Atheroma of the upper eyelid causes a person not only psychological discomfort, it poses a threat to the health of the eye. Pathological neoplasms on the eyelid can be single or multiple. It is formed by the Zeiss (mollium) glands, which produce a protective secretion for the cornea of the eye. In medical documents it is described as a sebaceous cyst. It is dangerous to treat an epidermal cyst on the eyelid on your own, especially considering that its symptoms may hide a malignant tumor.
What is eye atheroma: causes and mechanism of formation
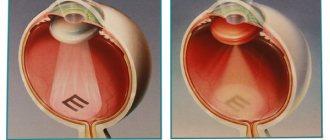
Atheroma on the eyelid appears due to an increase in the thickness and viscosity of the secretion of the Zeiss glands. Due to its high density, the fatty secretion cannot be evacuated to its destination, so it remains in the gland ducts. From excess sebum they stretch, the inflammatory process begins, and as a result the eyelid swells. Swelling completely blocks the ductal outlets of the gland. This is how cysts form on the eyelid.
Doctors associate the reasons for the thickening of the secretion of the Zeiss glands with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer, gastritis), as well as with pathology of the pancreas.
Why does atheroma occur?
The appearance of a cyst is caused by blockage of the outlet duct of the sebaceous glands. As a result, the sebum produced by the gland does not come to the surface, but accumulates inside. The duct increases in size, and the body’s defense system, trying to stop this process, forms a cyst of connective tissue in the form of a cavity around the atypical formation.
Factors leading to blockage of the sebaceous glands:
- Injury to the epidermis - skin cells, after being damaged by a blunt object, clog the lumen of the sebaceous gland duct.
- Low level of personal hygiene - dust particles and other contaminants must be regularly removed from the surface of the skin so as not to clog the excretory ducts of the glands.
- Hormonal imbalance, the predominance of male hormones - testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone - leads to changes in the functioning of the sebaceous glands, increased secretion of sebum and its thickening.
- Postmenopause - during menopause, the concentration of estrogen in the female body sharply decreases, which increases the likelihood of changes in the composition of sebum and the formation of atheroma.
Although atheroma most often occurs in adults, the congenital form of this neoplasm is rarely diagnosed in children. The cyst forms in front of the ear and looks like a small ball up to 2 cm in diameter. The cause of atheroma in children is a small defect of the epidermis in the area of the auricle. In the future, such atheroma does not develop and does not affect the child’s health.
Clinical picture of a regular and inflamed cyst
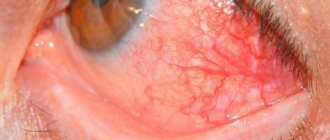
Initially, atheroma is a round subcutaneous ball that can be moved with a finger along with the skin of the eyelid. An ordinary epidermal cyst does not hurt, but despite this, it is often confused with a stye. Over time, the tumor enlarges and becomes an obstacle to vision, so it must be removed.
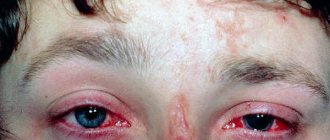
If the atheroma becomes inflamed and becomes purulent, which occurs under the influence of a bacterial infection (streptococci, staphylococci), then, if untreated, the neoplasm turns into an abscess cyst. This pathological condition manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- redness, swelling of the skin over the epidermal bump;
- feeling of pain in the area of inflammation;
- rapid increase in education;
- independent opening of the atheroma with isolation of the contents.
If the patient, even with an abscess, does not go to the ophthalmology clinic, then the pathology will soon be complicated by sepsis (blood poisoning).
Reasons for appearance
The causes of atheroma on the face are conventionally divided into external and internal. The former include hot climates and environmentally polluted areas - they contribute to hypersecretion of both sweat and sebaceous glands.
Internal reasons:
- seborrheic dermatitis (oily form);
- presence of acne on the face;
- dysfunction ;
- diseases of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland;
- hyperhidrosis – excessive secretion of sweat glands;
- skin damage due to bacterial infection;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- diseases of the adrenal cortex;
- reduced immunity.
Men often experience atheroma on the face as a result of increased production of testosterone in the blood. But in women, gland blockage can occur due to the application of oily cosmetics to the skin. Failure to comply with hygiene rules leads to contamination of pores and ducts, which is dangerous due to the formation of atheroma.
According to dermatologists, increased secretion of sebaceous glands on the face mainly occurs in teenage girls. As girls grow older, sebum production decreases in girls, and this happens faster than in men.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Women's skin dries out more and more with age, while in young people testosterone levels increase, and, as a result, more secretory fluid is produced, increasing the risk of developing atheromas on the face.
However, the cause of atheroma is not only the intense work of the sebaceous glands, but also their dystrophy. This occurs either during the aging period of the body, or in the presence of certain pathologies.
Complications
A small atheroma on the eye is harmless and painless. But as soon as it reaches the size of a pea, it can already cause vision loss.
Under the symptoms of atheroma at the initial stage of appearance, a malignant tumor may be hidden. Therefore, it is very important to establish the type of subcutaneous neoplasm and then begin its treatment.
Other possible complications that occur when a growth on the eyelid becomes infected are:
- furuncle;
- phlegmon;
- abscess.
These diseases can lead not only to vision loss, but also to impaired brain function.
As for cases of malignancy - the degeneration of a benign atheroma into a malignant one, this is impossible, since it is not a tumor. When an epidermal cyst suppurates, the tissues surrounding it undergo pathological changes, but even this condition does not lead to the degeneration of atheroma. Most often, blood poisoning occurs.
Brief characteristics and classification of atheromas
According to the mechanism of formation, histological structure and clinical manifestations, atheromas are classic cystic neoplasms, that is, cysts. And since these cysts are located in the skin and are formed from the structures of the epidermis, they are called epidermal or epidermoid.
Thus, the terms “epidermal cyst” and “atheroma” are synonymous, since they are used to refer to the same pathological neoplasm.
Despite the ability to grow and the presence of a membrane, atheromas are not tumors, and therefore, by definition, cannot be malignant or degenerate into cancer, even if they reach significant sizes. The fact is that the mechanism of formation of a tumor and a cyst is fundamentally different.
Treatment options
When an eyelid cyst ruptures on its own and all its contents come out, the disease still returns after a few weeks. For this reason, in ophthalmology clinics, atheroma of the upper or lower eyelid is treated only by planned removal. If it becomes inflamed and then begins to fester, then surgery is prescribed immediately. Additionally, such a patient, in order to relieve inflammation and increase the body's defenses, is prescribed antibiotics, as well as immunostrengthening drugs.
Conservative
Atheroma of the century is curable, but such a result can be achieved not by folk or traditional treatment, but by surgical medicine. Local medications help stop the growth of the epidermal lump and relieve inflammation. Medicines can draw out stagnant sebaceous secretions from it, heal the wound, but do not exclude relapse.
The list of safe folk remedies often used for atheroma of the century includes:
- Silver item. A ring, spoon or coin is applied 3 times a day for 30 minutes to the inflamed eyelid. Treatment lasts until the epidermal ball is reabsorbed (about a month).
- Chicken egg shell film - apply the wet side to the atheroma overnight. The procedure is repeated until recovery.
- Lamb fat - rub the sore eyelid at night, stop using it after the contents of the cyst are released.
- Watercress herb juice - under the influence of the components of the juice, the resorption and healing of the opened formations occurs. You need to take the juice daily for at least 2 months in a row.
Effective ointments for atheroma - Levomekol, Ichthyol, Vishnevsky. But ophthalmologists do not recommend using them on eyelids, since the products can damage the mucous membrane.
Radical
Complete removal of atheroma on the eyelid is usually performed surgically:
- The skin over the tumor is opened with a scalpel.
- Its capsule is cleaned and dehusked.
- Self-absorbing sutures are applied.
The patient needs to be prepared for the appearance of a scar at the site of the cyst after its removal.
Surgical treatment of atheromas is not used for inflamed tumors. There is a high probability that the surgeon will not be able to completely remove the cyst capsule. Subsequently, this will lead to the growth of the pathological fragment remaining under the skin.
If the inflamed lump has purulent contents, the surgeon opens it, cleans it of pus and drains the wound. As soon as the inflammation goes away, the patient is scheduled for surgery to remove the cyst shell.
Self-treatment of an epidermal lump in the eye area (steaming, heating, squeezing) can lead to infection and decay, and can also cause decreased vision.
Laser therapy is often used for atheroma of the eyelids. Removal is carried out using one of the following methods:
- Photocoagulation - used for tumors no more than 5 mm in diameter. The laser beam evaporates even cysts containing pus.
- Excision with membrane - prescribed for epidermal bumps no larger than 20 mm in size. During the operation, in addition to the laser beam, a scalpel and forceps are used, as in conventional surgery.
- Capsule evaporation - used for atheromas larger than 20 mm. First, the tumor capsule is cut, its contents are cleared with gauze swabs, then the shell is evaporated with a laser.
Another relapse-free method for removing sebaceous cysts is radio wave therapy. But it is used only for small epidermal bumps, without inflammation or suppuration. Radio waves affect the pathological lump in such a way that its tissues die and dissolve. At the site of the operation, only a crust remains, under which new skin is formed.
Is it possible to remove eyelid atheroma on your own?
Atheroma of the eyelid is a benign skin tumor that forms in the hair follicles. The causes of the disease are not fully known, but effective treatments exist.
Not all atheromas of the century pose a threat to human life, but some can be fatal. Knowing certain symptoms helps to identify a dangerous pathology in time and consult a doctor.
Diagnosis and types of atheromas
Atheroma is a collective name for epidermal cysts in the area of hair follicles with various etiologies and histologies. These include epidermal cyst, trichymemal cyst and steatocystoma. The British Association of Dermatologists distinguishes “true” from “false” atheromas.
Epidermal cysts are usually traumatic due to the breakdown of squamous epithelium into subepithelial tissue. The most common complication is rupture with secondary sepsis. Healing with atypical scarring occurs if the cyst is not surgically removed.
Epidermal cysts make up about 70% of all benign skin cysts and are most often seen on the hairless scalp, face, torso, feet and hands. Men suffer more than women.
The defeat occurs mainly in the 2-4 decades of life. Epidermal cysts are sliding subcutaneous nodules with a sticky consistency ranging in size from a few millimeters to 2-3 centimeters.
Doctors often use the term "atheroma" very inconsistently. Strictly speaking, the following variants of atheroma can be distinguished. “True” atheromas (epidermal cysts) form on the hair follicles - in the upper part where the hair emerges from the skin. They arise from skin cells and subcutaneous tissue.
The nodes appear spherical, convex and elastic. Epidermal cysts usually do not have an optically recognizable excretory duct. Horny cells and hair accumulate in the cyst; the contents smell unpleasant when the doctor opens the atheroma. True atheromas often occur in families and can be inherited.
“False” atheroma forms in the lower part of the hair follicles. The knots also feel rough, hard, and rubbery. False atheromas occur when one or more sebaceous glands become clogged, such as loose skin cells or dried sebum.
Examination is one of the methods for diagnosing atheroma of the eyelid
Fat does not come out and gradually accumulates in the tissues. The location of a blocked exit passage is sometimes recognized as a black dot. The cyst grows slowly because the sebaceous glands produce only a small amount of oil each day.
Atheroma can occur almost anywhere on the body because hair follicles and sebaceous glands extend throughout the skin. Atheroma on the head, neck, ear, chest, back, neck, face or genital area is not uncommon. However, most dermatologists do not always distinguish between “true” and “false”. Therefore, both forms are often called simply “atheroma.”
Therapy methods
Excision of atheroma without infection is relatively simple. It is important to remove the sebaceous duct and capsule. If the capsule is open or part of the duct remains in the skin, recurrence of atheroma is very high. Careful attention must be paid to complete removal, as this is often very difficult, especially if the capsule is damaged during removal.
Conservative treatment
Sometimes an abscess forms and pus accumulates in the atheroma. In this case, it is important not to touch the tumor. If a pustule bursts, bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause blood poisoning. This is especially dangerous when the atheroma is on the head - microbes can enter the brain.
In the case of inflamed atheroma, doctors first suppress the inflammation with antibiotics. Medicines spread infection. In addition, the doctor tries to ripen the atheroma with ointment. The ointment softens the skin, soothes pain and slows down inflammation. This also slows down sebum production and ensures that the abscess opens and drains faster.
Conservative treatment of eyelid atheroma includes ointment
For non-inflammatory atheroma, the ointment is of no benefit: although it compresses the atheroma, because the secretion is emptied, the capsule does not dissolve the neoplasm. It can only be removed surgically.
The surgeon then carefully opens the atheroma, removes the pus, and rinses with a disinfectant solution to remove as many germs as possible.
Only after the inflammation has passed after some time, the doctor removes the entire atheroma surgically. As with any surgery, wound pain may occur.
The larger the atheroma, the more pronounced they can be. Pain medications effectively control the symptoms of the disease.
Atheroma has no medical value. This means that the cyst may be unpleasant and cosmetically disturbing, but not a health hazard. In any case, atheromas have nothing to do with cancer. Health insurance companies usually do not cover atheroma removal for aesthetic reasons.
Removing a formation
The atheroma must be removed by a surgical specialist. He cuts the tumor out of the skin with a scalpel. The doctor not only removes the contents of the cyst, but at the same time removes the sebaceous glands from the capsule. There should be no remnants of coating or ducts on the skin, otherwise there is a high probability that the atheroma will grow again.
Small and moderate atheromas are removed under local or regional anesthesia. For large or inflamed atheromas, removal is a little more difficult and takes longer. Sometimes general anesthesia is needed.
Self-removal
Even if the atheroma is irritating or looks like a pimple at first, it is forbidden to remove it or pierce it with a sharp object. Anyone who tinkers with a cyst runs the risk of inflammation. Broken skin can allow bacteria and other germs to enter. The skin then swells, turns red and can cause quite a lot of pain.
You should always consult a doctor for atheroma.
Treatment of atheroma on the eyelid should be carried out by a specialist, because he works in sterile conditions. This avoids the risk of infection, but also that the atheroma grows again.
Possible complications
Atheromas are harmless in most cases. However, an inflamed tumor can also break through. As a result, bacteria are distributed throughout the body. Therefore, in case of signs of inflammation, there is a risk of delayed septic shock.
Relapse prevention and prognosis
There are no preventive measures in the strict sense of the word. However, regular skin care is recommended. Hairy skin areas deserve special attention. The prognosis of non-inflammatory atheroma is relatively favorable.
Source: https://oonkologii.ru/ateroma-veka-01/
How to prevent relapse
Since the formation of epidermal bumps provokes an altered secretion of the sebaceous glands, their resumption on the eyelids can be excluded if:
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Remove eye makeup in a timely manner.
- Wash with gentle cosmetic products.
- Eat right and lead an active lifestyle.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
A prerequisite for preventing the recurrence of epidermal cysts on any areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands is a healthy gastrointestinal tract, so all pathologies associated with it must be treated on time.
Symptoms of atheroma
Since the formation of atheroma is not accompanied by an inflammatory process, there are no symptoms such as weakness, fever, loss of appetite, hyperemia and changes in the surface layer of the skin. If the atheroma does not become inflamed, then no problems other than a cosmetic defect are recorded.
Location of the cyst:
- Back - most often occurs on the skin between the shoulder blades, although another area of this part of the body is not excluded;
- Head – face, back of the head, area around the ears, chin;
- Crotch;
- Coccyx;
- Armpits;
- Popliteal fossae.
In those areas of the human body in which there are no sebaceous glands (palms, feet), atheromas never form.
Diagnosis of the disease
One of the doctor's jobs is to rule out the presence of cancer. To do this, part of the formation (usually after its removal) is sent for histological examination.
Removal of atheroma using radio waves
Radio waves are a method for removing painless atheromas, the size of which does not exceed 3 centimeters.
When examining a patient, the doctor will easily identify facial atheroma by its external signs:
- visualization of clear boundaries of education;
- dense, elastic fabric structure
- relative immobility of the cyst upon palpation;
- in the central part of the surface of the atheroma there is a clogged duct , which is highlighted in black or bluish color.
Atheroma is usually differentiated from a lipoma, since they are similar in appearance. Some people call the formation of a sebaceous gland a wen, although this is incorrect.
During palpation, the surgeon can easily distinguish atheroma from lipoma: in the first case, when pressing with a finger on the bulge, it remains in place and does not change its shape.
In the second case, education seems to escape from under the fingers in the other direction. Thus, it is impossible to press it. The consistency of lipoma is distinguished by its softness and plasticity.
When excising a tumor, the doctor will immediately notice its membrane. By cutting the capsule in half, its contents will be clearly visible in the form of a curdled mass and you will be able to smell a peculiar unpleasant odor.
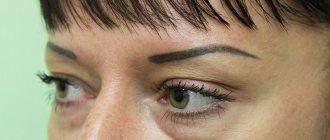
Atheroma of the eye area
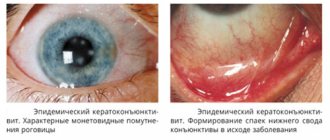
If the atheroma is located near the eyelid, it will look like a small white bump. It is often confused with a lipoma, papilloma, senile wart or chalazion. Atheromas on the upper eyelid are twice as common as on the lower eyelid, since there are more sebaceous glands in this area.
During night sleep, the secretory fluid, together with the tear fluid, flows into the medial corner of the eye and collects there, so in the morning the formation is especially pronounced. Cysts located near the eyes tend to become inflamed.
Nasal atheroma
The largest sebaceous glands are located on the nose. Most often they are observed on the outside of the wings of the nose, especially on the inside, since multiple small hairs grow there. Atheromas of the nasal area are differentiated from inflamed acne, boils on the inside of the nose, and dermoid cysts.
Formations of sebaceous glands, both small and large, can be observed on the forehead and cheeks. In these places, the formation of atheromatous processes is possible.
In the forehead area, the main number of sebaceous glands are located closer to the scalp; accordingly, blockages of the ducts occur there more often. On the cheek, atheromas are less common, but they bring a lot of trouble, since the skin in this area has greater relief.