chloramphenicol, sodium sulfate, sodium colistimethate are active antibiotic ingredients that provide a powerful antibacterial effect.
- Garazon. Gentamicin and betamethasone are the main substances in the composition. Pharmacological action – antiallergic and anti-inflammatory.
- Tetracycline drops. Antimicrobial drug based on tetracycline. Safety, effectiveness and low price are the advantages of the medicine.
Read more Instructions for using Pilocarpine eye drops
These and other substitutes should only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist. An incorrectly selected medication can cause complications or even worsening of the condition.